SHEEP HEART LAB
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Walls of right atrium
The inside of the posterior wall is smooth but the inside of the anterior wall is rough due to pectinate muscles which extend into the auricle
Interartrial septum
Between the right and left atria, a feature is the fossa ovalis
Fossa ovalis
A remnant of foramen ovale during prenatal and is used to refer to the same structure in postnatal
Foramen ovale
Its function was to connect the right atrium to the left atrium so that the oxygenated blood from the mother can be mostly in the circuit. This is because the lungs are not functional before birth
Pectinate muscles
They increase the surface area of the right atrium to handle volume changes. They are more common in the right atrium than the left
Trabeculae carnea
A series of ridges in the ventricles formed by raised bundles of cardiac muscle fibres. It aids in the conduction system of the heart and prevents suctioning in the ventricles
Walls of left atrium
The inside of the posterior and anterior wall is smooth because the pectinate muscles confined to the left auricle in the left atrium. This is because it receives less variation in blood flow
Ductus arteriosus
A temporary blood vessel in prenatal and results in oxygenated blood from the placenta flowing from the pulmonary trunk to the aorta, bypassing the non functional lungs
Ligamentum arteriosum
A remnant of ductus arteriosus during prenatal and is used to refer to the same structure in postnatal
Left coronary artery
This passes inferior to the left auricle and dived into the anterior interventricular and circumflex branches
Anterior interventricular branches
It is in the anterior interventricular sulcus and supplies oxygenated blood to the walls of both ventricles
Circumflex branches
It is in the coronary sulcus and supplies oxygenated blood to the walls of the left ventricle and atrium
Right coronary artery
Supplies oxygenated blood via atrial branches to the right atrium. It continues inferior to the right auricle and dived into the posterior interventricular and marginal branches
Posterior interventricular branches
It is in the posterior interventricular sulcus and supplies oxygenated blood to both ventricles
Marginal branches
Goes beyond the coronary sulcus and runs along the right margin of the heart to supply oxygenated blood to the wall of the right ventricle
Anastomoses
Connections in the body where two or more arteries supply blood to the same region, causing a connection
Collateral circulation
Anastomoses provide alternate routes for blood to reach a particular area or organ, providing detours or other pathways if the main pathway is blocked
Coronary sinus
A large vascular (thin walled with no smooth muscle to alter diameter) sinus in the coronary sulcus on the posterior surface of the heart where most of the deoxygenated blood from the myocardium empty. This empties directly into the right atrium
Great cardiac vein
In the anterior interventricular sulcus that empties areas of the heart supplied by the left coronary artery (both ventricles and left atrium)
Middle cardiac vein
In the posterior interventricular sulcus that empties areas of the heart supplied by posterior interventricular branch of the right coronary artery (both ventricles)
Small cardiac vein
In the coronary sulcus and empties the right atrium and auricle
Anterior cardiac veins
Drains the right ventricle and empties directly into the right atrium
Superior
Towards the head, upper part of the structure
Inferior
Away from the head, lower part of the structure
Anterior (Ventral)
Nearer to or at the front of the body
Posterior (dorsal)
Nearer to or at the back of the body
Medial
Nearer to the midline
Lateral
Farther from the midline
Intermediate
Between two structures
Ipsilateral
On the same side of the body as another structure
Contralateral
On the opposite side of the body as another structure
Proximal
Nearer to the origination of a structure
Distal
Away from the origination of a structure
Superficial
Towards or on the surface of the body
Deep
Away from the surface of the body
Midsagittal or median plane, midline
A parallel plane that divides the body into equal right and left halves
Parasagittal plane
A parallel plane that divides the body into unequal right and left halves
Frontal plane
A perpendicular plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior portions
Transverse/cross-sectional plane
A horizontal plane that divides the body into superior and inferior portions
Oblique plane
Passes through the body at an angle other than 90o
Cranial cavity
Formed by the cranial bones which contains the brain, continuous with the vertebral canal
Vertebral canal
Formed by the bones of the vertebral column which contains the spinal cord, continuous with the cranial cavity
Thoracic cavity
Formed by the ribs, the muscles of the chest, sternum, and the thoracic portion of the vertebral column. Within this cavity is the pericardial and mediastinum cavities
Pericardial cavity
A fluid-filled space that surrounds the heart (lined by pericardium) and two fluid filled spaces called pleural cavities (lined by pleura), one around each lung.
Mediastinum
Central part of the thoracic cavity, between the lungs and extending from the sternum to the vertebral column and from the first rib to the diaphragm. It contains all thoracic organs except the lungs
Diaphragm
Separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity
Abdominopelvic cavity
Extends from the diaphragm to the groin and encircled by the abdominal muscular wall and the bones and muscles of the pelvis. Separated into the abdominal and pelvic cavities
Abdominal cavity
The superior portion (lined by peritoneum) and contains the stomach, spleen, liver, gall bladder, small intestine, and most of the large intestine
Pelvic cavity
The inferior portions and contains the urinary bladder, portions of the large intestine, and internal organs of the reproductive system
Viscera
Organs inside the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
Serous membranes
Covers the viscera and lines the walls of the thorax and abdomen. It has a parietal (lines the walls of the cavities) and visceral layer (lines the viscera) and forms a space in between that contains serous fluid
Orientation differences between bipeds and quadrupeds
In bipeds (humans)
Anterior = Ventral → toward the front (belly side).
Posterior = Dorsal → toward the back.
Superior = toward the head.
Inferior = toward the feet.
In quadrupeds
Ventral = belly side (facing the ground → inferior in anatomical position).
Dorsal = back side (facing upward → superior in anatomical position).
Anterior = toward the head (cranial).
Posterior = toward the tail (caudal).
