Midterm 1: Units 1-9
1/354
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
355 Terms
cyanobactera
first photosynthetic organism living in aquatic conditions and producing oxygen; 2.8bya
ancestral algae
divided into two clades giving rise to different land plants; 1.6bya
land plant
nonvascular and capable of living out of water; 480mya
conifers
evolved after land animals; first gymnosperm living in moist environments; 320mya
ferns
reproduce via spores, do not have seeds or flowers; 250mya
angiosperm
reproduce via flowering and fruit, more advanced reproduction allows them to live in more areas than their coniferous counterparts; 125mya
radiocarbon dating
compares ratio of C-14 to C-12 via half life of the radioactive isotope
evolution
change in populations over very long periods of time. caused by genetic mutations that become favored depending on reproductive and survival benefits
natural selection
based on the idea of survival of the fittest, happens to individuals and can eventually cause speciation
taxonomy
classifying and naming organisms
phylogeny
evolutionary history of organisms
domains
three; largest taxonomic category
kingdoms
six; generalized groups of bacteria, archaea, and eukarya
plant characteristics
photosynthetic, stores sugar and starch, cellulose cell wall, anchorage / support / photosynthetic organs, diploid and haploid life cycle stages
alge lacks
specialized structures of anchorage, support, and photosynthesis
binomial nomenclature
linnaeus, Genus species, can include subspecies, varieties and cultivars
cladogram
demonstrates physical relationships between organisms
convergent evolution
unrelated species develop similar features due to being in similar environments
phylogenetics
study of evolutionary relationships based on genetics rather than physical traits; technically a theory because evolution is a theory
carbon
contains 6 protons, capable of creating 4 covalent bonds, basis for organic molecules, one of the essential elements
methane
simplest organic molecule; primary component of natural gas as a hydrocarbon
hydrocarbons
only C-H bonds, nonpolar, hydrophobic, store large amounts of energy, uncommon by themselves and break down to provide energy
SCHNOP
six essential elements (sulfur, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus) composing 99% of the weight of organic matter. major parts of macromolecules as functional groups
mineral deficiency
soil lacks a nutrient, water, or proper pH level
