MICR5831 L9: Protein Expression, Purification & Analysis 8/7/25
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Describe two strategies for purifying proteins from cloned genes (slide 4)
1) Overexpression of proteins → conventional chromatographic purification
-Protein mass, charge, hydrophobicity
-Purification requires specialist expertise, laborious
-Protein is in its original form
2) Overexpression → affinity chromatography
-Recombinant protein fused to a protein tag w/ affinity to a specific substrate
-Relatively simple, no specialist expertise required
-Tag/Fusion partner may have to be removed for protein to attain normal function
What characteristics of a fusion vector allow it to have high protein transcription and high protein expression? (slide 5)
1) Medium → High plasmid copies >20 copies/cell
2) MCS w/ directional cloning and flexible restriction sites
3) Strong Promoters
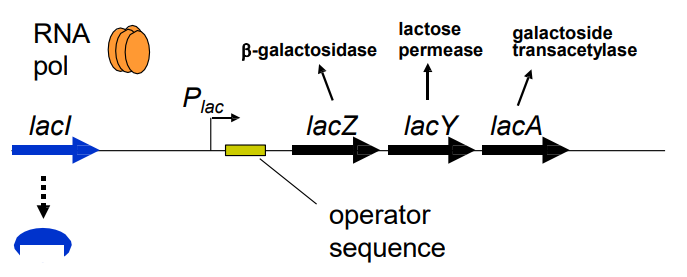
Describe the lactose metabolism operon, a cluster of genes transcribed from same promoter (slide 7)
1) Plac promoter – Transcribes lacZYA genes
2) LacI– Represses transcription from Plac
3) LacY – Imports lactose → cell
4) LacZ – Hydrolyses lactose → galactose + glucose → energy
5) LacA – Unknown function; not required for catabolism
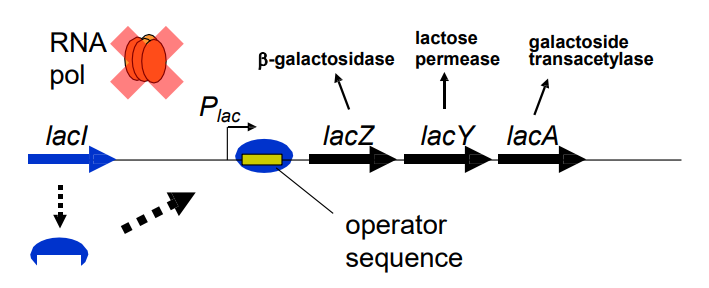
What happens to the expression of the lacZ operon in the presence of low levels of lactose? (slide 8)
-LacI repressor binds operator sequence
-Binds between Plac promoter and lacZ gene
-Prevents RNApol from transcribing lacZ genes
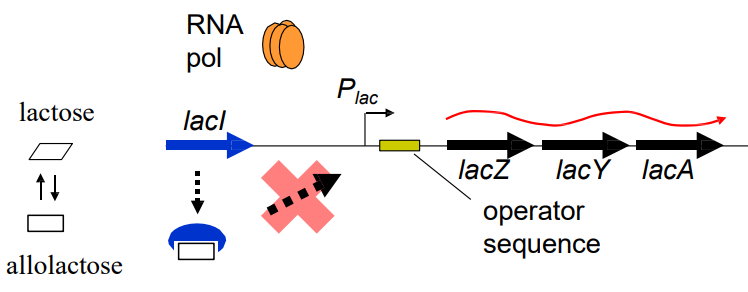
What happens to the expression of the lacZ operon in the presence of high levels of lactose? (slide 9)