Difference in sheep heart and human heart
In sheep, venous blood is drained via right ant. vena cava, left ant. vena cava, and post. vena cava causing the shape of the right atrium to be influenced and have three entrances
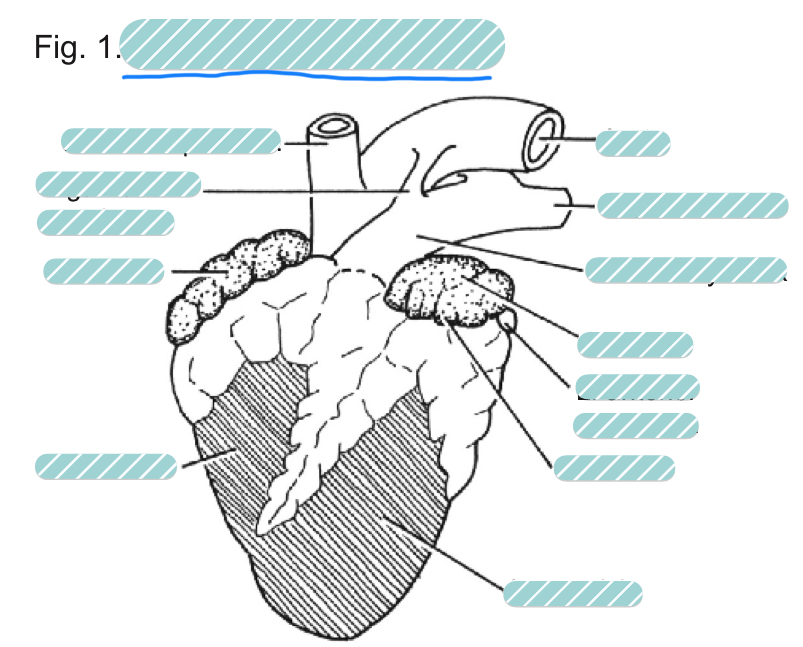
What is the underlined label?
A sheep heart from a ventral view
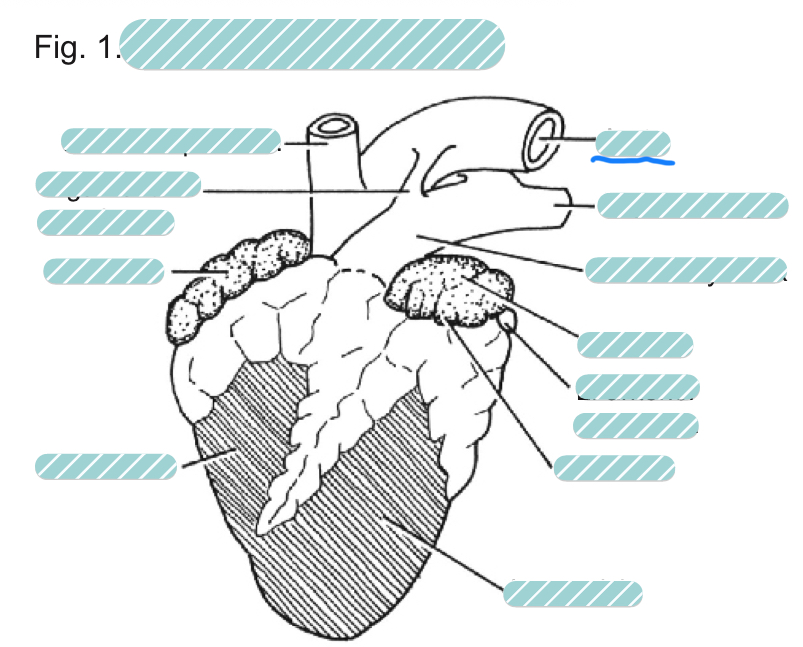
What is the underlined label?
The aorta of a sheep heart from a ventral view
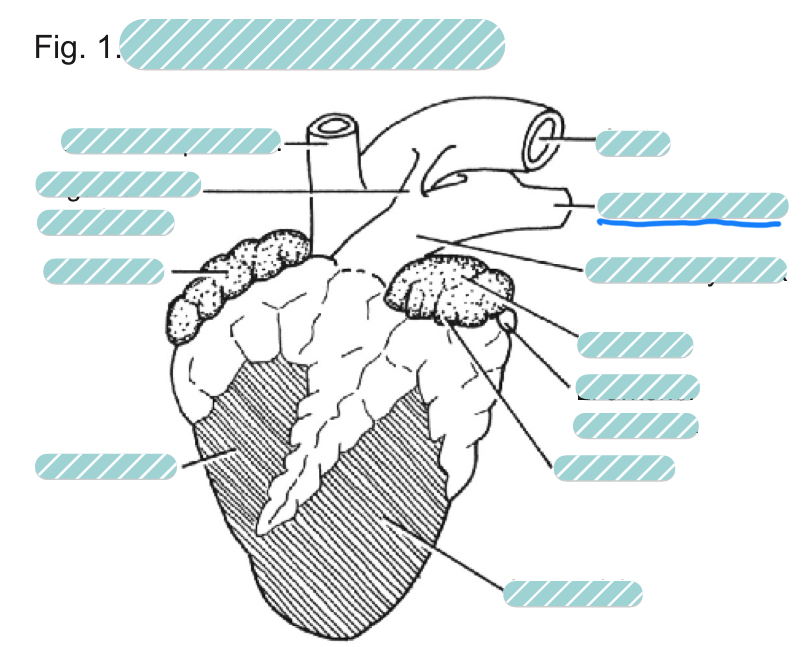
What is the underlined label?
The left pulmonary artery of a sheep heart from a ventral view
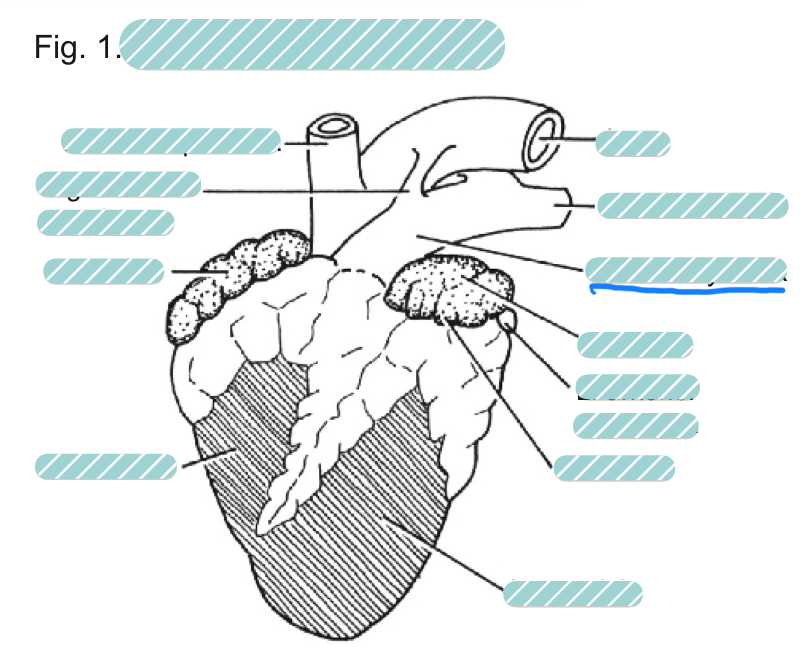
What is the underlined label?
