[PHYSICS] Electrical Safety
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Fire accidents
are common in the Philippines. Most of these accidents are caused by faulty electrical wiring.
electrical conductor
The human body is considered an _____, which means that current can easily pass through it.
Electrocution
refers to the injury suffered by a person due to electric shock.
100 ohms, half a million ohms
The human body's resistance varies depending on different factors. It can contain about ______ of resistance when immersed in seawater.
It may have about _______ if the skin is extremely dry.
Skin condition.
Skin thickness.
Pathway of the current.
Contact area.
Health and hydration.
Voltage and frequency of the current.
Factors that affect the body's electrical resistance (6)
Skin condition.
Dry skin has higher resistance than wet skin because moisture (like sweat or water) can help conduct electricity.
Skin thickness.
Thicker skin generally provides more-resistance to electrical flow.
Pathway of the current.
The resistance also depends on the path the electrical current takes through the body.
Contact area.
The amount of skin in contact with the electrical source also matters.
Health and hydration.
Someone who's well-hydrated and in good health might have lower resistance compared to someone who's dehydrated or has certain medical conditions.
Voltage and frequency of the current.
The resistance of the body also depends on the voltage and frequency of the electrical current.
Tingles
Effects of 0.001 A
Painful
Effects of 0.005 A
Muscle Spasms
Current as high as 0.010 A may cause ______, or the involuntary contractions of muscles.
sustained contraction.
When a current surpassing 10 milliampere reaches our flexor muscles (muscles that flex our joints), they may experience _______.
Muscle Spasms
The contraction causes a person to become fixated on the source of the current, making the shock more severe.
tendons and ligaments
Intense spasms in muscle spasms may also tear ______ and _____ and may even hurl a person distances away.
Cardiac Arrest
A current of 50 milliamperes is enough to cause _____ once it reaches the heart.
Cardiac Arrest
The heart itself is a muscle that operates through electrical impulses, but an external current may completely disturb its rhythm.
Tissue and Organ Burns
Above 100 milliamperes, current may cause wounds on the skin.
Tissue and Organ Burns
Sometimes, electrical burns may even injure internal organs that lead to loss of function and even death.
Muscle Spasms
Cardiac Arrest
Tissue and Organ Burns
(Tingles, painful, causes loss of muscle control)
Physiological Effects of Electrical Shock
Defective Electrical Wiring
refers to worn-out, damaged, ill-maintained, or corroded wires. They can cause power surges, sparking or arcing, fire, and power surges.
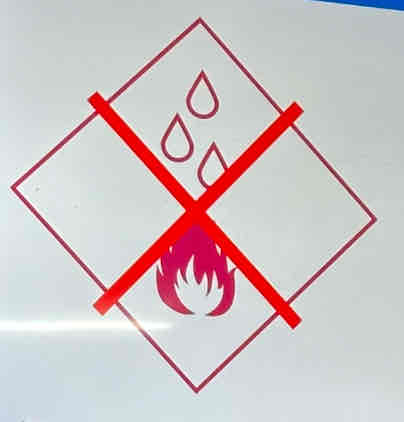

Dangers Related to Water and Other Fluids
Water is a good conductor of electricity.
Electrical outlets must be kept away from it.
Electrical appliances must not be used on wet surfaces or surroundings.
Water must not be used to extinguish electrical fires.
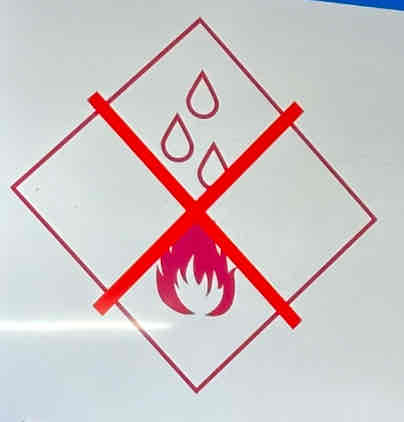

Water
is a good conductor of electricity. Outlets and appliances must be kept away from it and must not be handled with hands.
Overloaded Powerboards
Each powerboard has a maximum current rating specific to its structure and design. Overloading it, or connecting it to a longer powerboard, both increase the risk of fire.
Short-Circuiting
occurs when electric current flows through an unintended path, causing the current to flow excessively through the circuit.
Overloading
takes place when too many devices or appliances are connected to a similar socket, hence stretching the current demand and causing- overheating.
Electric shock
occurs when there is an appreciable electric potential difference between your body and another electrical source.
Electrocution
refers to the injury suffered by a person due to electric shock.
Coulomb’s Law
Relates the force between two single charges separated by a distance.
Electrical hazard symbol
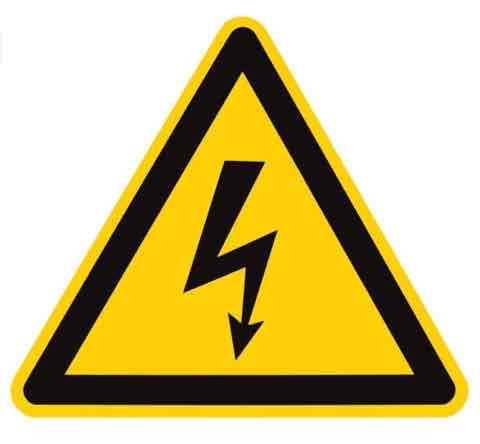

Danger sign

Do not extinguish with water

Underground wiring symbol
Electrically-classified environmental hazard symbol
