FBLA Introduction To Information Technology
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
LAN
Local Area Network
WAN
Wide Area Network
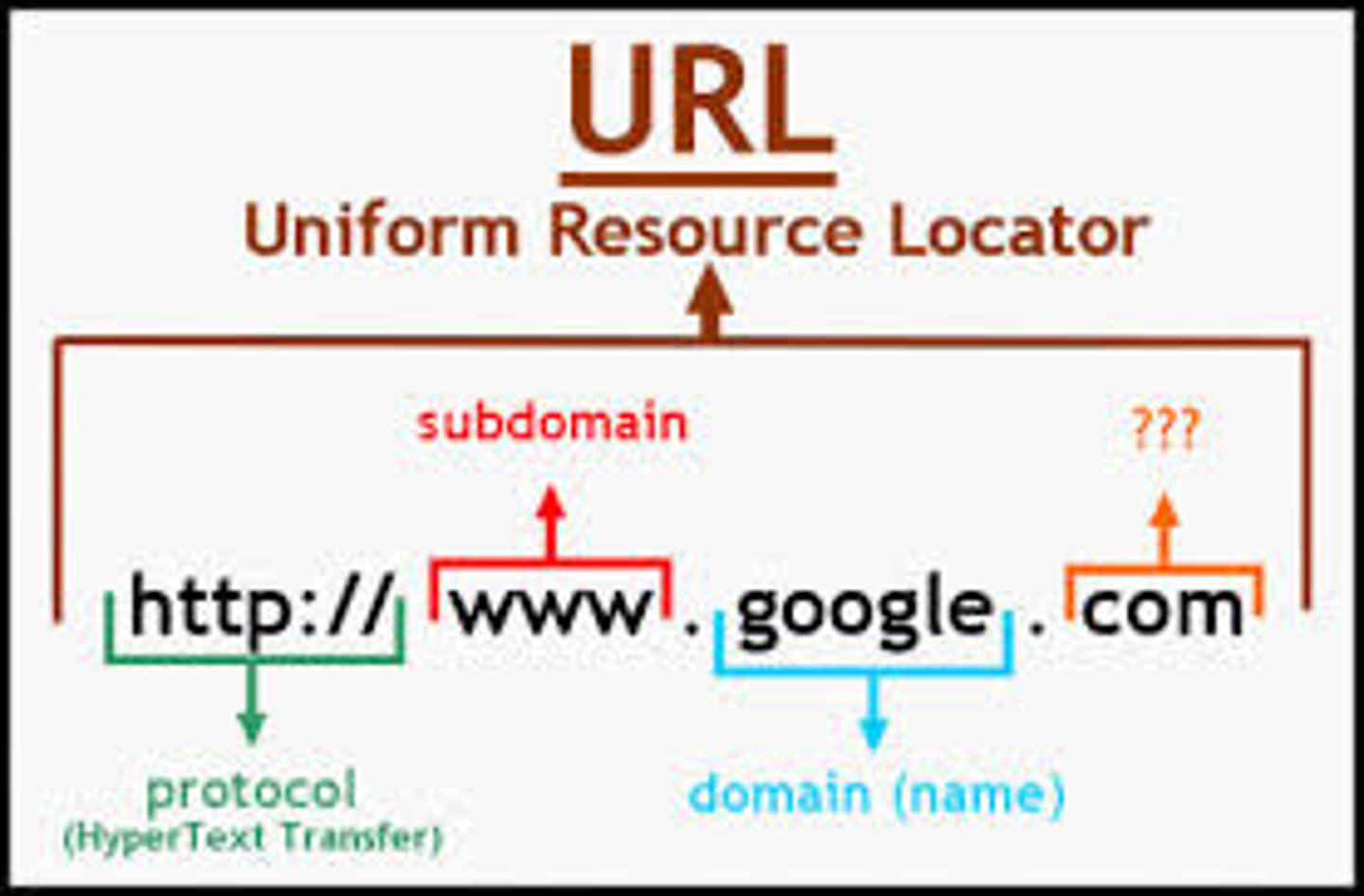
HTTP
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
HTML
Hyper Text Markup Language

RAM
Random Access Memory
ACL
Access Control List
ADC
Analog to Digital Converter
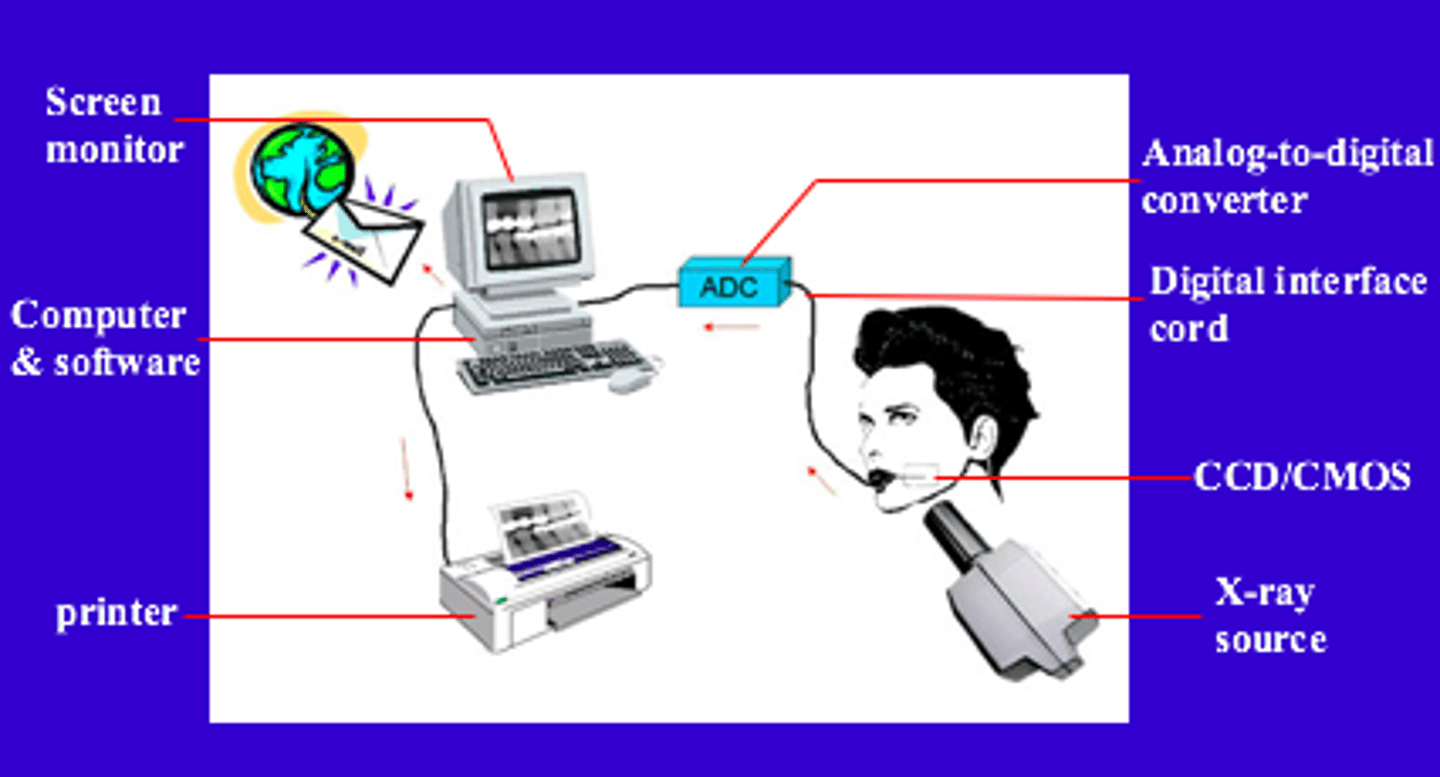
ADF
Automatic Document Feeder
APU
Accelerated Processing Unit
BSOD
Blue Screen of Death
CD
Compact Disc
CD-R
Compact Disc Recordable
CD-ROM
Compact Disc Read Only Memory
ATM
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
CD-RW
Compact Disc Re-Writable
CPU
Central Processing Unit
DCIM
Digital Camera Images
DMA
Direct Memory Access
DOS
Disc Operating Systems
DRAM
Dynamic Random Access Memory
DSL
Digital Subscriber Line
DV
Digital Video
DVD
Digital Versatile Disc
DVD +/- R
Digital Versatile Disc Recordable
DVD+RW
Digital Versatile Disc Re-Writable
DVD-RAM
Digital Versatile Disc Random Access Memory
DVI
Digital Video Interface
DVR
Digital Video Recorder
ECC
Error Correction Code
FTP
File Transfer Protocol
HTTPS
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
It
Information Technology
Kbps
Kilobits Per Second
NIC
Network Interface Card
OSD
On Screen Display
PMU
Power Management Unit
POP3
Post Office Protocol
RTF
Rich Text Format
SAN
Storage Area Network
SMART
Self Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology
SMS
Short Message Service
USB
Universal Serial Bus
VoIP
Voice Over Internet Protocol
VPN
Virtual Private Network
VRAM
Video Random Access Memory
W3C
World Wide Web Consortium
WAIS
Wide Area Information Server
WI-FI
Wireless Fidelity
WWW
World Wide Web
XHTML
Extensible Hypertext Markup Language