The pulmonary trunk of a sheep heart from a ventral view
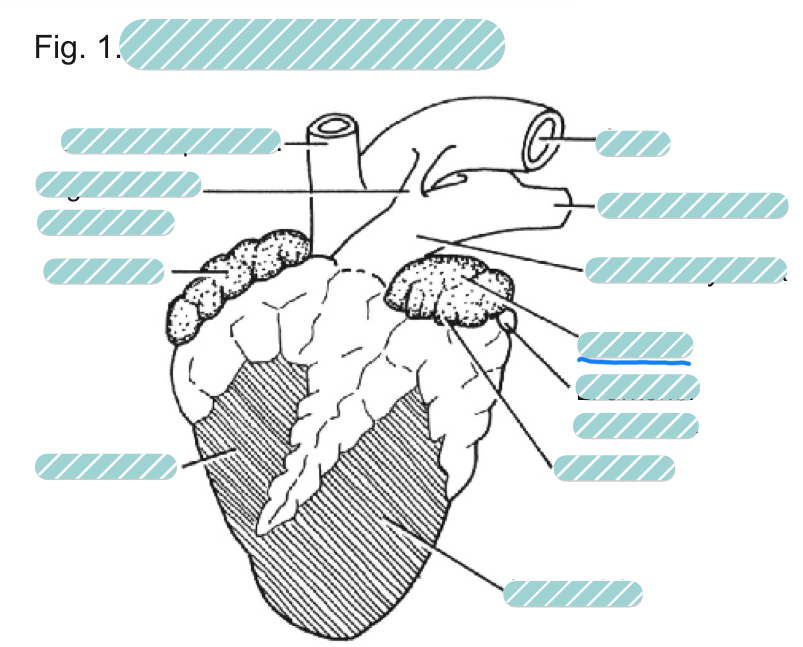
What is the underlined label?
The left atrium of a sheep heart from a ventral view
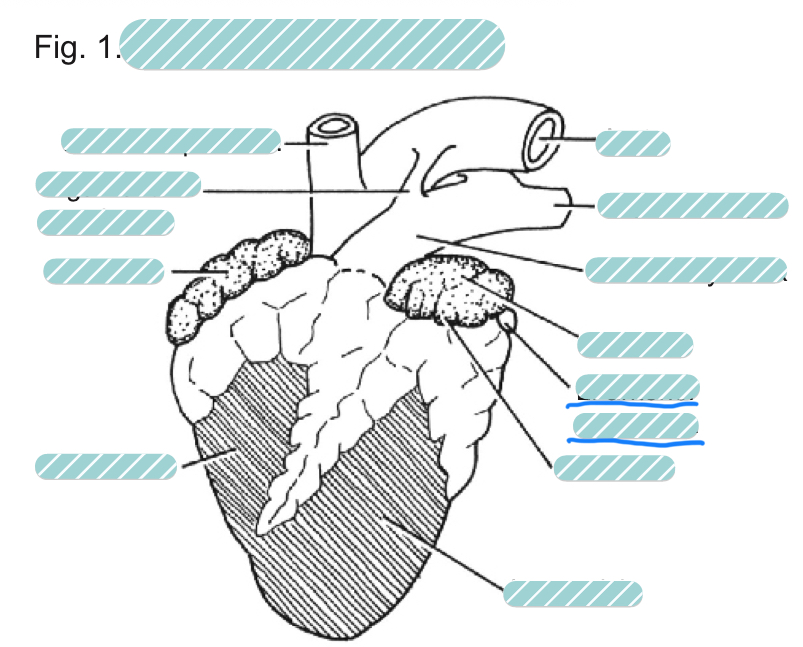
What is the underlined label?
The left anterior vena cava of a sheep heart from a ventral view
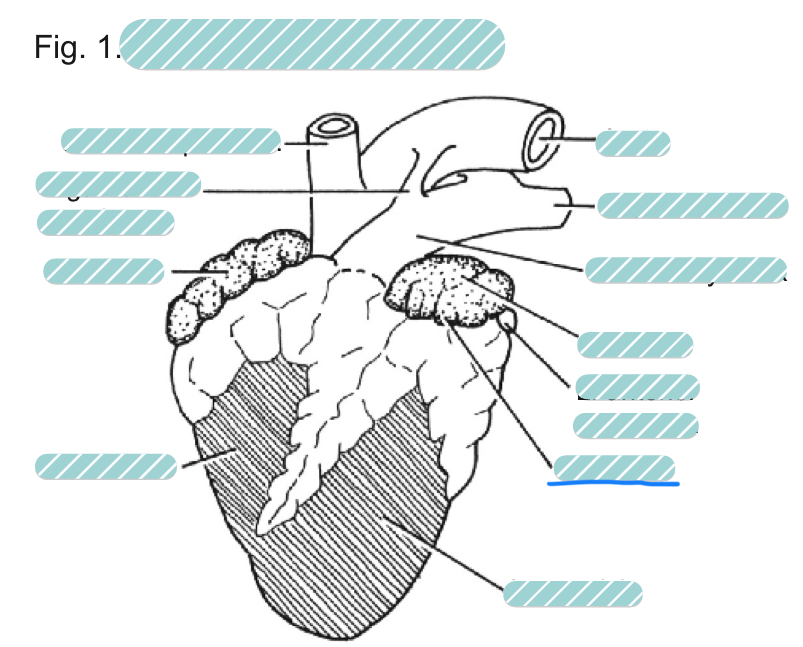
What is the underlined label?
