5 bio - anxiety disorder
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Anxiety disorders
What is the most common type of psychiatric disorder?
Mood disorders especially depression
What is anxiety disorder highly comorbid with?
excessive and persistent fear, anxiety, and disturbances in behavior.
How are anxiety disorders characterized according to APA (2013)?
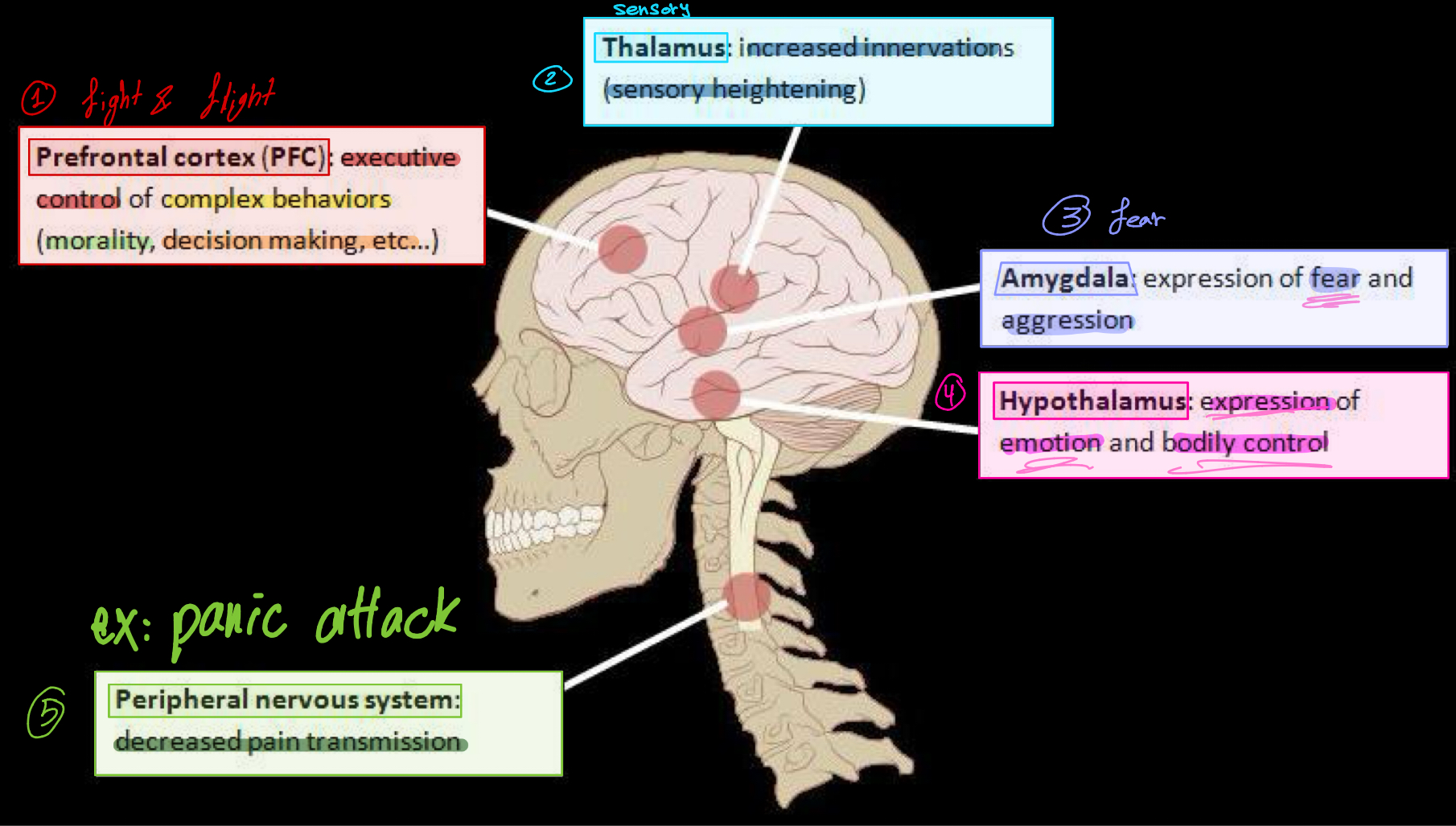
Which brain regions are involved in anxiety and what are their main functions?

Combination of genetic, Environmental & Psychological Developmental factors
Dysfunction in brain regions, circuits and connections
Life experiences
What are the main causes of anxiety disorders?
