ECON 2113 Final Exam Set
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1,2,3,4 = Finale
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What percentage of the world’s economics expereince scaracity?
100%
The “invisible hand” directs economic activity through
prices
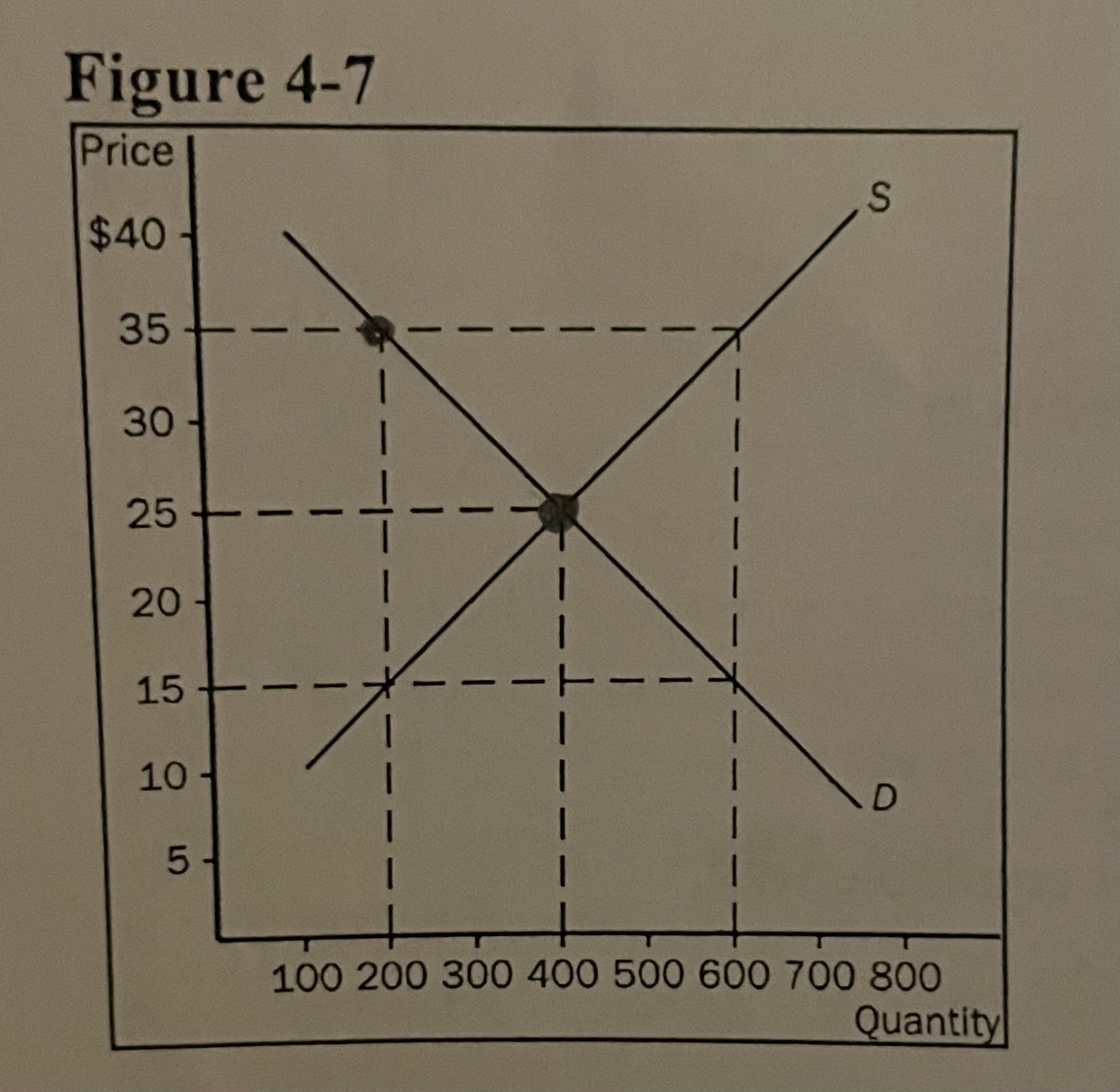
Refer to the image. At a price of $35. . .