The left auricle of a sheep heart from a ventral view
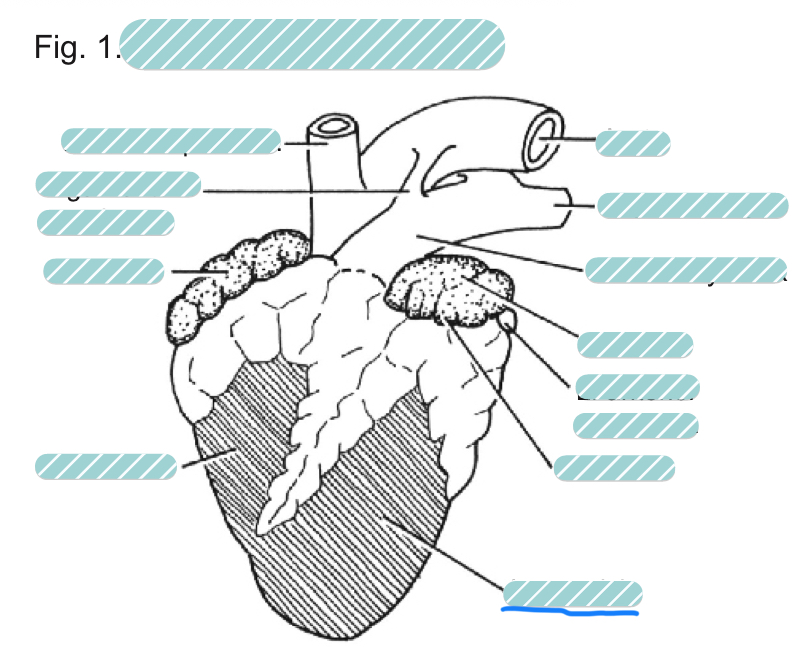
What is the underlined label?
The left ventricle of a sheep heart from a ventral view
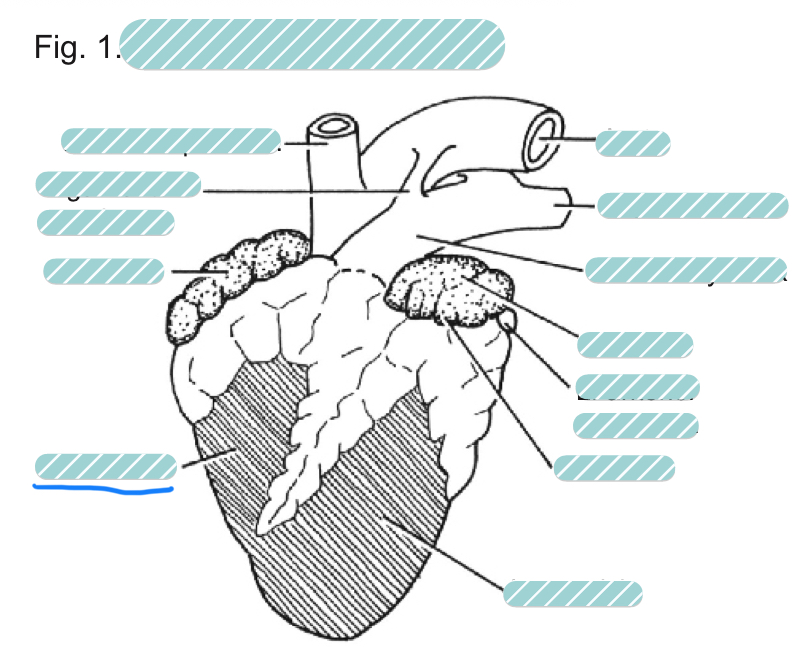
What is the underlined label?
The right ventricle of a sheep heart from a ventral view
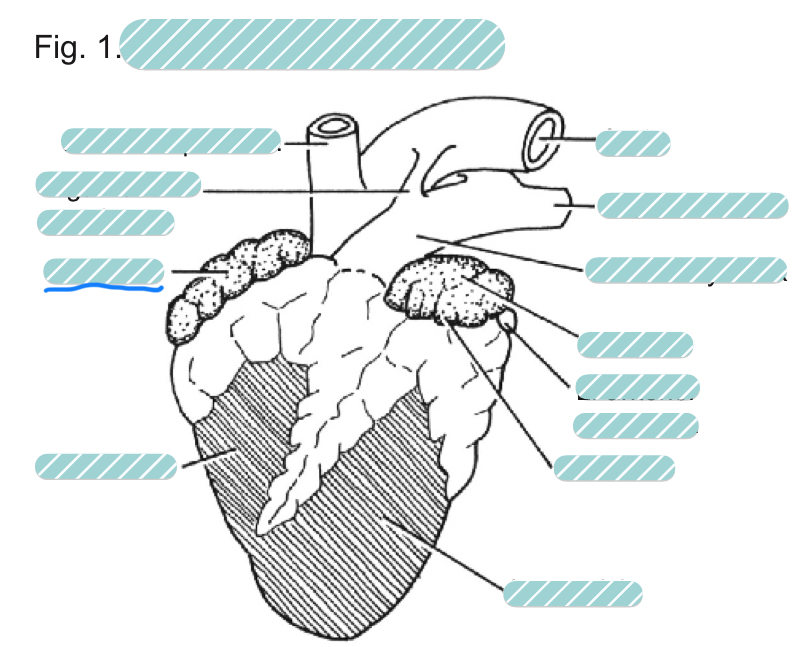
What is the underlined label?
The right auricle of a sheep heart from a ventral view
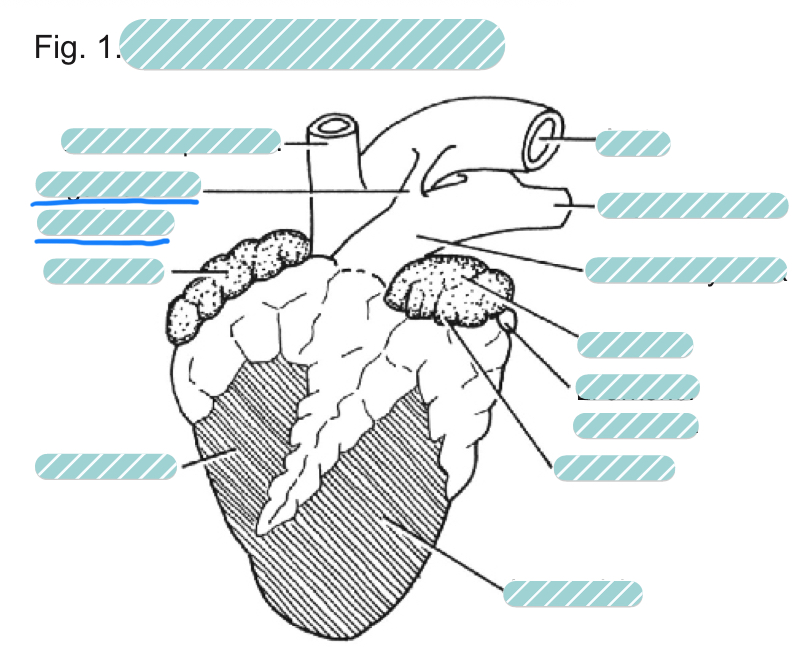
What is the underlined label?
