Session 10: Reviewing the Evidence - Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Type 1 error
False positive
Type 2 error
False negative
Systematic review
Summarized findings from multiple studies of a specific clinical practice question or topic that recommend practice changes and future directions for research; one of the strongest sources of evidence for evidence-based practice
Overview of primary studies that used explicit and reproducible methods
Meta-analysis
Quantitative synthesis of results of two or more primary studies that addressed the same hypothesis in the same way
What makes a review 'systematic'?
- Based on clearly formulated question
Types of participants
Types of interventions/controls
Type of outcome measures
Type of study
- Identifies relevant studies (systematic literature search)
Search terms
Data sources
Language & time-frame restrictions
- Appraises quality of studies
Systematic grading of evidence identified
- Synthesis of findings
Possibly including meta-analysis
How do you conduct a systematic review?

Advantages of a meta-analysis
- Greater statistical power
- Confirmatory data analysis
- Greater ability to extrapolate to general population affected
- Considered an evidence-based resource
- Facilitate synthesis of large number of study results
Disadvantages of meta-analysis
- Missing relevant studies
Poor literature search
Publication bias
Incorrectly excluding relevant studies during screening
- Difficulty during data extraction
Missing key information or results in different format
Errors in interpretation of results
- Variable quality of studies
- Meta-analyses
Heterogeneity between studies

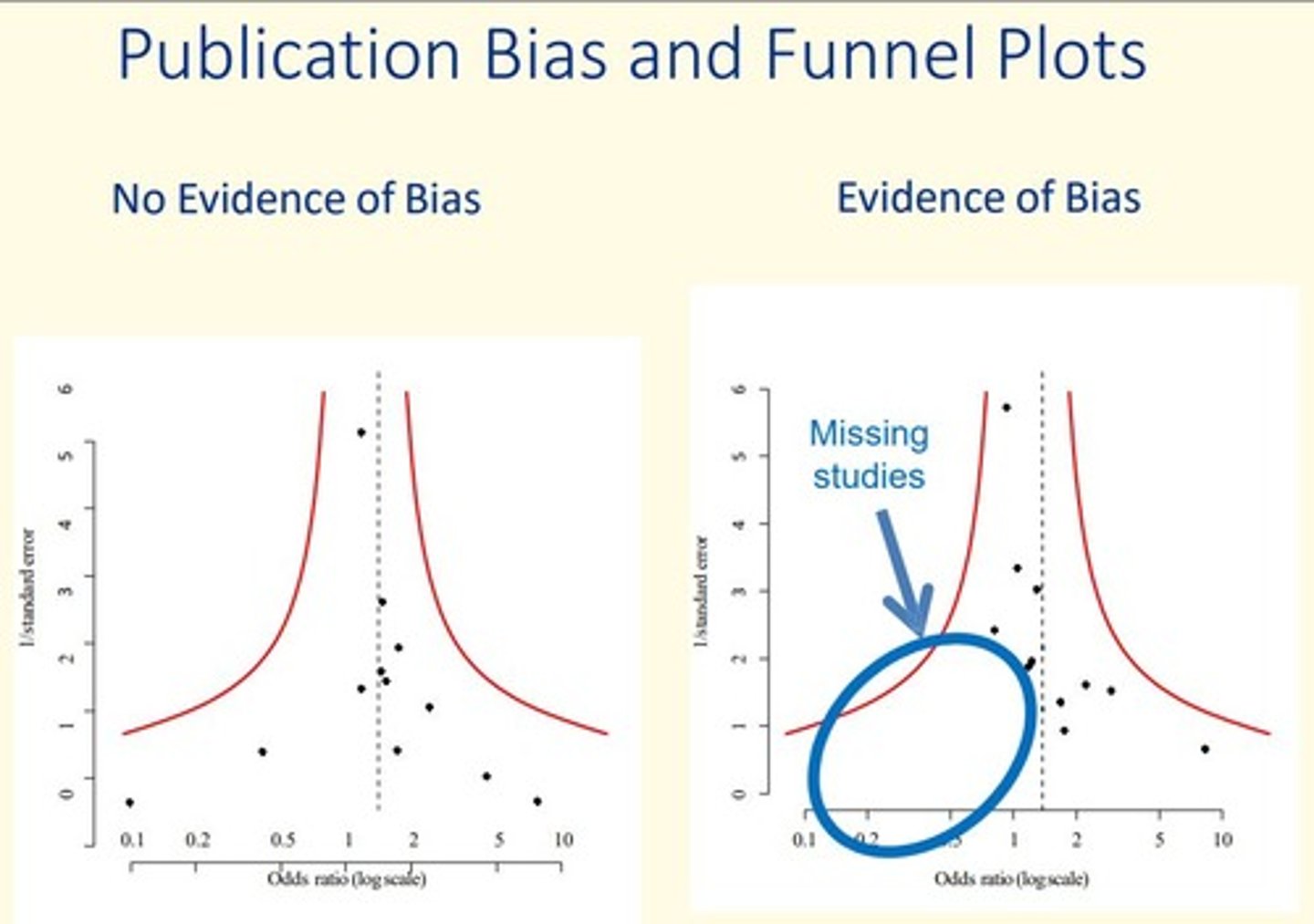
Publication bias
Studies with non-statistically significant results or 'unfavourable' results are less likely to be published
These studies are less likely to be found and included in systematic reviews.
Leads to bias in systematic reviews in demonstration of effect.
Checking for publication bias
- Check search strategy/protocol
- Funnel plots
- Statistical tests for publication bias
Variable quality in studies can be due to...
- Poor study design
- Poor write-up
- Poor protocol implementation
Some studies are more prone to bias/confounding than others.
Give examples of a study design that is less susceptible to this.
RCTs

