CFB 24: Citric Acid (TCA) Cycle
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Reactions of the TCA cycle take place within the...
Mitochondrial matrix
What can be transported across inner membrane?
Pyruvate, citrate, α-ketoglutarate, malate, ATP/ADP/Pi
What does not cross the inner membrane?
Acyl CoA, oxaloacetate, NAD+/NADH
TCA cycle
Oxidation of Acetyl CoA to CO2 and hydrogen atoms
What is the coenzyme on E1 of pyruvate dehydrogenase?
Thiamine pyrophosphate
Thaimine deficiency leads to
Beriberi
Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome
A young adult is seen with symptoms of fatigue and muscle cramps. The patient is diagnosed to have a thiamine deficiency. Which of the following metabolic acids is the most likely to accumulate under these circumstances?
Pyruvate
3 multiple choice options
What is the active arm on E2 of pyruvate dehydeogenase?
Lipoate
What reoxidizes lipoate to regenerate active coenzyme?
FAD
What is FAD derived from?
Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)
What does FAD do?
Accepts electrons from lipoate onto flavin ring
Symptoms of Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) deficiency
Angular stomatitis
Cheilosis
Glossitis
What does pyruvate dehydrogenase do?
Converts pyruvate to acetyl-CoA
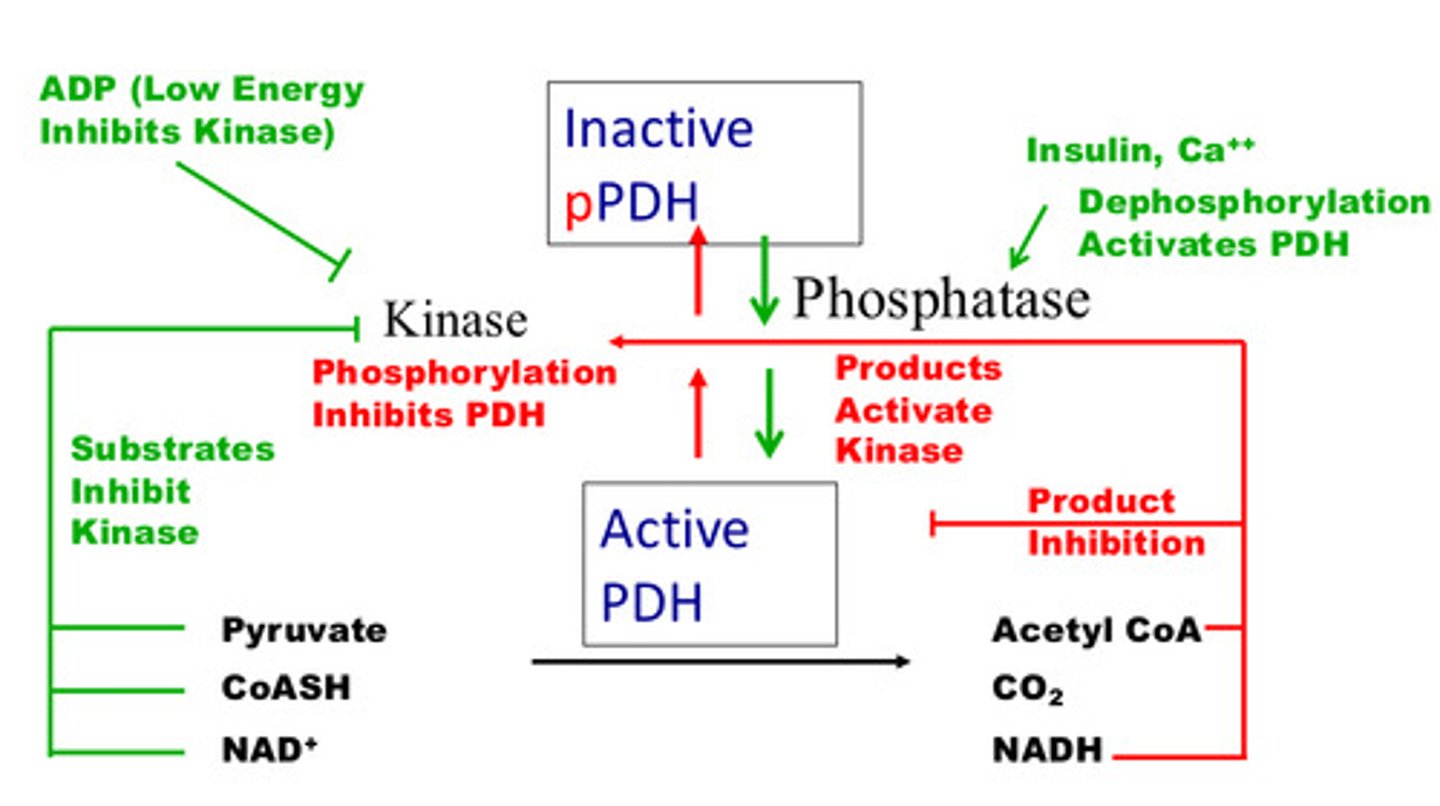
What inhibits PDH?
