Nutrition and Feeding Tubes
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
When patients lack access to nutrition, the body:
The body begins using its own reserves for energy
Body burns muscle, then fat
In acute care, the goal is to not surpass more than ____ hours NPO
48
NPO=
nil per os, nothing by mouth
nutritional support mind map
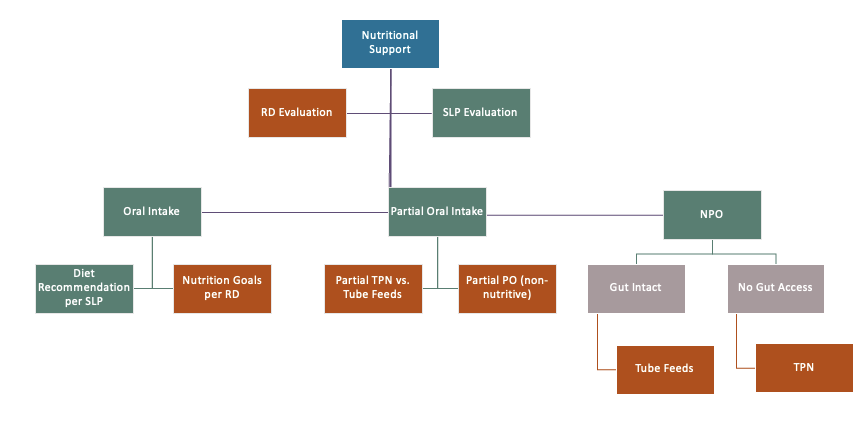
Formal evaluations
PMV
FEES
VFSS
Clinical
what do SLP evals determine?
full, partial, or no oral intake (NPO)
Considerations of duration of NPO
Must give MD/RD team an idea of how long until next eval
Anticipated length of NPO status to determine additional interventions moving forward
RD eval
medical history
dietary intake
clinical assessment
Recommendations for nutritional intervention
RD medical history
Meds, allergies
RD dietary intake
Food preferences, special diets
RD clinical assessment
BMI, weight
Signs of malnutrition
Labs
GI function
RD recommendations for nutritional intervention
Caloric/protein goals, supplementation need, weight maintenance
What is artificial nutrition?
Nutrition and hydration delivered via means other than oral intake
types of artificial nutrition
intravenous
enteral
intravenous
IV hydration
Total parenteral nutrition (TPN)
bypasses the stomach
enteral
Nasogastric (NG-tube)
Gastrostomy (G-tube)
Jejunostomy (J-tube)
Tube Feeding: Pt Population Considerations
nuerologically impaired
require long term intervention
chronic issues
HNC
Recommendation for oral intake may be described with 3 main categories, what are they?
oral
partial
NPO
What are the 2 main types of artificial nutrition?
intravenous
enteral
Why is it imperative to communicate with a pt’s team about an NPO status?
anticipaticated duration of we would estimate what the NPO status would be. important to determine if artificial nutrition is needed and what type
IV hydration
No protein or calorie nutrition- hydration only
Must make decisions about nutrition quickly
Allows for evaluation by SLP and RD for further treatment planning.
Very short term 1-3 days average (to by time on what the plan is)
IV hydration
Parenteral Nutrition
Intravenous administration of nutrients, fluids, or medications
Referred to as Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN)
Bypasses normal digestion via liquid chemical formula delivered to the bloodstream through IV catheter
Delivered via central line
Very expensive
Not a long-term or home-based solution (usually)
Parenteral Nutrition
How are IV hydration and parenteral nutrition similar?
intraenous- the way its delivered
How are IV hydration and parenteral nutrition different?
one is hydration
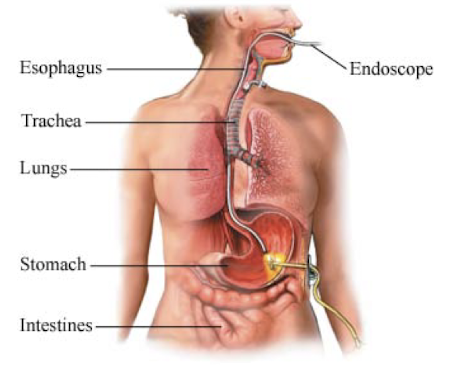
Nasogastric (NG) Tubes
Nasogastric tubes deliver nutrition via tube passed through the nose into the gut
Multiple sizes for multiple purposes
Should be removed/replaced by 14-21 days to reduce mucosal injury
NG tubes
Enteral feeding delivers nutrition directly to…
the stomach, duodenum, jejunum
what type of delivery for NG tubes?