Some studies are more prone to bias/confounding than others.
Give examples of a study design that is more susceptible to this.
Case-control studies

Solutions to issues with study quality
1) Define basic quality standard and ONLY include studies which satisfy this criteria e.g., only include RCTs
2) Systematically score each study for its quality (or risk of bias), then either...
- Incorporate quality score into weighting allocated to each study
- Undertake sub-group analyses

Variation in studies is known as ___
Heterogeneity
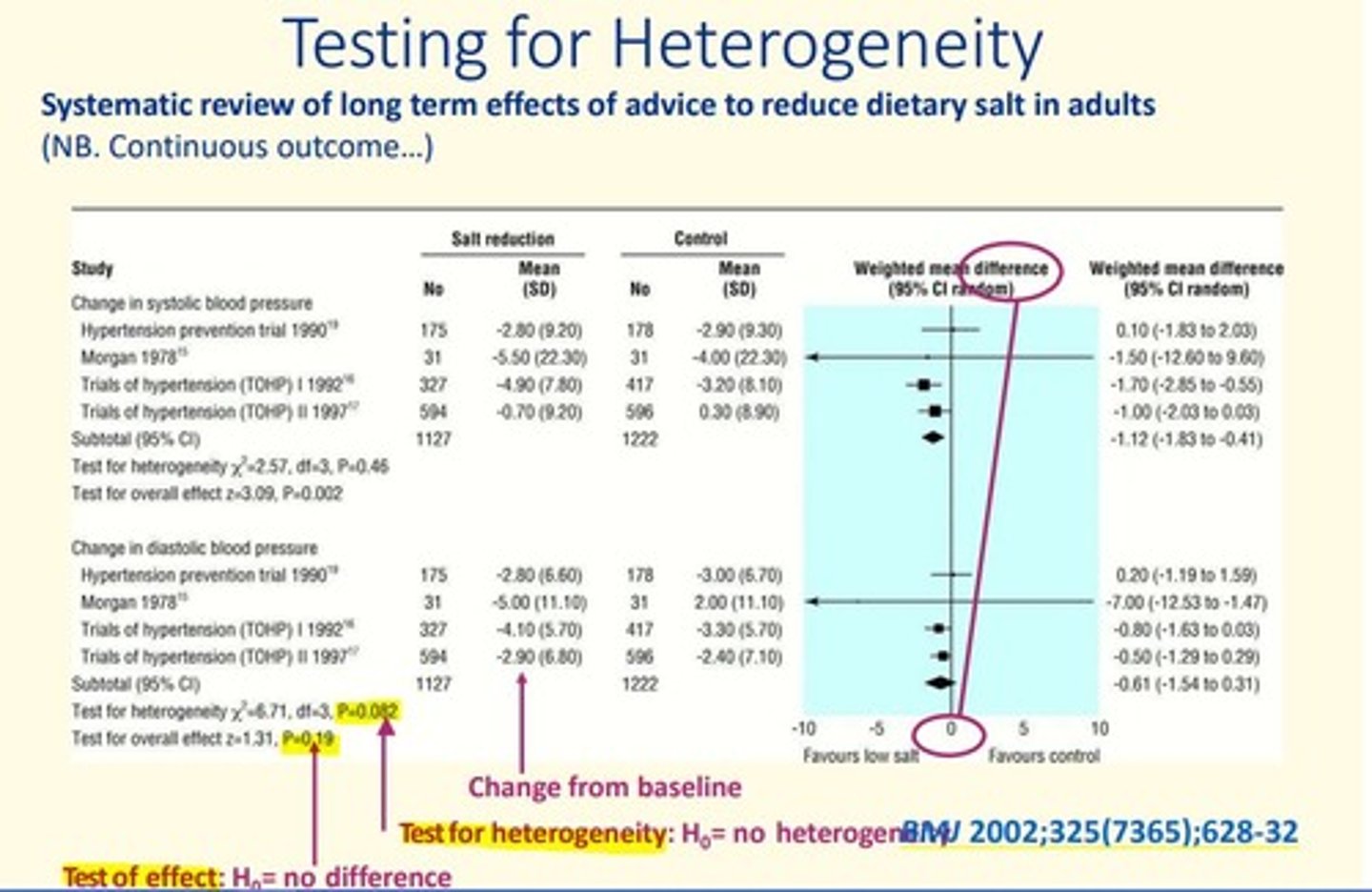
Testing for heterogeneity between studies
1) Statistical test for heterogeneity
2) Sub-group analysis
All studies in a meta-analyses should be similar in terms of...