a surplus would exist and the price would tend to fall
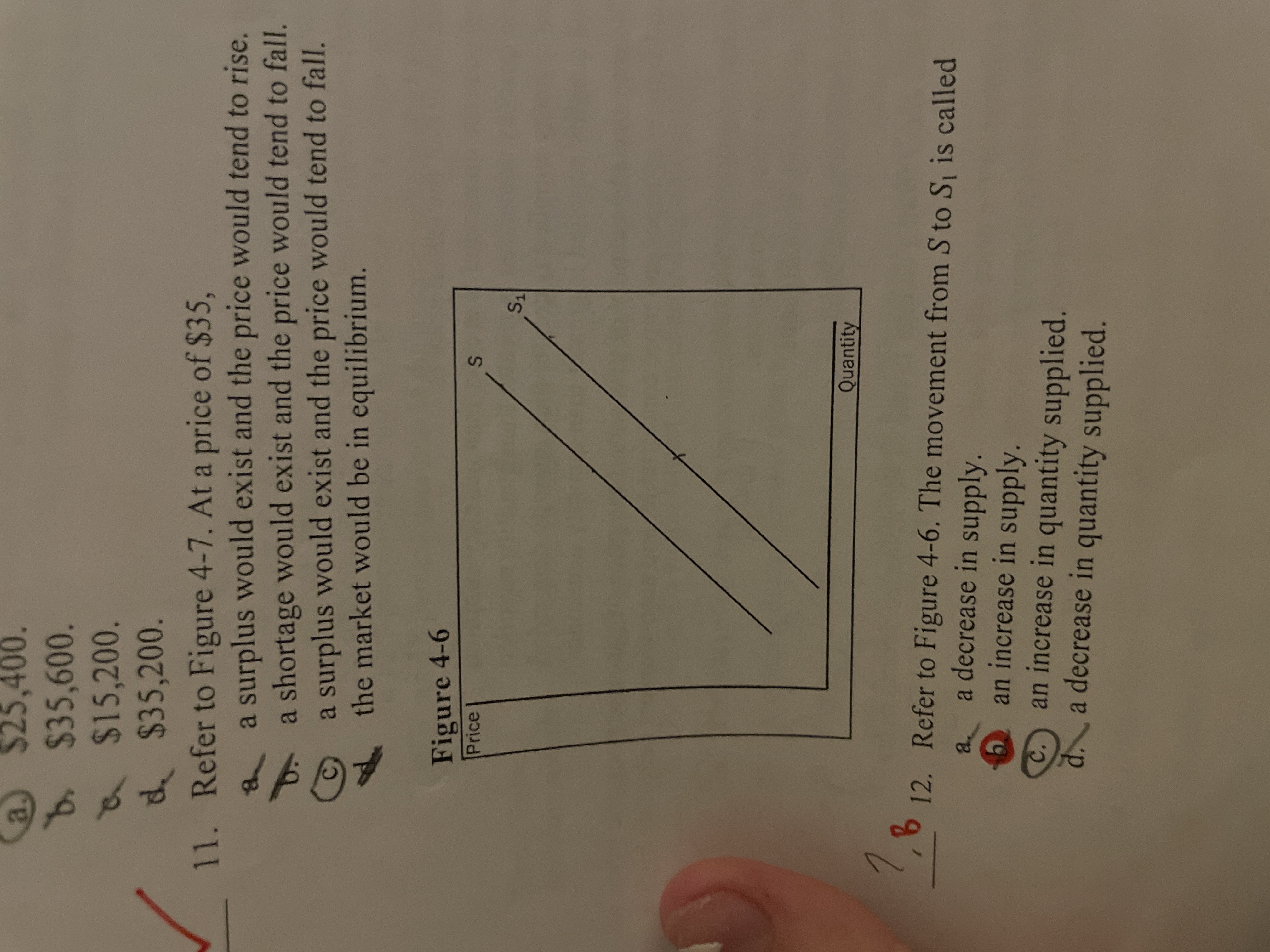
Refer to the image. The movement from S to S1 is called
an increase in supply
What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of new cars if the price of gasoline rises, the price of steel rises, public transportation becomes cheaper and more comfortable, and auto-workers negotiate higher wages?
