Trachea, Bronchus, Bronchiole
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What are the 6 organs of the air conducting portion of respiratory system?
Nostrils
Nasopharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchus
Bronchioles
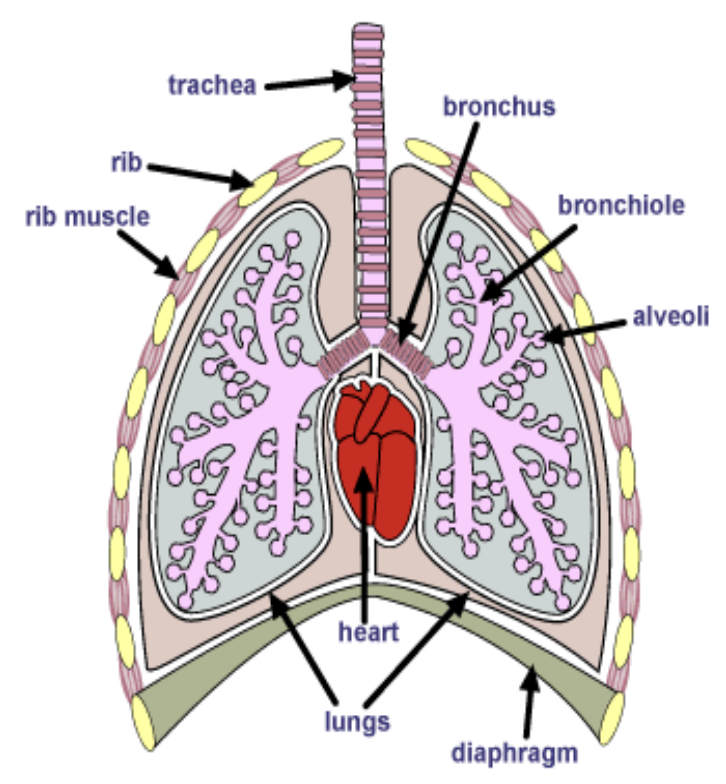
What are the 4 organs that make up the gaseous exchange portion of respiratory system? #009aff
Terminal bronchioles (maybe not)
Respiratory bronchioles
Alveolar duct (passageway branching from respiratory bronchiole)
Alveolar sac (group of alveoli)
Alveolus (smallest functional unit of lungs)
Trachea: #fe8c00
What are the 4 main histological layers of trachea?
4 main layers:
Mucosa #ffca00
Submucosa #00b41e