-Lactose → Allolactose (natural isomer)
-Allolactose binds LacI repressor
-RNApol binds to operator, transcribes from Plac promoter
-IPTG de-represses transcription of lacZYAgenes
How does IPTG, a synthetic structural analogue of allolactose work to change the expression of a lacZ promoter? (slide 9)
-Both IPTG + allolactose bind to LacI repressor
-De-repress transcription of lacZYAgenes
-RNApol can bind to operator sequence + Plac promoter
What are the important genetic features of pMALC2? (slide 11)
1) Ptac promoter
2) LacI repressor
3) Transcriptional terminators
4) Translational fusion with partner protein MalE
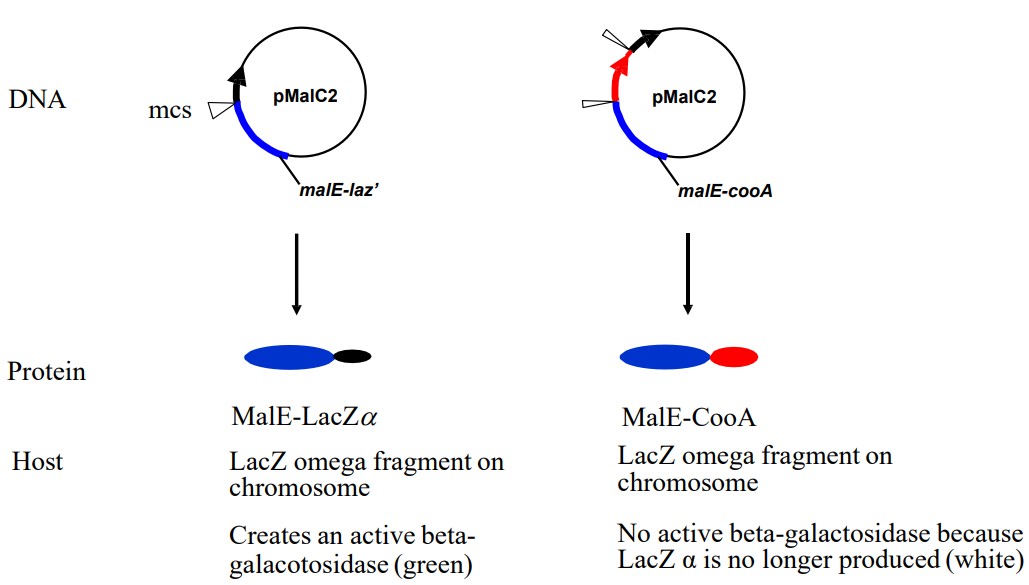
Explain the blue white screening mechanism that uses LacZ omega fragments on each chromosome in the pMalC2 vector. (slide 12)
1) MalE-LacZα
-Creates an active betagalacotosidase (green)
2) MalE-CooA
-No active beta-galactosidase because LacZ α is no longer produced (white)
What is the process for purifying MBP-fusion proteins? (slide 13)
1) Bind MalE-fusion protein to amylose resin, retained on column while others are washed off
2) Elute MalE-fusion protein from column with maltose (competitive displacement)
How does the polymerisation of acrylamide occur? (slide 16)
1) Mixture of acrylamide/bis-acrylamide (ratio of 29:1)
2) Polymerisation initiated with catalysts (ammonium persulphate + tetramethylethylenediamine) → porous gel
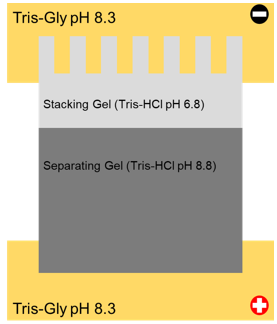
Using a diagram, explain the organisation of a SDS-PAGE electrophoresis gel and apparatus. (slide 17)
1) Stacking gel
-4% acrylamide
-Very porous
-Concentrate proteins at stacking/separating interface
2) Separating gel
