Cariology Exam One [Introduction to Microbiology: Banas]
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Eukaryotic Microbes:
- Fungi (molds and yeast)
- Parasites and worms
Eukaryotic microbes are
Single-celled or Multicellular
Prokaryotic Microbes:
Bacteria
Prokaryotic Microbes are:
Single-celled but may exist in chains or groups
Acellular Microbes
Viruses
Acellular Microbes are
Nucleic acid surrounded by proteins
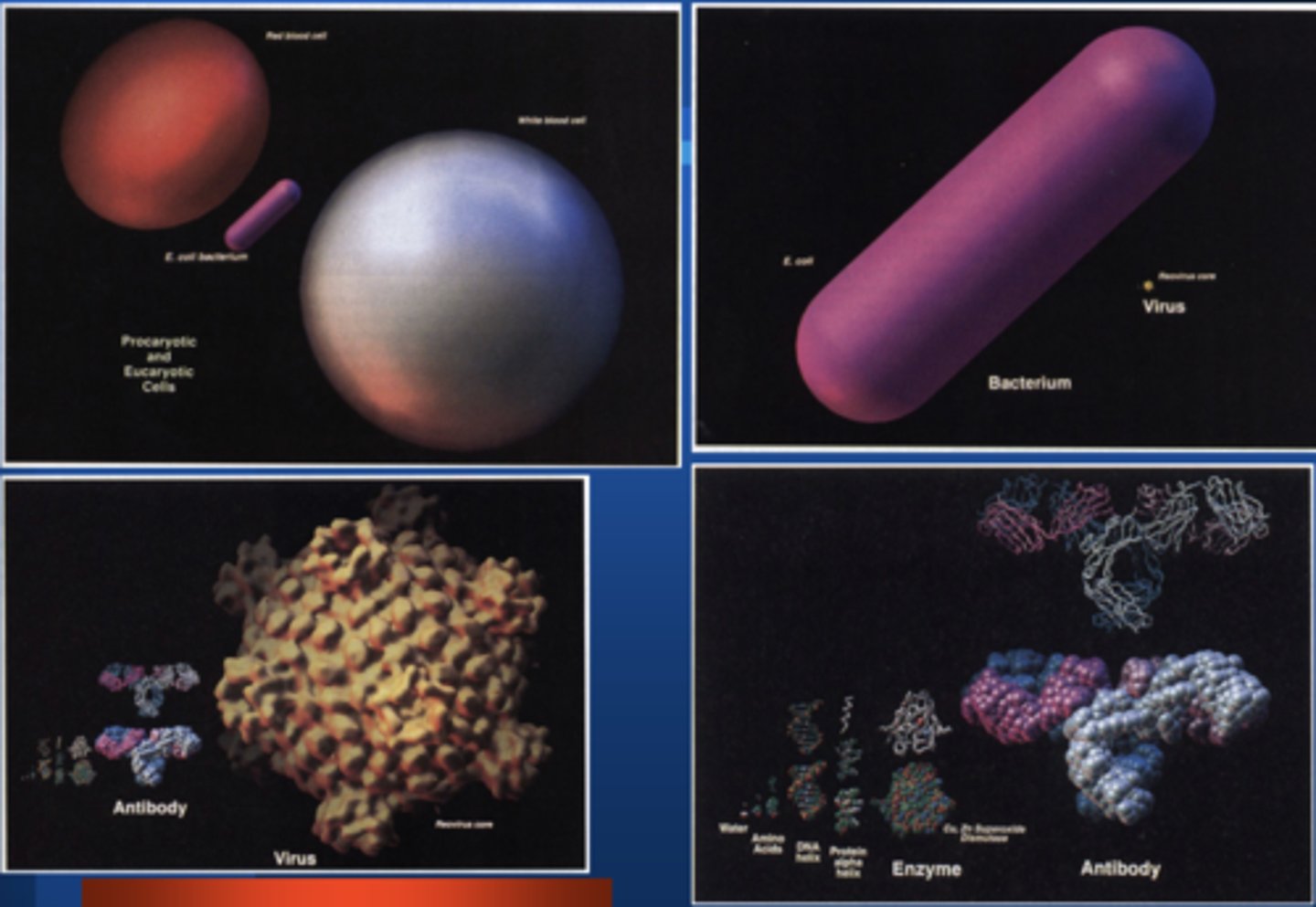
Microbes differ vastly in
Size
Typical brightfield microscope will have a ___x eyepiece and objective of ___,___,___
10x eyepiece
10x,40x,100x objectives
Brightfield microscope: Low power
100X magnification
Brightfield microscope: High-dry power
400x
Brightfield microscope: Oil immersion
1000X
Brightfield microscope: Magnification suitable for viewing eukaryotic cells
Low and high-dry
To satisfactorily assess bacterial morphology, viewing under __________ is necessary
oil immersion (1000X magnification)
Electron microscopy in its various forms has suitable resolving power in a range from
5000x to 1,000,000x
To see the structure of viruses requires magnification of approximately
> 20,000x
The microflora of the oral cavity can include
Yeasts, bacteria, and viruses
The primary inhabitants of dental plaque and causative agents of dental caries are
Bacterial species
Classification of Bacteria (that we need)
Gram Negative
Gram Positive
Cell wall-less
Archaebacteria
Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic: Eukaryotic
- Generally > 5μm
- Has a nucleus and other internal membrane-bound compartments
- DNA in diploid genome
- No cell wall except fungi
- Cytoplasmic membranes contains sterols
- 80S ribosomes (60S + 40S)
- mRNA must exit nucleus to be translated