The ligamentum arteriosum of a sheep heart from a ventral view
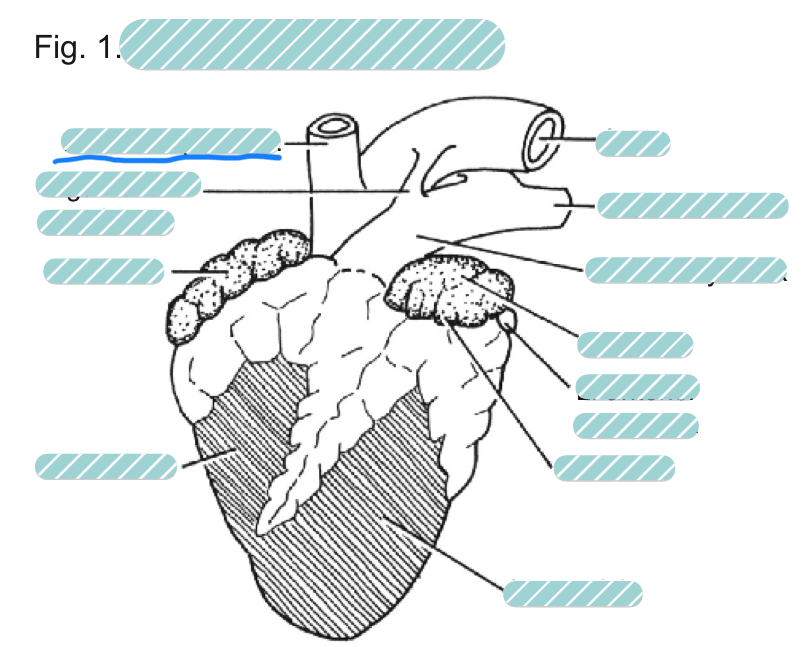
What is the underlined label?
The brachiocephalic artery of a sheep heart from a ventral view
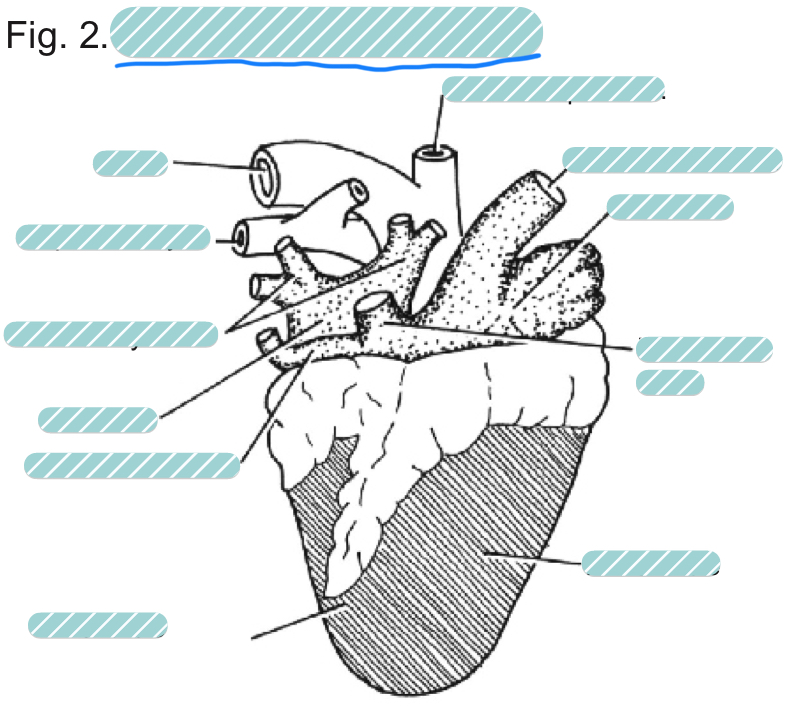
What is the underlined label?
The sheep heart from a dorsal view
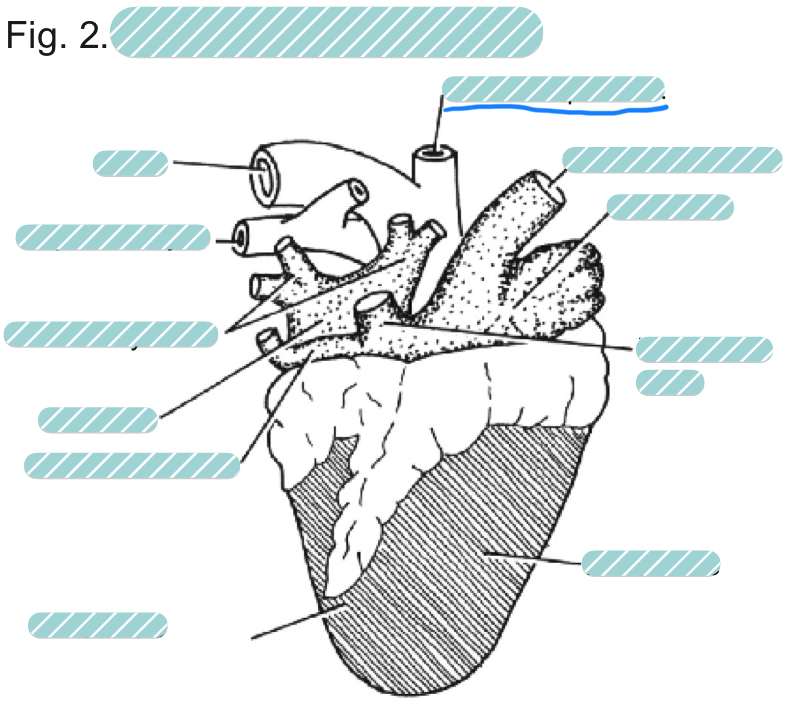
What is the underlined label?