-8% - 15% acrylamide
-Separation of proteins according to mass
What is the purpose of SDS in SDS-PAGE? (slide 18)
-Strong anionic detergent
-Denatures proteins
-Associates with protein → neg charge
What is the purpose of mercaptoethanol in SDS-PAGE? (slide 18)
-Reducing agent that breaks disulphide bonds
-Breaks bonds between thiol groups of cystine amino acids
-Denatures protein
Explain native and SDS PAGE and their relative advantages/disadvantages (slide 19 and 20)
1) SDS : Gel and electophoresis buffer contain SDS
-Cannot study natural protein-protein interactions or natural activities
-Predictable protein migration, high resolution separation technique
2) Native : No reducing agents/detergents/no boiling
-Can study protein-protein interactions and enzyme activities
-Unpredictable protein migration, mass determination not possible
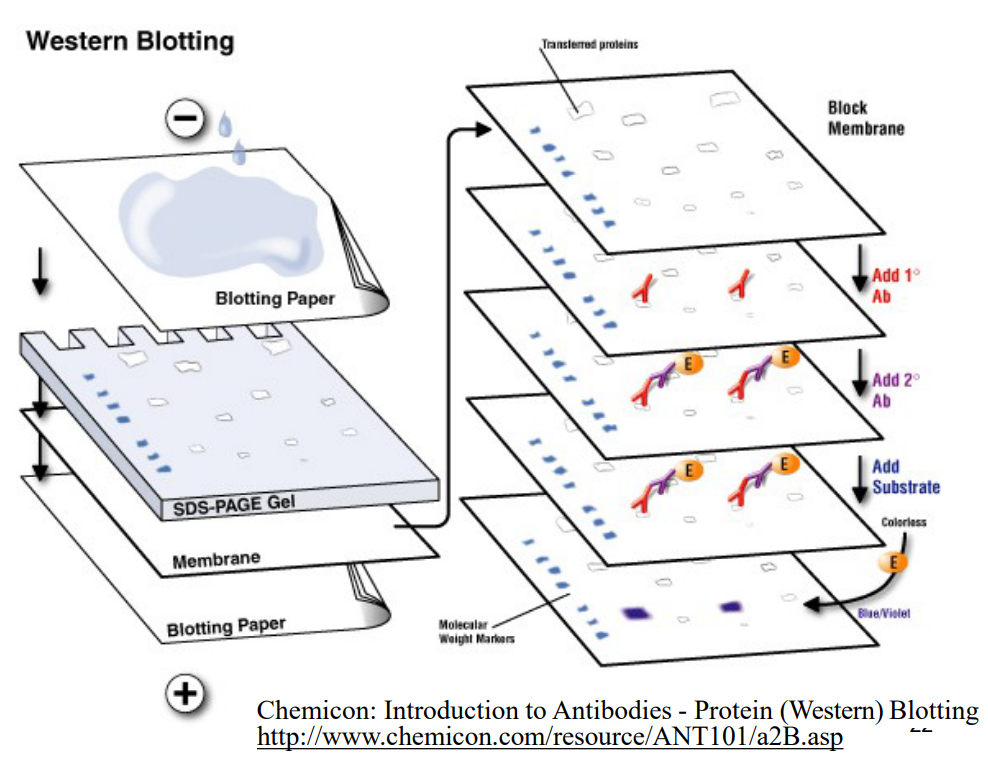
Using a diagram to illustrate, describe an outline for how Western blotting is performed. (slide 21 and 22)
1) Block non-specific protein binding sites on membrane by incubation with protein or mild non-ionic detergent (Bovine Serum Albumin, Tween 20)
2) Incubate membrane with antibody specific for protein of interest (eg. rabbit anti-MalE antibody)
3) Detect primary antibody binding with a secondary antibody-enzyme conjugate (eg. goat anti-rabbit IgG-alkaline phosphatase conjugate)
4) Detect enzyme activity of secondary antibody conjugate
Why would purifying recombinant proteins be useful?
1) Rational design of drugs
2) Vaccine development
3) Study biological activity/function
4) Study protein structure
How can you use recombinant protein purification to rationally design drugs?
