CHEM 86.1 UNIT 1: ATOMS AND THEIR QUANTITATIVE STUDY
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Elements
What is the simplest type of matter?
Compounds
Consist of two or more different elements that are bonded chemically.
Mixtures
Consists of two or more substances (elements and/or compounds) that are physically intermingled, not chemically combined.
Mass Conservation
Total mass of substances does not change during a chemical reaction
Law of mass conservation

Definite Composition
No matter what its source, a particular compound is composed of the same element in the same parts (fractions) by mass.
proportions, source
The ___ of elements for the same compound is same no matter what its ___.
Multiple Proportions
If element A and element B react to form two compounds, the different masses of B that combine with a fixed mass of A can be expressed as a ratio of small whole numbers
ratios of small whole numbers
The law of multiple proportions tells us that in two compounds of the same elements, the mass fraction of one element relative to the other element changes in increments based on ___
John Dalton
___: In 1808, presented his atomic theory of matter.
atoms, created or destroyed
All matter consists of ___, tiny indivisible units of an element that cannot be ___. (This derives from the “eternal, indestructible atoms” proposed by Democritus more than 2000 years earlier and reflects mass conservation as stated by Lavoisier.)
converted
Atoms of one element cannot be ___ into atoms of another element. In chemical reactions, the atoms of the original substances combine to form different substances. (This rejects the alchemical belief in the magical transmutation of elements.)
mass, properties, element
Atoms of an element are identical in ___ and other ___ and are different from atoms of any other ___. (This contains Dalton’s major new ideas: unique mass and properties for the atoms of a given element.)
chemical combination, ratio, definite composition
Compounds result from the ___ of a specific ___ of atoms of different elements. (This follows directly from the law of ___)
Mass Conservation
Atoms cannot be created or destroyed (postulate 1) or converted into other types of atoms (postulate 2). Therefore, a chemical reaction cannot possibly result in a mass change because atoms are just combined differently.
Definite Composition
A compound is a combination of a specific ratio of different atoms (postulate 4), each of which has a particular mass (postulate 3). Thus, each element in a compound must constitute a fixed fraction of the total mass.
Multiple proportion
Atoms of an element have the same mass (postulate 3) and are indivisible (postulate 1). The masses of element B that combine with a fixed mass of element A must give a small, whole-number ratio because different numbers of B atoms combine with each A atom in different compounds.
Cathode Rays
To discover the nature of an electric current, some investigators tried passing it through nearly evacuated glass tubes fitted with metal electrodes
(1) Ray bends in magnetic fielld - Consists of charged particles (2) Ray bends toward positive plate in electric field - Consists of negative particles
(3) Ray is identical for any cathode - Particles found in all matter
What are the observations and conclusions of the Cathode Rays experiment?
J. J. Thomson
In 1897, the British physicist ___ (1856–1940) measured the ratio of the mass of a cathode ray particle to its charge
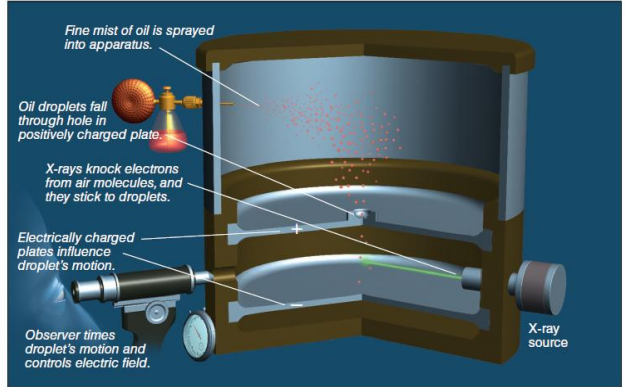
Millikan’s oil-drop experiment
___: In 1909, the American physicist Robert Millikan (1868–1953) measured the charge of the electron
X-ray, oil droplets, positively charged plate, magnetic field, mass
In Millikan’s oil drop experiment, __________ ejects electrons from the gas molecules in air, and these electrons become attached to __________. The negatively charged oil droplets then fall through the hole in the __________. By turning off the __________, Millikan measured the __________ of electrons based on the rate of fall of the oil droplets.
plum-pudding
Thomson proposed his “___” model—a spherical atom composed of diffuse, positively charged matter with electrons embedded in it like “raisins in a plum pudding.”