Family and twin studies: 40% of individuals with Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) have a relative with the same disorder.
What evidence supports the genetic role in anxiety disorders?
amygdala and hippocampus
brain imaging studies.
Which brain regions are mainly linked to anxiety disorders? And on what evidence?
Traumatic events can trigger anxiety in people already prone to it.
How do life experiences contribute to anxiety disorders?
Trauma
Stress
Personality
Other mental health disorders: Depression
Substance abuse
What are the main risk factors for developing anxiety disorders?
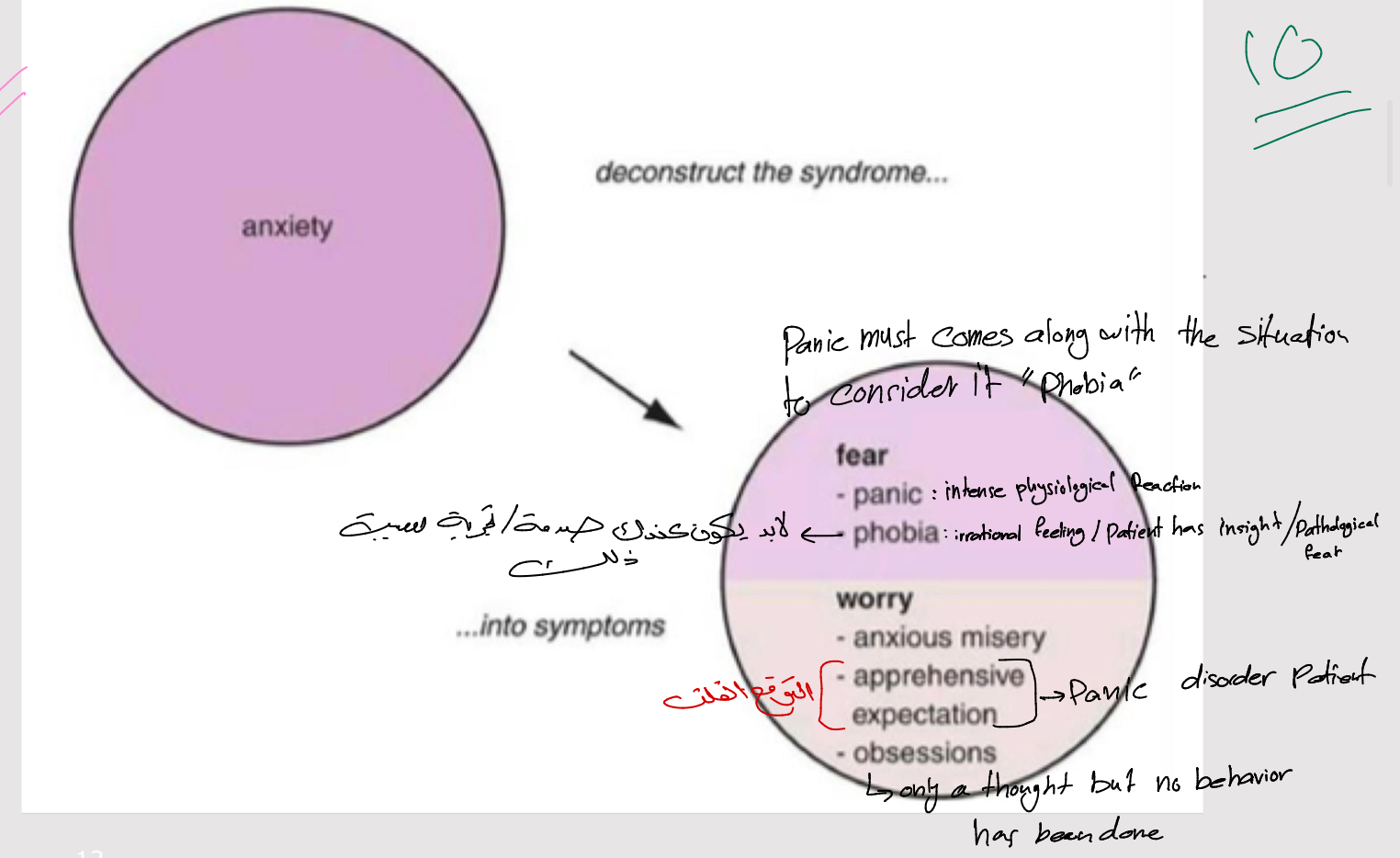
How can anxiety disorders be deconstructed into main symptom categories?