Cartilaginous layer
Adventitia
Trachea: Mucosa #ffca00
What can the mucosa be divided into?
2 layers:
Epithelium
Lamina propria
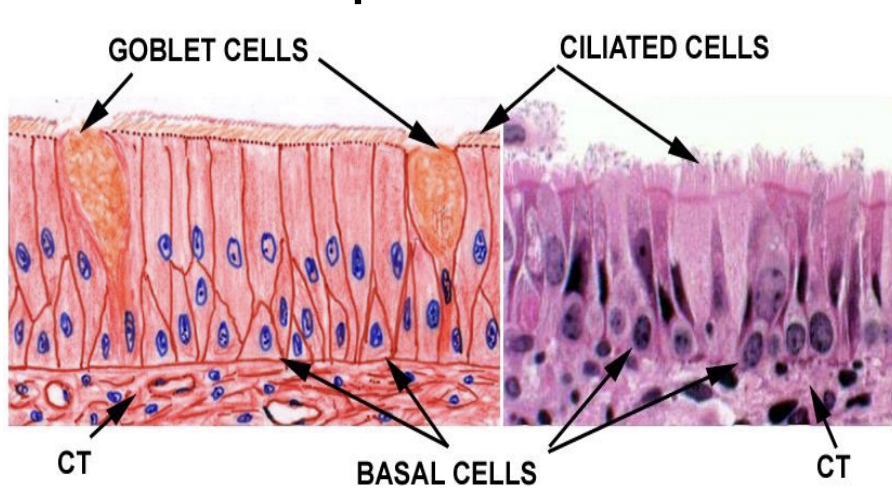
Trachea: Mucosa —> Epithelium #ffca00
What type
Contains what cells
What type: Pseudostratified ciliated columnar (typical respiratory epithelium)
Contains what cells:
Basal cells
Goblet cells
Brush cells
Clara cells
Neuroendocrine cells
Trachea: Mucosa —> Lamina Propria #ffca00
What type of layer
Contains
What type of epithelium
What type of layer: Layer of
Loose connective tissue and
Elastic fiber
Contains: Glands
What type of epithelium: Cuboidal
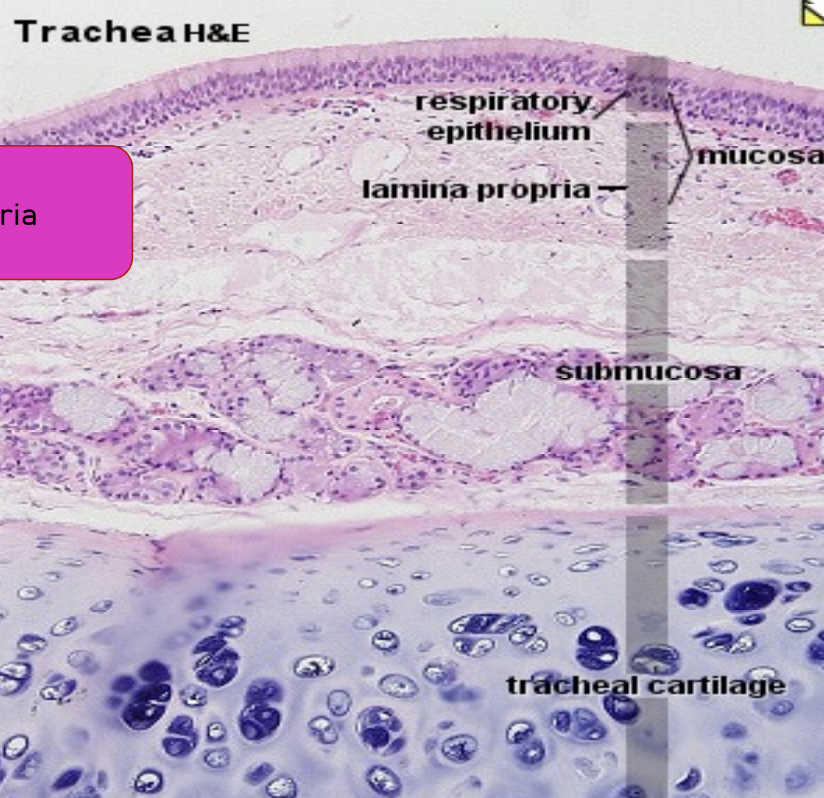
Trachea: Submucosa #00b41e