The shape of a local-area network (LAN) or other communications system.
Topology
The third layer of OSI
Network Layer
Every node has a circuit connecting it to every other node in a network. Is very expensive to implement but yields the greatest amount of redundancy.
Full Mesh Topology
The sixth layer of OSI
Presentation Layer
It refers to layout of a network. How different nodes in a network are connected to each other and how they communicate is determined by the network's topology.
Network Topology
This is a "hybrid" topology that combines characteristics of linear bus and star topologies. In a tree network, groups of star-configured networks are connected to a linear bus backbone cable.
Tree Topology
The physical layout of devices on a network. Every LAN has a topology, or the way that the devices on a network are arranged and how they communicate with each other.
Physical Topology
A networking framework to implement protocols in seven layers
Open System Interconnection (OSI)
The first layer of OSI model.
Physical Layer
The seventh layer of OSI model.
Application Layer
Fifth layer of OSI
Session Layer
Forth layer of OSI
Transport Layer
Second layer of OSI
Data Link Layer
Some nodes are organized in a full mesh scheme but others are only connected to one or two in the network.
Partial Mesh Topology
A group of two or more computer systems linked together. There are many types of computer networks, including the following:
Network
A topology where devices are connected to a central computer, called a hub.
Star Topology
A topology where a central cable -- the main wire -- that connects all devices on a local-area network (LAN).
Bus Topology
A local-area network (LAN) whose topology is a ring.
Ring Topology