Quiz 8: Properties and Laws of Gases
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1. There must be space in between gas molecules
2. Gas molecules move rapidly
3. Gas molecules collide w/ the container
4. Gas moves at a faster and higher temperature
What are the 4 general properties of gases?
Gas particles are in constant, random and rapid motion
Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases (KMT):
A gas consists of an extremely large number of very tiny particles that are in ___________, ____________and ____________ motion
constant motion
Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases (KMT):
All matter is made up of tiny particles that are in ______________
Temperature (Temp is related to KE)
Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases (KMT):
The average kinetic energy of gas particles is directly proportional to the _______________ of the gas
Individual gas particles
Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases (KMT):
The volume of _______________ are negligible compared to the volume of the whole gas
- random
- straight lines
Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases (KMT):
The motion of gas particles is ___________, and they move in ______________ until they collide with other particles or the walls of their container
- Faster
- Increases
As temperature increases, gas molecules move at a ______________ pace and kinetic energy _______________
- Heavier
- Slower
If temperature remains constant, gas molecules become ___________ causing them to move ____________ while kinetic energy remains constant
- Atmospheric pressure
- barometer
_____________________ is the pressure exerted by air molecules colliding with objects and is measured using a _______________
1 atm = 101325 Pa = 760 torr = 760 mmHg = 14.6959 PSi
Unit conversions for pressure:
____atm = _________ Pa = __________ torr = _________ mmHg = _________ PSi
1 atm = 101325 Pa = 760 torr = 760 mmHg = 14.6959 PSi
List the unit conversions for pressure
824 mmHg x (1 atm/760 mmHg) = 1.08 atm
Convert 824 mmHg to atm
824mmHg x (101325 Pa/ 760mmHg) x (1KPa/103 Pa) = 110. KPa
Convert 824 mmHg to KPa
1. Boyles law
2. Charles law
3. Avogadros law
4. Amontons law
What are the 4 Gas laws?
Boyles gas law
The relationship below is described by the ______________ gas law:
P (pressure) ∝ 1/V (volume) If T (temperature) and n (moles) are constant
Charles gas law
The relationship below is described by the ______________ gas law:
V ∝ T If P and n are constant
Avogadros gas law
The relationship below is described by the ______________ gas law:
V ∝ n If P and T are constant
Amontons gas law
The relationship below is described by the ______________ gas law:
P ∝ T If vtn are constant
Boyles law
Gas law:
_______________ states that pressure increases as volume of the container decreases
Charles law
Gas law:
_______________ states that volume increases as temperature increases
(volume decreases as temperature decreases)
Avogadros law
Gas law:
_______________ states that volume increases as moles increases
Amontons law
Gas law:
_______________ states that pressure increases as temperature increases
PV/T (Pressure x Volume/temperature)
The Combined Gas Law states that for a fixed amount of gas, constant = _____________
(P1V1)/ T1 = (P2V2)/ T2
What equation is used in the Combined Gaw Law?
T(K) = T(°C) + 273.15
The Combined Gas Law states that temperature needs to be converted to kelvin when solving for
(P1V1)/ T1 = (P2V2)/ T2
What equation is used to convert Celsius to kelvin?
Pressure and Volume
The Combined Gas Law states that __________ and __________ can be in any units as long as they are the same when solving for
(P1V1)/ T1 = (P2V2)/ T2
(P1V1)/ T1 = (P2V2)/ T2
(785 x 0.879)/ 295K = (337 x V2)/ 226K
V2 = 1.576
Find the final volume using the combined gas law:
P1 = 785mmHg
T1 = 22 degrees Celsius
V1 = 0.879L
P2 = 387mmHg
T2 = -47 degrees Celsius
P1V1 = P2V2
22.5 atm (760 torr/ 1 atm) = 17100 torr
(17100 x 41.0) = (5.15 x V2)
V2 = 136000 L
Find the final volume using the combined gas law:
P1 = 22.5 atm
V1 = 41.01L
T1 = T2
P2 = 5.15 torr
T(k) = 25 degree Celsius + 273K = 298K
(1.51 x 455)/298 k = (2.00 x 222)/ T2
2.305 T2 = 193k - 273
T2 = -80 degrees Celsius
Find the final temperature using the combined gas law:
P1 = 1.51 atm
V1 = 455mL
T1 = 25 degrees Celsius
P2 = 2.00 atm
V2 = 222mL
PV = nRT
What equation is used in the Ideal Gas Law?
R is the Ideal gas constant (0.08206 L atm/mol K)
What does the R stand for:
PV = nRT
(atm x L) = (mol x R x K)
The Ideal gas law states that the units for PV = nRT needs to be __________ = ___________
Standard temperature is 273K and standard pressure is 1 atm
What is the standard temperature and pressure (STP) values?
22.4 L
What is the molar volume of 1 mol of gas at STP?