Type of layer
Contains
Type of layer: Irregular dense connective tissue
Contains:
Tracheal glands (cuboidal epithelium)
Blood and lymphatic vessels
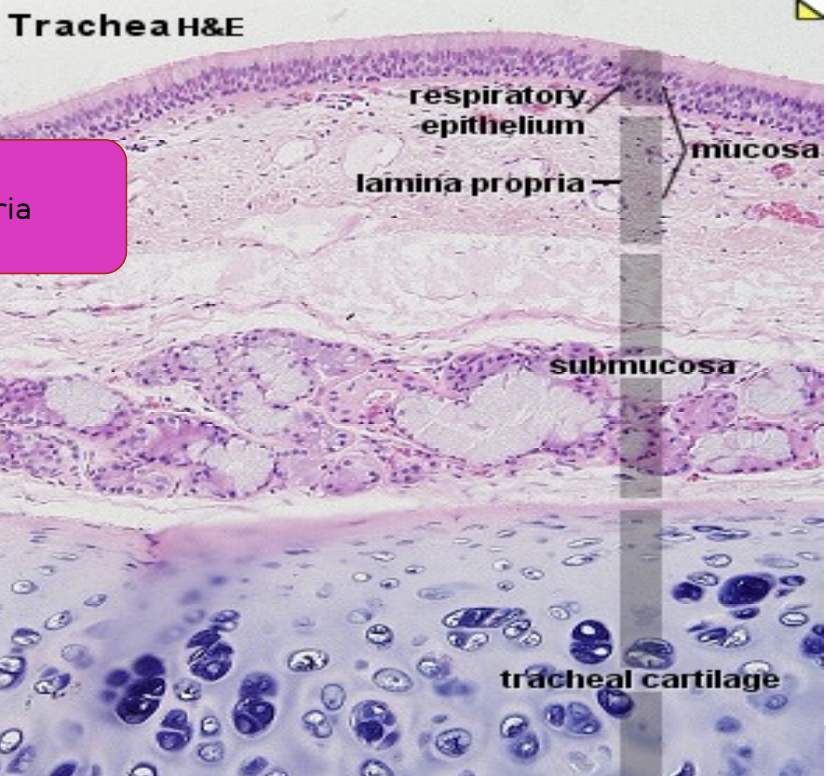
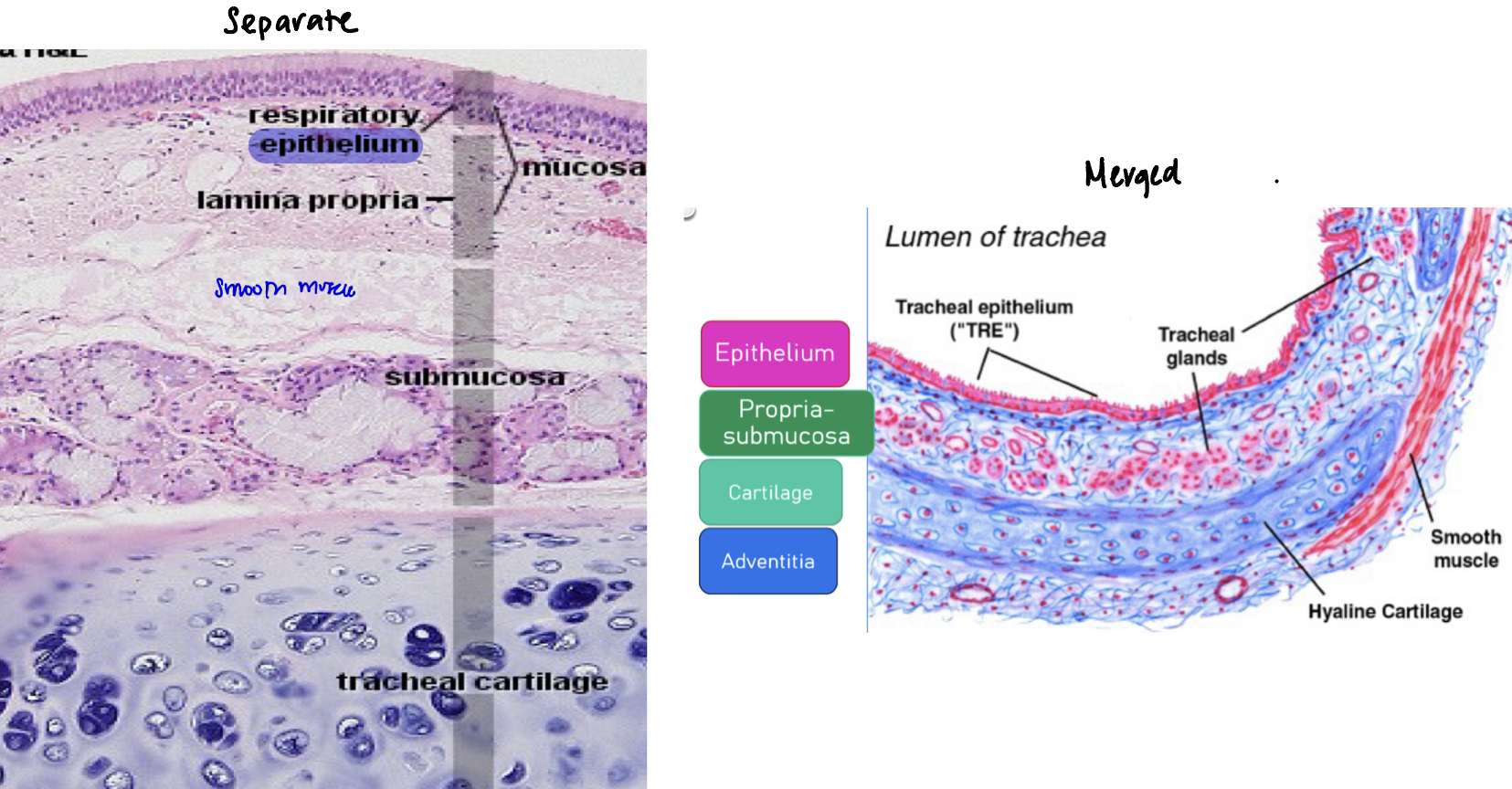
Trachea: Sometimes the lamina propria and submucosa are merged into propria submucosa
How can you tell it’s separated or merged?
Separate layers: There’s muscularis mucosae (smooth muscle layer) in between the 2 layers
Merged: There’s no muscularis mucosae in between the 2 layers
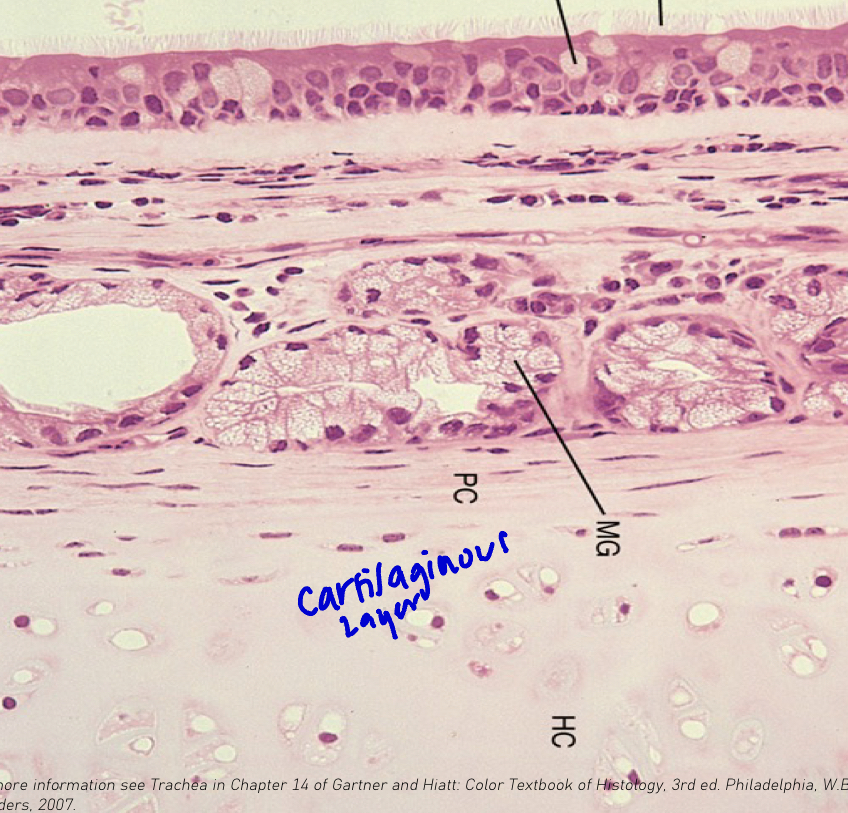
Trachea: Cartilaginous Layer
Shape of cartilage rings
Composition
Describe perichondrium
Shape of cartilage rings: C shape
