Animal Physiology Final Exam
1/234
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
235 Terms
sensory neurons
Sensors detect external stimuli and internal conditions and transmit information along these
CNS
Integration takes place here, this includes the brain and a nerve cord
PNS
Bring information into and out of the CNS
Dendrites
Most neurons have these, highly branched extensions that receive signals from other neurons
Axon
Typically a much longer extension that transmits signals to other cells at synapses
Axon hillock
Axon joins the cell body here
Synapse
junction between an axon and another cell
Synaptic terminal
passes information across the synapse in the form of chemical messengers called neurotransmitters
depolarization
membrane potential becomes less negative
repolarization
membrane potential returns to resting value
hyperpolarization
membrane potential becomes more negative then resting value
resting potential
concentration of K+ is greater inside the cell, while the concentration of Na+ is greater outside the cell
Many open K+ channels and fewer open Na+ channels
negative at rest
graded potential
Change in ion permeability causes change in membrane potential
vary in magnitude depending on strength of stimulus
more neurotransmitter → more ion channels open → larger magnitude of graded potential
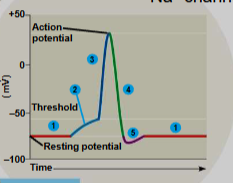
Action Potentials
triggered by net (combined) graded potential at axon hillock (trigger zone)
do not degrade over time or distance
travel long distances along membrane
all or none
must reach threshold potential to fire
voltage-gated Na+ channels open first (depolarization)
voltage-gated Na+ that opened begin closing
Voltage-gated Na+ channels mostly closed at top
K+ channels open more slowly (repolarization)
K+ channels close slowly, relative refractory period cause by open K+ channels
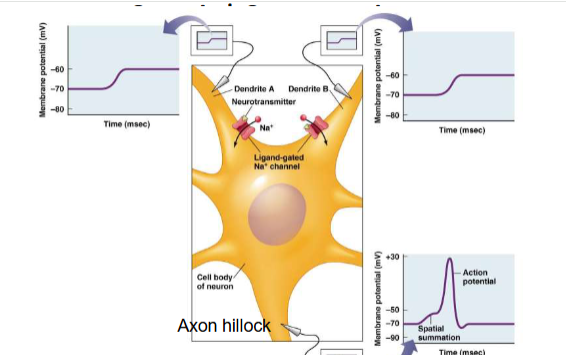
Spatial summation
Graded potentials from different sites influence the net change
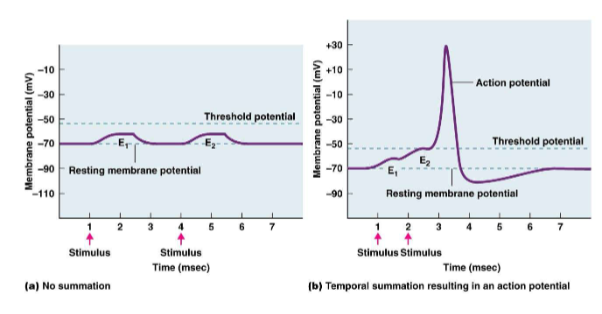
Temporal summation
Graded potentials that occur at slightly different times influence net change
Absolute refractory period
A second action potential cannot be initiated. Result of temporary inactivation of the Na+ channels
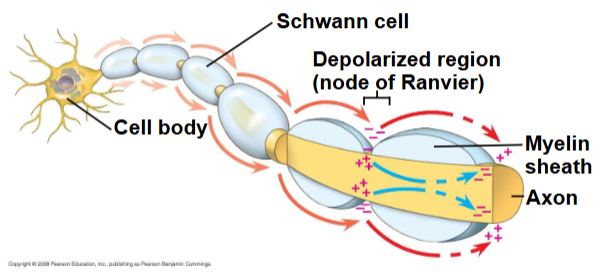
Nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath where voltage-gated ion channels are found, APs formed here. APS in myelinated axons jump between these in a process called saltatory conduction
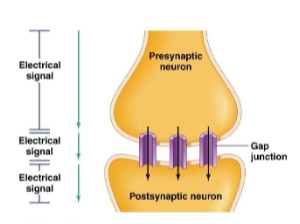
electrical synapses
Electrical current flows from one neuron to another via gap junctions
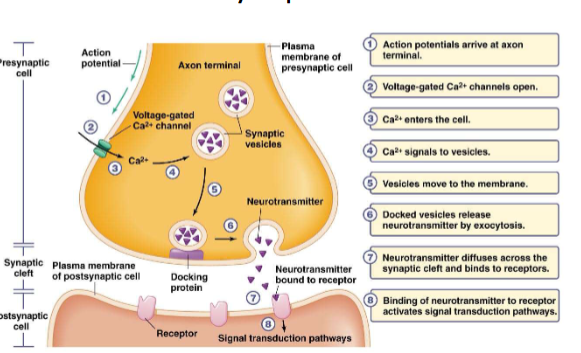
chemical synapses
chemical neurotransmitter carries information across the synapse (synaptic cleft)
Neurotransmitter action
Inhibitory neurotransmitter
cause hyperpolarization of membrane, make postsynaptic cell less likely to generate an AP
Excitatory neurotransmitter
cause depolarization of membrane, make postsynaptic cell more likely to generate an AP
Voltage-Gates Ca2+ Channels
concentrated around the axon terminal
open at the same tie or instead of voltage-gated Na+ channels
Ca2+ enters the cell, causing depolarization
Ca2+ influx is slower and more sustained than Na+ influx
slower maximal frequency of APs due to longer refractory period
Amount of Neurotransmitter Released
Ca2+ is affected by AP frequency. More open Ca2+ channels = more Ca2+
Factors that lower intracellular Ca2+ → binding with intracellular buffers and Ca2+ ATPases both lower Ca2+
High AP frequency means more Ca2+ influx, more neurotransmitter in synapse, stronger response in post-synaptic cell
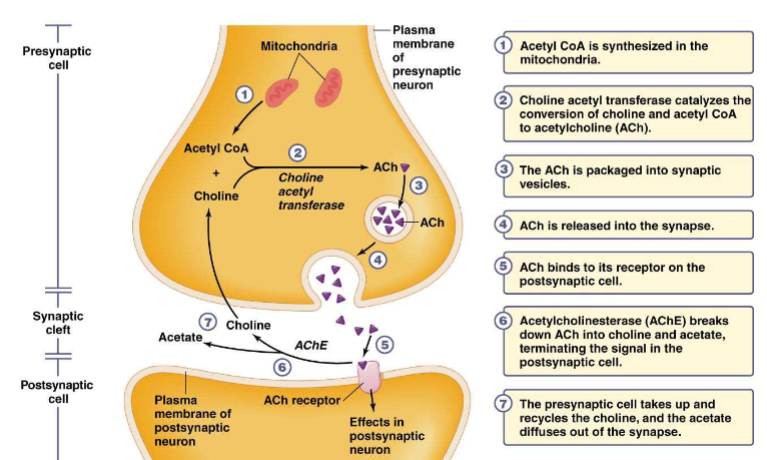
Acetylcholine
how it moves through the synapse
Striated muscle
skeletal and cardiac muscle
actin and myosin arranged in parallel
Smooth muscle
actin and myosin are not arranged in any particular way
Vertebrate skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscle consists of a bundle of long fibers, each a single cell, running parallel to the length of the muscle, each muscle fiber is itself a bundle of smaller myofibrils arranged longitudinally.
