unit 5 business
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
functions of financial department
records transactions
forecasts cash flow
prepares accounting information
prepares financial accounts
makes financial decisions
start up capital definition
financial sources needed by an entrepreneur when first starting a business to buy fixed and current assets
assets definition
items of value which are owned by the business
Intangible assets definition
assets that do not exist physically but can have value
e.g brand name, patent, copyright
working capital definition
finance needed by business to pay its day-to-day costs which do not involve the purchase of long-term, fixed assets
e.g wages, bills, materials
capital expenditure definition
spending by a business on fixed assets which will last for more than one year
Used during start-up or during expansion
product development, R&D, takeovers
revenue expenditure definition
money spent by a business on day-to-day expenses which don’t involve purchase of long-term assets, such as wages or rent
short term finance definition
loans or debts used to overcome cash-flow problems and the business expects to pay them back within one year
short term bank loans, overdraft
long term finance definition
loans or debts to finance purchases of fixed assets or business expansion and the business expects to pay them back in 5 years or longer
internal sources of finance
owners savings
retained profit
sale of unwanted fixed assets
sale of inventories
sale and leaseback
use of working capital
owners savings internal sources of finance advantages + disadvantages
advantages - no interest is paid, should be quickly available
disadvantages - savings may be too low, increases risk taken by owners which have unlimited liability
retained profit definition
profit remaining after all expenses, tax and dividends have been paid out, and which is reinvested back into the business
retained profit internal sources of finance advantages + disadvantages
advantages - does not have to be repaid, no interest
disadvantages - new business has no retained profit, small firms → don’t have enough retained profit to finance expansion, lower dividends → investors invest into other businesses
sale of unwanted fixed assets internal sources of finance advantages + disadvantages
advantages - makes better use of the capital tied up in the business, does not increase debts of a business, land + buildings often raise a lot of money
disadvantages - may take time to sell assets, not available to new businesses as they dont have any unwanted fixed assets to sell
sale of inventories internal sources of finance advantages + disadvantages
advantage - reduces opportunity cost + storage cost of high inventory levels
disadvantage - must be done carefully - if too many inventories are sold → customers disappointed since not enough goods a kept in inventory
external sources of finance
short term -
overdrafts
debt factoring
trade credit
long term -
bank loans
mortgage
debenture
leasing
share issue
hire purchase
overdraft external source of finance
Agreement with a bank that allows a business to spend more money than it has in its account up to an agreed limit. The loan must be repaid within 12 months
able to take at short notice → flexible for business
high interest rate → only used in case of short term cash flow problems
trade credit external source of finance
agreement between a business and its supplier that the business can pay for the supplied materials at an agreed time in the future
almost interest free
Regular delayed payments → risk of demanding payment upfront
no further deliveries until old ones are paid
any discount will be lost
debt factoring external sources of finance
selling trade receivables to improve business liquidity
immediate cash for the business
risk of collecting the debt becomes the factoring businesses problem
business does not receive 100% of the value of the debts
trade receivables definition
Amount owed to a business by its customers who bought goods on credit.
mortgage external source of finance
long term loan used to buy land or buildings
interest is paid every year
similar to bank loan
debenture external sources of finance
bond issued by a company to raise long term finance usually at fixed rate of interest
used to raise large sums of money
owner of bond receives interest + full price upon maturity date
leasing external sources of finance
using a fixed asset by paying a fixed amount per time period for a fixed period of time.
ownership remains with leasing company
used with machines
no big one time payment needed
high interest rates
hire purchase external source of finance
purchase of an asset by paying a fixed repayment amount per time period over an agreed period of time.
The asset is owned by the financing firm
until the final repayment.
purchasing firm responsible for maintenance + repairs
higher interest rates
no big one time payment needed
Bank loan external source of finance
finance provided by a bank which the business will repay with interest over an agreed period of time
share issue external source of finance
source of permanent capital available to limited liability companies after they sell their shares
capital does not have to be repaid however shareholders expect dividends
no interest
risk of takeover
authorised share capital definition
maximum amount of shares a business is allowed to sell
government grants source of finance
often offered to startups/small/medium sized businesses
do not have to be repaid
often with strings attached e.g business has to relocate
crowd funding source of finance
Financing a business idea by obtaining small amounts of capital from a large number of people, most often using internet and social medias
include how investors benefit after enough money is raised
if total amount is not raised finance has to be repaid
can be a fast way to raise large sums
micro funding source of finance
Small amounts of capital loaned to entrepreneurs in less developed countries where finance is often difficult to obtain.