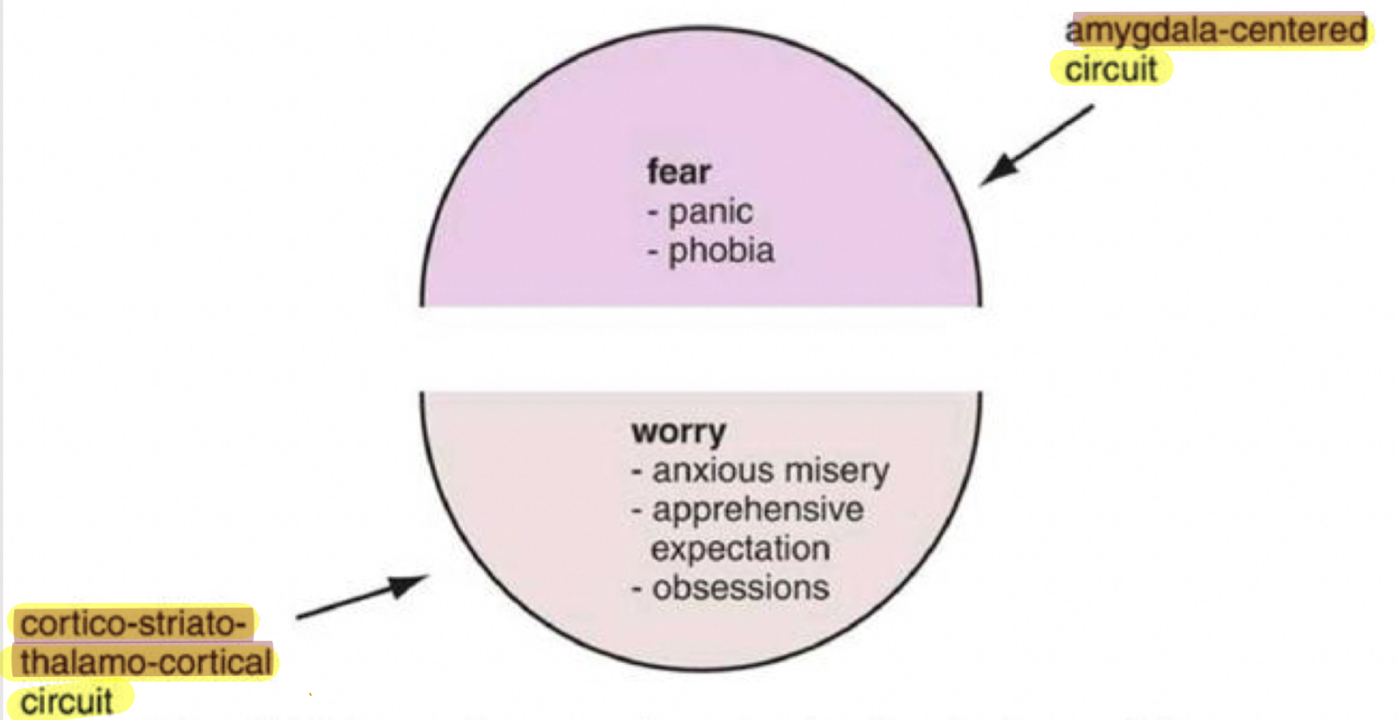
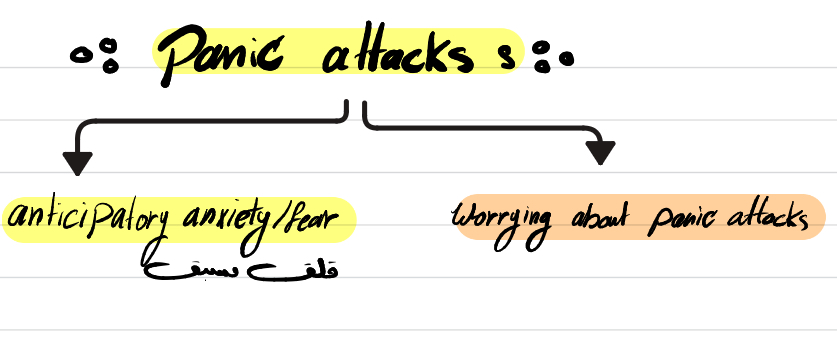
What are the main (core) symptoms of panic attacks?
