Ciliary body and Iris
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Please double check the week :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What are the 3 main function of the ciliary body?
Produces aqueous for the blood
Contains muscle to change lens curvature
Produce and maintain zonules of zinn
What is the ora serrata?
Junction between retina and ciliary body
What is the anterior surface of the ciliary body called?
Pars plicata
What is the posterior surface of the ciliary body called?
Pars plana
What are the key features of pars plana and pars plicata?
Pars plana is smooth and flat
Pars plicata is ridged
What forms the ciliary process?
Pars plicata surrounds iris, folded increase SA
How does the ciliary process happen?
Suspensory ligaments (fibres of zonules) release fibrillin protein
Attaches to pars plicata
What are the 3 parts of the ciliary body?
Ciliary epithelium
Ciliary stroma
Ciliary muscle
Good diagram that shows parts of the eye
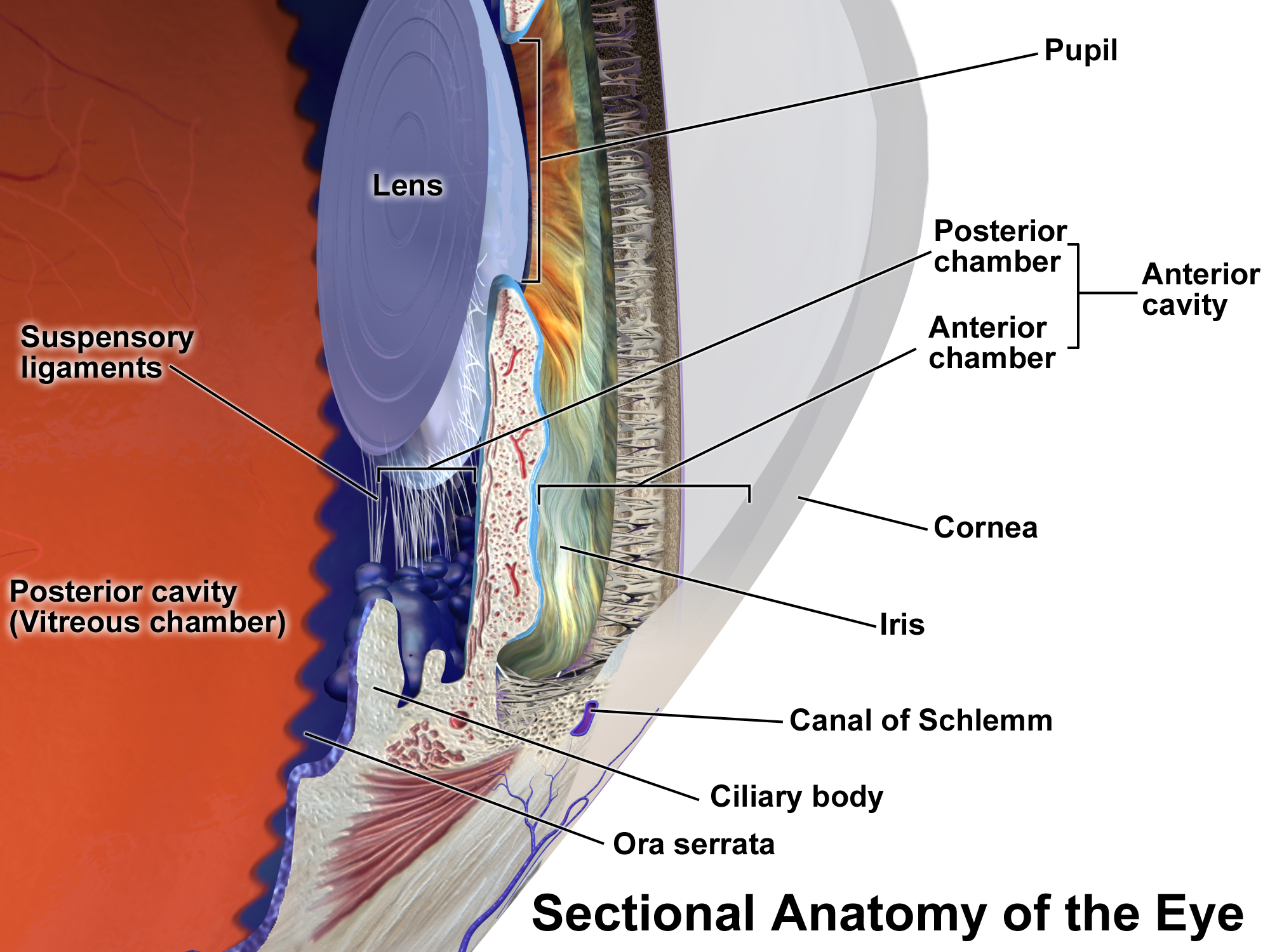
What is the ciliary epithelium
2 cubical epithelium cells that cover ciliary body surface
What is the inner layer in the ciliary epithelium?