Myofibril types
thin filament: consists of two strands of actin and one strand of regulatory protein
thick filament: staggered arrays of myosin molecules
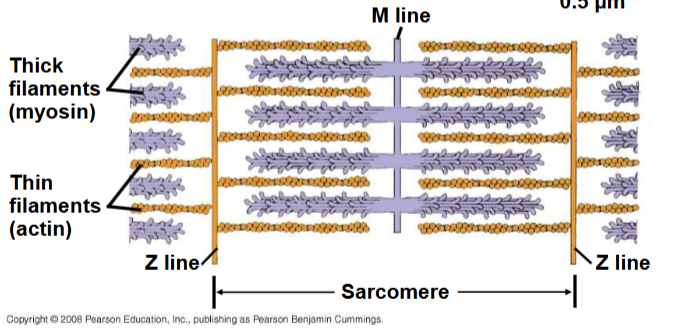
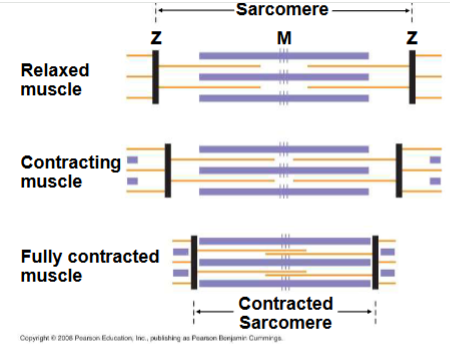
Sarcomere
Filaments slide past each other longitudinally, producing more overlap between thin and thick filaments. For a muscle to contract, myosin-binding sites must be uncovered, when Ca2+ binds to a set of regulatory proteins called the troponin complex. Muscles contract when concentration of Ca2+ is high, stops when Ca2+ is low.
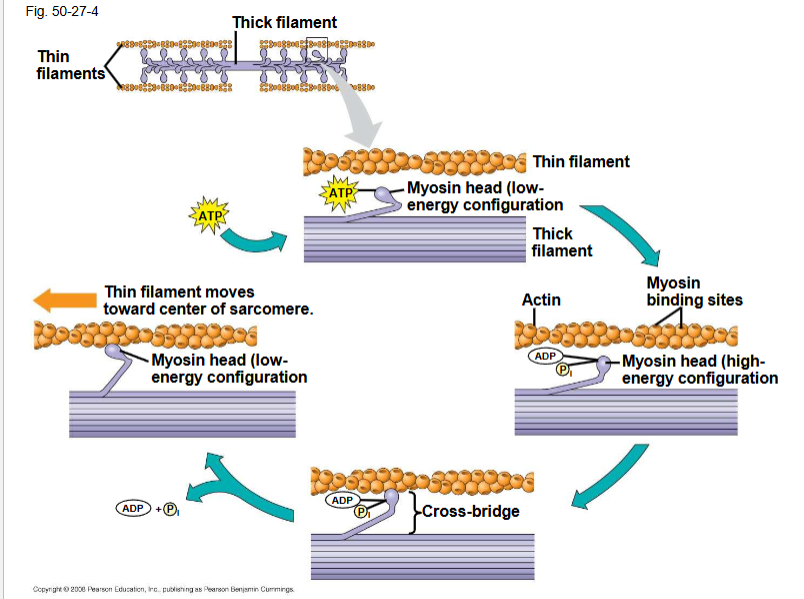
Cross bridge cycle
A skeletal muscle fiber contracts only when stimulated by a motor neuron. When a muscle is at rest, myosin-binding sites on the thin filament are blocked by ther regulatory protein tropomyosin
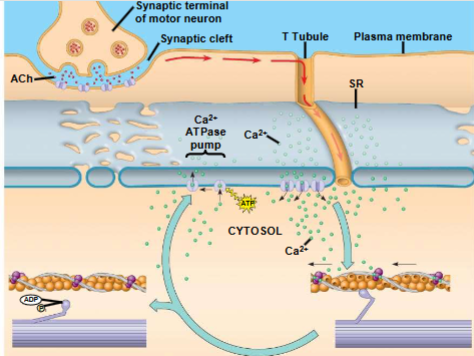
Role of S.R. and calcium in regulating contractions
synaptic terminal of the motor neuron releases the neurotransmitter acetylcholine
acetylcholine depolarizes the muscle cell, causing it to produce an action potential
AP travels to interior of muscle fiber along transverse (T) tubules
AP along T-tubule causes the SR to release Ca2+
Ca2+ binds to troponin complex on the thin filaments
this binding exposes myosin-binding sites and allows the cross-bridge cycle to proceed
Graded contractions
Extent and strength of contraction can be voluntarily altered.
varying number of fibers that contract
varying rate at which fibers are stimulated
Recruitment of multiple motor neurons results in stronger contractions
Muscle twitch
Results from a single AP in a motor neuron. More rapidly delivered APs produce graded contraction by summation
Tetanus
Smooth and sustained contraction produced when motor neurons deliver a volley of action potentials
Oxidative muscles
Rely on aerobic respiration to generate ATP, many mitochondria, rich blood supply, much myoglobin. Binds oxygen more tightly than hemoglobin does.