The brachiocephalic artery of a sheep heart from a dorsal view
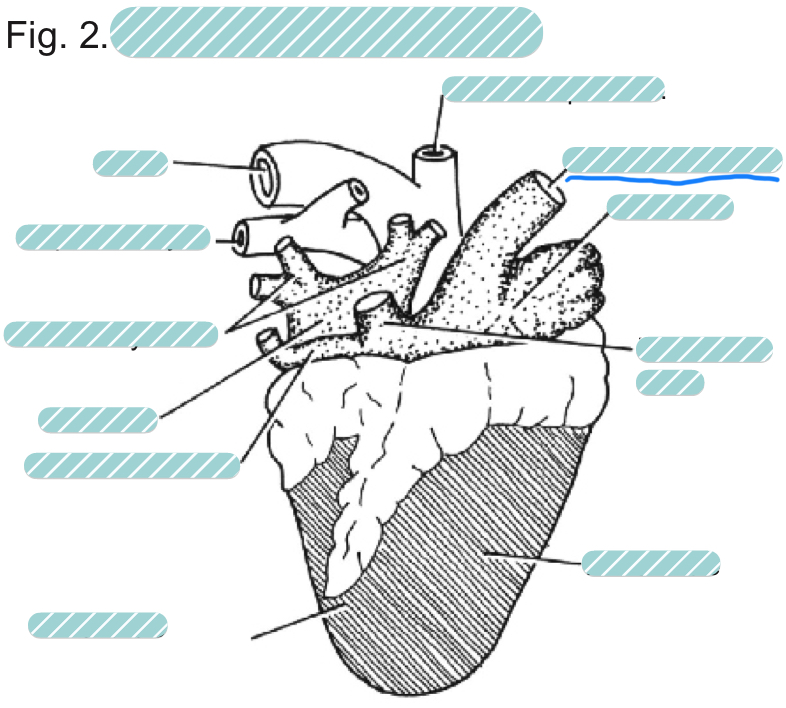
What is the underlined label?
The right anterior vena cave of a sheep heart from a dorsal view
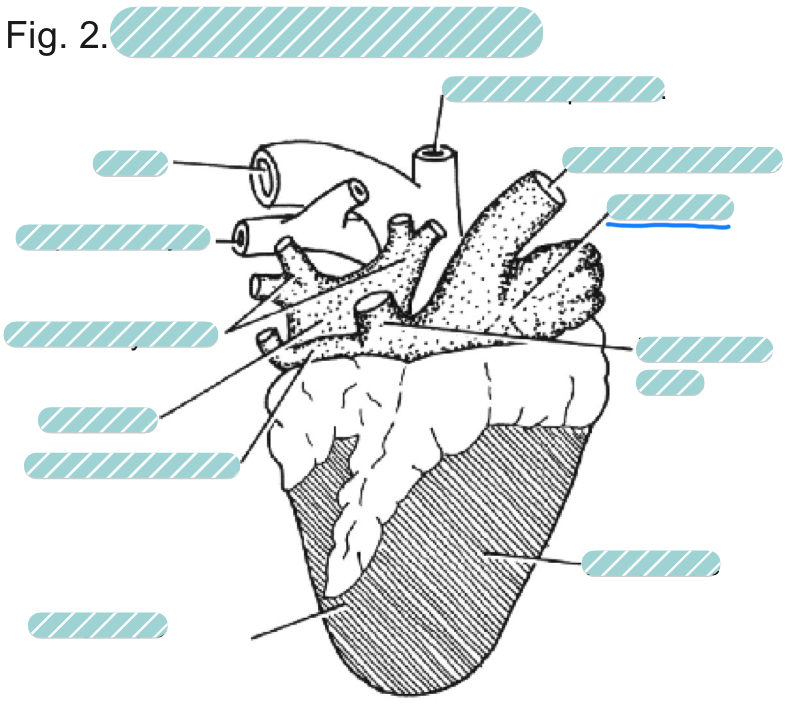
What is the underlined label?
The right atrium of a sheep heart from a dorsal view
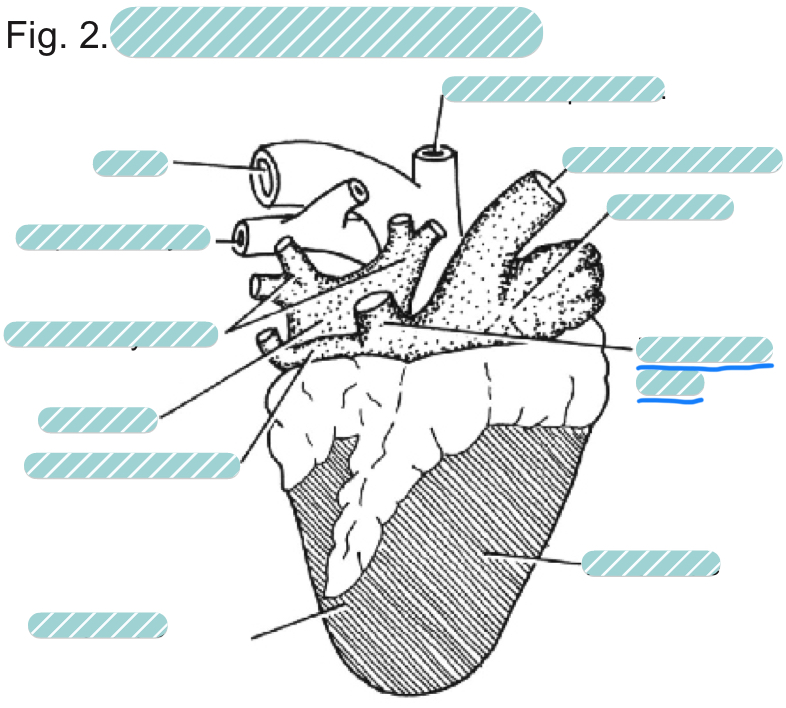
What is the underlined label?
The posterior vena cava of a sheep heart from a dorsal view
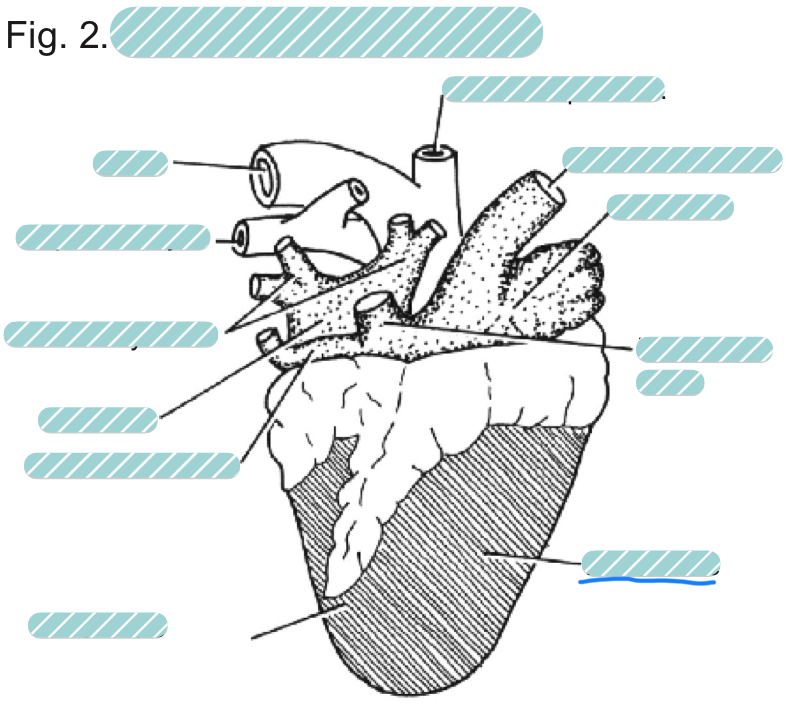
What is the underlined label?