Non pigmented
On the outside
Anterior continuation of nervous part of retina
What is the outer layer in the ciliary epitheium?
Pigmented
Continuation of retinal pigment epithelium
What do the epithelium layers even do?
Both produce aqueous humor, act as filter
What is the ciliary stroma?
Bundles of loose connective tissue which is rich in blood vessels and melanocytes
What is the ciliary muscle?
Smooth muscle fibres forming bulk
What is the difference is strength between smooth and striated muscle?
Smooth is more elastic but more actin and myosin in striated so stronger
What happens when the ciliary muscle contracts?
Pulls ciliary body forward
Release tension in suspensory ligament
Increases refractive power
What is the thickness of the corneal epithelium?
50 microns thick, 5-6 cells
What cell types do corneal epithelium contain?
squamous, wing, basal
Where are the goblet cells?
Conjunctiva
What do goblet cells produce?
Mucus
To widen the palpebral fissure, the upper plate is pulled by which 2 muscles?
Levator aponeurosis
Muller’s muscle
What happens in parasympathetic and sympathetic stimulations to ciliary muscles?
Parasympathetic stimulation, muscles contract
Sympathetic stimulation, muscles relax
What is the iris?
Thin contractile pigmented diaphragm with pupil
Where is the iris?
Suspended aquous humour between cornea and lens
What is the ciliary margin / root of the iris?
Periphery of iris attached to anterior superior body
What is the pupillary ruff?
Dark pigmented ring to shield iris from excess light and stop scattering
What is the function of the iris?
Regulate the amount of light entering the eye
What is the size of the human iris?
12mm
What is the size of the human pupil?
1-8mm
What is heterochromia?
Two different eye colours
What determines the colour of the iris?
Pigment of melanocytes
What is the central pupillary zone?
Anterior eye of iris which controls size
What is Fuch’s cypt?
Benign cystic lesion in iris
What does a Fuch’s cyst look like?
Small clear and round blister
What causes Fuch’s cyst?
no clear cause, could be trauma or surgery
What is the treatment of Fuch’s cyst?
No treatment but can have laser therapy
Microscopically what 2 zones does the iris consist of?
Stroma and 2 epithelia layers
What is the stroma of the iris made of?
Vascular connective tissue
Collagen fibres, fibroblasts, melanocytes, nerve fibers and smooth muscle
What do sphincter pupillae muscles do?
Smooth muscle fibres that allows pupil to constrict
What are dilator pupillae muscles?
Thin myoepithelium cells that contract for pupil to dilate
What are the 2 main zones of the iris anterior surface?
Central pupillary zone and peripheral ciliary zone
Separated by collarette
What are contracted furrows?
Folds that form on posterior iris
Where are contracted furrows found?
Pupillary region close to margin
What can cause contracted furrows?
Folding of iris tissue as dilates and contracts due to change in light levels
What do contracted furrows do?
Help accommodate structural changes in iris as dilates or constricts
Reduces mehacnical stress
What are concentric furrows?
Circular ridges on the outer ciliary region
What do concentric furrows look like?
Circles giving iris patterned appearance near edge
What do concentric furrows do?
Provide flexibility to peripheral iris ensuring smooth movement during dilation and constriction