- Respiration in mitochondria
- Sexual or asexual reproduction
Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic: Prokaryote
- Generally 0.5-3.0μm
- No nucleus and no internal membrane-bound compartments
- Single, circular haploid genome
- Usually a peptidoglycan cell wall
- No sterols
- 70S ribosomes (50S + 30S)
- Transcription and translation occur together
- Respiration in plasma membrane
- Asexual reproduction
Bacteria can be visualized without stain by using
phase contrast or darkfield light microscopy
Bacteria are more commonly stained using a simple stain or the differential stain called the _____ and visualized by brightfield microscopy
Gram stain
Gram staining: Gram Positive
1. Fixation
2. Crystal violet (Dark purple)
3. Iodine treatment (Light purple)
4. Decolorization (Does not effect: Light purple still)
5. Counter stain (does not effect)
Purple stained
Gram staining: Gram Negative
1. Fixation
2. Crystal violet (Dark purple)
3. Iodine treatment (Light purple)
4. Decolorization (Colorless)
5. Counter stain (Pink)
Pink stained
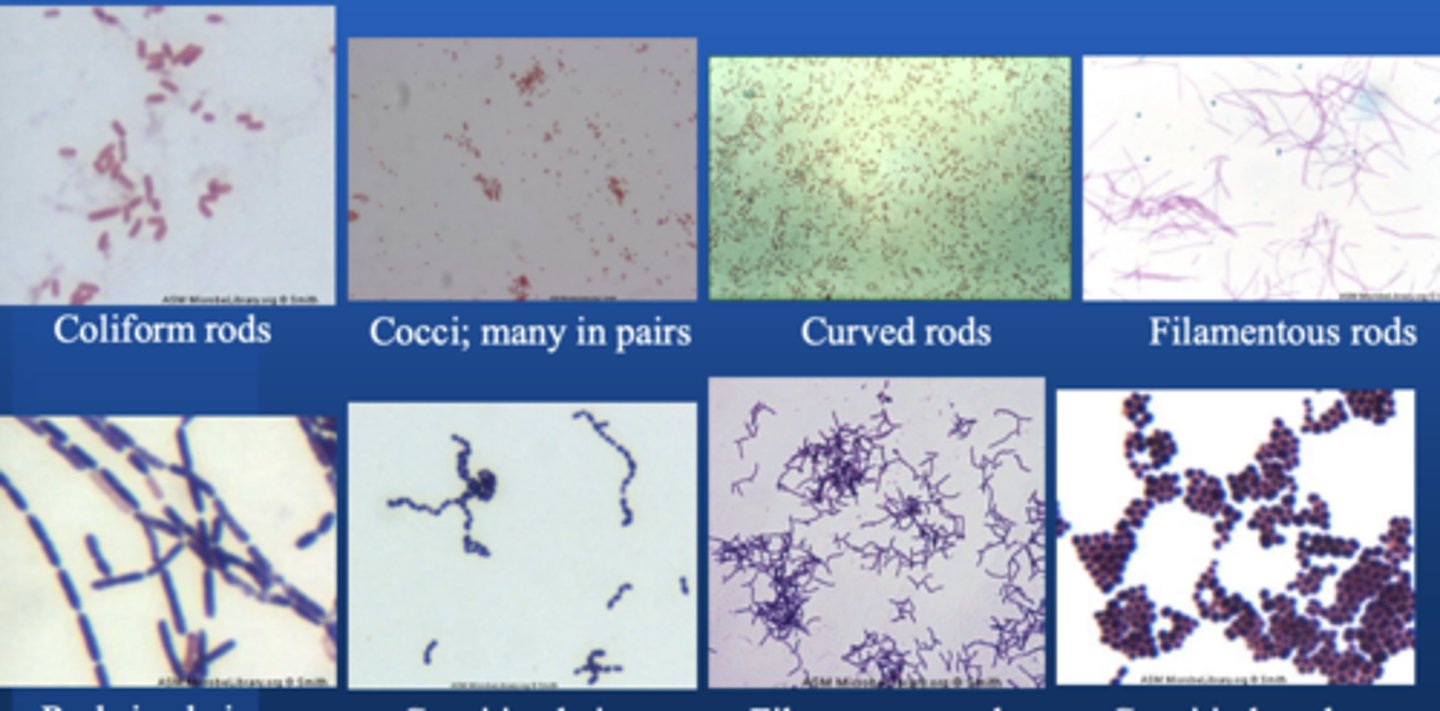
Bacterial Shapes
Cocci
Rods
What corresponds to the Gram reaction
Cell wall anatomy
Peptidoglycan
Repeating disaccharides; the amino acid crosslink is always attached to the N-acetylmuramic acid moiety
Cross-linking is
the connection between amino acid side chains.
This connection is often direct in Gram-Negative, but via a penta-glycine bridge in Gram-Positive
What type of bacteria are more extensively cross-linked
Gram Positive
Different Structures between gram + and gram - membrane
Gram +
- Has a thicker peptidoglycan layer
- Teichoic acids
- Lipoteichoic acids
Gram -
- Has a thinner peptidoglycan layer
- Lipopolysaccharides
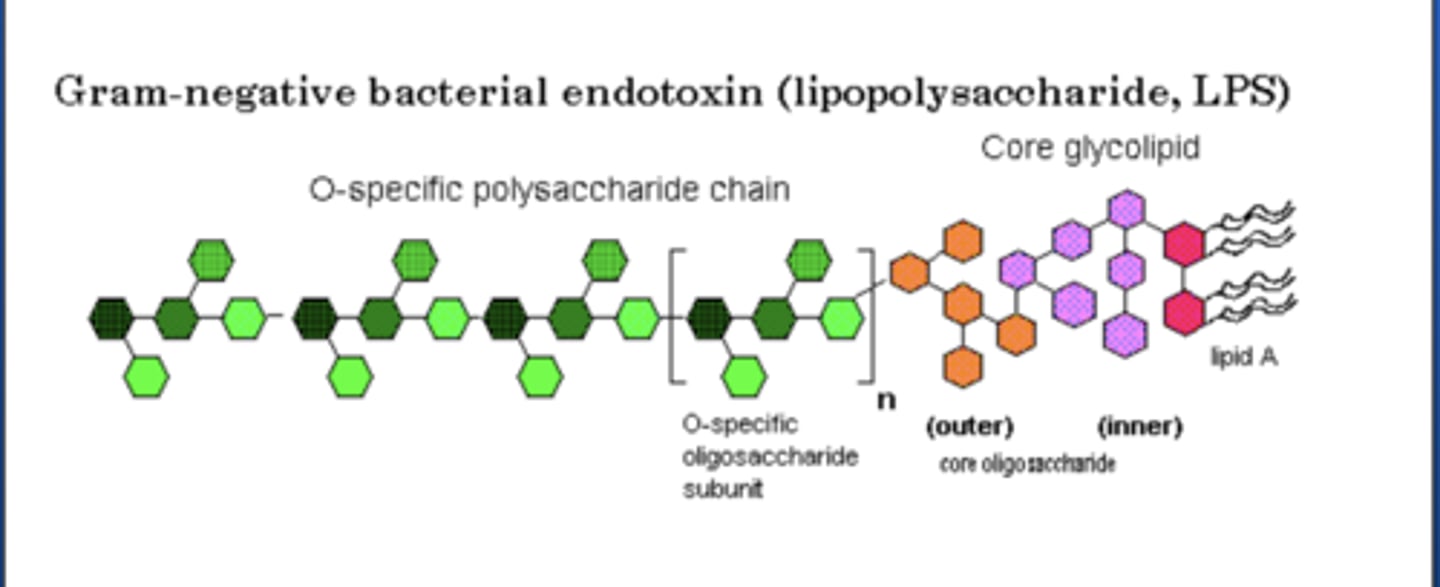