The right ventricle of a sheep heart from a dorsal view
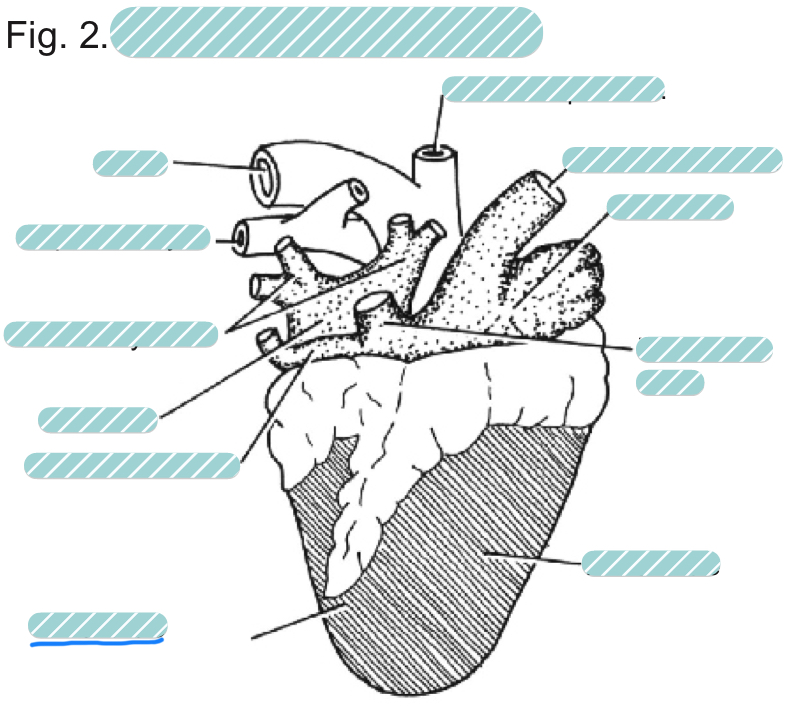
What is the underlined label?
The left ventricle of a sheep heart from a dorsal view
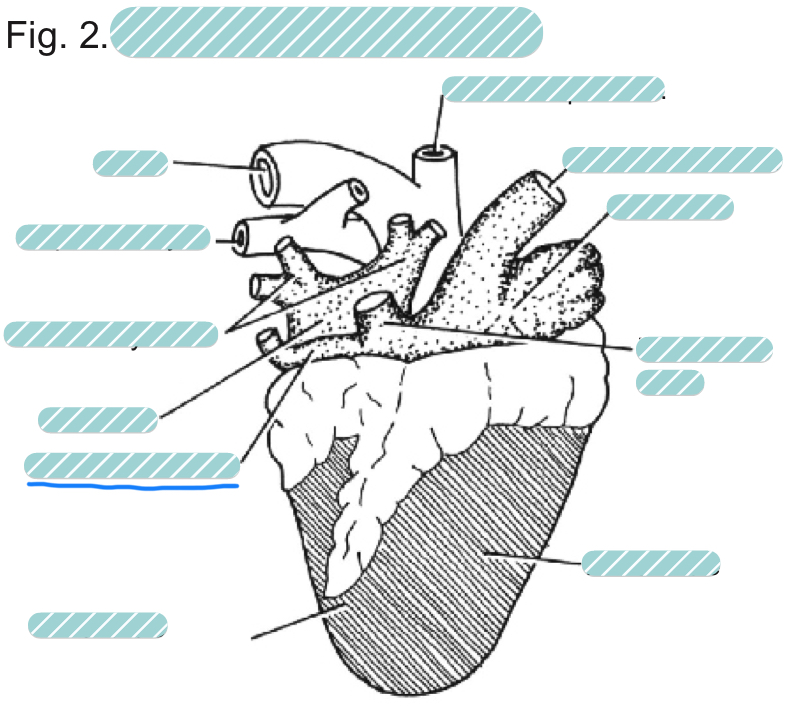
What is the underlined label?
The left anterior vena cava of a sheep heart from a dorsal view
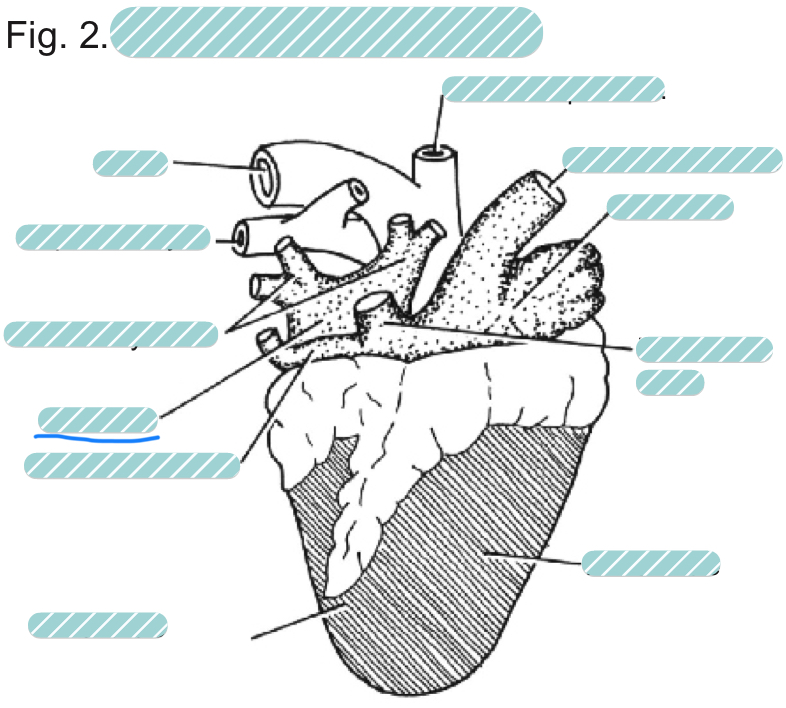
What is the underlined label?