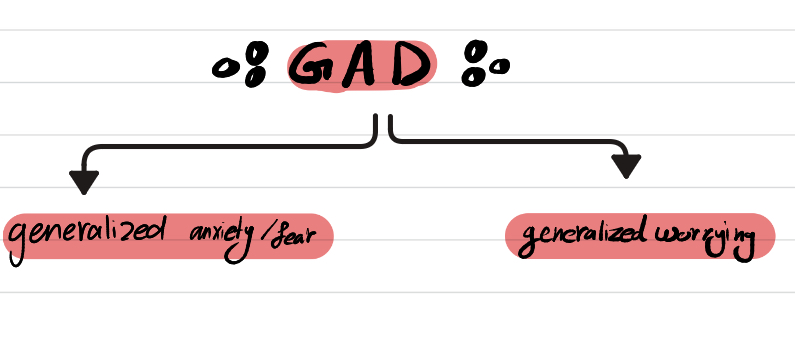
What are the main (core) symptoms of Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)?

What are the main (core) symptoms of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)?
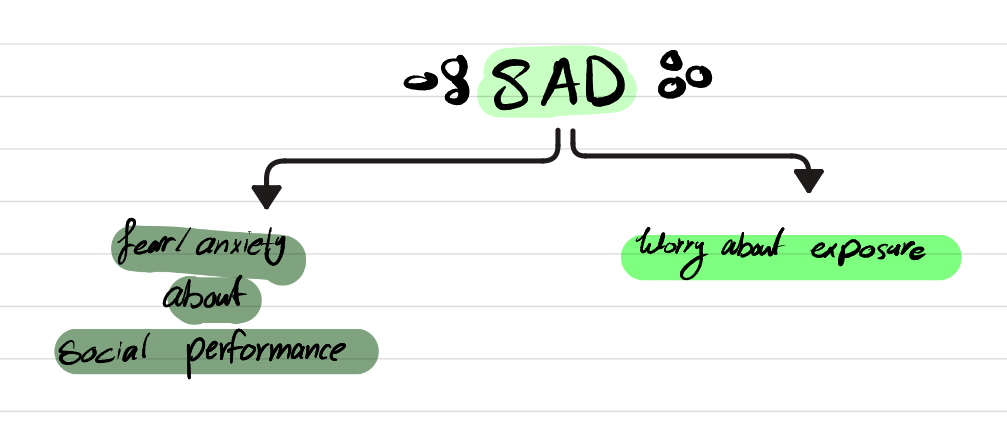
What are the main (core) symptoms of Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD)?
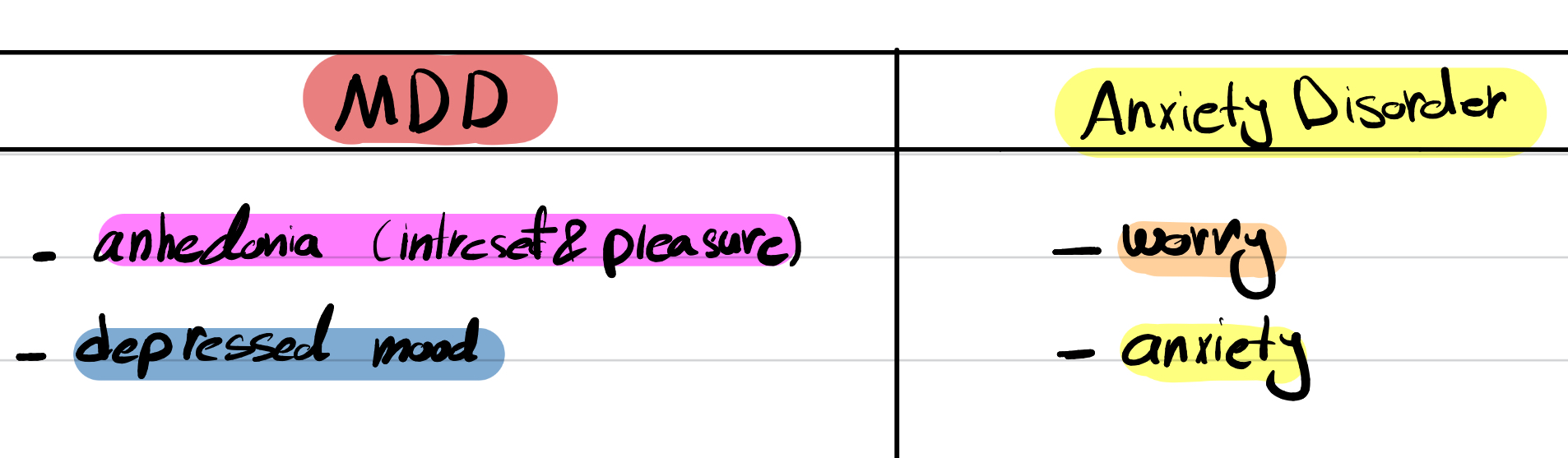
Compare between the main (core) symptoms between a major depression disorder and anxiety disorder?
each symptom is linked to dysfunction
in a particular brain mechanism or circuit.