Composition: Chondrocytes in lacunae
Describe perichondrium: Dense connective tissue surrounding the cartilage
Trachea: Adventitia
What
Composed of
Contains
What: Outermost dense connective tissue layer
Contains: Blood vessels, nerves and fat
As the airways divide, what happens to the
Diameter
Respiratory epithelium
Goblet cells
Clara cells
Glands, CT and cartilage
Elastic and smooth muscle tissue
Diameter: Smaller
Respiratory epithelium: Shorter
Goblet cells: Fewer
Clara cells: More numerous
Glands, CT and cartilage: Less
Elastic and smooth muscle tissue: Increase
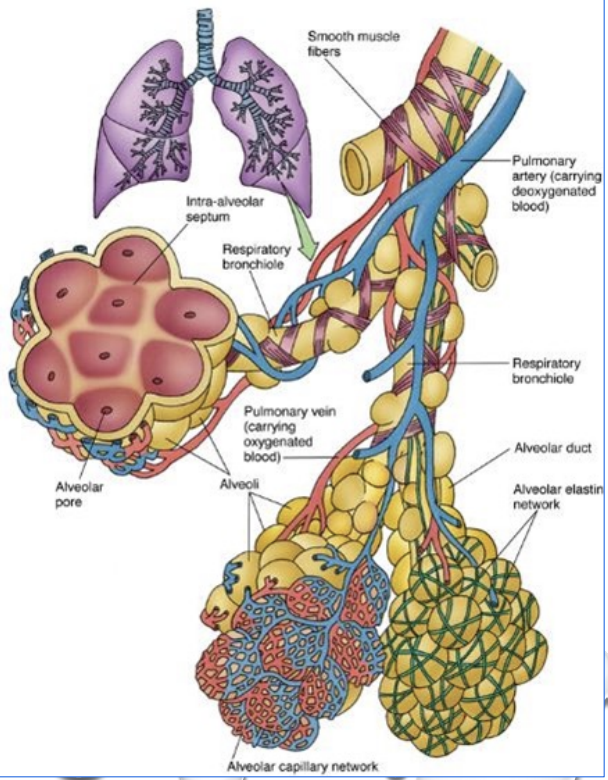
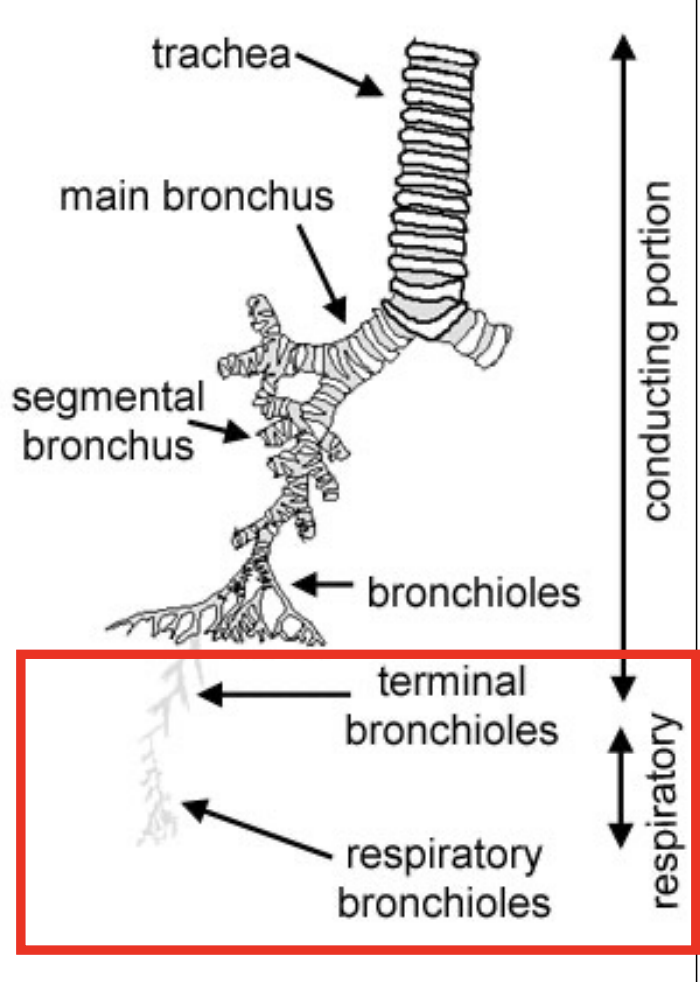
What is the organisational chart of the lungs?