-Inhibit protein function/activity → kill microbes or inhibit mechanisms of pathogenesis
-EX: Neuraminidase inhibitors such as Relenza® (influenza)
Name some recombinant vaccines that require protein purification to work
-Hepatitis B vaccine
-Pertussis toxoid vaccine
What are two strategies for expression and purification of recombinant proteins?
1) Expression Vectors
2) Expression Vectors + Purification Vectors (Fusion)
What is this strategy for recombinant purification?
1) Expression Vectors
-Overexpression of proteins
-Chromatographic purification of proteins
-Requires specialist expertise, laborious
-Protein will have its original form/function
What is this strategy for recombinant purification?
2) Expression + Purification Vectors (Fusion Vectors)
-Overexpression and affinity chromatography
-Recombinant protein fused to a protein "tag"(fusion partner) with affinity to a specific substrate
-Relatively simple, no expertise required
-Fusion partner should be removed for protein to regain normal function
What are some general characteristics of Expression Vectors?
1) Medium to high plasmid copy number (>20 copies/cell)
2) Multiple cloning site (mcs)
3) Strong regulated promoters
Why is it advantageous for Expression Vectors to have medium-high plasmid copy numbers?
-Easy to extract from host & manipulate
-Multiple copies → higher protein expression
Why is it advantageous for Expression Vectors to have an Multiple Cloning Site (MCS)?
-Flexibility in choice of restriction sites
-Allows directional cloning
Why is it advantageous for Expression Vectors to have strong regulated promoters?
Ptre or Ptac→ high level transcription → high level expression of protein
What are some other strongly regulated promoters besides Ptrc and Ptac with high levels of protein expression?
1) T7 RNA polymerase/promoter
2) AraC/Para
What is this?
-2 hexameric sequences at - 35 and -10 positions relative to transcription start point
-Separated by 15-20 bp
-Bind RNA polymerase → initiate transcription
E. coli promoters
What promoter is strongest in E. coli?
Consensus 070 dependent promoter
True or False: The more a promoter sequence deviates from the consensus sequence, the stronger it will be
False
True or False: The more a promoter sequence deviates from the consensus sequence, the weaker it will be
True
True or False: The genes belonging to an operon will each have different promoters
False, same promoter
How would you regulate transcription of the Lac operon responsible for lactose catabolism/breakdown?
Use the following:
1) LacI Repressor
2) LacY
1) Represses transcription from Plac (lac operon)
2) Imports lactose into cell
How would you regulate transcription of the Lac operon responsible for lactose catabolism/breakdown?
Use the following:
1) LacZ
2) LacA
1) Hydrolyses lactose → galactose + glucose → energy
2) Unknown function, not required for lactose catabolism
What will happen to the transcription of lactose catabolism/breakdown genes in this situation?
-Low levels of lactose in medium
-Reduce lactose catabolism gene transcription
-LacI repressor binds operator sequence
-Prevents RNA polymerase from transcribing genes
How does LacI repressor prevent RNApol from transcribing genes during low levels of lactose expression?
-Binds operator sequence
-Between promoter and lacZ gene
What will happen to the transcription of lactose catabolism/breakdown genes in this situation?
High
-Induce catabolism genes transcription → energy
-Allolactose isomer binds LacI repressor, stops it
-RNAPol transcribes Plac operon
-IPTG de-represses lacZYA genes transcription
How does allolactose (a natural isomer of lactose) encourage lactose catabolism gene transcription during high levels of lactose expression?
-Binds LacI repressor so it cannot bind operator sequence
-RNAPol transcribes from Plac operon
How does IPTG (Isopropyl B-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside) encourage lactose catabolism gene transcription during high levels of lactose expression?
-Synthetic structural analogue to allolactose
-Able to de-repress lacZYA gene transcription
Name one example of Lac repression systems being adapted to expression vectors
Vectors carrying Prac and Ptrc promoters often have lac operator and LacI repressors (lacI, laclq)
What are characteristics of expression vector pTrc99A?