2.00mol x (22.4L/ 1 mol) = 44.8L
What is the molar volume of 2 mol of gas at STP?
PV = nRT
n = 1.22g x (1 mol/ 4.0026g) = 0.305 mol
P (5.50L) = (0.305mol x 0.08206 x 298K)
P = 1.36 atm
We have 1.22g of He gas at 25 degrees Celsius in a 5.50L drum. What is the pressure of He gas?
PV = nRT
(1.00atm x 2.00L) = n (0.08206 x 273K)
n = 0.0893 mol
0.0893 mol x (16.04g/1 mol) = 1.43g
Solve for the grams of CH4 (16.04 g/mol)
V = 2.00L
T = 273 K
P = 1.00 atm
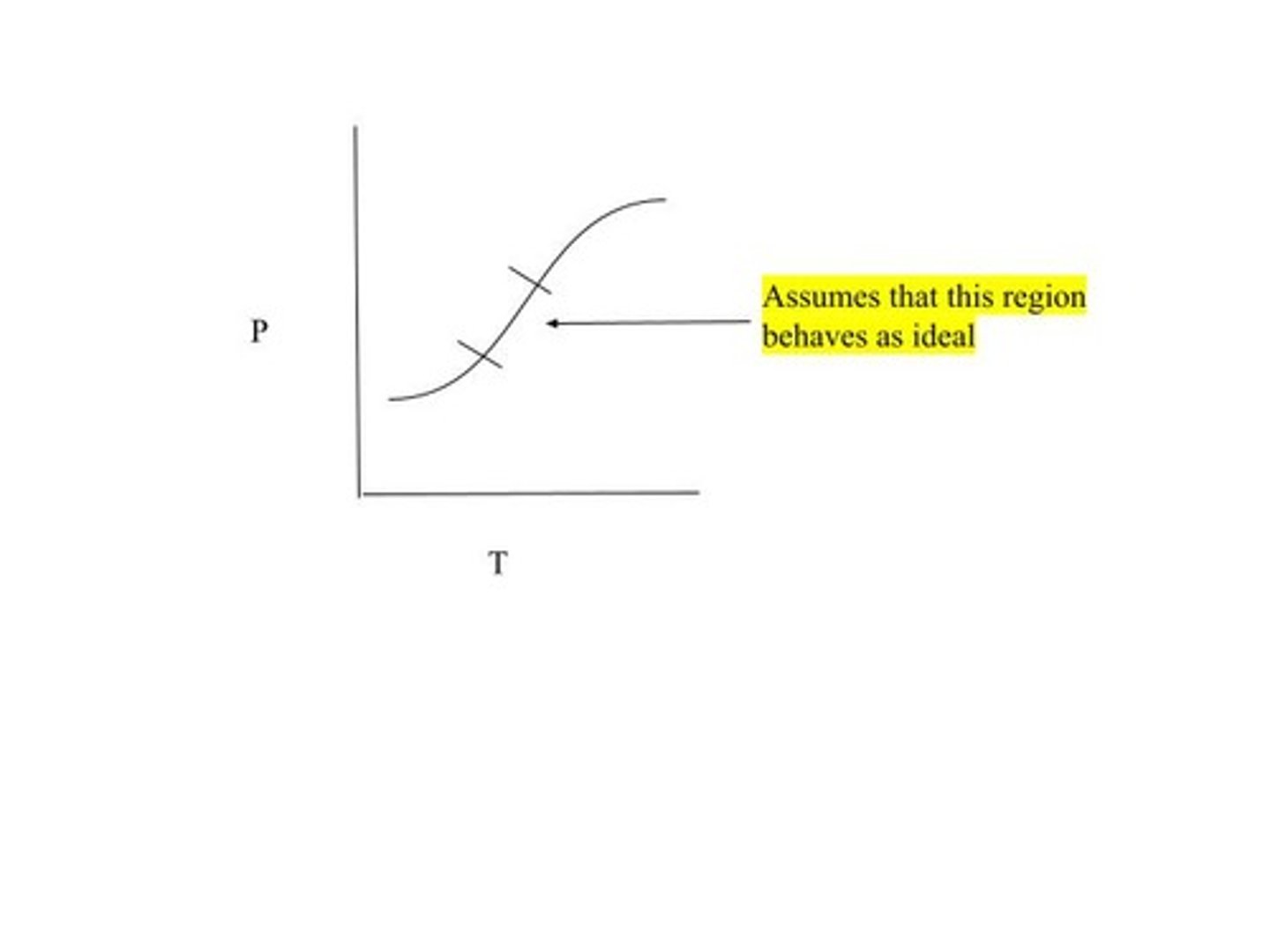
Real gas, Ideal gas is shown as a straight linear line (hence the assumption that the mid-section of this graph behaves as ideaL)
The graph shown is a visual of ____________