Trachea —>
Extrapulmondary bronchi —>
Intrapulmonary bronchi —>
Respiratory bronchioles (gas exchange occurs) —>
Alveolar ducts —>
Alveolar sacs
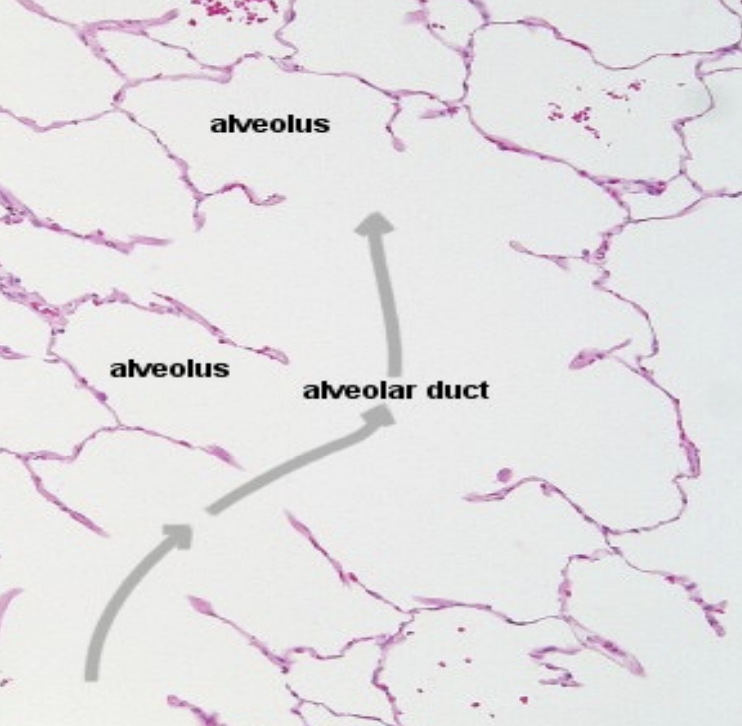
Lungs: Bronchus
What
Epithelium
Has what type of cartilage
Type of muscle present
Mucosa is
Lined with
As diameter decreases, what happens to the
Cartilage
Smooth muscle
What type of secretions occur
What specialised cells are present
What: Air-conducting passage
Epithelium: Pseudostratified ciliated COLUMNAR epithelium
Has what type of cartilage: Hyaline
Type of muscle present: Smooth muscle
Mucosa is: Rugated
Lined with: Typical respiratory epithelium
As diameter decreases, what happens to the:
Cartilage: Decline as plates
Smooth muscle: Increases
What type of secretions occur: Mucous/serous secretions
What specialised cells are present: BALT
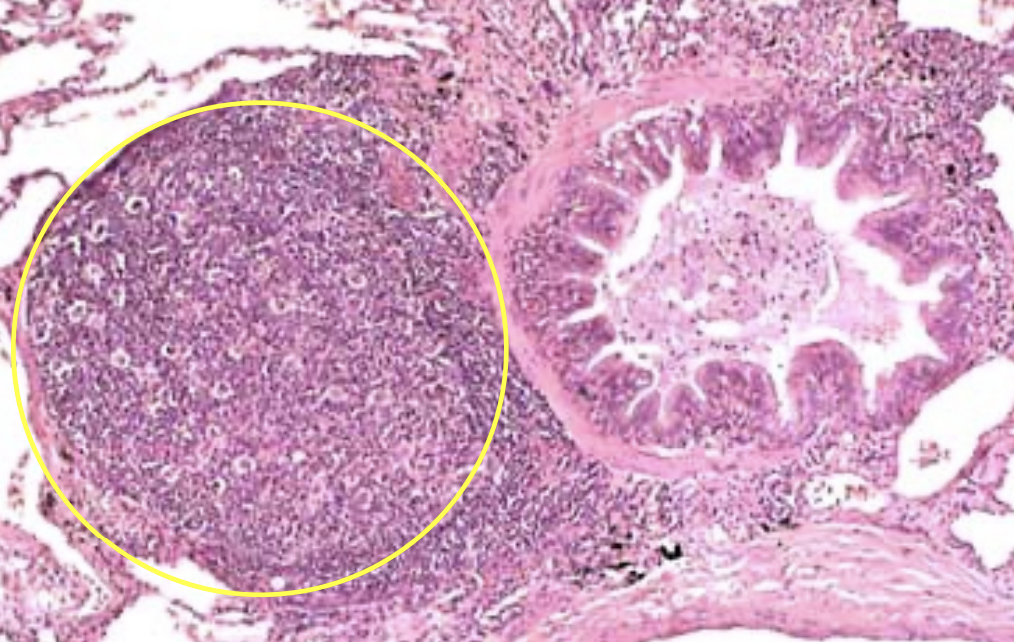
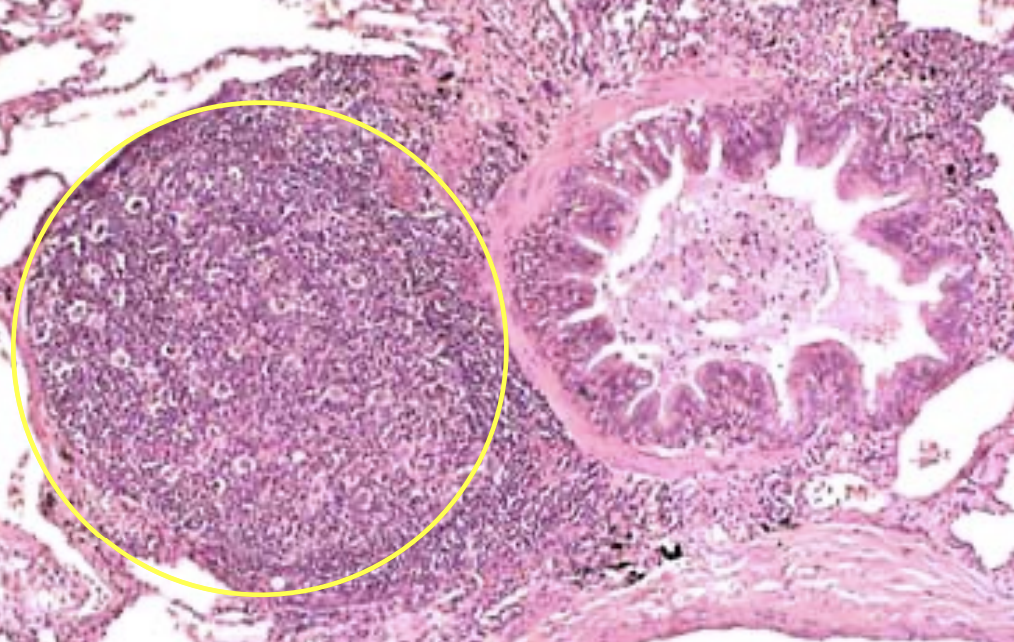
Lungs: What is within the yellow circle and then beside it?