-Strong transcriptional terminators downstream of cloning site
-rrnB T1 and rrnB T2 avoid destabilizing plasmid during high level transcription
What are these strong transcriptional terminators found in expression vector pTrc99A?
-Avoid destabilizing plasmid during high level transcription
rrnB T1 and rrnB T2
What is fusion vector is this?
-Used for synthesis of fusion proteins
-Recombinant fusion proteins are fused with Maltose-Binding Protein (MBP)
-Improves protein solubility and folding in E. coli
pMal-C2
What is this?
-Combining the coding sequences of two or more genes so they are both transcribed and translated into a single, larger polypeptide chain
-Also known as protein or gene fusion
Translational fusion
What are some characteristics of fusion vector pMal-C2 that make it similar to other expression vectors?
1) Ptac promoter
2) lacl repressor
3) Transcriptional terminators
What must happen before pMal-C2 undergoes translational fusion with MalE?
Gene is cloned
What N-terminal partner protein does pMal-C2 undergo translational fusion with?
MalE (Maltose Binding Protein)
What happens after pMal-C2 fusion vector clones its gene and undergoes translational fusing with MalE?
-Affinity with amylose resin
-MalE can be released from the fusion protein via digestion with Factor Хa
What is this?
-Factor Xa
-Protease that digests/cleaves peptide backbone
-Used to break apart MalE and fusion protein
What is this?
-Has affinity for amylose resin/multimers of maltose
-Retained on column after other proteins are washed off during fusion protein purification
MBP (Maltose-Binding Protein)
What happens when you purify and wash a column with MalE-fusion protein?
-Binds to amylose
-Remains on column after washing
What would you use to elute/competitively displace MalE-fusion protein from the column?
Maltose
What is this region used during fusion protein purification?
-Amino acid motif that gets recognized
-Ile Glu Gly Arg
Factor Xa protease cleavage site
What happens when Factor Xa protease recognizes the cleavage site?
-Fusion/recombinant protein is separated from MBР (MalE)
-Can capture MBP on the column, collect released protein in the eluate
Which fusion vector is this?
-Ptac promoter
-lacIq repressor
-N-terminal fusion partner: glutathione-S-transferase
pGEX
pGEX is fusion partners with glutathione-S-transferase.
1) Name the affinity chromatography medium
2) Name what elution occurs with
3) Name the enzyme that cleaves the fusion partner
1) Glutathione-agarose
2) Elution with glutathione
3) 3C protease found in Rhinovirus
Which fusion vector is this?
-PT7 promoter from bacteriophage T7
-No known repressor
-N-terminal hexahistidine fusion partner: Hexahistidine
pRSET
pRSET is fusion partners with Hexahistidine (6xHis)
1) Name the affinity chromatography medium
2) Name what elution occurs with
3) Name the enzyme that cleaves the fusion partner
1) Nickel-sepharose
2) Elution with imidazole (structural analogue of histidine)
3) Enterokinase (EK)
What separation technique is this?
-Mixture of acrylamide/bis-acrylamide (ratio of 29:1)
-Polymerization initiated with catalysts → porous gel
Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE)
What catalysts are used during SDS-PAGE?
Ammonium persulphate + tetramethylethylenediamine
What type of SDS PAGE gel is this?
-4% acrylamide, very porous (on top)
-Concentrate proteins in sample during electrophoresis at the stacking/separating interface
Stacking gel
What type of SDS PAGE gel is this?
-8% - 15% acrylamide (on the bottom)
-Determines pore size of the gel matrix
-Separation of proteins according to mass
Separating gel
How do you prepare a sample for SDS-PAGE?
-Boil in loading buffer
-SDS and reducing agent
What is this?
-SDS (Sodium dodecyl sulphate)
-Strong anionic detergent, denaturing agent
-Denatures proteins
-Associates with protein → Neg (-) charge
Name two examples of reducing agents combined with SDS to make SDS-PAGE loading buffer
1) 2-mercaptoethanol
2) Dithiothreitol
What is this?