Glycolytic muscles
Use glycolysis as primary source of ATP, less myoglobin, tire more easily
slow-twitch muscles
Type 1, contract more slowly, can contract more times before fatiguing, oxidative
fast-twitch muscles
type 2, contract more rapidly, can contract fewer times before fatiguing, glycolytic OR glycolytic and oxidative
muscle growth
Muscle size can be increased, number of muscle cells cannot be increased, number of actin and myosin filaments within a muscle cell can be increased
Satellite cells
Responsible for muscle growth and repair. Stressed muscles release IGF which stimulates satellite cell proliferation and differentiation
Myoglobin
Protein that binds oxygen more tightly than hemoglobin does
Fuels for muscles
short- moderate length, high- intensity activity: glucose is main fuel, controlled by insulin and cortisol
sustained high activity: glycogen depeted, triglycerides mobilized
Capillaries for O2 delivery to muscles
Rate of oxygen delivery depends upon capillary density, blood flow is determined by vascular tone and oxygen affinity of hemoglobin
Capillary tortuosity
Capillaries are not straight, O2 levels decline along length of capillary, region of muscle may be served by many capillaries that weave back and forth in areas that need more oxygen. Angiogenesis (synthesis of new blood vessels)
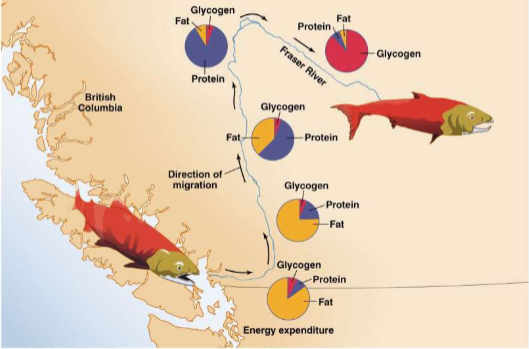
Metabolic transitions
For prolonged exercise, metabolic fuels must be mobilized for ATP production
Photoreception
ability to detect a small proportion of the electromagnetic spectrum from ultraviolet to near infrared
Photoreceptors
range from single light-sensitive cells to complex, image-forming eyes. Vertebrates and “higher” invertebrates have ciliary photoreceptors in their eyes.
ciliary photoreceptors
have a single, highly folded cilium
folds form disks that contain photopigments.
photopigments are molecules that absorb energy from photons
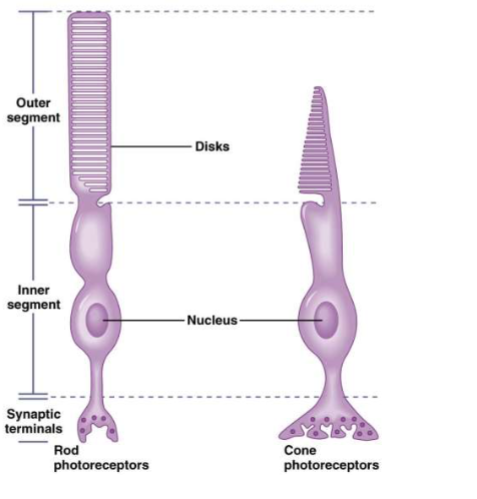
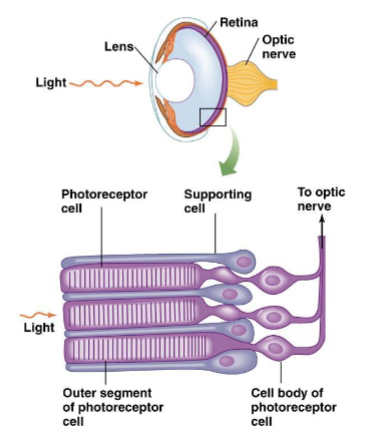
vertebrate photoreceptors
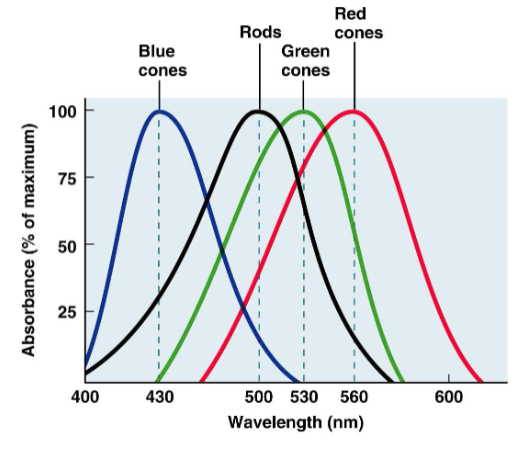
vertebrates have ciliary photoreceptors; rods (black and white) and cones (color)
both have inner and outer segments (outer segments contain photopigments and inner segments form synapses with other cells)
Rods
ciliary photoreceptor
outer segment is rod shaped
sensitive to very dim light
one type of photopigment
Cones
ciliary photoreceptor
outer segment is cone shaped
sensitive to brighter light
up to three types of photopigment in mammals
Photopigments
2 parts
Chromophore
derivative of vitamin A (ex: retinal), absorption of light converts bond from cis to trans
Opsin
G protein-coupled receptor protein
opsin structure determines photopigment characteristics (ex: wavelength of light absorbed)
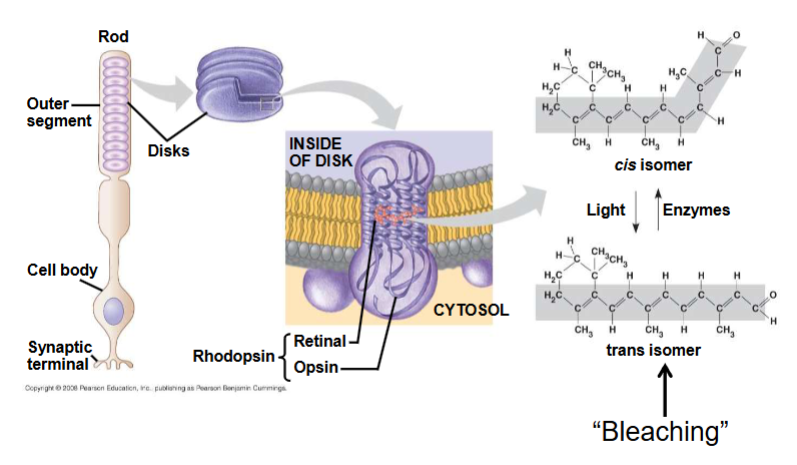
Phototransduction
Steps in photoreception
chromophore absorbs energy from photon
chromophore changes shape from cis to trans