What does it mean that anxiety symptoms are related to specific malfunctions in brain mechanisms?
A treatment approach that
targets specific symptoms
based on their underlying brain dysfunctions
What is a symptom-based therapeutic strategy?
ما المقصود بالاستراتيجية العلاجية المعتمدة على الأعراض
True
Same underlying brain mechanism for all anxiety disorders; but the cause can be different. ✅❌
False
Same underlying brain mechanism for all anxiety disorders; and the cause can’t be different. ✅❌
Sleep problems
poor concentration
fatigue
psychomotor/arousal disturbances.
What symptoms overlap between anxiety and depression?
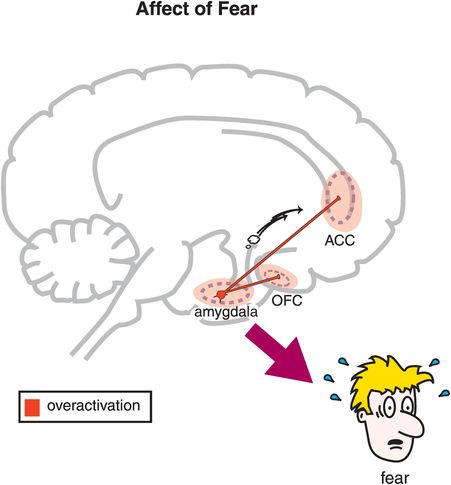
amygdala
anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)
orbitofrontal cortex (OFC).
Which brain structures are primarily involved in the neurobiology of fear?
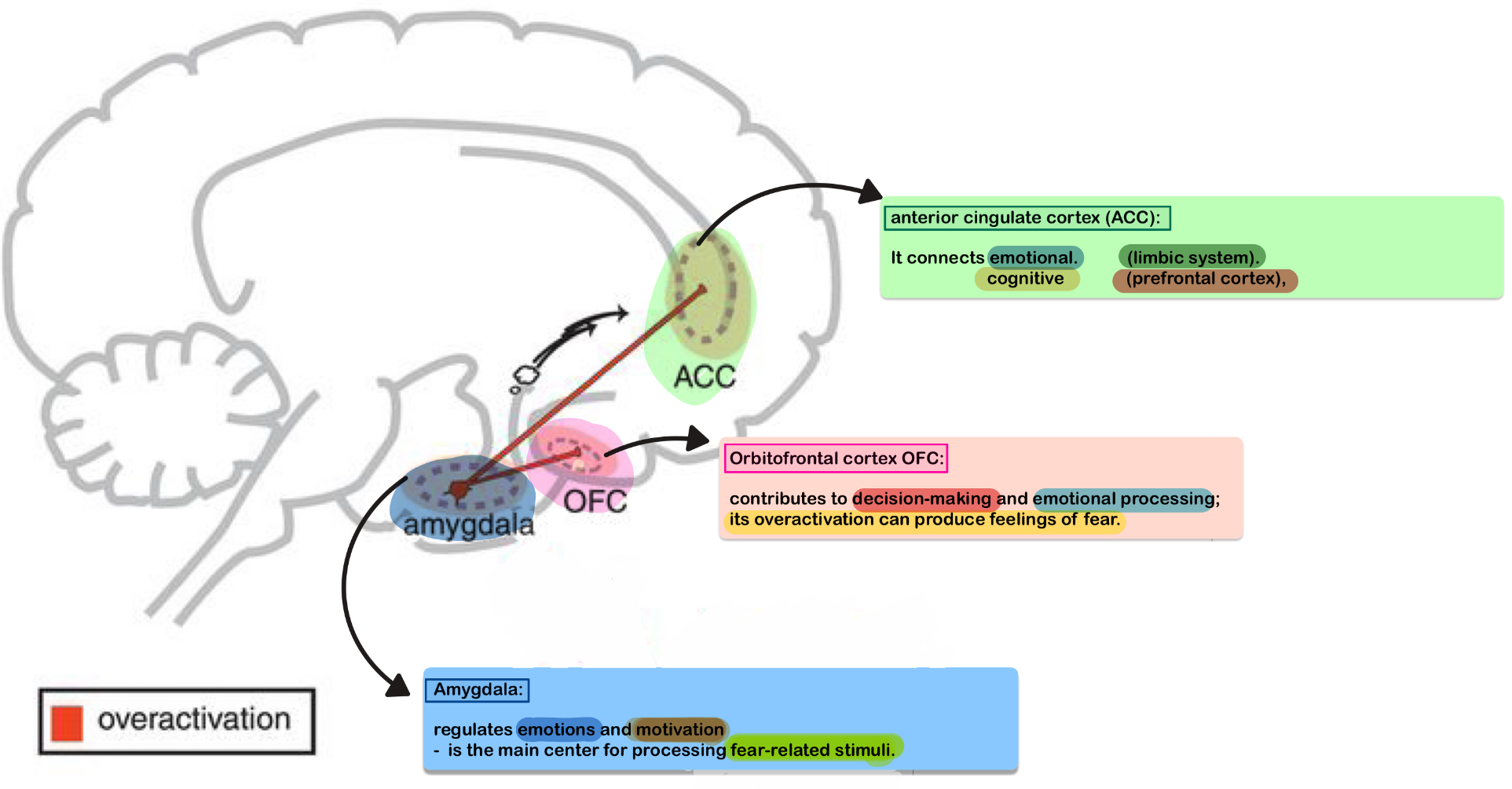
What is the function of brain structures that are primarily involved in the neurobiology of fear?
Through reciprocal connections between
amygdala
anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)
orbitofrontal cortex (OFC).
overactivation of these circuits may produce fear.❗🛑
How are feelings of fear regulated in the brain?
integrates sensory and cognitive input
determines whether a fear response will appear,
then triggers multiple fear responses through connections with other brain regions.