Yellow circle: BALT
Beside it: Bronchiole
Lungs: Bronchiole #006dff
It’s also an air conducting passage, but how is it different from bronchus?
Epithelium
Which cells decrease
Which cells increase
Lamina propria
Are there glands?
What is present
What occurs to the adventitia
Different from bronchus:
Has only smooth muscle
No cartilage
Epithelium: Simple cuboidal ciliated epithelium
Which cells decrease:
Goblet cells
Basal cells
Which cells increase: Clara cells
Lamina propria:
Are there glands: No (glandless connective tissue)
What is present: Smooth muscle
What occurs to the adventitia:
No cartilage
But extensive network of elastic fibers around smooth muscle layers
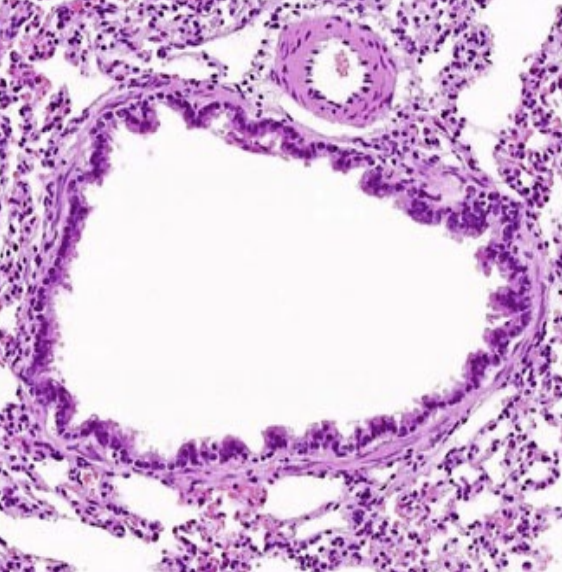
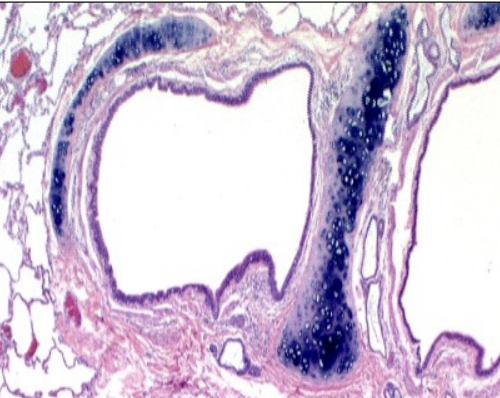
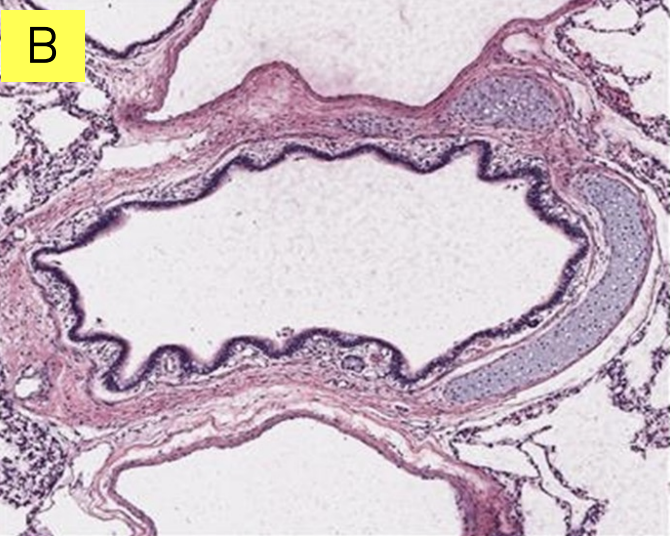
Lungs: Is it bronchus or bronchiole?