nutrition & medication
diameter of NG tube
larger diameter (16 Fr)

suction of NG tube
Stomach pumping
Ingestion of poisons
Small bowel obstructions
Dobhoff Tubes (Type of NG tube) DHT
Small bore (8fr)
More comfortable
Medications clog frequently

NG Tube Complications
Tissue damage
Bleeding
Infection
Aspiration
Need for physical restraints
Patients frequently pull
NG may have bridle
Describe the difference between a general NG tube and a dobhoff tube
the size, diameter, NG is larger
NG: suctioning as needed
DHT: nutritional delivery
List 2 possible complications of an NG tube
mucosal damage, infection, bleeding, pain
2 types of G-tube
Surgical
Percutaneous
Used when tube feeding is anticipated for 30 days or more
G-tube
Gastrostomy Tube (G-tube): what are some complications?
Requires sedation to place
Do not eliminate aspiration
Shown to increase discomfort
Do not improve functional status
Must flush with water to keep clear
Surgical (open) G-tube
Surgical procedure with placement at the stomach
Usually reserved for patients already going to OR
May be needed if unable to place endoscopically or radiologically
Potentially due to anatomic obstruction
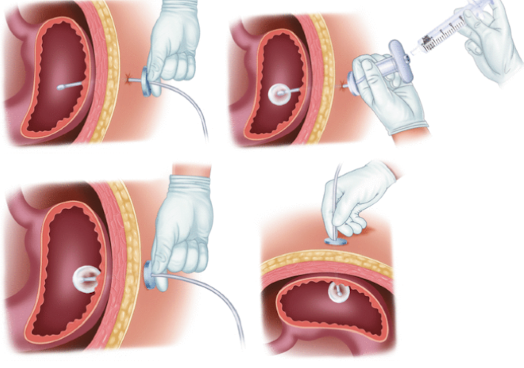
Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG tube)
Placed via endoscope and guidewire pull through
Cheaper and quicker to perform
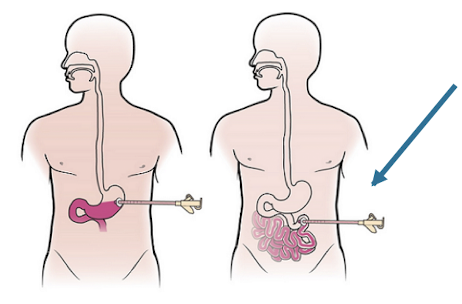
Jejunostomy Tube
Tube directly placed in the jejunum (small intestine)
Performed in the OR
Can be advanced from a G-tube to a J-tube if feeds not tolerated
Used frequently in those who reflux tube feeds
Feeding Tube Complications
feeding-related
tube-related
stoma site
feeing-related complication
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea (NVD)
Due to rapid feeding, formula intolerance, gut bacteria imbalance
Aspiration
Body position (HOB >30 degrees)
tube-related complication
Dislodgement
Blockage
stoma site complication
Infection risk, bleeding, and skin breakdown around stoma
Formula chosen by who and for what needs?
RD/MD to meet patient’s nutritional needs
feeding delivery methods
bolus feeds
intermittent feeds
continuous feeds
cyclical feeds
bolus feeds
Larger volume over shorter time period (15-30 mins); syringe or gravity bag
intermittent feeds
Smaller volume over longer time period (20-60 mins); pump or gravity bag
continuous feeds
Small volume delivered slow and continuously; pump
cyclical feeds
Small volume delivered continuously over set time period; pump
Keys of Nutritional Intervention
Multidisciplinary approach to nutrition intervention is ideal
SLP is a key member of the team when it comes to the patient + medical team making informed decisions about nutritional intervention(s)
Neither the patient or the medical team are REQUIRED to follow our recommendations because they are just that... recommendations!