activated chromophore dissociates from opsin “bleaching”
opsin activates G-protein transduction pathway
ion channels open or close
change in membrane potential
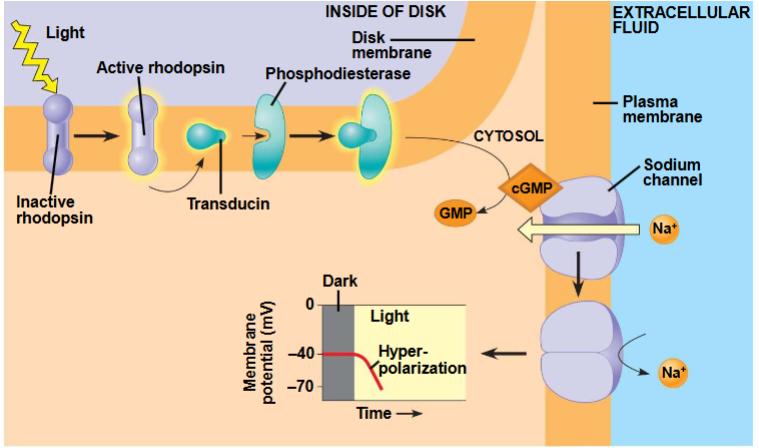
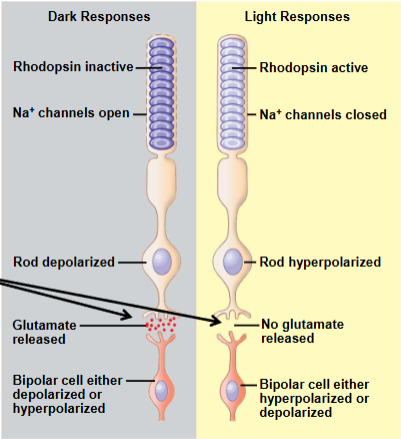
Light vs. dark on rods and cones
In the dark- rods and cones release the neurotransmitter glutamate into synapses with neurons called bipolar cells
Bipolar cells are either hyperpolarized or depolarized in response to glutamate
In the light- rods and cones hyperpolarize, chutting off glutamate
the bipolar cells are then either hyperpolarized or depolarized
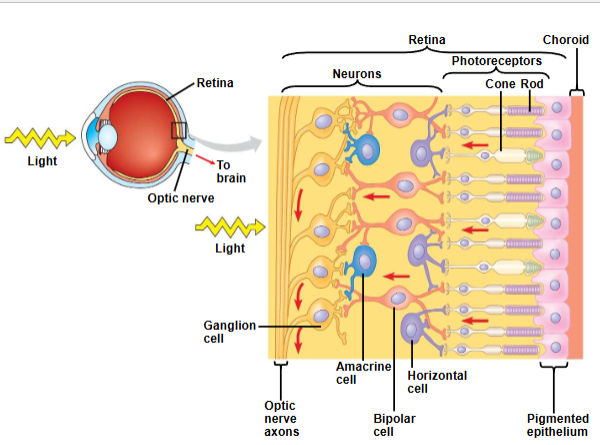
Other types of neurons that contribute to information processing in the retina
transmit signals from bipolar cells to the brain; these signals travel along the optic nerves, which are made of ganglion cell axons
horizontal cells and amacrine cells help integrate visual information before it is sent to the brain
interaction among different cells results in lateral inhibition, a greater contrast in image
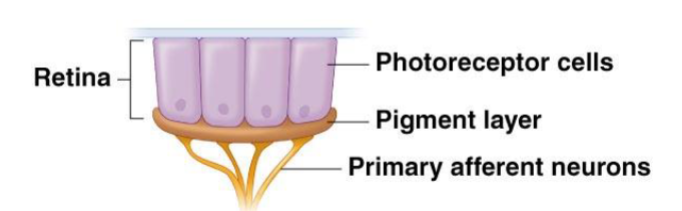
Flat sheet eyes
weak sense of direction and good sense of intensity.
Often in larval forms or as accessory eyes in adults
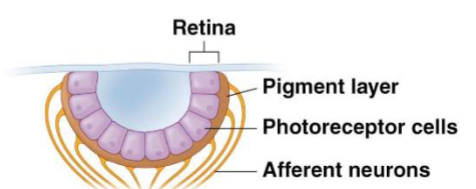
cup shaped eyes
Retinal sheet is folded to form a narrow aperture
discrimination of light direction and intensity
light-dark contrast
poor image formation (poor resolution)
vesicular eyes
present in most vertebrates
lens in the aperture improves clarity and intensity
lens refracts light and focuses it onto a single point on the retina
image formation, good resolution
convex eyes
annelids, arthropods
photoreceptors radiate outwards, convex retina
eyespots
cells or regions of a cell that contain photosensitive pigment, protist Euglena
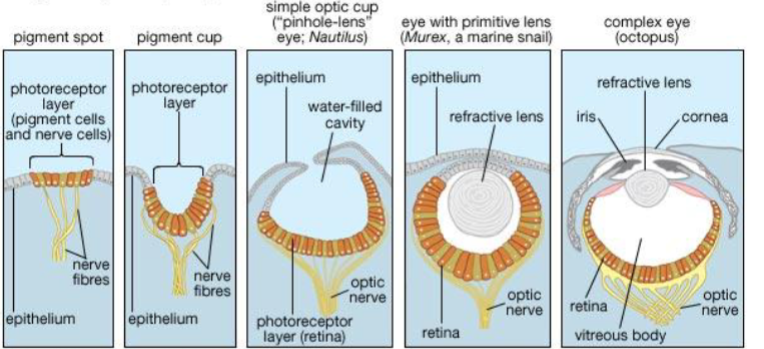
Stages of eye complexity in mollusks
pigment spot- light, dark, limited direction ex: limpets
pigment cup- light, dark, good direction ex: slit shell mollusk
simple optic cup- light, dark, very good direction, very blurred, dark, small image ex: nautilus
eye with primitive lens- light, dark, excellent direction, blurry image ex: murex
complex eye- light, dark, excellent direction, very sharp, very sharp image ex: octopus
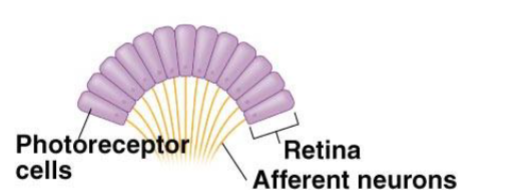
Cephalopod eye and retina
photoreceptors are on the surface of the retina
supporting cells are located between photoreceptor cells, no outer layers of cells associated with photoreceptors
axons of photoreceptors form optic nerve
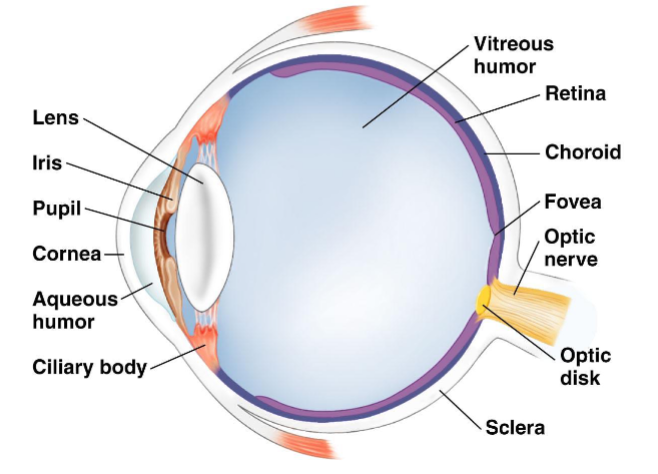
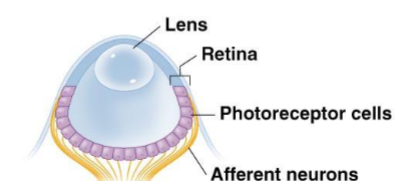
Structure of the vertebrate eye
sclera- white of the eye
cornea- transparent anterior layer
retina- layer of photoreceptor cells plus pigmented epithelial cells
choroid- pigmented layer behind retina
tapetum- layer in the choroid of nocturnal animals that reflects light