Bronchiole
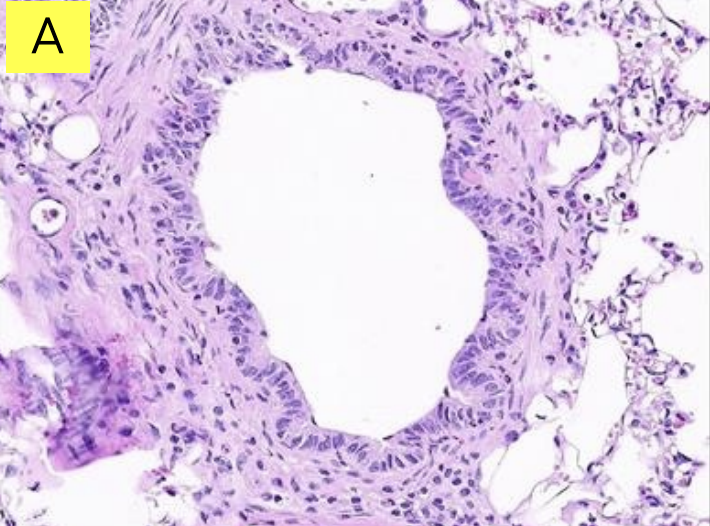
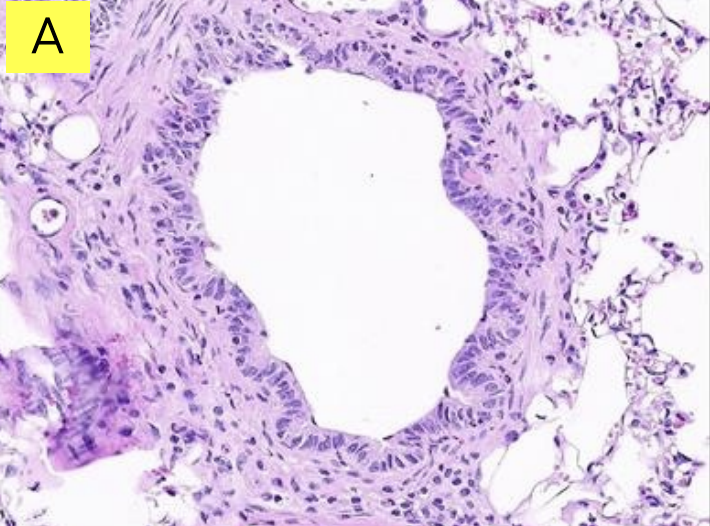
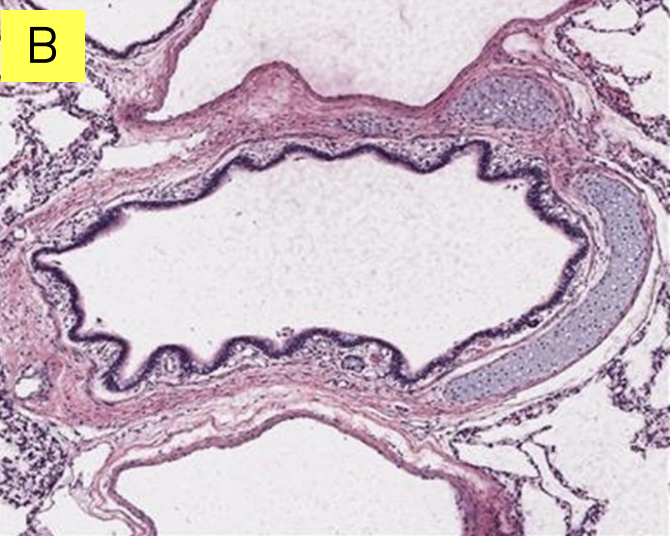
Lungs: Is it bronchus or bronchiole?
Bronchus
Lungs: Respiratory Bronchiole
Continuation of
Interrupted by
What is the epithelium
What occurs to the epithelium, lamina propria and smooth muscle
Continuation of: Terminal bronchioles
Interrupted by: Thin-walled alveoli (outpocketing)
