Antimicrobial drugs
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Synthetic Drugs
chemical substances produced artificially in a laboratory
Isoniazid
inhibits mycolic acid synthesis. Effective against mycobacterium tuberculosis
Ethambutol
Inhibits mycolic acids
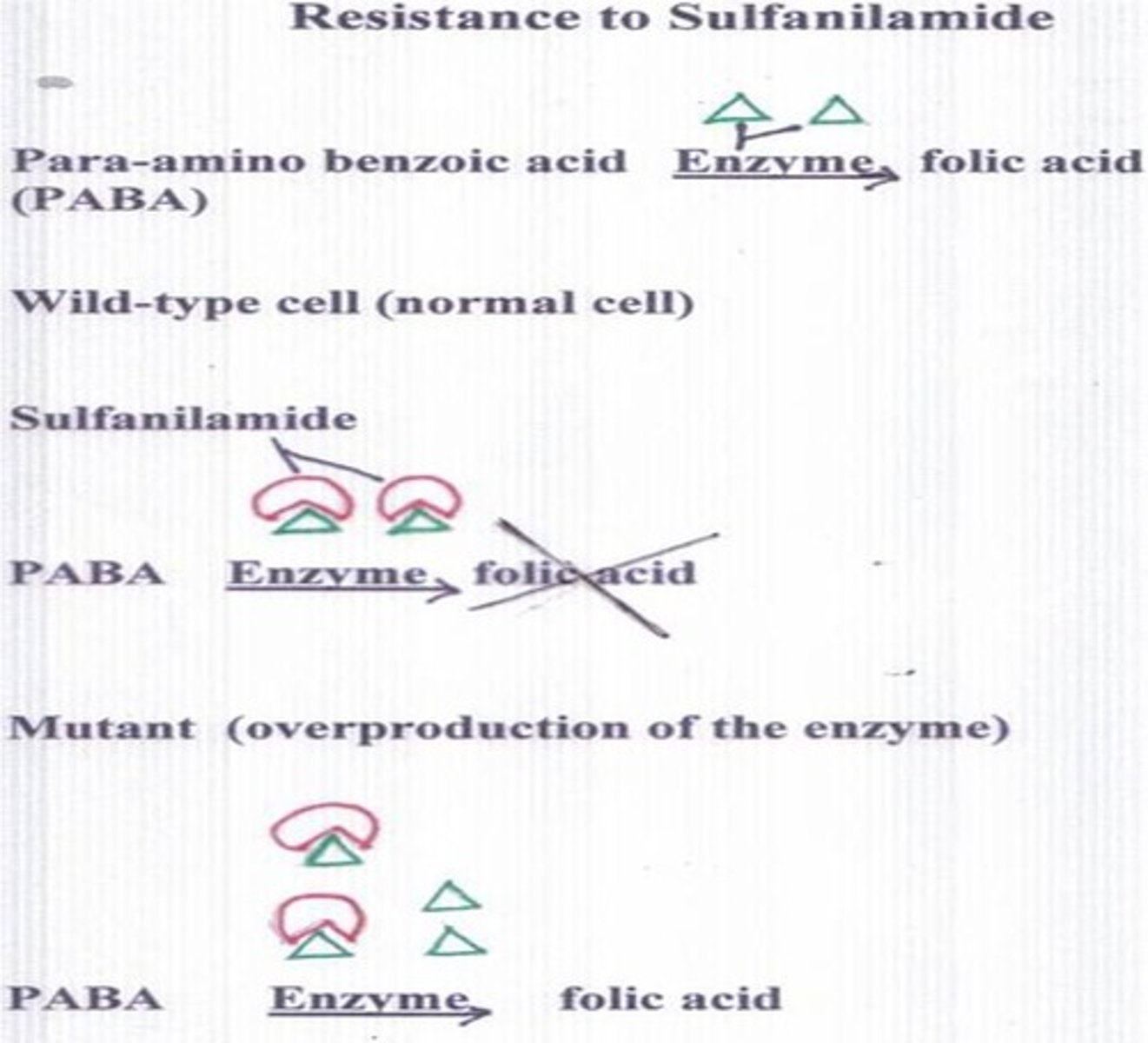
Sulfanilamide
Inhibits folic acid synthesis. PABA is the enzyme that produces folic acid. Sulfanilamide is a competitive inhibitor for PABA.
Fluroquinolones
inhibits DNA synthesis. Used to treat Typhoid fever.
Penicillin
Antibiotic - Made from a mold called Penicillium notatum - inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis
Bacitracin
Antibiotic - Bacillus - Inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis, used for topical applications.
Polymyxin
Antibiotic - Bacillus - Damages plasma membrane, used as a topical treatments
Rifampin
Antibiotic - Streptomyces (Bacteria) - Inhibits RNA synthesis, treats TB
Amphotericin B
Antifungal Drug - Made by Streptomyces (Produced by Bacteria) - Damages plasma membrane - systemic mycosis - Histoplasmosis
Nystatin
Antifungal Drug - Streptomyces (Produced by Bacteria) - Damages membrane - Treats Candida infections.
Acyclovir
Antiviral Drug - Inhibits the synthesis of viral DNA - effective against herpes virus.
Zidovudine (AZT)
Antiviral drug - Inactivates the reverse transcriptase - can cause anemia in some cases. Used to treat HIV infection.
Chloroquine
Antiprotozoan drug - Treats Malaria
Metronidazole
Antiprotozoan drug - Inhibits metabolism in an anaerobic environment. Treats Giardiasis and Amoebic dysentery.
Niclosomide
Antihelminthic drugs - Inhibits ATP synthesis in mitochondria - Treats tapeworm infection
Praziquantel
Antihelminthic drug - Damages plasma membrane - Treats fluke infestations.
Mebendazole
Antihelminthic drugs - Inhibits microtubule formation - roundworm infestations.
How can a bacteria develop resistance to antibiotics through mutations?
Mutations can result in the overproduction of the enzyme that is being inactivated by the drug