These loans are usually repaid after a relatively short period of time
factors influencing source of finance
amount of finance required
length of time when finance is needed
size + legal form of business
existing borrowing
profitability of business
desire to keep ownership of business
will banks lend ?
is cashflow forecast available?
is business plan available?
is a forecasted income statement available?
will the loan be secured?
why is the loan needed?
will shareholders invest ?
are the future prospects for a company good?
how do company dividends differ from other companies
how has the companies share price level varied?
cash inflow
sums of money received by a business during a period of time
e.g sales revenues, payment by debtors, borrowing, sales of assets, investments
cash outflow
sums of money paid out by a business during a period of time
e.g Expenditures to buy materials, paying wages & bills, paying off debts, buying fixed assets
cash flow
cash inflows and cash outflows over a period of time
net cash flow, positive cash flow, negative cash flow
net cash flow - cash inflow - cash outflows
positive cash flow - cash inflows > cash outflows
negative cash flow - cash inflows < cash outflows
cash flow management
Ensures that the business has enough cash whenever they need to pay their employees, suppliers, etc.
why are cashflow forecasts important
prevent negative cash flow
convince banks to provide loans
to help managers plan ahead
how to solve short term cash flow problems
hire purchase, leasing
bank loan
overdraft
all more expensive than delaying purchase by one month
ask customers to pay trade receivables quicker
negotiate longer trade credit with supplier
what is meant by liquidity of a business
ability of a business to pay its short term debts
how to measure business liquidity
working capital
Enough working capital to pay debts → business is liquid
working capital cycle definition
Time it takes from buying raw materials, making these into goods for sale, finding buyers for them and receiving payments from customers
factors that affect amount of working capital
level of inventories - less inventories → less working capital needed
trade credit terms - longer trade credit → less working capital needed
length of production process - short production process → less working capital
how quickly the business finds customers - quickly → less working capital
trade receivables terms - shorter credit sales → less working capital
overhead costs
day-to-day operating expenses of a business, but not directly related to creating a product
e.g rent, insurance, marketing, wages of sales people
cost of goods sold
direct costs of producing the goods sold by a company: costs of material & production labor
e.g costs of flour, sugar to make a cake, baker’s wages
profit vs gross profit vs retained profit
profit - difference between total revenue and total costs
gross profit - difference between revenues and direct production costs.
retained profit - profit remaining after all expenses, tax and dividends have been paid, which is then reinvested back into the business”
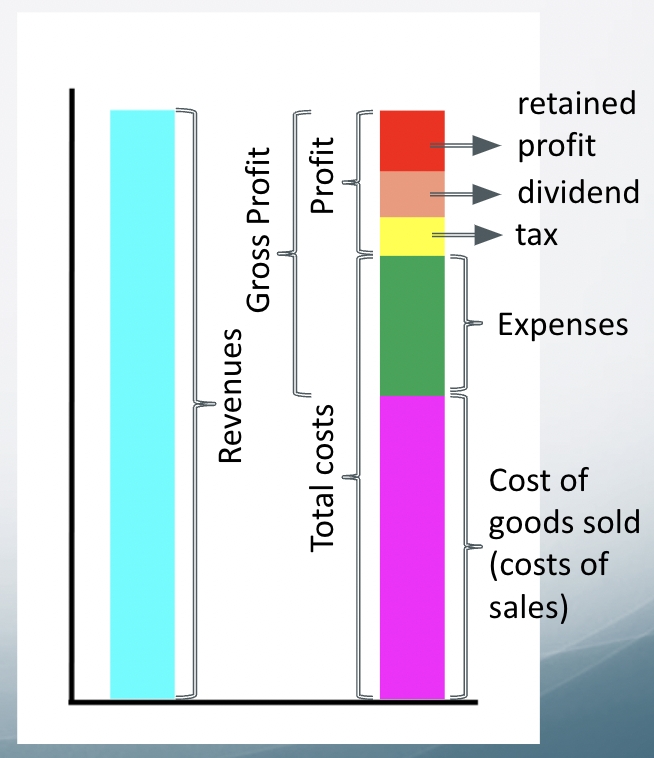
dividends
payment, out of profit, to shareholders as reward for their investment
why is profit important
As a reward for business owners for the risk of investing into business
To attract investors who provide additional funs for business expansion
As a measure of success of a business & performance of managers
Source of finance: retained profit as an internal source of finance
To decide whether to continue making & selling a product or not
To decide if to expand the business / buy fixed assets
cash flow vs profit
cash flow - pays day to day expenses → important to business short term + long term
profit - measure of success of business → important long term
How do the following directly affect cash flow and profit?