Acetyl CoA, NADH, ATP, CO2
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is inhibited by _______________.
Phosphorylation
Inhibitor PDH kinase is activated by ______ and inhibited by ___________.
Activated by product
Inhibited by substrates
Is PDH kinase activated/inhibited by low energy (ADP)?
Inhibited
Dephosphorylation _________ PDH.
Activates
What promotes dephosphorylation?
Insulin (well-fed) and Ca++ (exercise)
Summary of pyruvate dehydrogenase regulation
A 15-month-old child presents with sudden onset cough and hyperventilation along with evidence of metabolic acidosis. She has past history of recurrent vomiting, episodes of abnormal posturing, and has been showing regression of developmental milestones. Biochemical examination revealse persistently elevated serum lactate levels with a high lactate pyruvate ratio.
PDH deficiency
Greater than 50% of PDH complex deficiency arise from a defect in ______ pyruvate dehydrogenase from alpha 1.
PDHA1
Most common treatment for PDH deficiency
Cofactor supplementation (Thiamine B1)
Ketogenic diet
Carnitine supplementation
8 intermediates of the TCA cycle
Citrate
Isocitrate
α-ketoglutarate
SuccinylCoa
Succinate
Fumarate
Malate
Oxaloacetate
What is an aresnic target?
α-KGdH
NADH is at complex _ and gives _ ATP
FADH2 is at complex _ and gives _ ATP
NADH, I, 3
FADH2, II, 2
Energy from glutamate occurs especially in what cells?
Intestinal epithelial
A particularly important part of the TCA cycle is connecting _____ _____ to _______.
Amino acids to glucose
Anaplerotic pathways
Pathways that replenish/increase TCA cycle intermediates
What is the point of activating pyruvate carboxylase?
Make oxaloacetate as a way of providing more TCA cycle intermediate
What activates pyruvate carboxylase?
Acetyl-CoA
What two enzymatic steps in the TCA cycle result in production of CO2 through oxidative decarboxylation?
Isocitrate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
3 multiple choice options
An increase in which of the following ratios causes an increase in the activity of regulated enzymes of the TCA cycle?
NAD+/NADH
3 multiple choice options
What does a high NAD+/NADH ratio mean?
Low NADH. NADH is usually an inhibitor, so when low on inhibitor, the cycle runs better!
Succinate dehydrogenase mutations are associated with what?
Phaeochromocytoma and paraganglioma
Fumarase mutations cause predisposition to what?
Cutaneous and uterine leiomyomas (fibroids) and kidney cancers
Isocitrate dehydrogenase mutations are associated with what?
Variety of tumors
Pyruvate is interconvertible with what?
Alanine and lactate
What produces acetylCoA for the TCA cycle?
Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH)
PDH exploits _ important coenzymes and exhibits many general principles of enzyme regulation.
5
What introduces actylCoA into the TCA cycle?
Citrate synthase
The 8 reactions of the TCA cycle connect what?
Carbohydrate, fatty acid, and amino acid metabolism
AcetylCoA is oxidized to CO2 as what are made?
NADH, FADH2, and GTP
Electron transport uses coenzymes to drive an electrochemical gradient that ___ ________ uses to make ATP.
ATP synthase (up to 12 ATP/AcetylCoA)
Cycle intermediates are produced from/used to make _____ _____. What is an energy source?
Amino acids; glutamate
The TCA cycle connects amino acids to _______ production
Glucose
What is the name of the intermediate concentrations that regulate the TCA cycle?
Anaplerotic reactions
What small molecules regulate the TCA cycle?
NADH, Ca++, ATP, ADP
The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC) is a three-enzyme complex that decarboxylates pyruvate to acetyl-CoA, linking glycolysis to the TCA cycle. All of the following vitamins/coenzymes are involved in the pyruvate decarboxylation reaction except:
Biotin
3 multiple choice options
Glycolysis takes glucose and converts it into pyruvate. Depending on the environmental conditions and the needs of the cell, pyruvate can then be most directly converted into all of the following except?
Serine
3 multiple choice options
Which compound inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase and activates pyruvate carboxylase?
Acetyl CoA
3 multiple choice options
Which step in the TCA cycle produces a high energy nucleotide?
The conversion of α-ketoglutarate to succinyl CoA
3 multiple choice options
The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate. Which of these claims about the citric acid cycle is incorrect?
The cycle is cytoplasmic
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following enzymes are the most important control points for the TCA cycle?
Isocitrate and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenases
3 multiple choice options
What describes the process of electron transport. and ATP synthesis?
Protons are imported into the matrix driving ATP synthase
3 multiple choice options