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
- Endotoxin
- Component of almost all Gram-Negative
- Only acts as endotoxin when released from lysed bacterial cells
- Lipid A portion is the most toxic
- Can be responsible for septic shock
- Endotoxin from different species possesses different toxic potential
Lipopolysaccharide structure
- Lipid A portion
- Inner and outer core glycolipid
- O antigen (specific subunit)
QUESTION: Which of the following allows direct access to extracellular substances that attach the peptidoglycan component of the cell wall?
1. Gram Positive
2. Gram Negative
1. Gram positive
- Don't have to go through an outer membrane in order to get to the peptidoglycan
It is impossible to avoid bacteria we must
coexist
We have evolved an association with
bacteria in our environment
In most instances the association with bacteria is
commensal or mutualistic
A normal flora
Stimulates and strengthens our immune system, synthesizes certain vitamins, and helps reduce the opportunities for colonization with pathogenic species
Who lives where: Skin
- Mostly Gram +
- difference between dry and moist areas
Who lives where: Oral
- Mix of Gram + species
- Differences based on distinct niches
Who lives where: Urigenital
- Mostly skin organisms but can be acidogenic species like lactobacilli
Who lives where: Digestive tract
- Mostly Gram - anaerobes
- spares in stomach and small intestine
- Colon heavily populated
BACTERIAL PROPERTY: Adhesion
HOST RESPONSE:
- Mechanical
-- barriers, swallowing, peristalsis, coughing, flow of urine, cell sloughing, oral hygiene
-Innate immunity
-- Lysozyme, pH, Phagocytosis
- Adaptive immunity
-- Ig, cT Cells
BACTERIAL PROPERTY: Invasion, phase variation
HOST RESPONSE:
- Adaptive immunity
BACTERIAL PROPERTY: Toxins (endotoxins, exotoxins)
HOST RESPONSE:
Adaptive immunity (keep bacterial population low)
BACTERIAL PROPERTY: Degradative enzymes
HOST RESPONSE:
Adaptive immunity (keep bacterial population low)
BACTERIAL PROPERTY: Metabolic byproducts (acid)
HOST RESPONSE:
- keep bacterial population low
- Buffering by saliva
Bacteria that can cause disease are called
Pathogens
The pathogen establishes an infection leading to
symptoms of disease
Properties of bacteria that make the host sick are called
virulence factors
Disease symptoms in the host often contribute to
dissemination of the pathogen
Other times disease can result from overgrowth of
particular normal microflora species, or if the normal flora can be introduced into normally sterile sites
- Opportunistic infection
Dental caries and periodontal disease are generally considered
opportunistic infections that result from changes in the ecology of the oral microflora
The altered composition of the microbiome in the oral cavity by opportunistic bacteria is said to be in
dysbiosis
Endodontic infections might be considered an example of the
oral microflora contaminating a normally sterile site
SUMMARY: Bacteria are classified as prokaryotes, have variety of shapes, and can usually be classified as either
Gram positive or Gram negative
SUMMARY: The Gram reaction is based upon differences in the cell wall which in turn plays a role in
where the organism can best survive and which influences clinical care
SUMMARY: We have a normal microflora that is particularly rich in
the oral cavity
SUMMARY:
Bacteria have a variety of means for
The host has several means
Bacteria:
Colonizing and propagating
Host:
Designed to limit bacterial population