iris- two layers of pigmented smooth muscle
pupil- opening in iris allows light into eye
lens- focuses image on retina
ciliary body- muscles that change lens shape
aqueous humor- fluid in the anterior chamber
vitreous humor- gelatinous mass in the posterior chamber
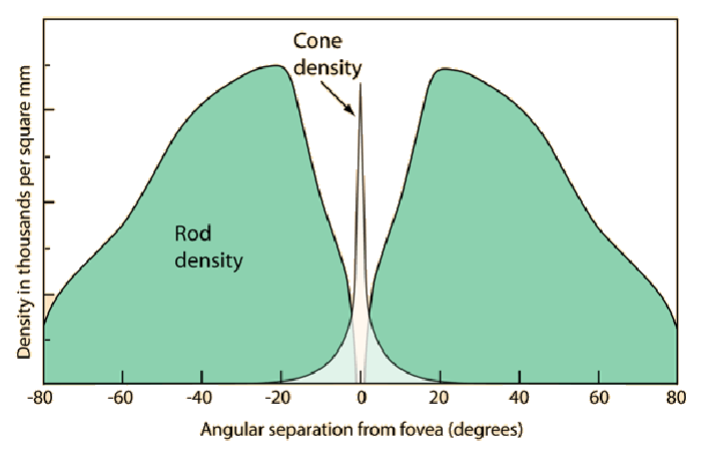
Fovea
region in center of retina, overlying bipolar and ganglion cells are pushed to the side (so more direct light path)
contains only cones, color vision, provides the sharpest images
image is focused on the fovea
Brain processes the visual signal
AP travels from retina to brain
optic nerves→ optic chiasm → optic tract → lateral geniculate nucleus → visual cortex
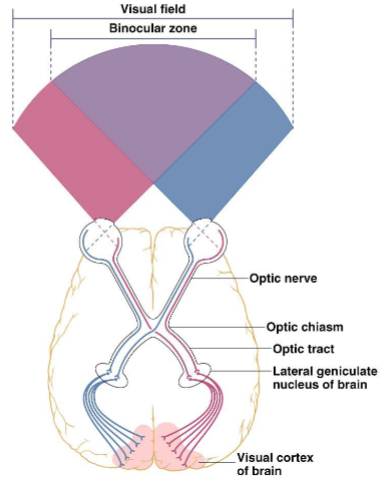
binocular vision
eyes have overlapping visual fields
combine and compare information from each eye to form a 3D image
depth perception
info from left field of view going to left brain, info from right field of view going to the right brain
optic chiasm
optic nerves meet at the _____ near the cerebral cortex and cross, with information from the right visual field sent to the left hemisphere of the brain and vice versa

Color vision
detecting different wavelengths of visible light
requires photopigments with different light sensitivities
most mammals see 2 colors (dichromatic)
humans see 3 (trichromatic) or 4 (tetrachromatic) colors
birds, fish, reptiles see 4 or 5 (pentachromatic) colors
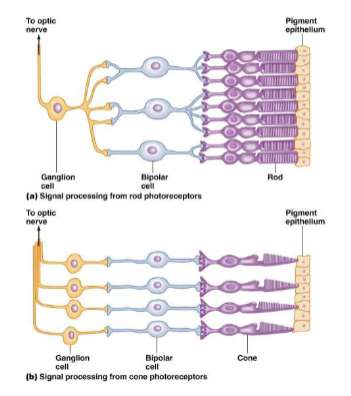
Rods vs Cones
Rods
convergence- many rods synapse with a single bipolar cell, many bipolar cells synapse with a single ganglion cell
ganglion cells have large receptive field
poor resolution (fuzzy image)
Cones
each cone synapses with a single bipolar cell
each bipolar cell connects to a single ganglion cell
ganglion cell has small receptive field
high resolution
on- center ganglion cells
stimulated by light in center of receptive field
inhibited by light in periphery of receptive field
off- center ganglion cells
stimulated by dark in center of receptive field
inhibited by dark in periphery of receptive field
signal processing in the retina
on and off regions of the receptive field of ganglion cells improve contrast of light and dark
photoreceptors in center and periphery inhibit each other by lateral inhibition
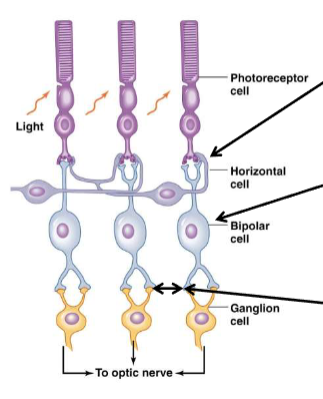
Lateral inhibition in the retina
horizontal cells are primarily (maybe all) inhibitory, and act on photoreceptors
bipolar cells can either be inhibited or excited by photoreceptors
amacrine cells are primarily inhibitory, acting mainly on bipolar cells
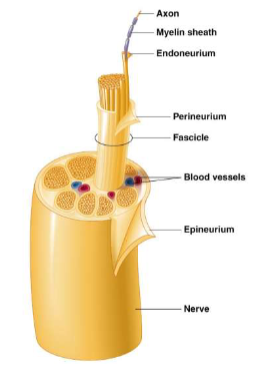
nerve structure
bundles of myelinated and sometimes unmyelinated axons enclosed in several layers of connective tissue
Spinal nerves
branch from spinal cord
enter and exit between adjacent vertebrae
named based on region of vertebral column from which they emerge
mixed nerves
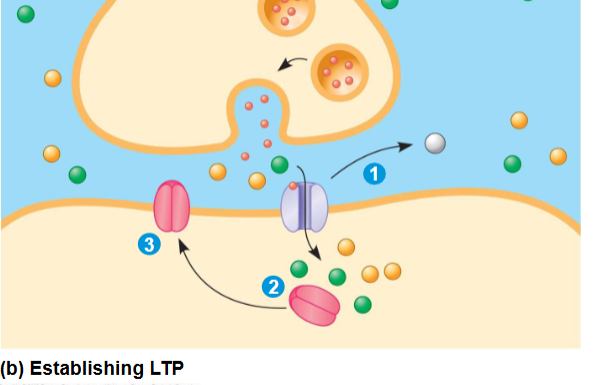