The left atrium of a sheep heart from a dorsal view
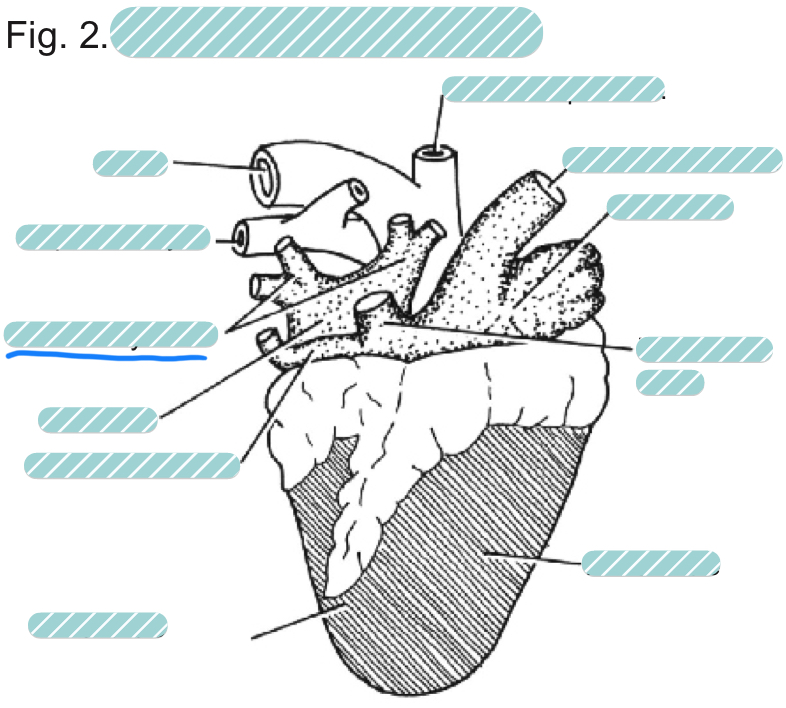
What is the underlined label?
The pulmonary veins of a sheep heart from a dorsal view
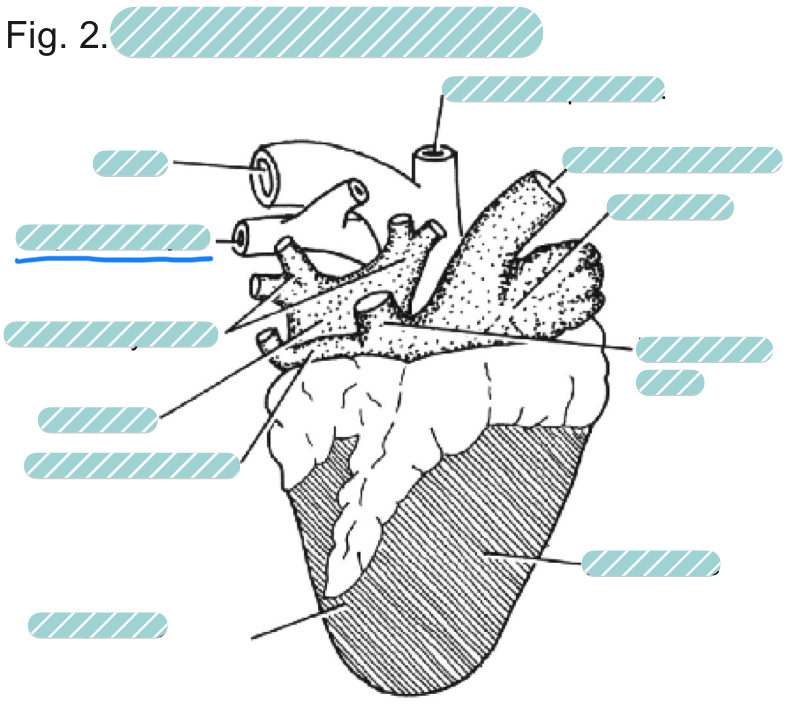
What is the underlined label?
The left pulmonary artery of a sheep heart from a dorsal view
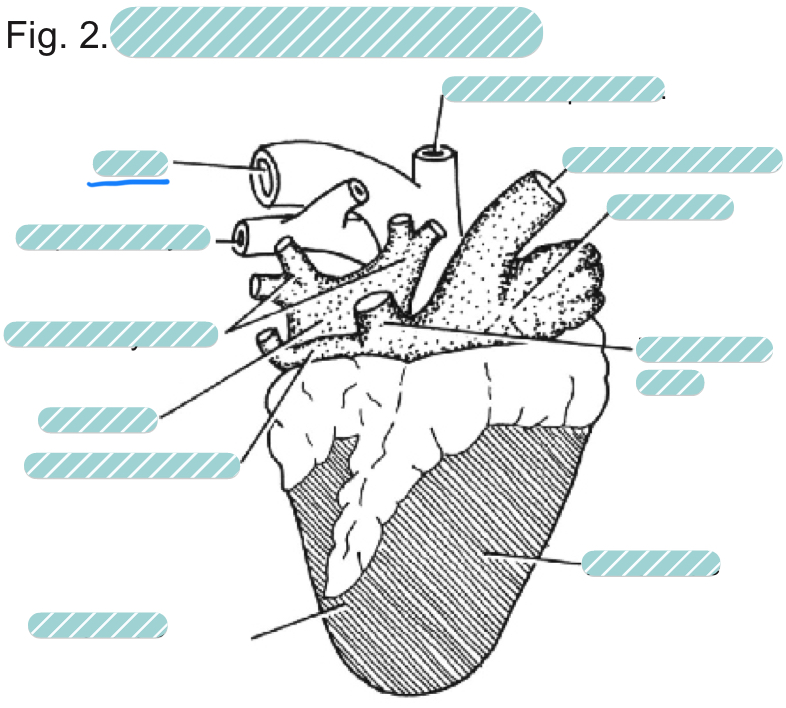
What is the underlined label?
The aorta of a sheep heart from a dorsal view