Demand and supply - booklet 1
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What is a wage?
A wage is a price reward incentive signal and cost for firm
Describe demand for labour
It is derived
Factors influencing a firms demand labour and explain
An increase in demand means increase demand for labour
Higher productivity implies more attractive labour
And increased wage rate increases unit labour cost so demand falls
Complementary labour costs increase like national insurance commission or pension contributions decrease demand
If the price of other factors of production such as capital is cheaper firms may substitute workers
What is the marginal productivity theory of demand for labour?
Demand labour is dependent on the marginal revenue product. - the productivity of workers and price of goods workers are producing.
What is marginal revenue product and marginal product of labour?
Marginal revenue product is the change in a firms revenue resulting from employing one extra worker when all other factors are kept equal
Marginal product of labour is the changing output that results from employing one more worker
State the assumptions of MRP theory
All factors of production, other than labour or fixed
Workers are homogenous
Market is perfectly competitive
Evaluate assumptions of MRP
The model applies to competitive markets where profit maximising behaviour is assumed.
However many other factors determine wages such as monopoly trade unions and minimum wages and public versus private sector.
The model does not fit the public sector because it is not about revenue. It is hard to measure and governments have budgetary constraints. Private sector is more commercially driven so MRP model works better.
Is the law of diminishing marginal returns?
The law of diminishing marginal returns states that as a producer as one more factor of production to a fixed quantity of other factors the output increases but less than proportionally.
Formula for MRP
MRP =MPL x price
MRP = MC
Who sets the wage?
The industry
What is the elasticity of demand for labour?
Percentage change in quantity of labour demanded divided by percentage change in wage rate
Explain the factors affecting elasticity of demand
1. Labour costs as a percentage of total costs - a flavour is more expensive high percentage of total costs than labour demand is wage elastic
Ease and cost of factor substitution - when a firm substitutes easily and cheaply with capital labour demand is elastic
3. Time period - in the long run it is easier for firms to switch factor inputs so demand is elastic
Define economic inactivity
When people of the labour force do not work due to caretaking responsibilities, early retirement, or education
Define labour supply
Number of workers willing and able to work in a given time period at a given wage rate
What is the participation ratio?
The number of people in the labour force employed or unemployed/ total working age population x100
What is supply of labour to an industry influenced by?
Net advantages, both pecuniary and non-pecuniary
State pecuniary factors
Wage rate
Opportunity to work overtime
Bonuses
State non-pecuniary factors
Flexibility of hours
Promotion
Qualification and skills
Holidays
Training
Job Security
Pleasant working condition
Explain Factors affecting elasticity of supply of labour
Qualifications and skills - more needed means a last inelastic
Length of training - longer means inelastic
Immobility labour - higher immobility means in elastic
Time - in the short run it is inelastic as it takes people time to respond to changes in relative wages
Explain how the substitution and income affect affect supply of labour
The substitution effect affects supply of labour caused by a change in the opportunity cost of leisure
The income affect is an effect on individual supply of labour caused by change inability to buy leisure
What are wage differentials?
Differences in pay between various occupations and sectors of the economy
What is economic inactivity?
When people of the labour force work due to caretaking repsonsibilies, early retirement or studying and the unemployed.
Show how a competitive firm decides on the number of worker to employ
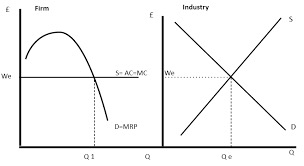
Discuss the extent to which MRP theory can explain wage differentials between footballers and nurses
Footballers generate revenue through ticket and merchandise sales so the model does not work as it is difficult to measure the MRP of nurses as they bring no monetary value when employing one extra
To what extent do differences in productitivty and human capital explain wage differentials?
- Higher productivity per worker (MRP) = inelastic PED
- profit orientation - private sector employment are profit orientated and can increase productivity so there is greater wage differential
Other factors: choice of part time = lower wages, wage discrimination, labour in monopsonist market, trade unions