Long Term Potentiation (LTP)
Form of learning, involves an increase in the strength of synaptic transmission
involves 2 glutamate receptors
if the postsynaptic neuron is heavily stimulated, the set of receptors present on the postsynaptic membranes changes
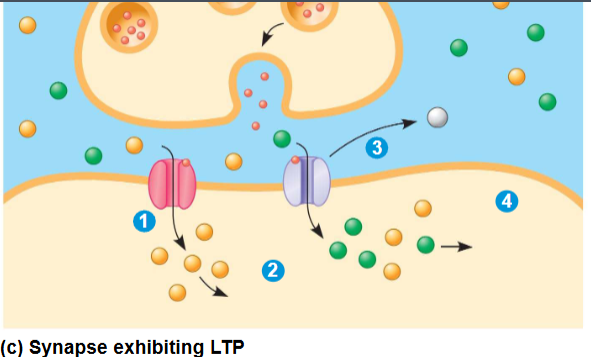
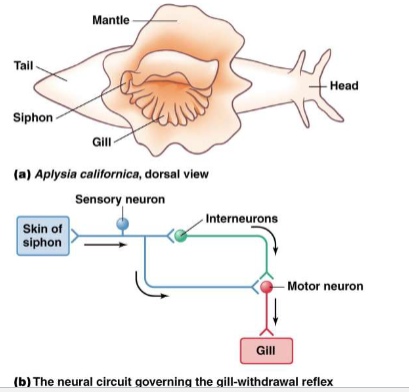
Habituation
decline in response to a stimulus after repeated exposure
allows animal to ignore unimportant stimuli and focus on novel stimuli
caused by changes in the presynaptic axon terminal at the synapse with the motor neuron (inactivation of some voltage gated Ca2+ channels= lower neurotransmitter release)
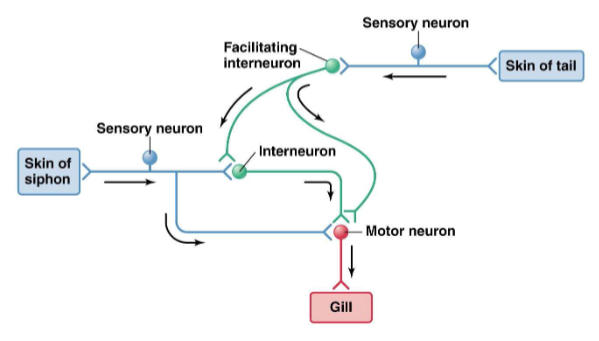
Sensitization
increase in the response to a gentle stimulus after exposure to a strong stimulus
caused by changes in the presynaptic axon terminal
Involves a secondary circuit
serotonin released by facilitating interneuron → binds to receptors → activation of G-proteins → inactivation of K+ channels → higher AP duration → Ca2+ influx → higher neurotransmitter release by sensory neuron
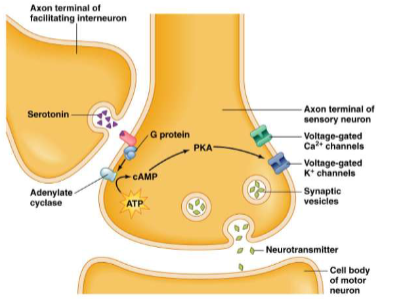
Serotonin
Keeps voltage-gated K+ channels deactivated. Can’t repolarize or hyperpolarize, more likely to fire
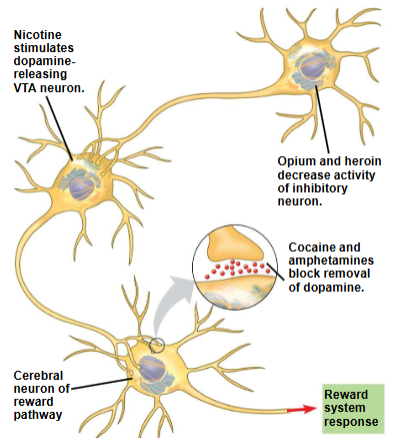
Drugs and the brain’s reward system
some drugs are addictive because they increase activity of the brain’s reward system. These include cocaine, amphetamine, heroin, alcohol, and tobacco
Addiction is characterized by compulsive consumption and an inability to control intake.
Addictive drugs enhance the activity of the dopamine pathway
Drug addiction leads to long-lasting changes in the reward circuitry that cause craving for the drug
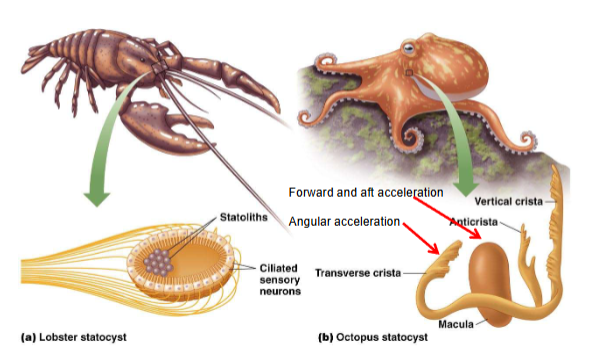
Statocysts
organ of equilibrium in invertebrates
hollow, fluid-filled cavities lined with mechanosensory neurons
statocysts contain statoliths (dense particles of calcium carbonate, movement of statoliths stimulate mechanoreceptors)
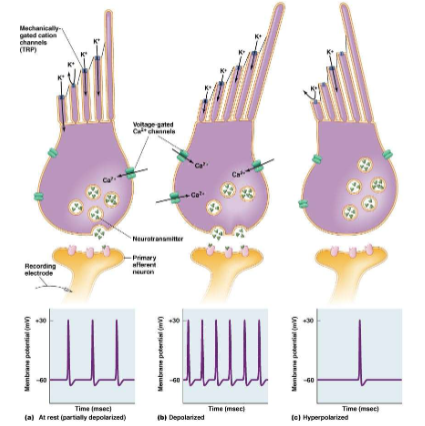
Vertebrate hair cells
mechanoreceptor for hearing and balance
modified epithelial cells ( not neurons)
cilia on apical surface (kinocilium is a true cilium, stereocilia is a microvilli). Tips of stereocilia are connected by proteins (tip links)
mechanosensitive ion channels in stereocilia (movement of stereocilia → change in permeability)
change in membrane potential
change in release of neurotransmitter from hair cell
Neutral position- channels open and K+ flowing in, cell releasing some neurotransmitter. APs fire at intermediate frequency in afferent nueron
bent hard to right: all K+ channels open, more Ca2+, more APs in afferent neuron
bent hard to left: most K+ channels closed, some Ca2+, rare single AP
operate opposite of other cells. External rich in K+, internal rich in Na+
Lateral line system
most fish and aquatic amphibians have a lateral line system along both sides of their body.