Business takes a bank loan:
Business buys a new machine:
Business sold goods, but will receive money for it next month
1 - Cash increases, profit unchanged
2 - Cash decrease profit unchanged
3 - Cash unchanged, profit increased
how can a profitable business run out of cash
buy too many fixed assets at once
offer too long trade credit period
expanding too quickly
too many inventories
income statement
financial statement which records the revenue, costs and profits of a business for a given period of time (usually once a year)
necessary for strategic decision making
how is the income statement important for shareholders + lenders
shareholders - high profit → high dividends + increase in market price of shares
lenders - higher profit → safe to pay loans on time
how is the income statement important for managers + employees
managers - high profit → business done well + source of finance for expansion
employees - high profit + chance of bonuses
how is the income statement important for government + suppliers
government - higher profit → higher tax revenue
suppliers - higher profit → promise of future purchases of their supplies
balance sheet / statement of financial position definition
an accounting statement that records assets, liabilities and owner’s equity of a business at a particular date
needs to be done by incorporated businesses at the end of each financial year
owners equity
amount owed by business to its owners, including capital and retained profit
money invested by owners
net assets formula
total assets - total liabilities
= working capital
capital employed formula
non current liabilities + shareholders equity
a balance sheet shows
Assets that the business owns and their value
What the business is owed and its value
What the business owes and its value
How the business finances its activities
Amount of working capital
disadvantages of balance sheets
shows the financial position of a business for only one particular day
value of assets/liabilities can be changed quickly
does not show trends / flows
value of non current assets might not reflect the market value of them
not a good indicator of how much a business is worth
how do banks + share holders benefit from balance sheets
banks - know if it is risky to lend money
shareholders - see how much business is worth + if it is managed well
capital employed definition
shareholders equity + non current liabilities → the total long term and permanent capital invested in a business
profitability definition
the measurement of the profit made relative to either the value of sales achieved or the capital invested in the business
who is profitability important for
investors when deciding which business to invest into
directors + managers to assess if the business is becoming more/less successful overtime → might lead to changes in operations to improve profitability
how to measure profitability ?
gross profit margin
profit margin
return on capital employed
Gross profit margin, profit margin, return on capital employed formula
gross profit - (gross profit/revenue) x 100
profit - (profit/revenue) x 100
return on capital employed - (net profit/capital employed) x 100
higher gross profit margin means…
higher revenues without similar increase in cost of sales
keeping revenues and lowering costs of goods sold
good has more added value (added value = selling price - direct costs)
profit margin description
profit earned per 1$ revenue
affected by cost of goods sold + revenue + expenses
higher profit margin means …
higher revenues without similar increase in costs of sales, keeping revenues and lowering cost of goods sold
lower expenses (overheads)
what does the difference between profit and gross profit mean
difference = expenses
small difference → low expenses → costs controlled well
big difference → high expenses → costs controlled poorly
Analysis of return on capital employed
ROCE increases over time → business is getting more profitable
if ROCE of business A > ROCE business B → Business A = more profitable
ROCE high → business is using resources efficiently
how to measure liquidity - ratio
current ratio
acid test ratio
current ratio - formula + optimum value + limitation
current assets/current liabilities
optimum value → between 1.5 and 2
limitation → inventories are the least liquid form of current assets → including them can skew the current ratio significantly
analysis of current ratio
below 1.5 → risk of not having enough cash to pay short term debts → cash flow problems
more than 2 → business has too much cash in unprofitable assets → missing on potential gains
why are inventories less liquid
it takes time to sell finished goods
when goods are sold on credit → business needs to wait for customer to pay
Acid test ratio optimum value + formula
(current assets-inventories)/current liabilities
optimum value - 1
analysis of acid test ratio
if less than 1 - risk of not having enough cash to pay short term debts → cash flow problems
if more than 1 - business has too much cash in unprofitable assets → missing on potential gains
profitability vs liquidity
a lot of cash → increases liquidity but limits profitability as is not used to buy profit making assets
a lot of non current assets → limits liquidity in short run but increases profitability in long run
Benefits of ratio analysis
Stakeholders can compare ratios over time → can identify trends
No need to investigate all financial statements to get the information → information received quickly
Stakeholders can compare results with other businesses to see how well the business is doing
Limitations of ratio analysis
Ratios compare past data → does not predict the future
Ratios do not include all strengths & weaknesses that affect profitability (e.g. quality of human capital)
Financial statements prepared in different ways from company to company → harder to compare
Effect of external factors, (e.g. laws, exchange rates, economic factors, not considered)
Who cares about ratio analysis pt 1 - owners+shareholders, potential investors, lenders, managers
owners + shareholders - more profit → higher investment, business market value increases → wealth
Potential investors - comparing dividends between businesses
Lenders - high profit + liquidity → safe (lenders get back money + interest)
Managers - are financial objectives achieved? , more retained profit → can buy more technologies,
Who cares about ratio analysis pt 2 trade payables, government, employees, customers
trade payables - does business have enough working capital to pay goods on credit?,higher profits → chance of expansion → more need for raw materials → chance to increase supplier revenue
government - higher profit → more tax revenue, higher revenue + profit → higher employment → government spends less on unemployment
employees - more profit + revenues → job security + chance to negotiate higher wages
customers - higher profits + revenues → business will continue to producing goods + profit reinvested to increase the quality