-1.60 x 10-19 C, -1.76 x 108 C/g , 9.10 x 10-28 g
e - charge =___
Thomson’s charge/mass of e- = ___
e - mass = ___
CONST03
In calculator, e - mass is saved as ___
Rutherford’s Gold-foil experiment, Ernest Rutherford
___: In 1910, New Zealand–born physicist ___ (1871-1937) tested the Plum-Pudding model
nucleus, electron, 1840x
✔atoms positive charge is concentrated in the ___
✔proton (p) has opposite (+) charge of (-) __
✔mass of p is ___ mass of e- (1.67 x 10- 24 g)
Chadwick’s experiment, James, neutron, nucleus
____: After more than 20 years, in 1932, ___Chadwick (1891–1974) discovered the ___, an uncharged dense particle that also resides in the ___
1.67 x 10-24 g
n mass ~ p mass = ___
CONST02, CONST01
In calculator, n 0 mass is saved as__ and p + mass is ___
nucleus, protons
Due to the small mass of electron, the total mass of an atom must come from the ___ but not from the ___ alone
Atom
an electrically neutral, spherical entity composed of a positively charged central nucleus surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons.
nucleus
An atomic ___ consists of protons (p+ )and neutrons (n 0 ).
protons, electrons
An atom is neutral because the number of ___ in the nucleus equals the number of ___ surrounding the nucleus.
Atomic Number
number of protons in nucleus
Mass Number
number of protons + number of neutrons = atomic number (Z) + number of neutrons
Atomic Symbol
Element symbol based on its English, Latin or Greek name
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons in the nuclei.
Cation
A neutral atom that loses an electron; Ion with a positive charge.
Anion
: A neutral atom that gains an electron; Ion with a negative charge
Wavelength (lambda, λ)
Distance between identical points on successive waves
Amplitude
Vertical distance from the midline of a wave to the peak or through.
Frequency (nu, ν)
number of waves that pass through a particular point in 1 second (Hz= 1 cycle/s)
electromagnetic waves
In 1873, Maxwell proposed that visible light consists of ____.
Electronic radiation
____ is the emission and transmission of energy in the form of electromagnetic waves.
3.00 x 108 m/s
Speed of light (c) in vacuum = ___
speed, frequencuy, wavelength
All waves of electromagnetic radiation travel at the same ___ through a vacuum but differ in ___ and, therefore, ___.
All electromagnetic radiation
λ · ν = c
Blackbody Problem
___: Changes in the intensity and wavelength of emitted light as an object is heated are characteristic of blackbody radiation, light given off by a hot blackbody
Quantum Theory
___: In 1900, Max Planck (1858-1947) assumed that hot, glowing objects could emit (or absorb) only certain quantity of energy (quantum).
h x v
E = ___
Planck’s Constant (h), CONST06
___ = 6.62606957 x 10-34 J·s = 6.626 x 10-34 J·s (In calcu saved as ___)
Photoelectric effect
___: When monochromatic light of sufficient frequency shines on a metal plate, a current flows.
presence of threshold frequency, absence of time lag
It was thought that the current arise because light transfer energy that frees electrons from the metal surface. However, it offers two confusing features: the ___ and the ___.