Contains mechanoreceptors with hair cells that detect and respond to water movement.
Array of neuromasts within pits or tubes running along the side of the body
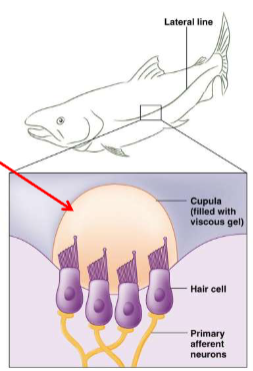
neuromast
Hair cells and cupula (stereocilia embedded in gelatinous cap)
detect movement of water
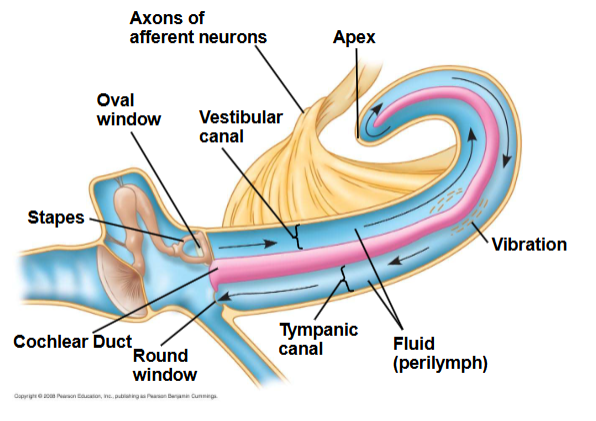
Sound wave traced through ear
Stapes pushes sound wave through, goes all the way around to round window.
Cochlear duct is where the readings of vibrations happen
Sheet of afferent neurons coming off the cochlea makes up the auditory nerve
Pinna acts as a funnel to collect more sound, middle ear bones increase the amplitude of vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the oval window
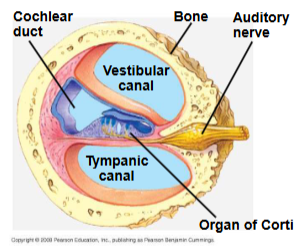
vestibular and tympanic canal filled with fluid (high Na+, low K+, same as interstitial fluid)
Cochlear duct (high K+, low Na+), contains hair cells. Has a tectorial membrane.
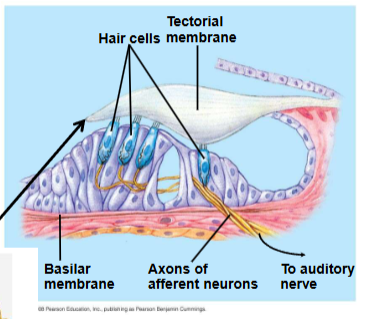
Tectorial membrane doesn’t touch bottom of vestibular canal. Hair cells are stuck to bottom of tectorial membrane, sits on basilar membrane (moves up and down when part underneath moves)- we sense that as sound.
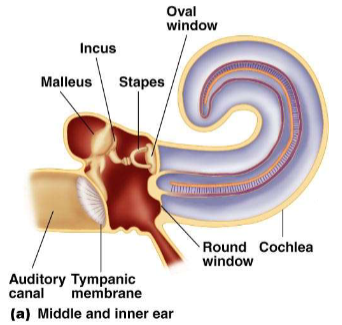
Structure of mammalian middle ear
Perilymph- fills vestibular and tympanic ducts. Similar to extracellular fluids (high K+ and low Na+)
Endolymph- fills cochlear duct, different from extracellular fluid (high K+ and low Na+)
Organ of corti- hair cells on basilar membrane, inner and outer rows of hair cells, sterocilia embedded in tectorial membrane in cochlear duct (filled with endolymph)
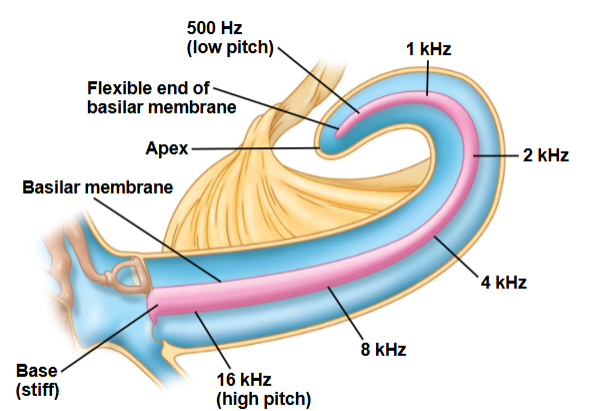
encoding sound frequency
Basilar membrane is stiff and narrow at the proximal end and flexible and wide at distal end.
high frequency sound vibrates stiff end
low frequency sound vibrates flexible end
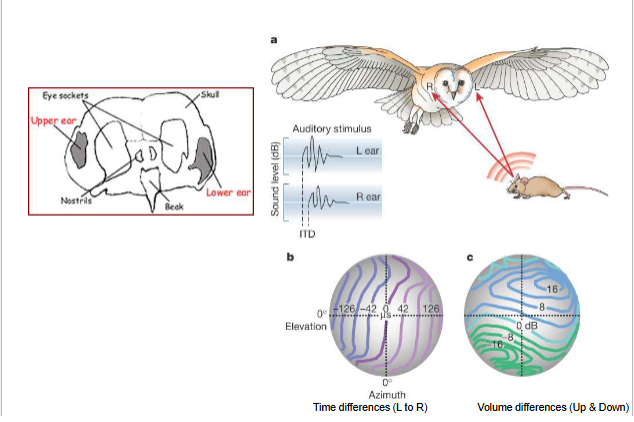
Owl ears
Brain uses time lags and differences in sound intensity to detect location of sound.