mineral toxicity
typically happens with heavy metals such as chromium, nickel and cobalt. plants can adapt to the excess nutrients via natural selection
functional groups
attach to CH backbones and contribute to a change in shape of molecules and therefore alter their functions
metabolism
primary and secondary metabolites, chemical reactions necessary for maintaining life
lipids
long HC chains that can be saturated or unsaturated, hydrophobic and nonpolar, very important to cell membranes, energy storage, and information transfer
lipid examples
almonds, canola, peanut, sunflower, olive
steroid
add fluidity to cell and used as signal molecule in hormones and cholesterol
carbohydrates
polymers of sugar, energy and structural support, carbonyl and hydroxyl groups, starch and cellulose
carbohydrate examples
wheat, rice, sweet potato, sugarcane, corn
proteins
polymers of 20 amino acids, arise from RNA, composed of amino and carboxyl group, four structures, do everything but store energy
protein examples
beans, lentils, peas
nucleic acid
transmit genetic information in the form of DNA and RNA via a phosphate, pentose, and nitrogenous base. nucleotide monomers linked via phosphodiester linkages
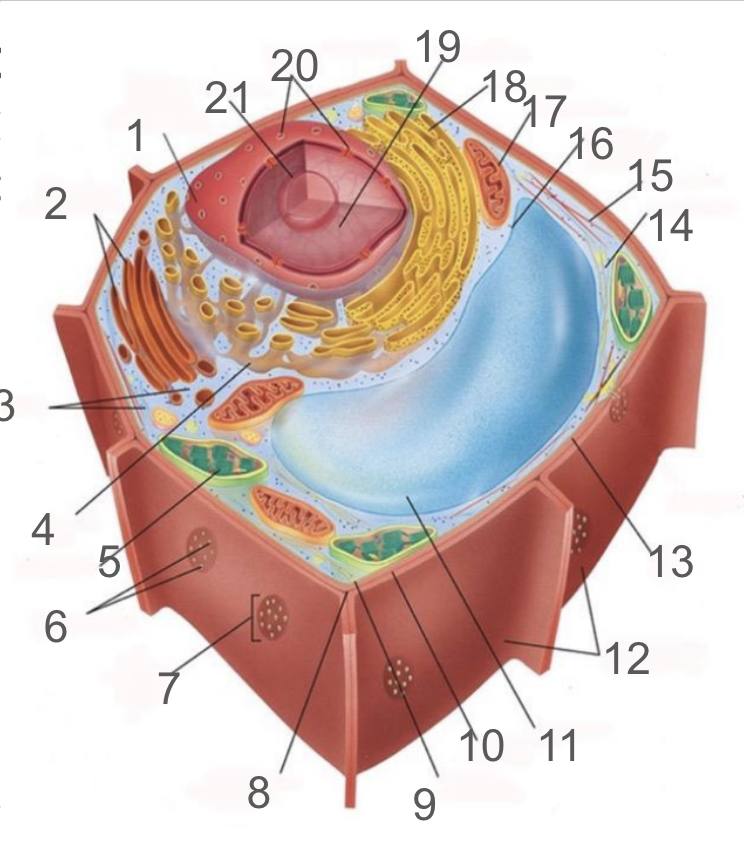
#1 and its function
nuclear membrane, double membrane involved in the endomembrane system, contains bound ribosomes
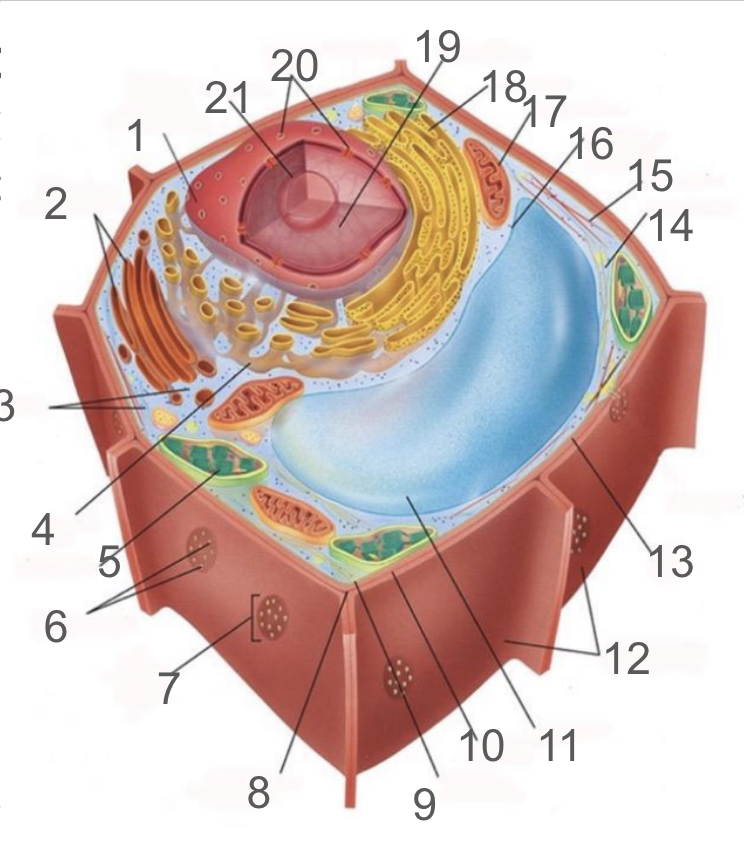
#2 and its function
dictyosome, endomembrane system, processes proteins and lipids, forming face receives vesicles from RER and maturing face releases vesicles to plasma membrane
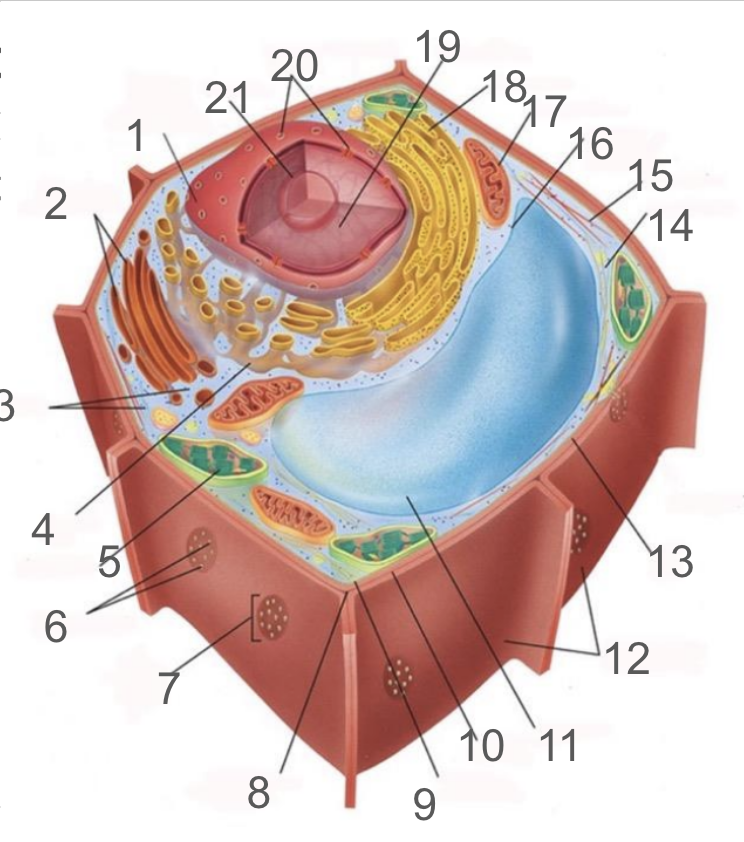
#3 and its function
cytoplasm; refers to the contents of the cell excluding the membrane and vacuole. liquid portion is cytosol, connected to cytoplasms of other cells via plasmodesmata, surrounds organelles and cytoskeleton
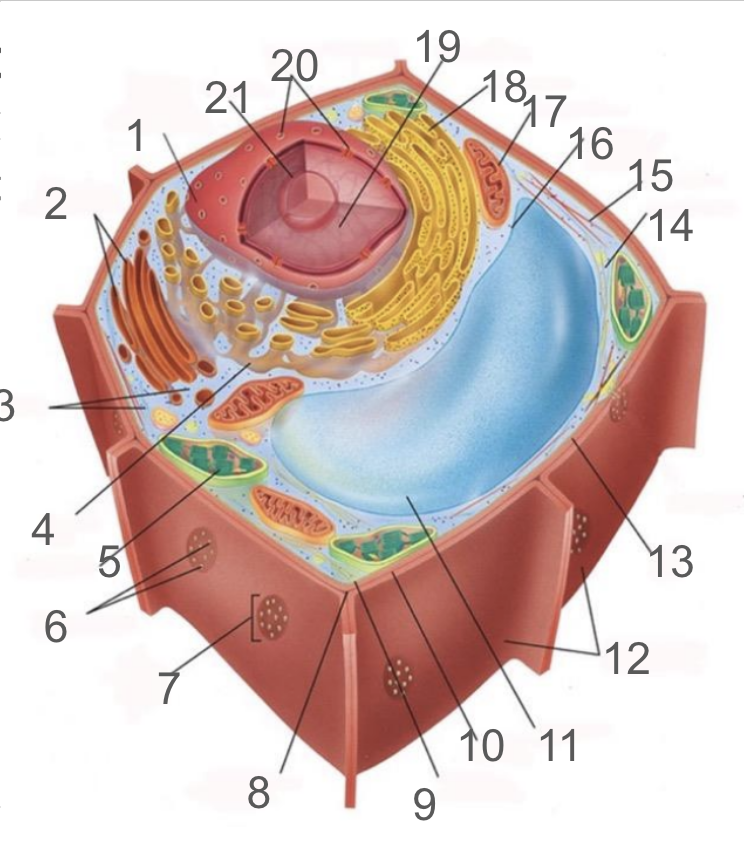
#4 and its function
smooth endoplasmic reticulum; responsible for lipid synthetisis as membrane assembly, package material in phospholipid vesicle membranes
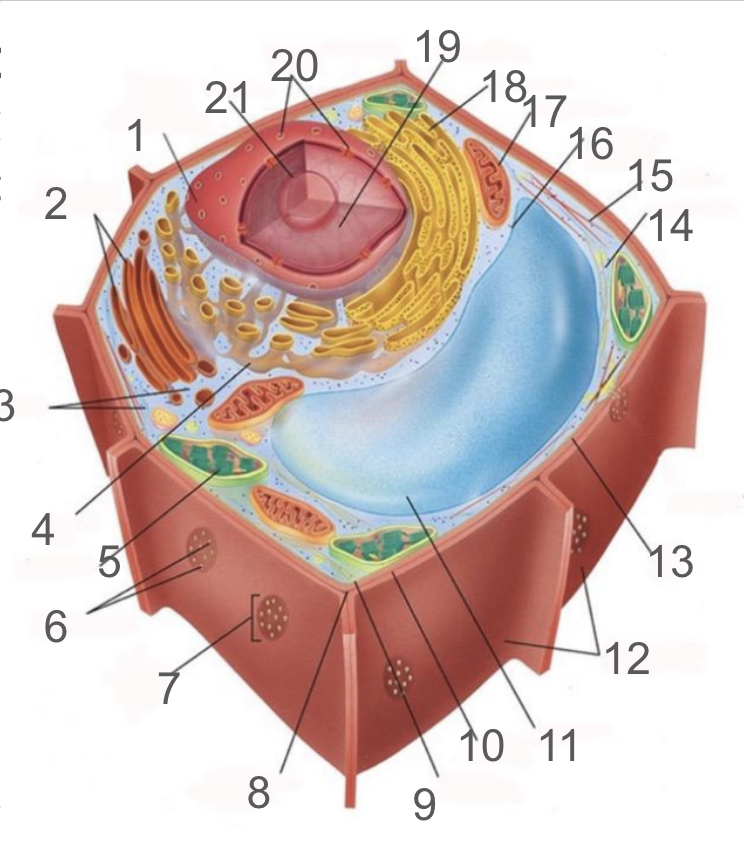
#5 and its function
chloroplast; photosynthetic organelle transforming CO2 and H2O into oxygen and glucose, double membraned and contain chlorophyll within thylakoids of grana and lumen surrounded by stroma
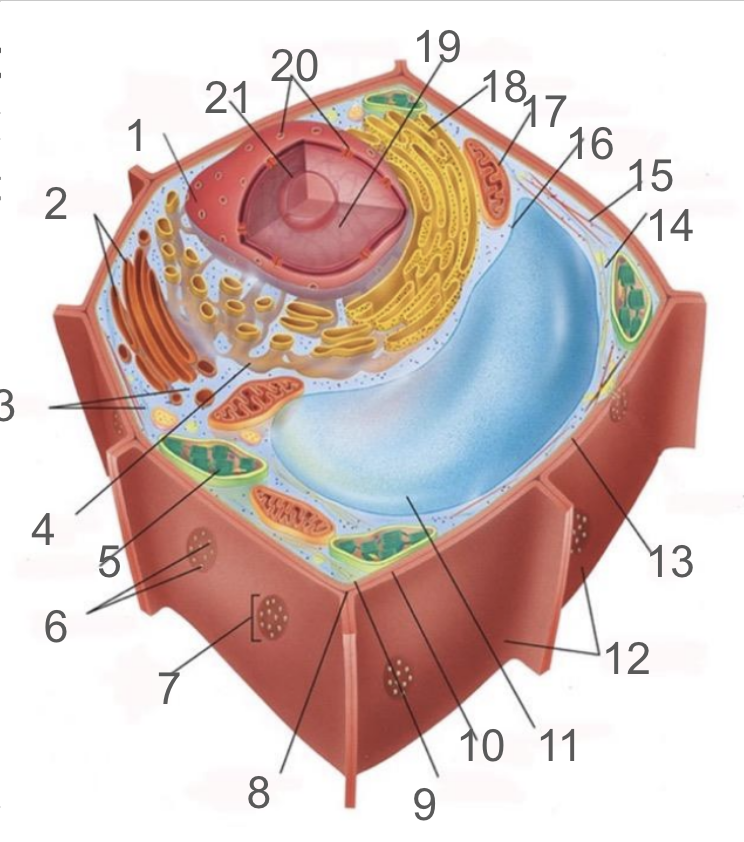
#6 and its function
plasmodesmata; membrane bound tubes connecting cytoplasms, acting as transport pathway that allows water and small solutes to pass through