What is the role of the amygdala in fear?
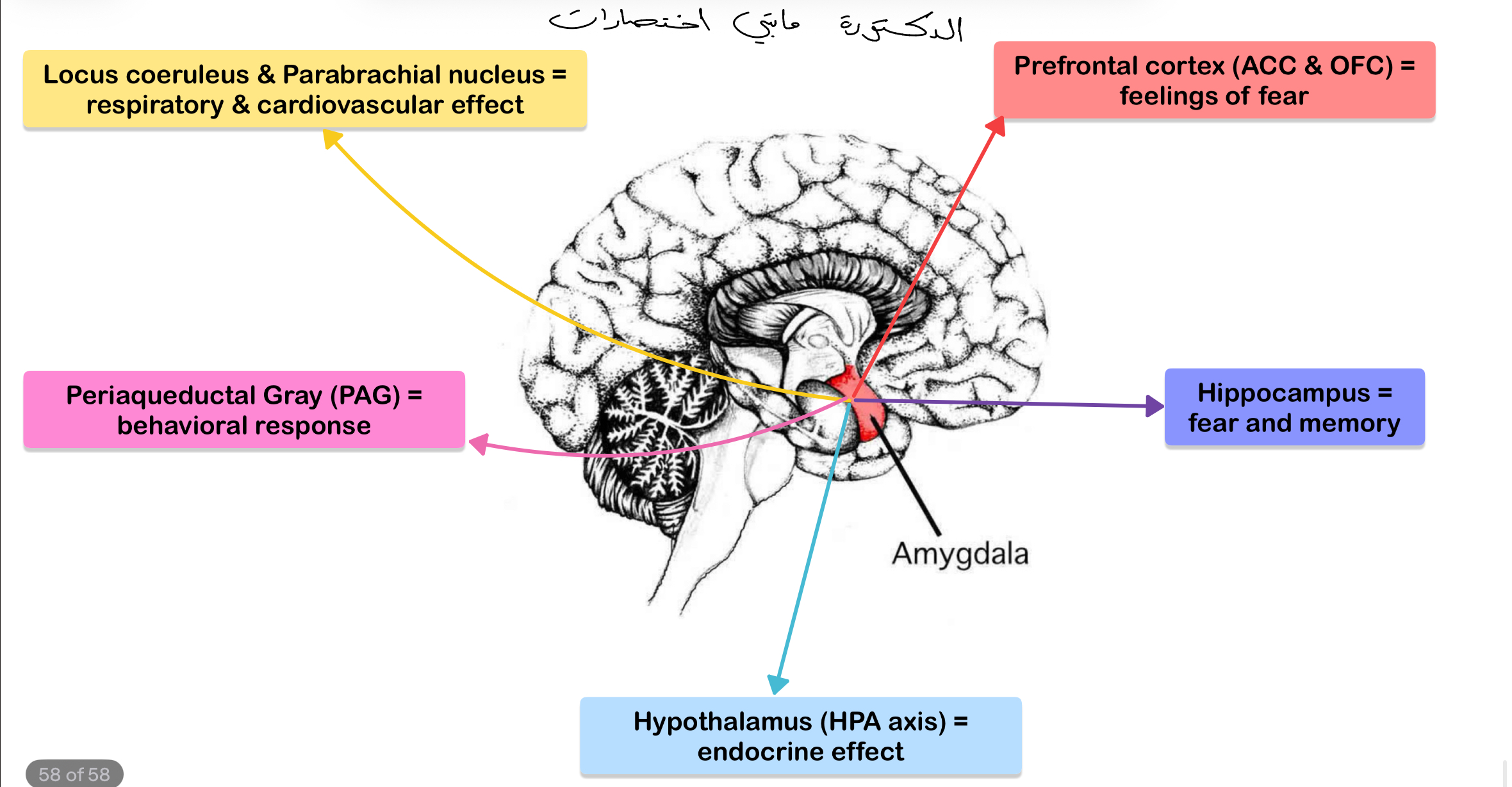
Which brain regions are connected to amygdala in fear responses and their functions?
Glutamate
GABA
5-HT (serotonin)
NE (norepinephrine)
CRF (Corticotropin-Releasing Factor)
Which neurotransmitters are involved in fear neurocircuitry?
Fear conditioning
What plays a central role in anxiety & fear?

What are the main stages of fear conditioning?
maladaptive fear learning
overgeneralization
Many anxiety disorders are based on (-,-,-), leading to (-) of fear.
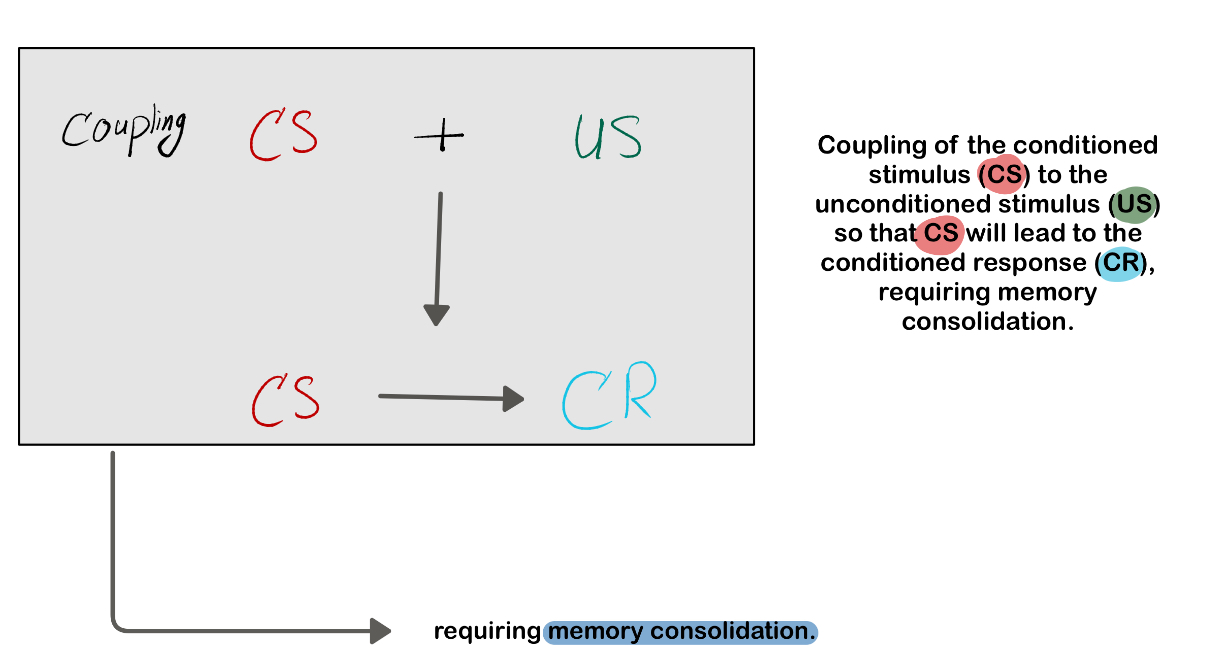
What happens during the acquisition phase of fear conditioning?