-Reducing agent of SDS PAGE
-Intermolecular disulfide bonds broken to separate subunits
-Internal disulfide bonds broken to denature protein completely
Mercaptoethanol
Where are disulfide bonds formed before they are broken by reducing agents like Mercaptoethanol for SDS-PAGE?
-Between thiol groups
-Found on cysteine amino acids
True or False: Both the gel and electrophoresis both maintain a negative charge on proteins due to SDS content
True
True or False: During SDS, the charge:mass ratio will fluctuate as proteins migrate and separate based on their mass
False, charge:mass ratio remains constant
What is a sign that SDS-PAGE protein denaturation is complete?
-Proper migration
-Accurately reflects mass/size
-Good resolution or separation of proteins
What are the advantages of using denaturing gels for SDS PAGE?
-Predictable migration of proteins on gel
-High resolution separation technique
What are the disadvantages of using denaturing gels for SDS PAGE?
-Cannot study natural protein-protein interactions since complexes are dissociated
-Cannot study natural activities eg. enzymatic activity, receptor binding
What separation technique is this?
-No reducing agents/detergents/no boiling
-Proteins are in native state
-Different shapes, charges
-Migrate according to size, shape and charge
Native PAGE
True or False: Proteins in their native state will all look alike
False, they will have different shapes and charges
What are the advantages of Native PAGE (no denaturing SDS)?
-Can study protein-protein interactions (structures are maintained)
-Can see pilin-pilin and protein-chaperone interactions
-Can study enzyme activities (zymogram), binding activities with other molecules
What are the disadvantages of Native PAGE (no denaturing SDS)?
-Protein migration unpredictable
-Mass determination not possible
What stains can you use to detect proteins in SDS and native gels?
1) Coomassie Blue staining
2) Silver staining (more sensitive)
3) Sypro Ruby, other sensitive dyes
What is this protein detection technique?
-Identify specific protein expression in a complex mixture (100s to 1000s of proteins)
Western Blot
How does Western Blot work?
1) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from PAGE gel to a membrane
2) Block non-specific protein binding sites on membrane by incubation with protein
3) Incubate membrane with antibody specific for protein of interest
4) Detect binding of primary antibody with a secondary antibody-enzyme conjugate
5) Detection based on enzyme activity of secondary antibody conjugate
What is the first step of Western Blot?
Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from PAGE gel → membrane
True or False: Western Blot only works with SDS denaturing gel
False, it works with both denaturing and native gel
What membrane can proteins be electrophoretically transferred to via Western Blot?
1) Nitrocellulose
2) PVDF
What happens after electrophoretic transfer of proteins from PAGE gel to a membrane during Western Blot?
Block non-specific protein binding sites on membrane by incubation with protein
What protein can you use to block non-specific proteins from binding to the membrane during Western Blot?
-Bovine Serum Albumin
-Tween 20 (mild non-ionic detergent)
Why do we block non-specific protein binding sites on the membrane during Western Blot?
-Stops antibodies binding non-specifically to the membrane and other proteins
-Reduces background reactivity
What happens after non-specific protein binding sites on the membrane are blocked during Western Blot?
Incubate membrane with 1st antibody that is specific to protein of interest
What would you use this for during Western Blot?
-Rabbit anti-MalE antibody
-1st antibody that is specific to protein of interest
-Incubate membrane with it
What happens after incubating the membrane with an antibody specific to the protein of interest during Western Blot?
Detect binding of primary antibody with secondary antibody-enzyme conjugate
What would you use this for during Western Blot?
-Goat anti-rabbit IgG-alkaline phosphatase conjugate
-Secondary antibody-enzyme conjugate
-Use to detect binding of primary antibody
What happens after detecting the binding of a primary antibody to a secondary antibody-enzyme conjugate?
Detection based on enzyme activity of secondary antibody conjugate