Radiology- test 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Who created the first xray and when?
Wilhelm Conrad roentgen Nov 8th 1895
Crooks
First xray tube
HC snook
Increased electricity
Coolidge tube
Hot cathode
Thomas Edison
Fluoroscopy
Clarence daily
First martry
George Eastman
Plastic film
Roentgen
Image of wife's hand
Procedure?
1 . Position anatomy
Aligns xray tube
Set exposure factors
Activates exposure switch
Production?
A vacuum
Electron source
Target for electrons
High potential diff between electron source and target
Radiation
Travels in straight lines
Affects biological tissues
can penetrate the body
Cannot be detected by human senses
X ray tube housing
Protective and supports
Collimator
Controls size of radiation field
light provides centering lines
Transformer and control console
Provides high voltage
In shielding control booth
Fluoroscopic equipment
Dynamic images
Allows radiologist to view and record
mA
Milliamperage , quantity
Quantity of electrons produced at the cathode
• Measure of the Current flow rate in the x-ray tube
• Impacts receptor exposure/ optical density
Time
Exposure time, secs, milliseconds
kVp
Kilovoltage, quality
SID
Source image distance, affects intensity of beam
-Size distortion magnification
Computed radiography(CR)
Image receptors
Requires reader
Cassette places into reader
Digital radiography (DR)
Special tables and upright devices
Built in radiation receptors
PACS
Hardware tech used to manage digital images
Receptor exposure optical density
Overall blackness of image
Image contrast
Differences in adjacent structures
Image detail sharpness
Size of pixels
Patient motion
Size and shape distortion
Variation in size and shape
Magnification size
-Foreshortens
-Elongates
Alara
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
Law of Bergonie + Tribondeau
Age, metabolic rate, Mitotic rate, and differeniation
Ethincal Principles
Beneficence= Goodness
Non-maleficence= No evil
Veracity= Truth
Fidelity= Faithfulness
Justice= Fairness
Autonomy= Self determination
Informed consent
Understandable language, Authorization clause, Disclosure clause, Signature, Witness
Intential circumstances
Assalt, battery, false imprisonment, invasion of privacy, defamation of character
Unintential circumstances
Malpractice, negligence, gross negligence, Contributory negligence