sound in right ear first (sound located to the right)
sound louder in right ear (sound located to the right)
rotation of head helps localize sound
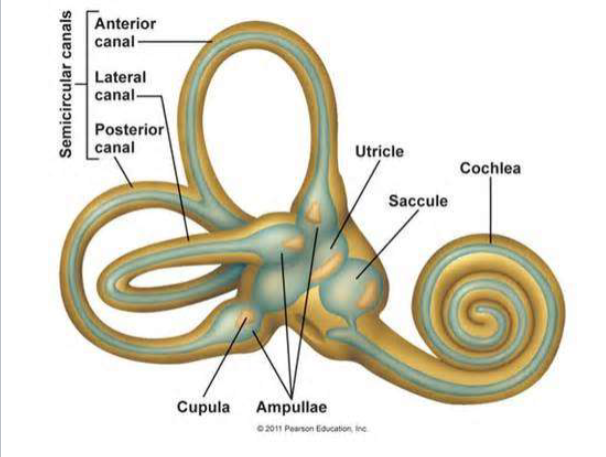
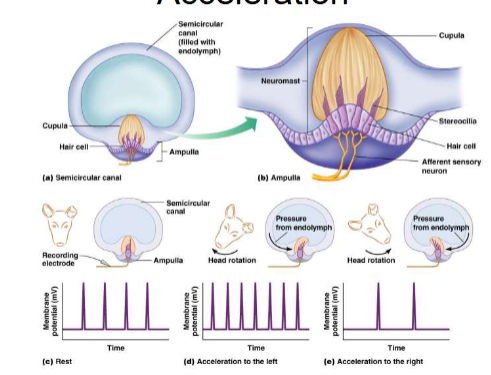
Vestibular apparatus
detects movements.
3 semi-circular canals (can hear in all 3 dimensions) with enlarged region at one end (ampulla)
two sack-like swellings (utricle and saccule)
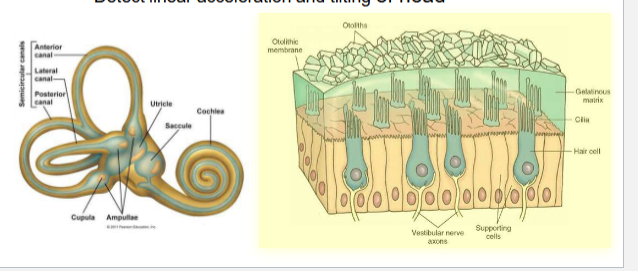
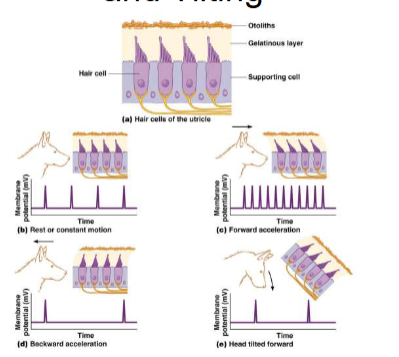
Macula
present in utricle and saccule
mineralized otoliths suspended in a gelatinous matrix
stereocilia of hair cells embedded in matrix
>100,000 hair cells
detect linear acceleration and tilting of head
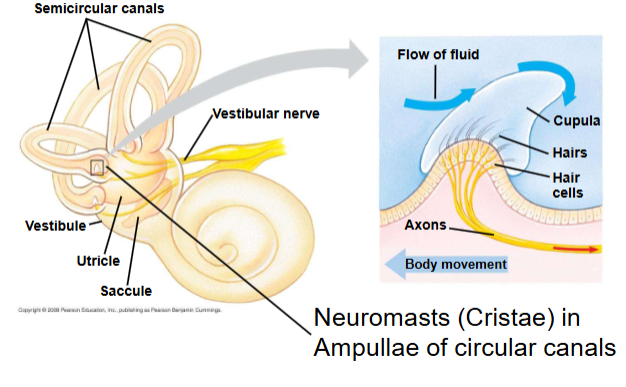
Cristae
Neuromasts (cristae) in ampullae of circular canals. They detect angular acceleration
Down-regulation
Target cells can alter receptor numbers. Target cell decreases number of receptors, often due to high concentration ligand (insulin resistance)
Heart’s role in pumping blood
Left side of heart pumps and receives only O2 rich blood, right side receives and pumps only O2 poor blood
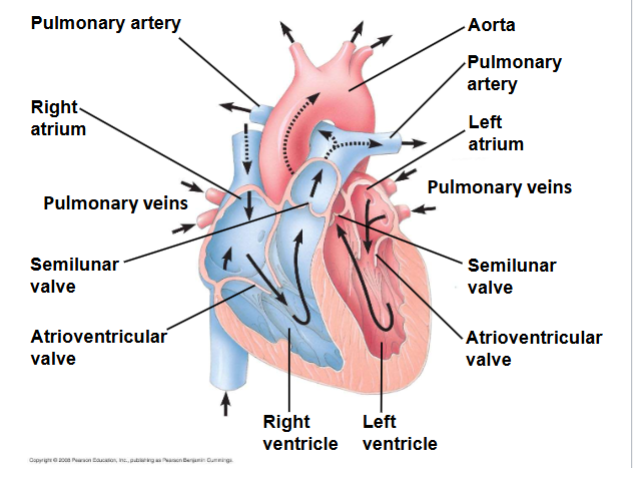
Path of blood through the heart
Blood flows into right ventricle, is pumped to lungs to get O2, O2 rich blood from lungs enters heart at left atrium and is pumped through the aorta to the body tissues by the left ventricle. Blood returns to the heart through the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava, which flows into the right atrium to the right ventricle.
Aorta
Provides blood to the heart through the coronary arteries and moves blood from the left ventricle to the body tissues. Semilunar valves contorl blood flow to the aorta and the pulmonary artery
Stroke volume
Amount of blood pumped in a single contraction
Cardiac output
volume of blood pumped into the systemic circulation per minute and depends on both the heart rate and stroke volume
control of contraction
vertebrate hearts are myogenic (cardiomyocytes produce spontaneous rhythmic depolarizations)
Cardiomyocytes are electrically coupled via gap junction to ensure coordinated contractions