bio test unit 3 (cells)
1/32
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Cell Theory
All organisims are composed if cells
The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms
All cells come from preexisting cells
Prokaryotic cells
Bactiria don’t have a nuclues DNA is stored in Bacterial Chromosomes
Eukaryotic Cells
plant and animal cells
have diffrent regions so diffrent things happen in diffrent places
Componets of a Prokaryote cell (just look over)
Only in prokaryote: Nucleoid
In both Prokaryote and Eukaryote
DNA
Plasma membrane
cell wall-are not in animal cells
Ribosomes
Cytoplasm
Componets of Eukaryote (just look over)
Only in Eukaryote:
Nucleus
Golgi Appartous
Mitochondria
Lysosme
ER
In Both Prokaryote and Eukaryote:
DNA
Plasma membrane
cell wall-are not in animal cells
Ribosomes
Cytoplasm
What are the two types of Eukaryote cells
Plant cells and Animal cells
Componets of Plant cell (look over)
Only in Plant Cells:
Cell Wall
Central Vaculome
Chloroplast
In Both Plant and Animal Cells:
Nuclues
Ribosons
ER
Mitochondria
Golgi Apparatus
Plasama membrane
Cyotoskeleton
Componets of Animal cell (look over and compare to plant cell)
Only In Animal cells:
lysosomes
Centrosome with centrioles
In Both Animal and Plant Cells:
Nuclues
Ribosons
ER
Mitochondria
Golgi Apparatus
Plasama membrane
Cyotoskeleton
Nucleus
Large organelle that contains DNA.
Nuclear Membrane
This cell part controls what can move into and out of the nucleus.
Ribosomes
Small structures that use the instructions from the nucleus, written in mRNA, to build proteins.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Membrane bound network of tubes and flattened sacs has ribosomes attached and is involved in protein synthesis.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Membrane bound network of tubes and flattened sacs lacks ribosomes and its main role is to make lipids and phospholipids.
Lysosomes
A sac-like organelle contains enzymes that break down material, cell debris and worn out organelles.
Vacuoles
Large vesicles that act as a storage place and are especially large in plant cells.
Mitochondria
Cellular respiration occurs in this organelle, where the chemical energy in glucose is converted to ATP.
Chloroplast
The site of photosynthesis where light energy is converted into chemical energy in sugar molecules.
Plasma membrane
The cell part that surrounds the cell and controls what can move in and out.
Cell Walls
This somewhat rigid structure, made of cellulose, surrounds plant cells providing protection and support.
Cilia and Flagella (maybe need to know?)
Cell appendages that aid in the movement of cells.
What organells fit into the catagory of Genetic control of the cell
Nucleus, Nuclear membrane, and Ribosomes
What organells fit into the catagory Energy Processing
Mitochondria |
Chloroplast |
What does it mean that Membranes are selectivly permeable
It means that membranes allow certain substances to pass through while restricting others, thus controlling the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
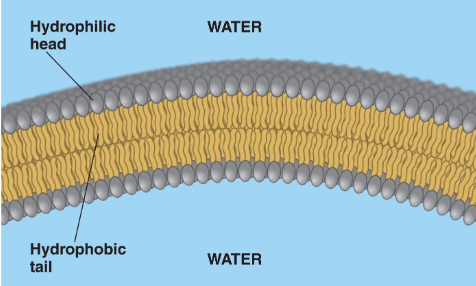
explain how Phosopolipid bilayer is structured
the hydrophillic heads face the outside while the hydrophobic tail are on the inside meeting another set of hyrophobic tails with hydrophillic tails facing the outside
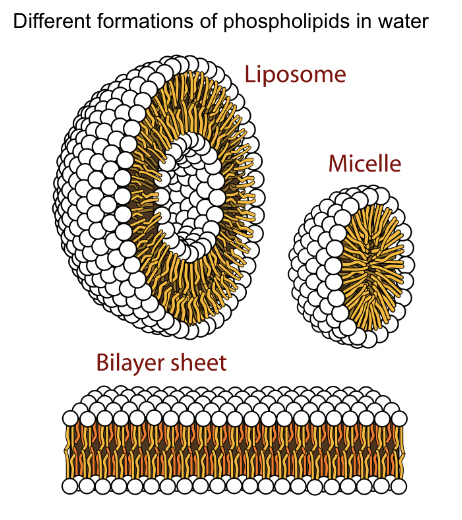
What are the diffrent formations of Phosopolipds in water and descriebe what they look like
Liposome, Micelle, Bilayer sheet
How can a membrane be fluid?
It moves, allowing particles to move around each other.
Describe Movement of phospholipids
lipid bilayer is fulid interactions between tails are weak and always break
Movement of the lipids is lateral within layer
What is diffusion
Diffusion is the tendency of particles to spread out to fill up avaliable space- Equilibrium
How do Large polar and Charge soultes move across the membrane
Large, polar, and charged solutes move across the membrane through transport proteins
Examples: water, glucose, K+, Na+,
Active transport
Against concentration gradient
Active process (requires energy)
Solutes pumped against their concentration gradient through transport proteins.
Active process: Energy required in the form of ATP.
Active transport proteins function as pumps for specific solutes.
Osmosis:
facilitated diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane. Water moves from high free water concentration to low free water concentration
Osmosis is important for regulating the water balance of the cell
Exocytosis
(Out of cells)
Export of larger material, like proteins or carbohydrates, out of the cell.
Examples:
Secretion of digestive enzymes to intestine
Secretion of insulin to the bloodstream
Endocytosis
(Into cells)
Import of larger material, including “food,” virus, and bacteria, into the cell.
Examples:
Phagocytosis of “food particles,” including fluid, large molecules, viruses, and bacteria.
Receptor mediated endocytosis of specific molecules like cholesterol.