4 things you need to prove malpractice
Defendent had a duty to provide care to patient
Patient sustained some loss or injury
Defendent is responsible
The loss is attributable to negligence or improper practice
What two thins does the Joint commission require you to ask?
Name
Date of Birth
AIDET
Acknowledge
Introduce
Duration
Explanation
Thanks
If someone is in altered state of consciousness, what 2 things should you remember?
They cannot remember instructions
Not responsible for their actions
5 stages of grief
Denial
Anger
Bargaining
Depression
Acceptance
Bacteria
Single celled, Grow independent, no host, Can adapt and mutate, Endospores
Ex. TB, Strep throat, E. Coli
Viruses
Subcellular, Smallest, needs host, carry own DNA or RNA
ex. Flu, Hep B, Covid, Chicken Pox
Fungi
Macroscopic or Microscopic, 2 forms, single celled, molds (spore formation)
ex. Athletes foot, ringworm, respiratory infections
Prions vs Protozoa
Smallest + least understood Unicellular
No RNA/DNA Free Living
Resistance to body defense Form Cysts
Can multiply Live Between insect and human (ex. malaria
Chain of infection
Pathogenic organism
Resevoir infection:
-Moisture
–Nutrients
–Suitable temperature
Portal of exit
Mean of transmission
Portal of entry
Susceptiable host
REPEAT
Aquired Immunity
Long term, Develops antibodies
Vaccines, or catching the illness
Passive immunity
Short term, injection of antibodies
Mother to child ( breast feeding)
HAI
Health associated infection, nonsocmial infection, timeframe involved
-Sources : Urinary catheters, surgical wounds
ex. MRSA, VRE, C-DIFF
Medical Asepsis
Microdilation process, hand hygiene, Cleaning techniques, disinfection, isolation techniques
Surgical asepsis
Sterile environment, do not reach over, do not walk between kit and doctor, do not leave unattended
-Process of creating area completely free of pathogens
Methods of sterilization
Chemical, Convential gas, Gas plasma, Dry heat, autoclaving- steam under pressure, most used, quickest and most convenient
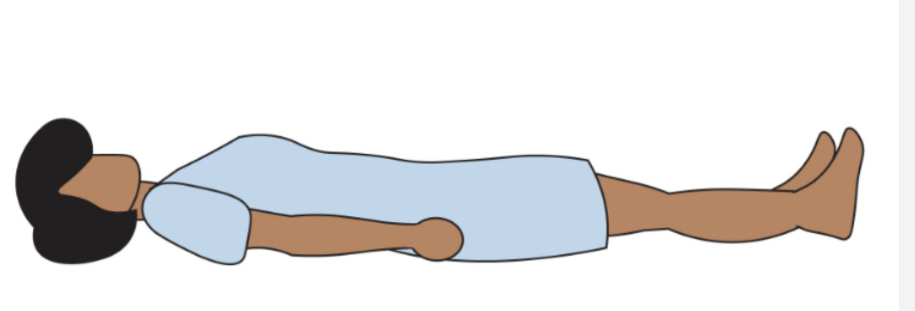
Supine
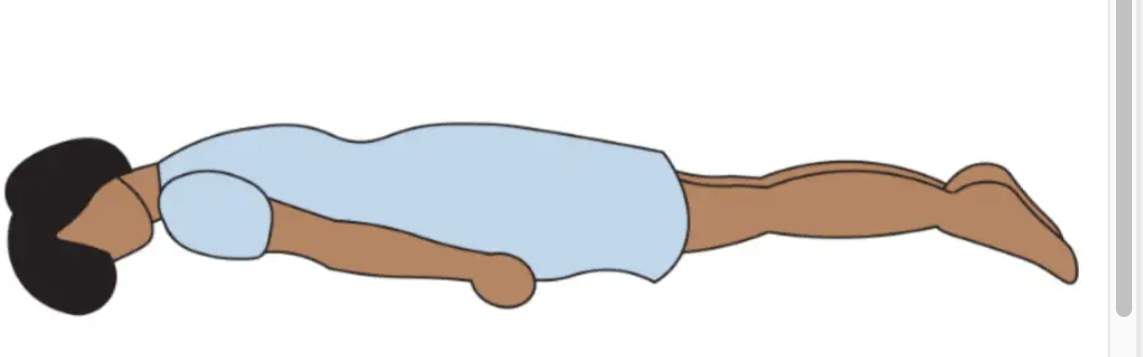
Prone
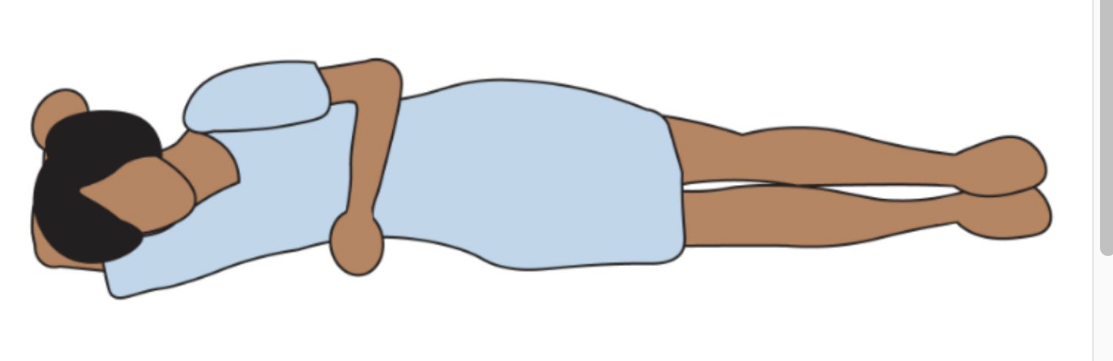
Lateral recumbent
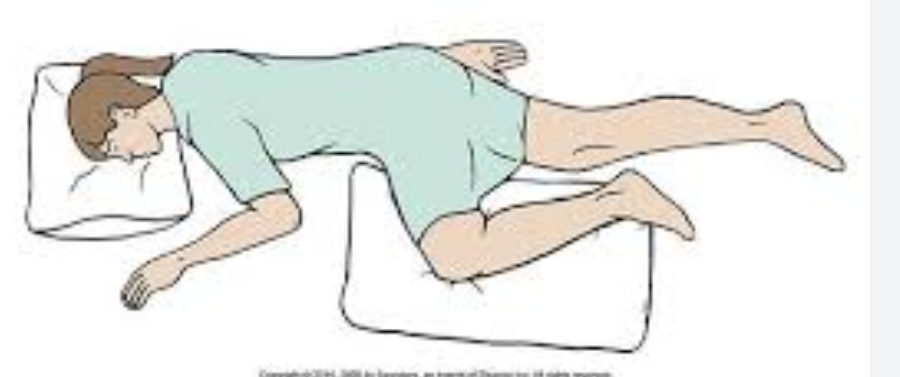
Sims
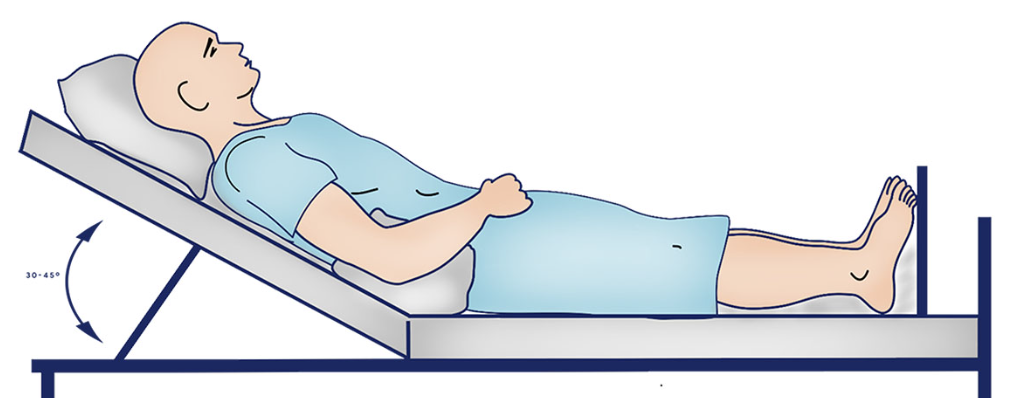
Fowler
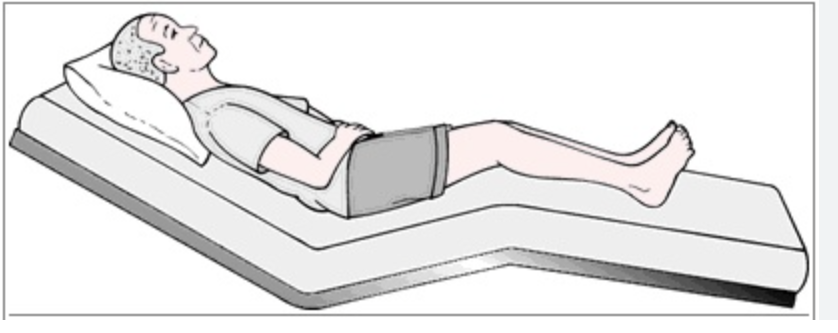
Semiflower