Repeated consolidation
of the memory after retrieval,
which can strengthen or modify the fear response.
What is reconsolidation in fear conditioning?
CS loses the ability to elicit the CR,
usually by presenting CS without the US repeatedly.
What is extinction in fear conditioning?
blocking or enhancing its activation
at the right time
can affect fear learning and memory.
What is the essential role of the amygdala in fear conditioning?
Glutamatergic NMDA receptors
adrenergic β1 receptors.
Which receptors in the amygdala are important for fear conditioning?
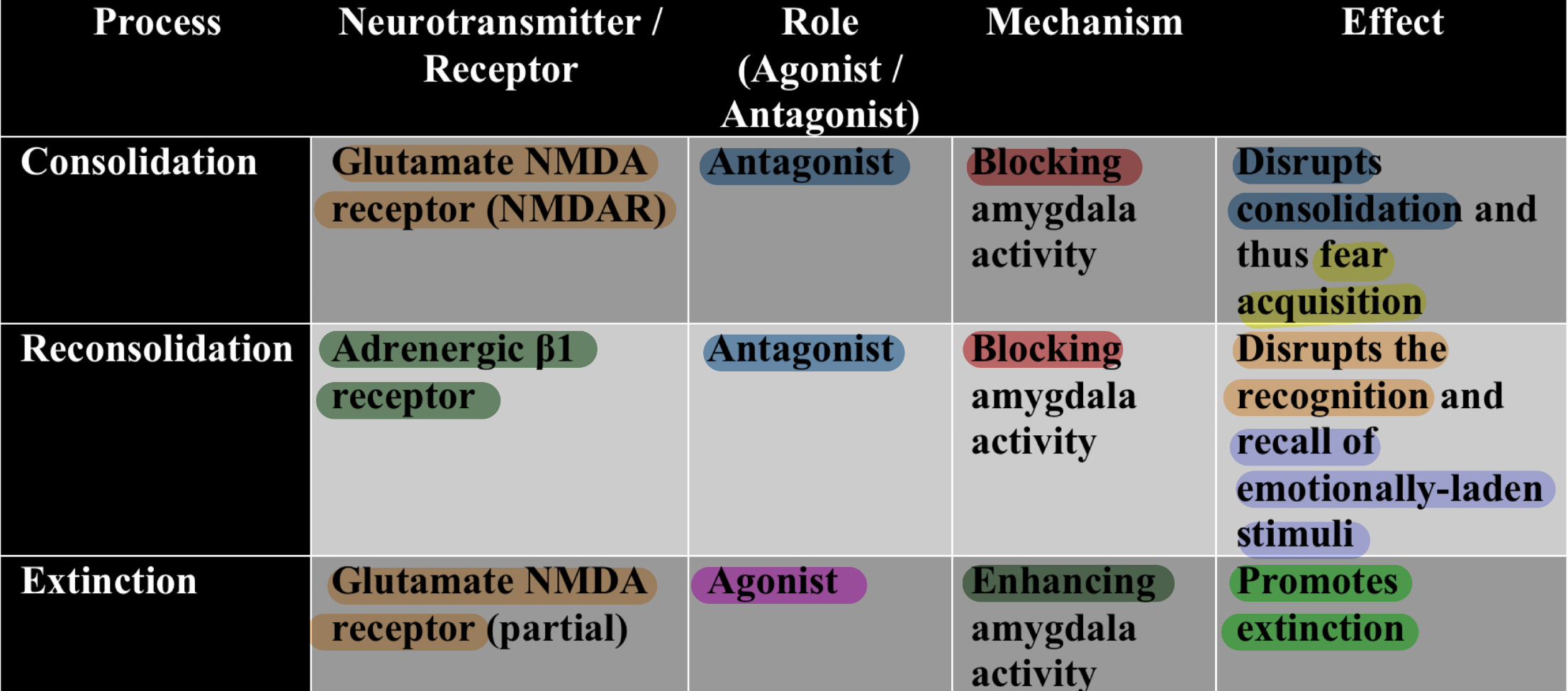
Summarize the role of amygdala receptors and their modulation (agonist vs antagonist) in fear memory processes: consolidation, reconsolidation, and extinction?