Einstein
___ proposed that light is a particulate, quantized into tiny “bundles” of energy called photons.
Presence of threshold frequency
___: A photon of a certain minimum energy must be absorbed to free an electron from the surface.
Absence of time lag
___: As long as the threshold frequency is met, electrons immediately ejected.
(quantized) energy values
Electrons (e- ) can only have specific ___
lower
Light is emitted as e - moves from one energy level to a ___ energy level
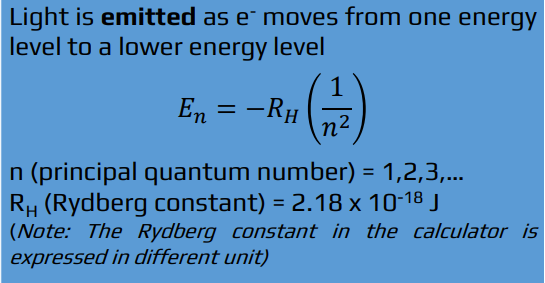
Erwin, quantum-mechanical model of the H atom
Quantum Mechanics: In 1926, ___ Schrödinger (1887–1961) derived an equation that is the basis for the ___
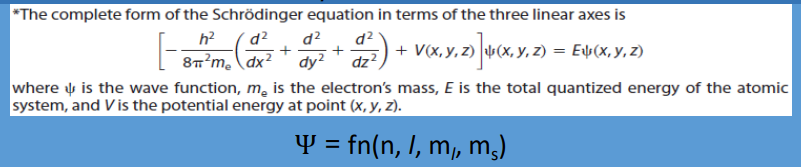
distance of e - from the nucleus
n = principal quantum number = 1, 2, 3, 4, … = ___
shape of the “volume” of space that e - occupies
l = angular momentum quantum number = 0, 1, 2, 3, …, n-1 = ___
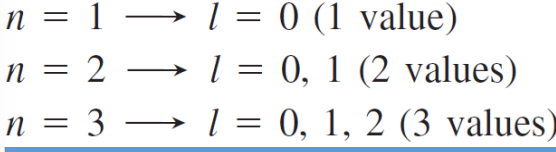
s, sharp, p, principal, d, diffused, f, fundamental
l = 0 = ___ = ___
l = 1 = ___ = ___
l = 2 = ___ = ___
l = 3 = ___ = ___
orientation of the orbital in space
ml = magnetic quantum number = -l, …, 0, …, +l
= ___
spin quantum number
ms = ___ = -1/2 or +1/2 = orientation of the orbital in space
Pauli’s Exclusion Principle
___: no two electron in an atom can have the same four quantum numbers
shell
electrons with the same value of n
subshell
electrons with the same value of n and l
orbital
electrons with the same values of n, l, and ml
2
An orbital can hold how many electrons?
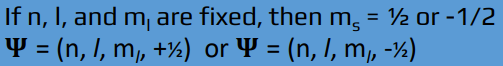
1 possible orbital
s orbital – ___
3 possible orbitals
p orbital - ___
5 possible orbitals
d orbital - ___
7 possible orbitals
f orbital - ___
Hund’s rule
___: “If more than one orbital in 1 a subshell is available, electrons will fill empty orbitals before pairing up.”
Electron Configuration
distribution of electrons in an atom
Aufbau’s Building-up Principle
___: Electrons must completely fill up lower energy levels before filling up the next higher energy level
Valence electrons
___: Electrons occupying the outermost shell
Differentiating Electron
___: Last entering electron in the configuration of an element
Isoelectronic
___: atoms or ions of different elements that have the same electronic configuration
representative elements
For ___, elements form ions to become isoelectronic with the nearest noble gas
transition metals
For ___, electrons from the outermost shell are the first to be removed. (“First In, First Out”)
half-filled or completely filled
Exceptions: There are atoms gain extra stability when their d subshells are ___.
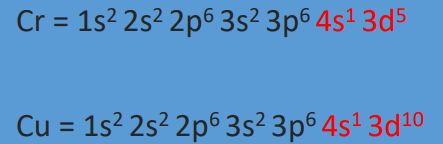
Diamagnetism
___: slightly affected by magnet; all electrons are paired
Paramagnetism
___: greatly affected by magnet: contains an unpaired electrons
paramagnetic
2 unpaired electrons = ___
diamagnetic
all electrons are paired = ___