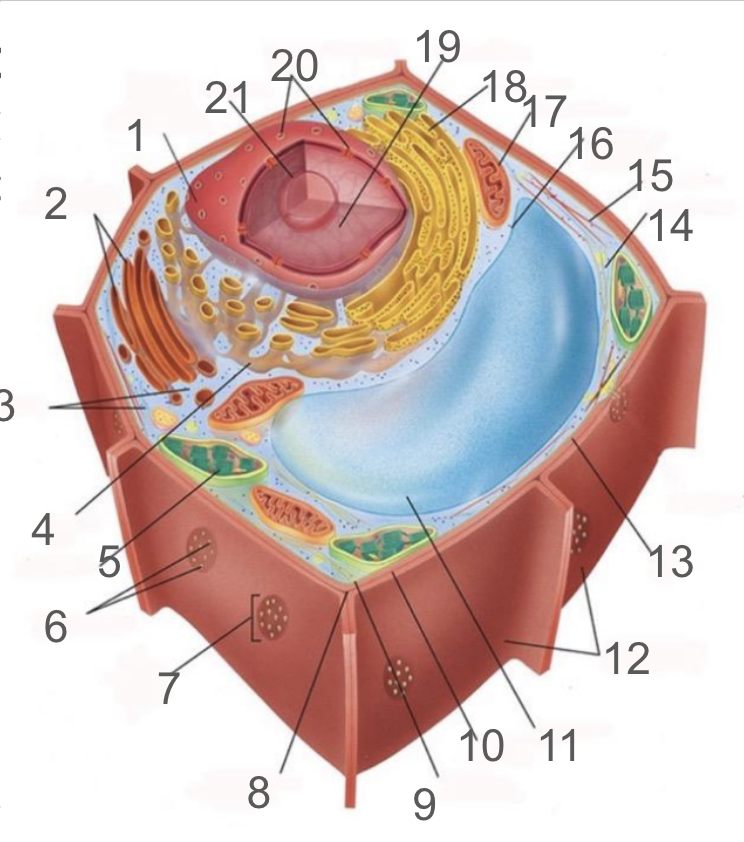
#9 and its function
cell membrane; composed of phospholipid bilayer and is semipermeable, serves as boundary between protoplast and envrionment, consist of integral and peripheral proteins
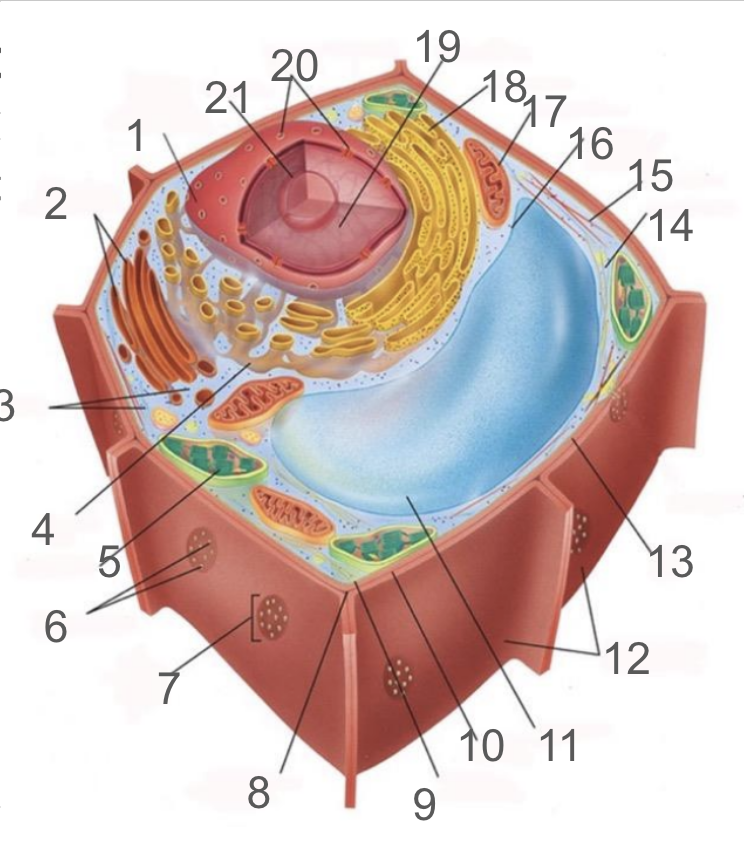
#10 and its function
middle lamella; intercellular cement composed of pectin
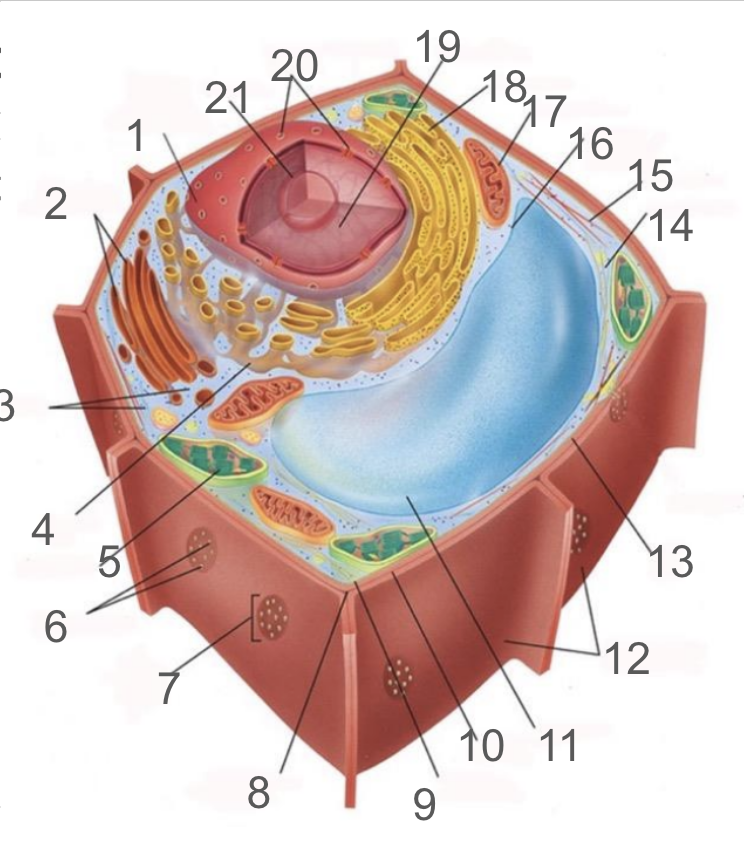
#11 and its function
vacuole; bound by single-membrane tonoplast, stores pigments, waste, recycles organelles and is responsible for turgor and cell expansion / shrinkage
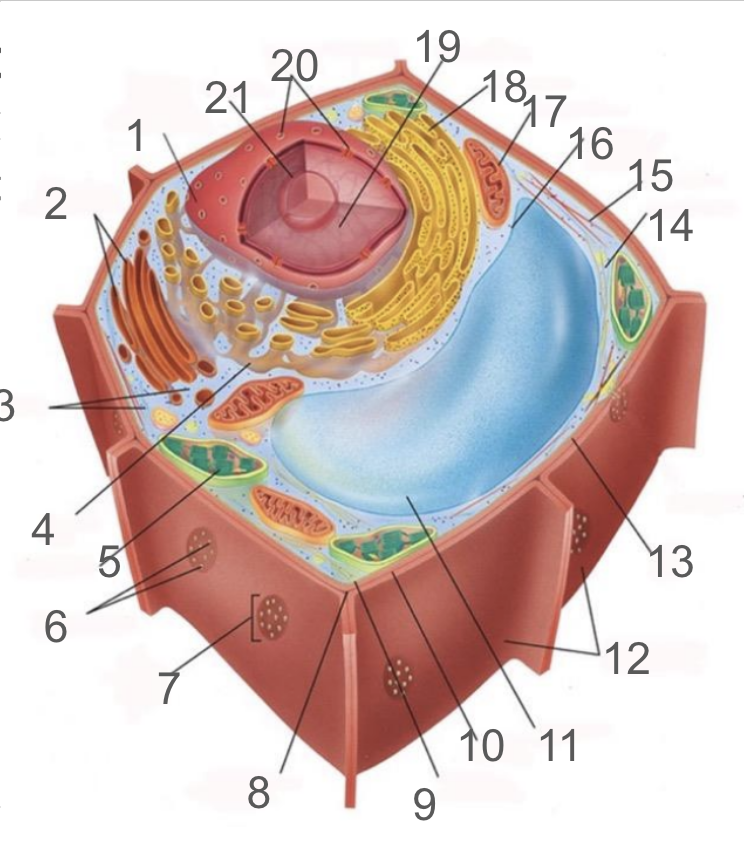
#13 and its function
cell wall; composed of cellulose microfibrils, protect cells, maintain shape, prevent excess water uptake, site of some metabolic reactions, primary and secondary cell walls
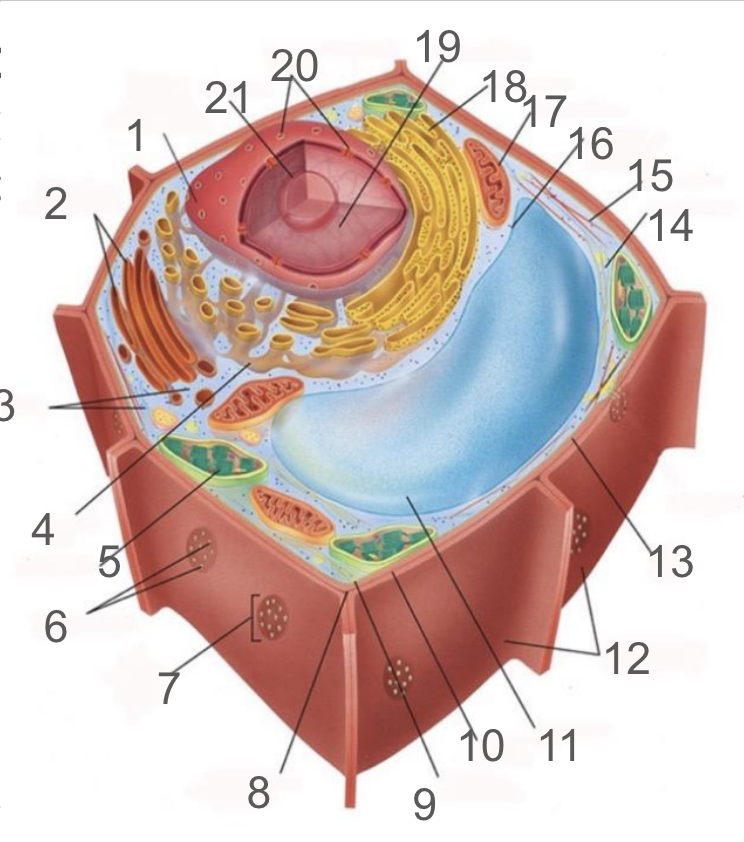
#14 and its function
actin filaments; helical protein filament part of cytoskeleton, involved in cytoplasmic streaming and powered by myosin motor proteins
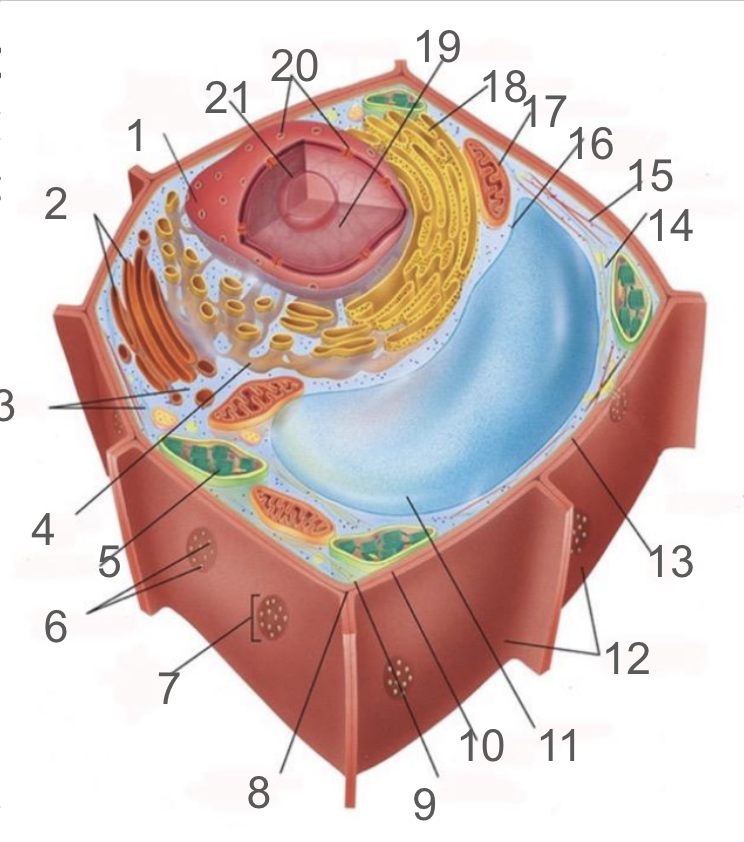
#15 and its function
microtubule; composed of alpha and beta protein dimers that create a hollow tube and the network. Move chromosome via spindle fibers, responsible for cell motility, compression resistance, and movement of organelles