Quantity will fall and the effect on price is ambigous
Elasticity of demand is closely related to the slope of the demand curve. The more responsive buyers are to a change in price, the demand curve will be
flatter
Suppose the price elasticity of demand for basketballs is 1.20. A 15% increase in price will result in
an 18 percent decrease in the quantity of basketballs demanded
T/F: Tuition is the single-largest cost of attending college for most students
false
T/F: The law of demand states that the quantity demanded of a product is postively related to price
false
T/F: If the demand for a good falls when income falls, the good is called an inferior good
false
T/F: A movement along a supply curve is called a change in supply while a shift of the curve is called a change in quantity supplied
false
T/F: A market economy cannot produce a socially desirable outcome because individuals are motivated by their own self-interest
false
T/F: A supply curve slopes upward because, all else equal, a higher price means a greater quantity supplied
true
T/F: The demand for Rice krispies is more elastic than the demand for cereal
True
The area below a demand curve and above the price measures
consumer surplus
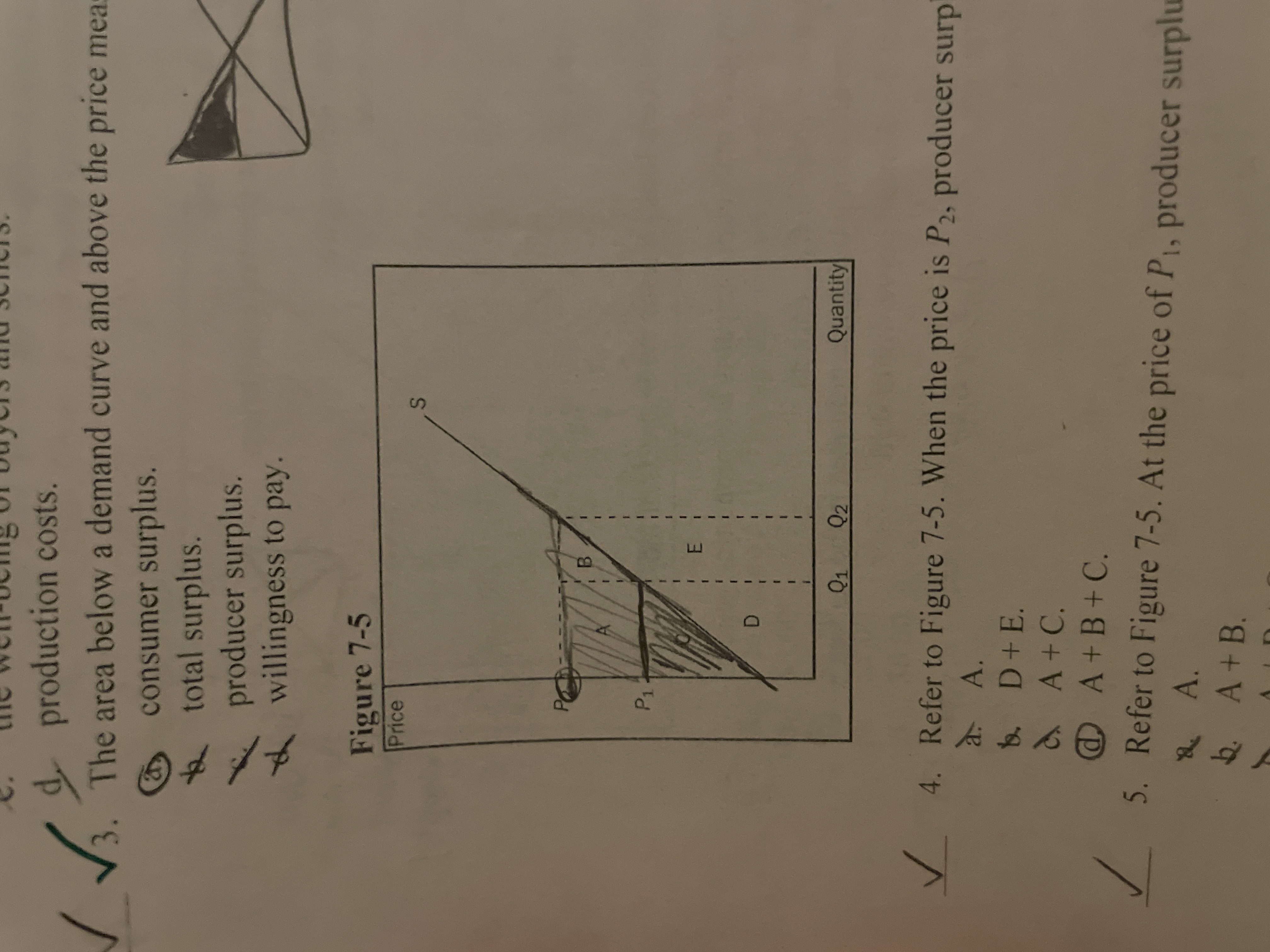
Refer to the image. Area A represents
the increase in producer surplus to those producers already in the market when price rises from P1 to P2
The marginal seller is the seller who
would leave the market first if the price were any lower
Efficiency occurs when
total surplus is maximized
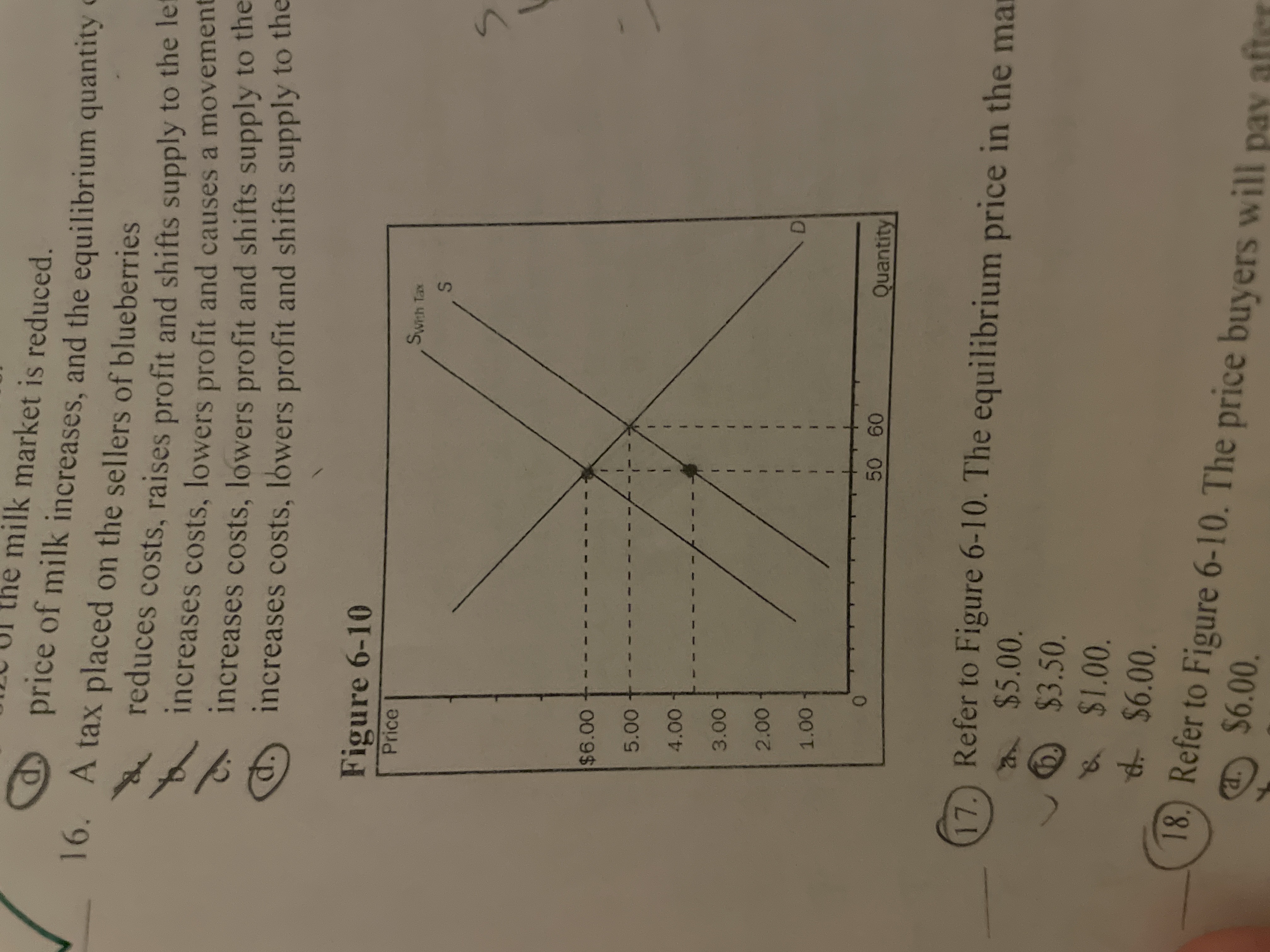
A tax placed on the sellers of blueberries
increases costs, lowers profits and shifts supply to the left (upward)