1) Participant profile
2) Interventions/treatments/exposures & controls
3) Outcomes measured
4) Study design
5) Statistical analysis used
PICO
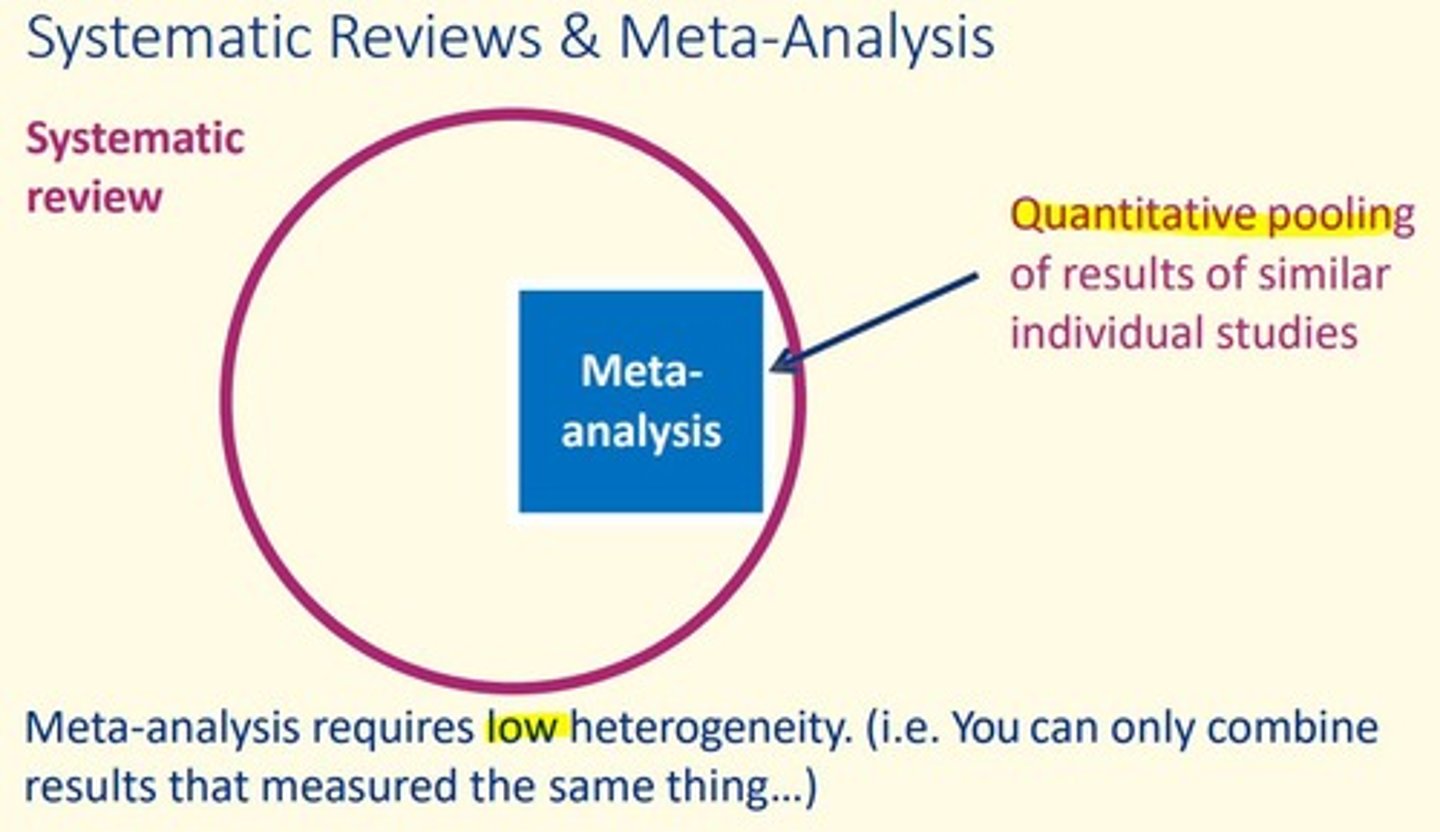
A meta-analysis requires ___ heterogeneity
A meta-analysis requires LOW heterogeneity
Name some tools which can be used to critically appraise systematic reviews & meta-analysis
Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP)
Meta Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE)

Features of a systematic review
Explicit
Transparent
Reproducible
Formal protocol
Features of meta-analysis
Quantitative synthesis of primary data
Summarise effect sizes and their uncertainty
Displayed as Forest plot