Unit 2 Vocabulary
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Agricultural Density
farmers per unit of arable land
Physiological Density
people per unit of arable land
Arithmetic Density
people per unit of land
Pro-natalist
encourages the population to have more babies
Anti-natalist
discourages the population to have more babies
Asylum Seeker
someone who is seeking international protection as a refugee but claim for refugee status hasn’t been determined
Brain Drain
the massive emigration of talented professionals leaving their home country for better opportunities
Carrying Capacity
the maximum population size an environment can hold
Chain Migration
People move to a location because other from their community have previously migrated there
Circulation
temporary, repetitive movements that recur on a regular basis
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
the number of births in a given year per 1,000 people in a given population
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
the number of deaths in a given year per 1,000 people in a given population
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
the number of deaths of children under the age of 1 per 1,000 live births
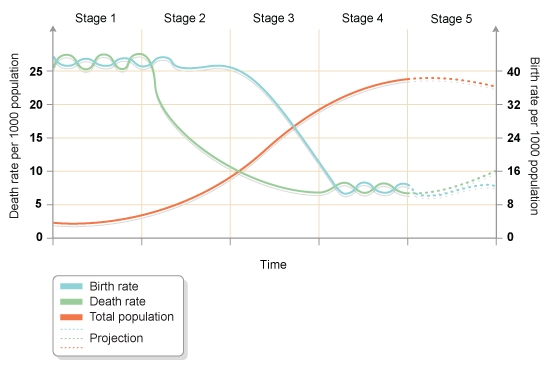
Demographic Transition Model
Demographics
data about the structures and characteristics of human populations
Dependency Ratio
The number of people under the age of 15 and over 65 who depend on the working population
Doubling Time
the numebr of years in which a population growing at a certain rate would double
Emigration
movement away from a location
Forced Migration
people are compelled to move by economic, political, environmental, or cultural factors
Friction of Distance
the longer a journey is, the more time, effort, and cost it will involve
Gravity Model
Bigger the city = more opportunities = more people move in
smaller the city = less opportunities = less people move in
Guest Worker
Migrants who travel to a new country as temporary laborers
Immigration
movement to a location
Internal Migration
movement within a country's borders
Internally Displaced Person (IDP)
people who have been forced to flee their homes by conflict, violence, persecution or disasters
REMAIN in countries boarders
Interregional Migration
movement from one region of the country to another
Intervening Obstacles
obstacles put in place that could prevent migration such as needing to have a visa/passport
Intervening Opportunities
something that causes migrants to pause their journey by choice
Life Expectancy
the average number of years a person is expected to live
Malthusian Theory
World Population is growing FASTER than world food supply
Population is exponential
Food Supply is linear/limited
Neo-Malthusian
Scholars today still support Malthus’s overall
BUT instead of food, they are comparing it to other resources, such as energy resources
Migration
the permanent movement of people from one place to another
Mobility
all types of movement from one location to another, whether permanent or temporary
Net Migration
the difference between the number of emigrants and immigrants in a location, such as a city or a country
Overpopulation
population growth outstrips the resources need to support life
Population Distribution
where people live in a geographic area
Population Pyramid
A pyramid showing the sex and age composition of a community

Pull Factors
a positive cause that attracts someone to a new location
Push Factors
a negative cause that compels someone to leave a location
Quota Laws
laws that limit the number of immigrants allowed into the country each year
Rate of Natural Increase (RNI)
rate at which a population grows
Ravenstein's Migration Laws
Most people move rural to urban
every migration flow has a counter-migration
most international migrants move to the big city
families are less likely to move
most people move a short distance because of distance-decay.
Refugee
a person who is forced to leave his or her coutnry for fear of persecution or death
Remittance
money earned by an emigrant abroad and sent back to his or her home country
Returnee
to return to one's home country after being displaced
Sex Retio
the proportion of males to females in a population
Step Migration
series of smaller moves to get to the ultimate destination
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
the average number of children one woman in a given country or region will have during her childbearing years
Transhumance
the seasonal migration from the highlands to the lowland pastures
Transnational Migration
immigrants to a new country retain strong cultural, emotional, and financial ties to their country of origin and may regularly return for visits
Voluntary Migration
people make a choice to move to a new place