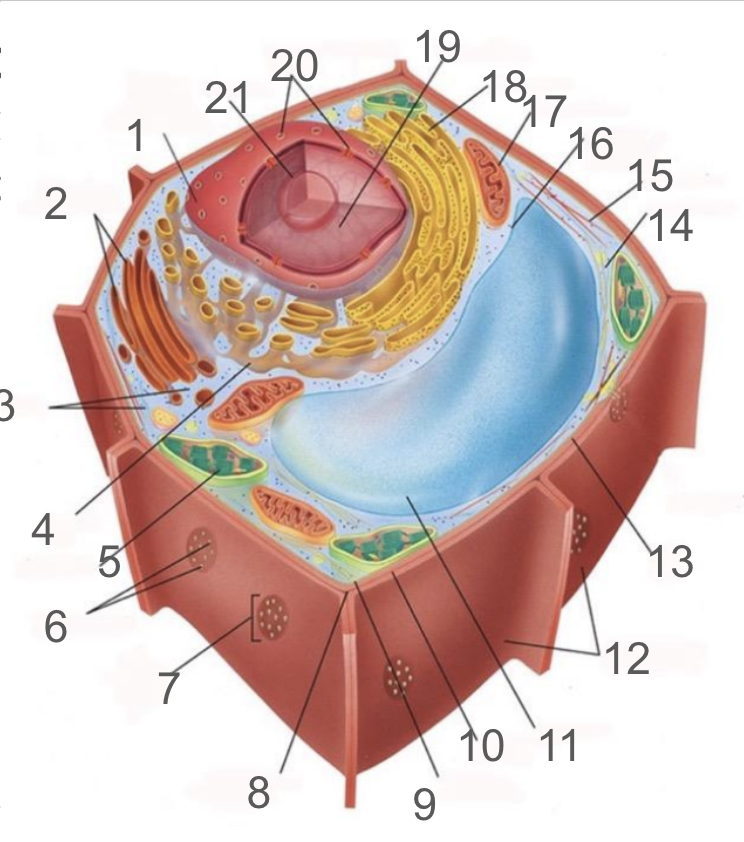
#17 and its function
mitochondria; generates ATP via cellular respiration and enclosed in two phospholipid bilayer membranes: smooth outer membrane and folded inner cristae. Inside is the mitochondrial matrix consisting of enzymes, DNA and ribosomes
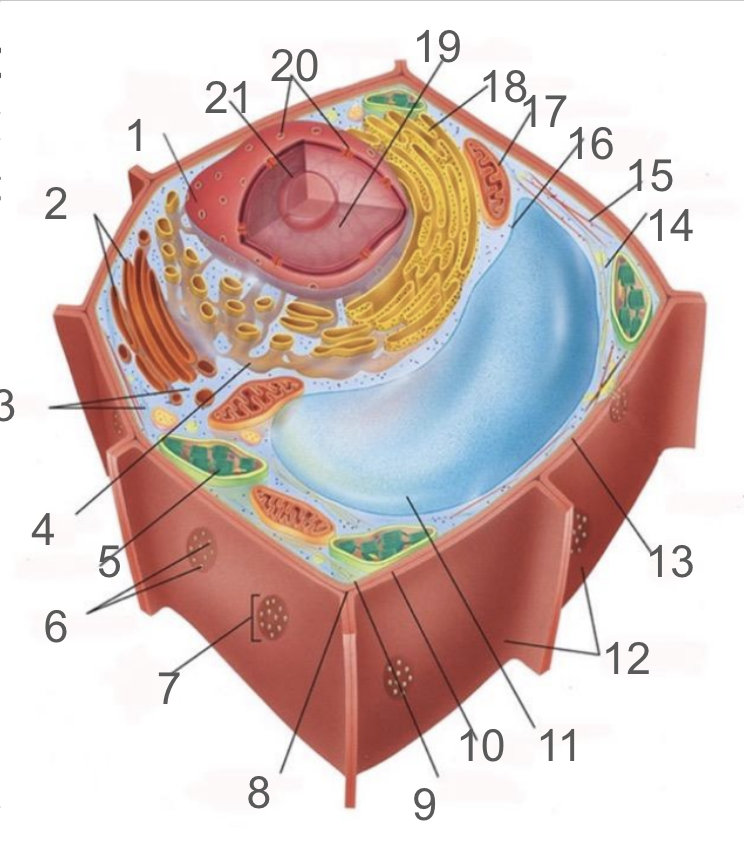
#18 and its function
rough er; protein production and transport
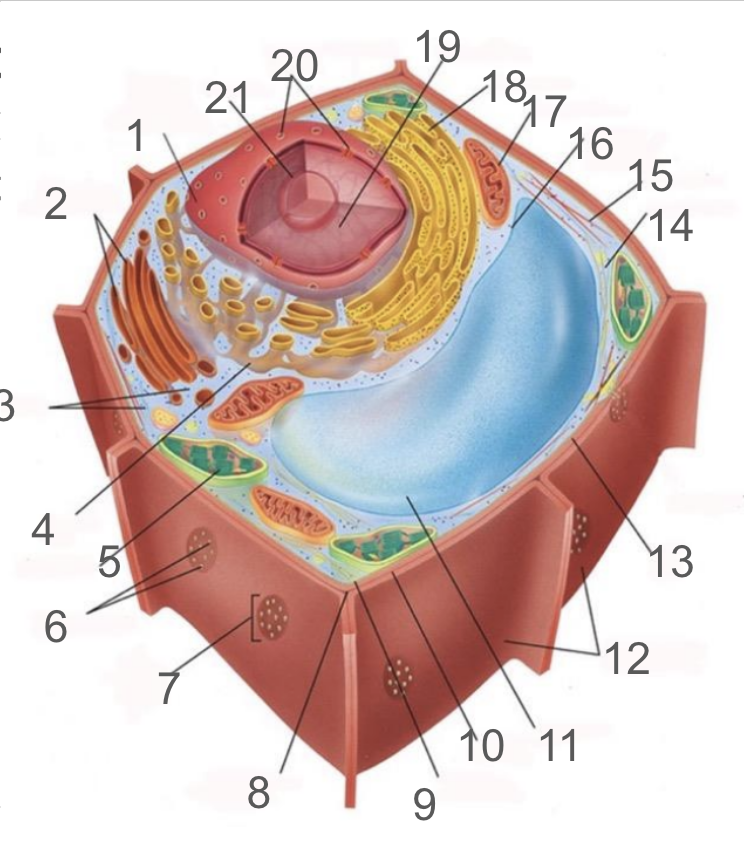
#21 and its function
nucleolus; produces ribosomes by synthesizing rRNA and dictates stress responses
primary cell wall
rigid, outermost layer composed of cellulose
secondary cell wall
rigid inner layer only in some types of cells after elongation stops, usually contains lignin
cellulose microfibrils
wrap around protoplast to resist expansion
lignin
in woody tissue, toughens cell wall
transport protein
allow hydrophilic molecules and ions to pass
channel proteins
opening allowing certain molecules to diffuse through
carrier proteins
dependent on ATP, change shape to transport across membrane
thylakoids
contain chlorophyll within the chloroplast
grana
stacks of thylakoids
lumen
inside of thylakoids
stroma