Refer to the image. The amount of tax imposed in this market is
$2.50
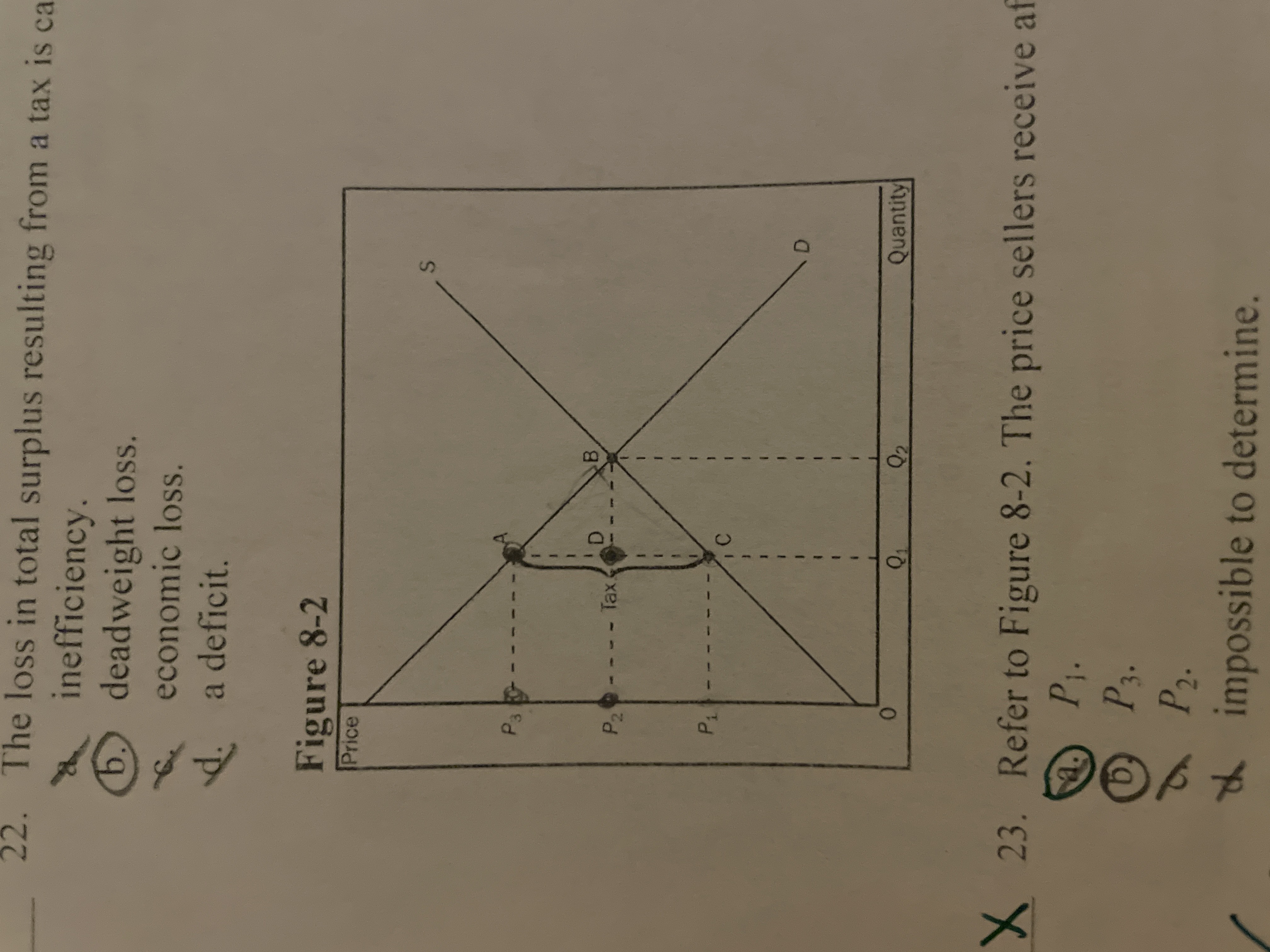
Refer to the image. The price sellers recieve after the tax is
P1
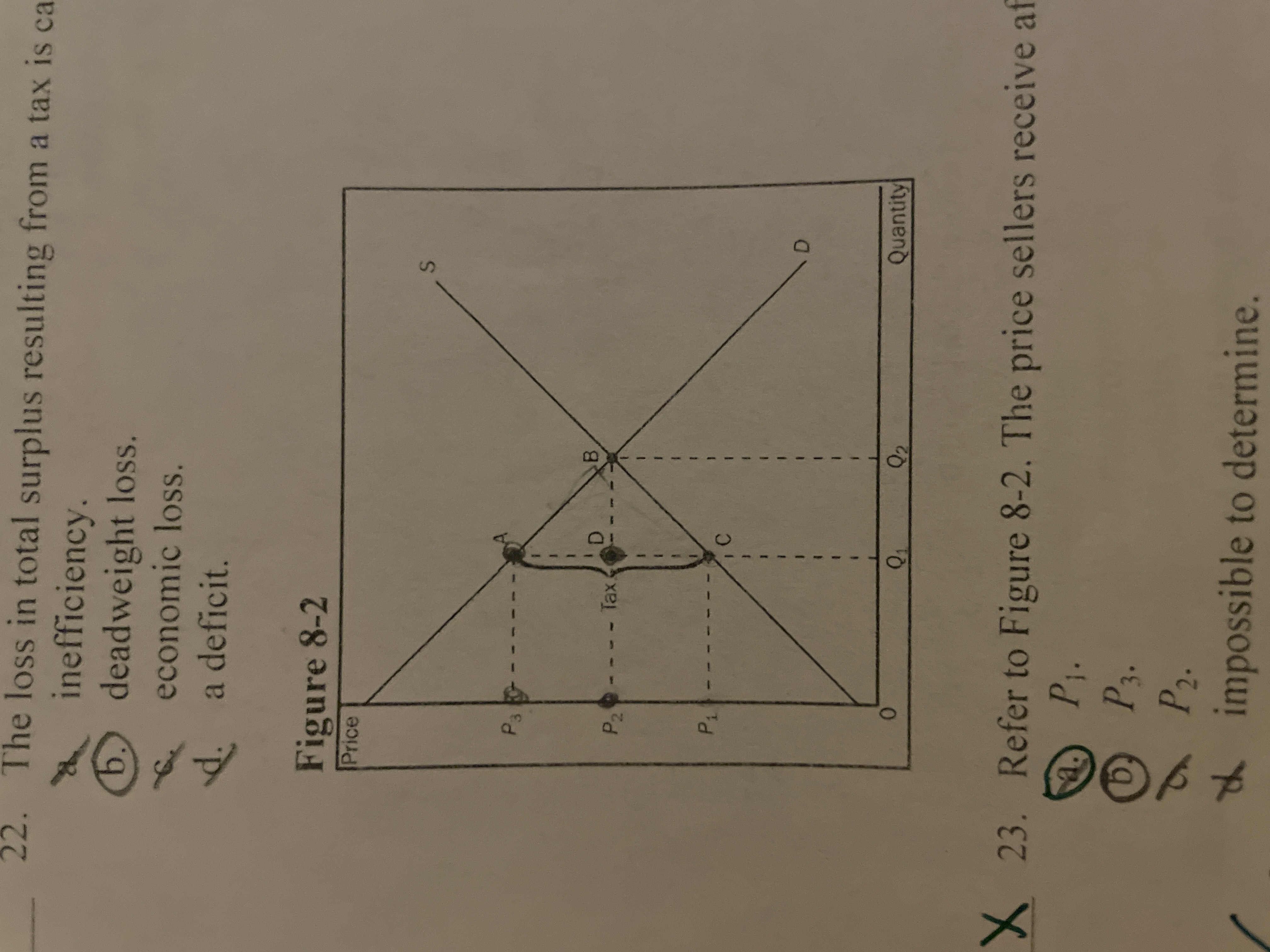
Refer to the image. The amount of tax revenue recieved by the government is equal to the area
P3 A C P1
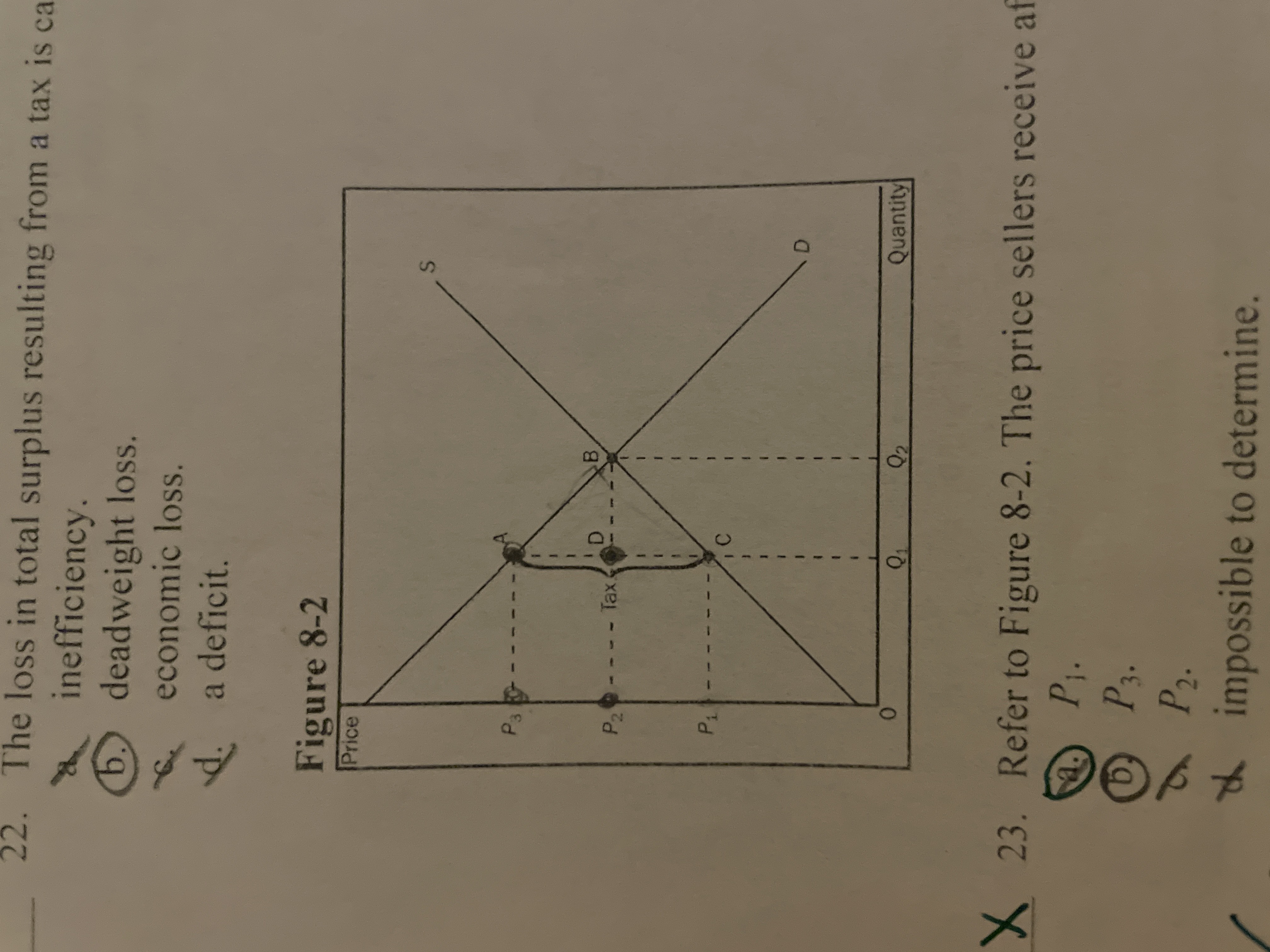
Refer to the image. The amount of deadweight loss associated with the tax is equal to
A B C
T/F: If a tax is imposed on the buyer of a product, the tax incidence will fall entirely on the buyer to pay more