What is the epithelium: Simple squamous
What occurs to the epithelium, lamina propria and smooth muscle: Altered in the occurrence of alveoli
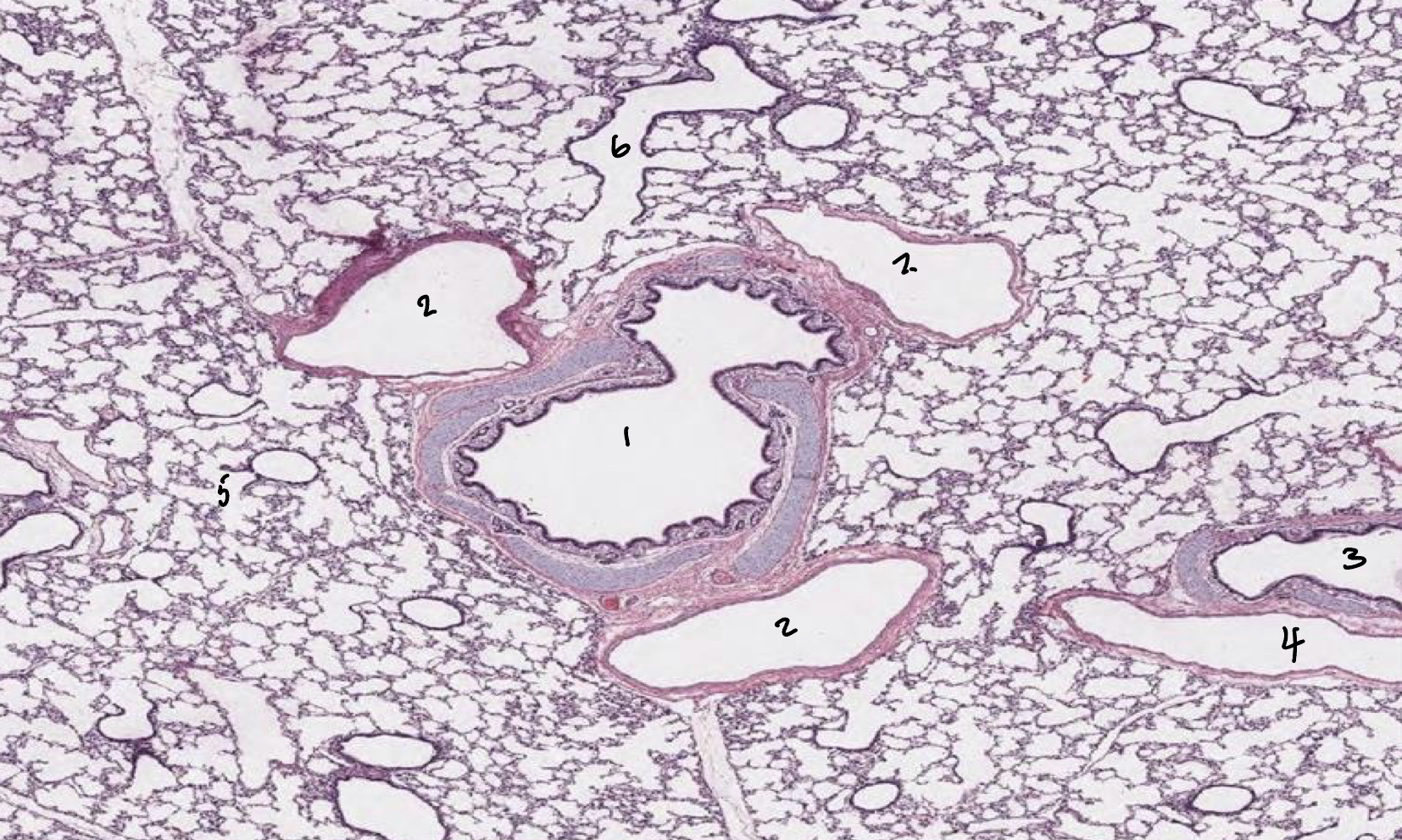
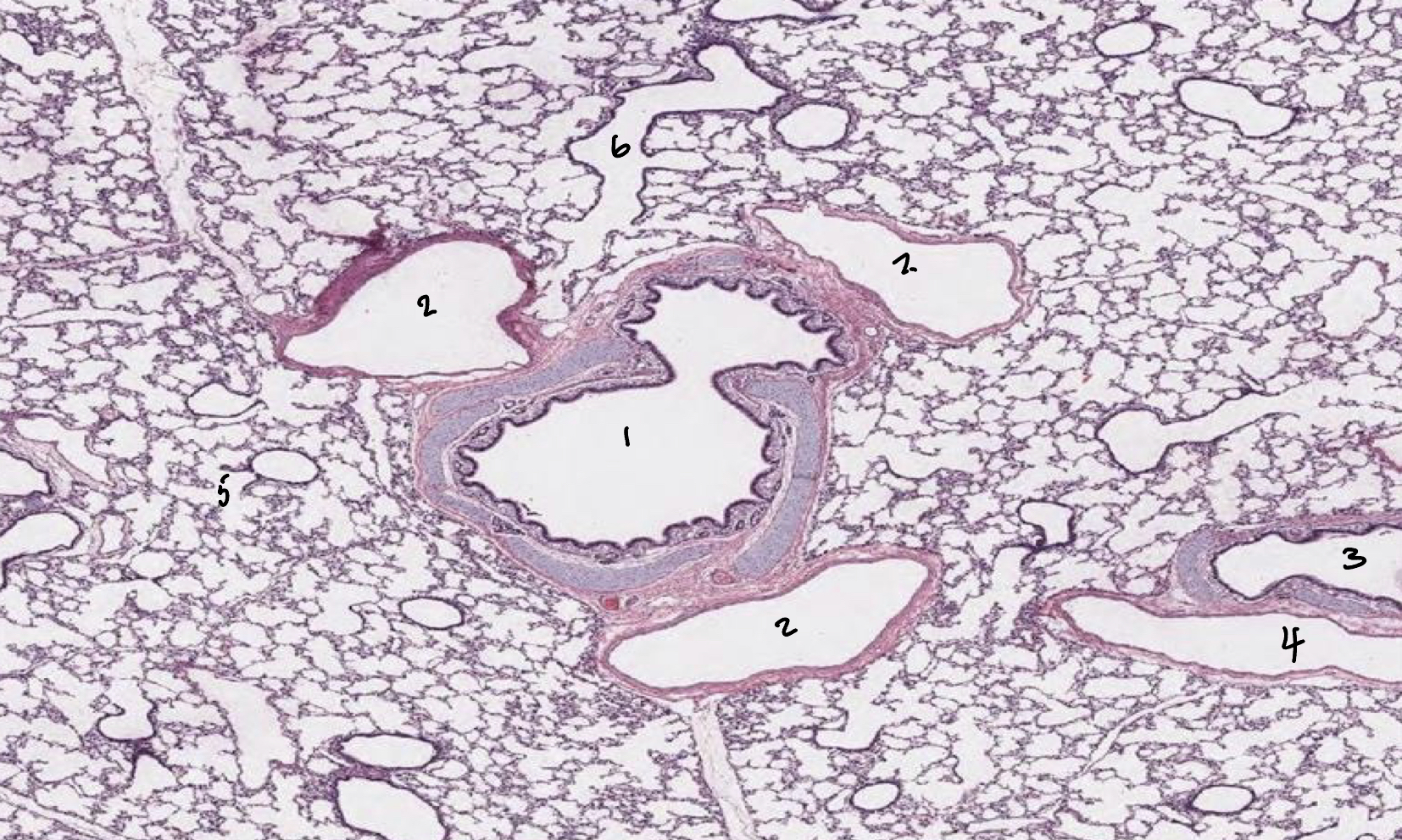
Lungs: Label 1-6
1: Bronchus
2: Bronchiole
3: Bronchus
4: Bronchiole
5: Alveolar duct
6: Respiratory bronchiole
Not alveolar duct because it has a wall so it’s a passage