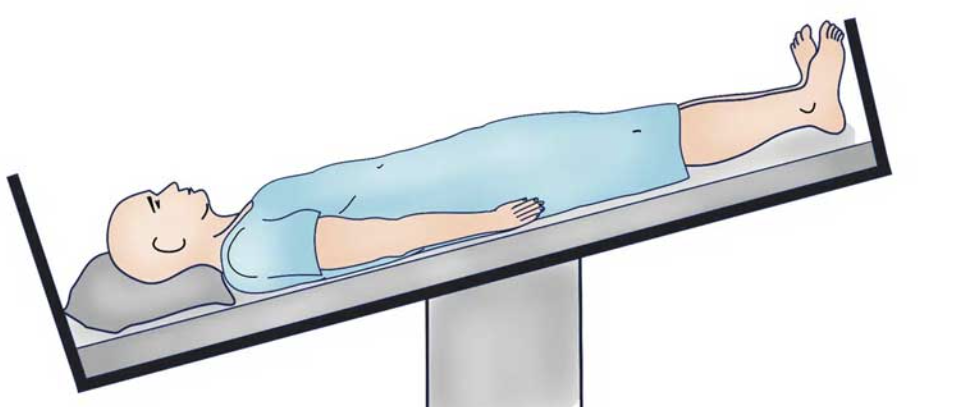
Trendenlenburg
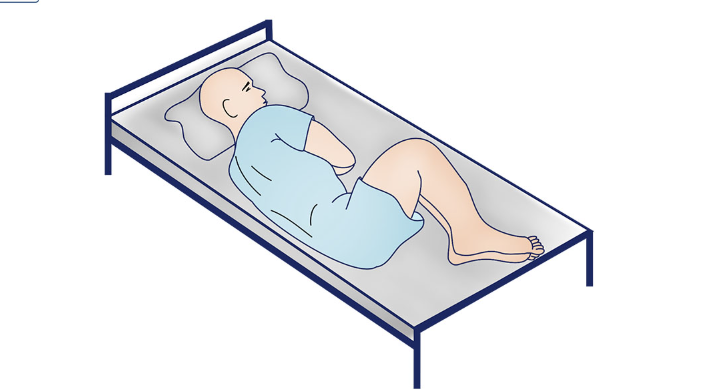
Knee Chest
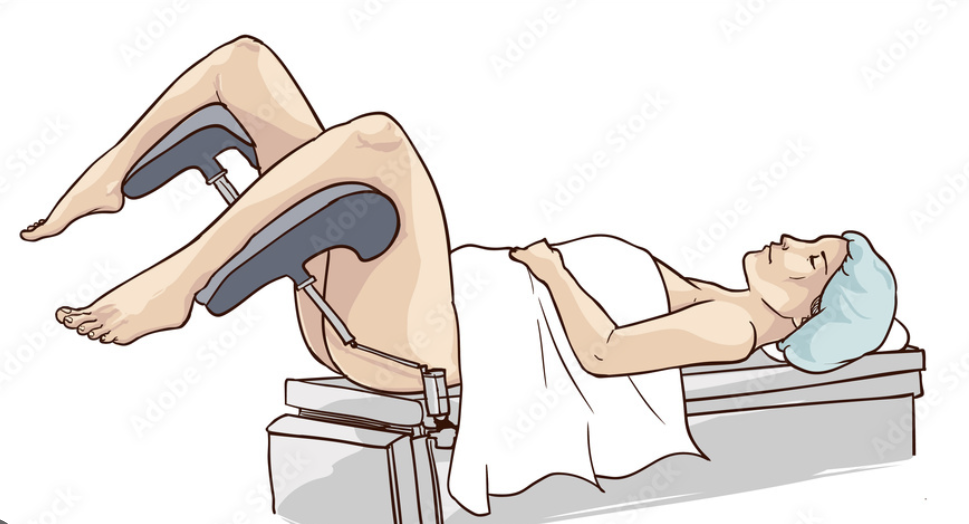
Lithotomy
Fomite
Containmented things, uninary catherer
Vectors
Bites
Vehicles
Food, water, anything you eat
Airborne
Droplets smaller than 5mm
Droplet containmenation
Droplets greater than 5mm
-Flu, covid, mumps, rubella
3 principles of radiation safety
Time, distance, shielding
Erthyema
Skin burn, radation burn
OSL
Optically stimulated luminescence
-badge to measure occupational exposure
GY (RAD)
Radation to tissue
Slevert (REM)
Occupational
Res ipsa loquitur
– the thing speaks for itself
Respondeat superior
– let the master respond
JRCERT
Joint Review Committee on Education in Radiologic Technology (JRCERT)
-Establishes educational standards/ accreditation for radiologic technology programs
RT (R)
Registered Technologist - Radiography
What combination of KVP, mA and time combination give the patient the lowest dose
High kvp, Low mA, low time
OID
Object to image distance
-Size distortion magnification
-more OID = more magnification
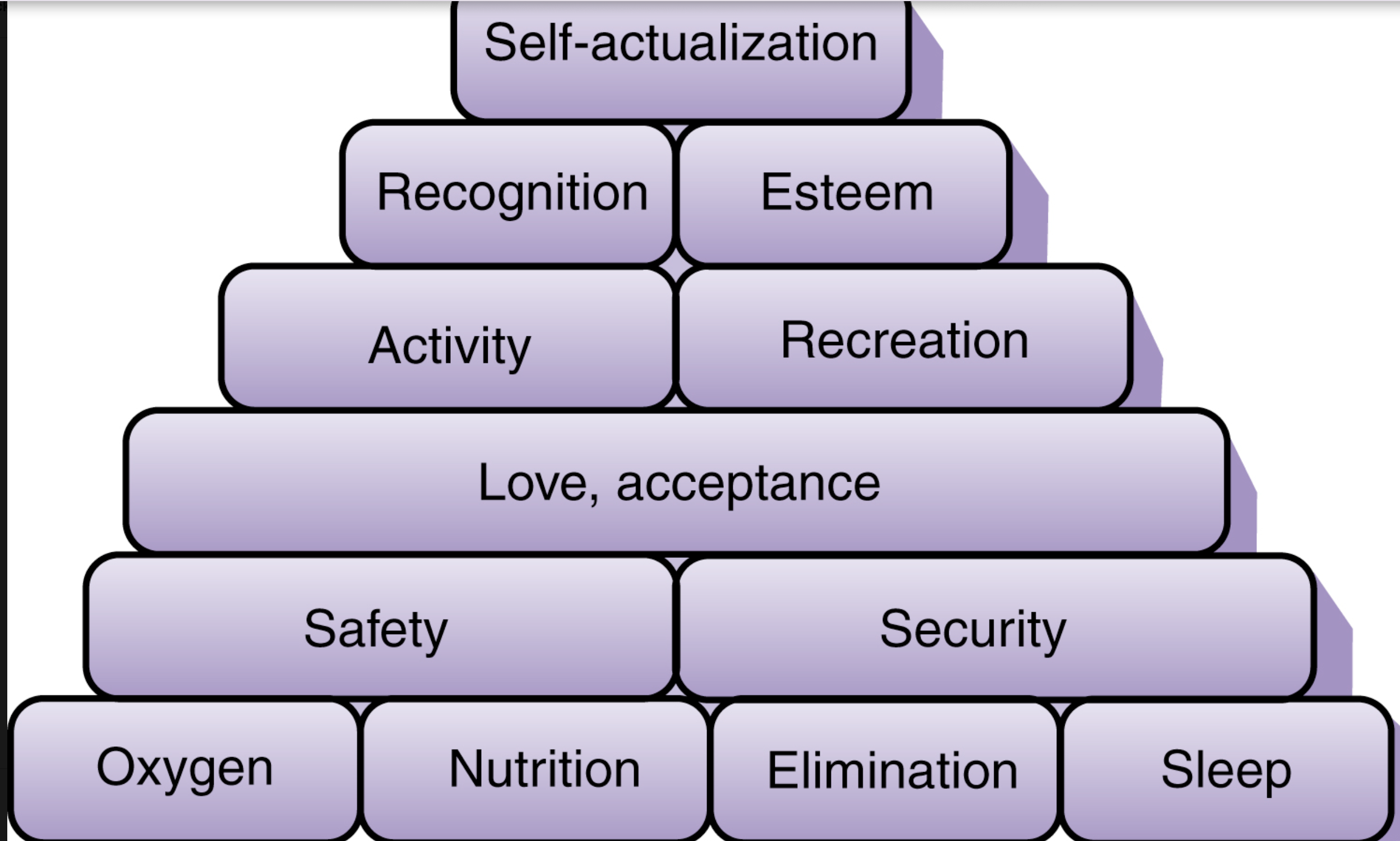
Maslow Hierarchy of Needs