fluid surrounding thylakoids containing DNA, enzymes and ribosomes
semiautonomous
contain their own DNA, can replicate independently to some degree but still reliant on nucleus
etioplasts
colorless chloroplasts
chromoplast
store bright pigments in fruit and flowers
amyloplast
store starch
elaioplast
synthesize oil
microfilaments
two stands of actin responsible for organelle movement and cytoplasmic streaming
forming face
part of the dictyosome that receives vesicles from the rough endoplasmic reticulum
maturing face
part of the dictyosome that releases vesicles to the plasma membrane
meristem
region of active cell division
G1 phase
cell grows and carries out normal metabolic activity
S Phase
DNA replication
G2 phase
cell continues to grow and prepare for division
genome
complete set of nuclear genetic material in a cell
chromosome
single DNA molecule wrapped around histone proteins
chromatide
one of two identical sister chromotids connected by a centromere
prophase
chromosomes condense, spindle fibers form and attach to kinetochore proteins, nuclear envelope dissolve, chromatids join at centromere
metaphase
chromosomes align at the plate with help of spindle fibers
anaphase
microtubules shorten and pull chromatids to opposite poles, cell elongates
telophase
nuclear envelopes form, chromosomes decondense, microtubules break down, cell plate forms
cytokinesis
cytoplasm divides
phragmoplast
microtubules send dictyosome vesicles to forming cell plate
totipotency
cells can differentiate into any other type of cell
primary meristems
responsible for primary growth (growth in an apical-basal pattern of length)
secondary meristems
responsible for secondary growth (growth in a radial pattern of concentrically arranged tissue systems by increasing diameter)
tissues
simple and complex
tissue systems
ground, vascular, and dermal
organs
leaves, stems, roots, floral parts
ground tissue system
make up the bulk of the plant body, fills the space between vascular and dermal systems
vascular tissue system
conductive xylem and phloem tissue
dermal tissue system
epidermal tissue
parenchyma
thin primary cell walls, living at maturity, photosynthesis / storage / secretion
collenchyma
primary cell walls with uneven thickness, non-lignified and provide flexible support
sclerenchyma
primary and lignified secondary cell wall, dead at maturity
scleried
circular bundles of sclerenchyma
fiber
elongated strands of sclerenchyma
xylem
conducts water
phloem
conducts food