Binocular eye movements
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
what are eye movements in which both eyes move in the same direction called
versions
what are all the version movements and which direction do they point
Dextroversion (rightwards)
Laevoversion (leftwards)
Sursumversion (upwards)
Deosursumversion (downwards)
Dextrocycloversion (top of the eyes moves to the right)
Laevocycloversion (top of the eyes moves to the left
Binocular eye movements in which both eyes move in the opposite direction (disconjugate) are called
vergences
what are all the vergence movements and which direction do they point
Convergence (eyes move inwards)
Divergence (eyes move outwards)
R supravergence (RE upwards = LE downwards)
R infravergence (RE downwards = LE upwards)
Incyclovergence (eyes roll inwards towards nose)
Excyclovergence (eyes roll outwards away from nose
what is Herings law of equal innervation
movement of one eye is accompanied by a movement of the other eye of equal amplitude and velocity, either in the same or opposite directions
what are the 4 Maddox classifications of vergence
tonic
disparity
accommodative
proximal
what is a tonic vergence
the amount of vergence present when no other cues to vergence are available. This is the baseline or resting vergence position of the eyes, present even in the absence of any specific visual stimuli.
what is accomodative vergence
This is the vergence response driven by the need to focus on a target at different distances, as the eyes converge or diverge to maintain a clear image
what is disparity vergence
vergence component that is induced by retinal disparity. • Vergence eye movements are made to ensure that the two fovea coincide
what is proximal vergence
evoked by stimuli that give the impression of being nearer or further. This vergence is stimulated by cues related to the perceived distance or nearness of a target, such as the size of the target or the presence of other objects in the scene
how many degrees is equivalent to 1 prism dioptre
0.57
what factors affect alignment of both eyes
Anatomical factors.
The basic tonus of the extraocular muscles.
The eyes’ accommodative power and
The fusion reflex (the presence of a fusion
stimulus
what is hetrophoria
latent deviation of the eyes.
Which means it occurs, if present, when the stimulus to fusion is removed.
The uncovered eye does not move
when the occluder is removed the eye will return to its original position
when a cover is placed in front of one eye, the covered eye will deviate: the eye movements are called …
Not move – orthophoria
Inwards – esophoria
Outwards – exophoria
Upwards – hyperphoria
Downwards – hypophoria
what is a tropia
manifest deviation of the eyes.
In this position the eyes are turned all the time).
when occluded the eyes dont move
what are the types of tropia and what directions do they moves
Outwards – esotropia
Inwards – exotropia
Upwards – hypotropia
Downwards – hypertropia
what are the methods of measuring a heterophoria
Maddox Rod
Maddox Wing
Von Graefe
Know normal values of H and V heterophoria in population
what is the method for horizontal phoria - maddox rod
The horizontal Maddox rod is used to measure horizontal phoria.
The patient looks at a spot of light (usually at a distance).
Orthophoria: The spot and line intersect.
Heterophoria: The spot and line appear apart.
Prism is used to align the two and measure the size of the phoria.
what is the method for esophoria - maddox rod
A Maddox rod is placed in front of the patient's right eye (RE).
The patient reports seeing a 4Δ esophoria.
The red line appears to the "right" of the light spot due to the horizontal deviation.
Maddox Wing - Measurement of Phoria at Near
Used to measure phoria at near.
The device has a septum to dissociate the eyes.
There are 3 scales: horizontal, vertical, and cyclophoria.
Each scale has numbers and directions (e.g., eso, exo, hypo, hyper).
One eye sees the scale, the other sees the "arrow.
Maddox Wing - Procedure
The patient holds the Maddox Wing in place.
The patient reports if they can see both the scale and the arrow.
The number where the arrow points is recorded as the size and direction of the heterophoria.
Von Graefe Method - Fusion and Dissociation
Fusion is broken using prism, causing dissociation and diplopia.
Horizontal phoria is measured with about 6 prism diopters (Δ), base down (BD) or base up (BU).
The patient sees 2 images (one above the other), misaligned if heterophoria is present.
The amount of prism required to align the images equals the phoria.
what are Normal Findings for Heterophoria
Horizontal Phoria:
Distance: 1 exo (SD ±2) prism diopter.
Near: 3 exo (SD ±3) prism diopter.
Vertical Phoria:
Orthophoria (no vertical deviation).
define vergence
simultaneous movement of the pupils of the eyes towards or away from one another during focusing
how to calculate AC/A ratio using the gradient method
change in phoria in dipoters / change in accommodation in diopters
what does the Ac/A ratio represent
the amount of convergence in prism diopters that is induced per diopter of accommodation
how to measure AC/A ratio using the calculated method
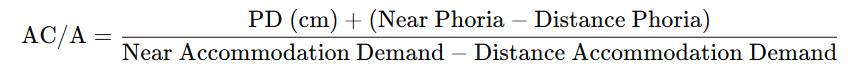
what does an AC/A ratio with converge excess suggest ( higher than 6:1 )
can suggest that the patient converges too much when they accommodate, leading to esophoria or excessive near vergence
what does an AC/A with a convergence insufficiency ( lower than 3:1) suggest
may suggest the patient has difficulty converging their eyes for near tasks
which conditions does AC/A ratios help solve
esophoria and exophoria
what is the worth 4 dot test
test assesses how well the eyes can align and fuse two images. The patient is shown a set of four dots with different colors, and the examiner can evaluate the patient's ability to fuse the images together (i.e., no double vision)
what is a synoptophore (or Stereopter)
a device that presents two images to each eye, and the patient is asked to align them. The examiner can then adjust the images to measure how well the eyes can converge or diverge.