false
T/F: The area above the demand curve and below the price measures the consumer surplus in a market
false
T/F: Consumer surplus is the amount a buyer actually has to pay for a good minus the amount the buyer is willing to pay for it
false
T/F: The incidence of a tax depends on whether the tax is levied on buyers or sellers
false
T/F: Often, the tax revenue collected by the governement equals the reduced welfare of buyers and sellers caused by the tax
false
T/F: Because taxes distort incentives, they cause markets to allocate resources inefficiently
true
T/F: When there is deadweight loss we can be certain that the entire society experiences a loss
True
Economic profit is equal to
total revenue minus the opportunity cost of producing goods and services
The efficient scale of the firm is the quantity of output that
minimizes average total cost
Average total cost is increasing whenever
marginal cost is greater than avergae total cost
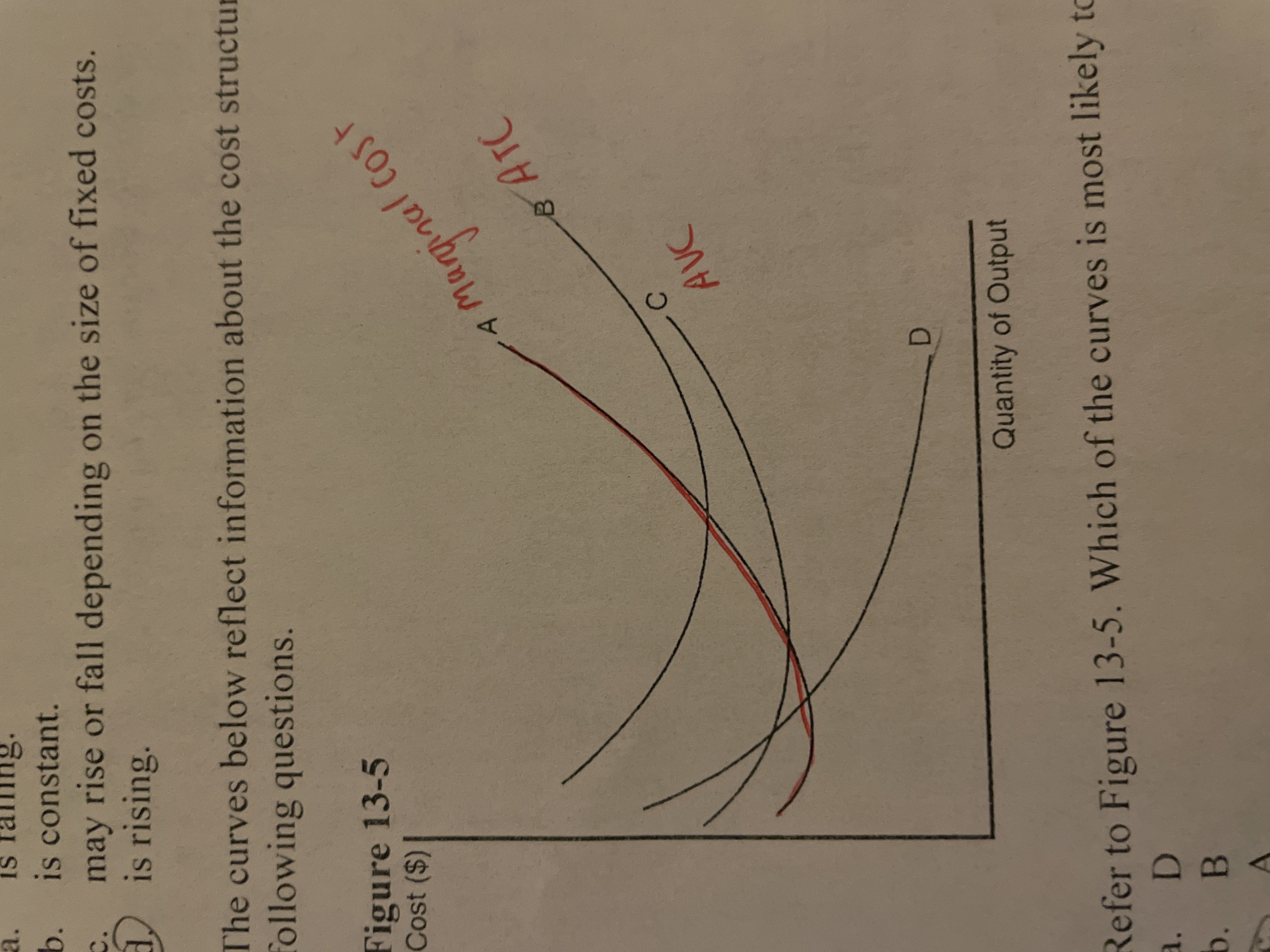
Refer to the image. Which of the curves is most likely to represent marginal cost?
Curve A
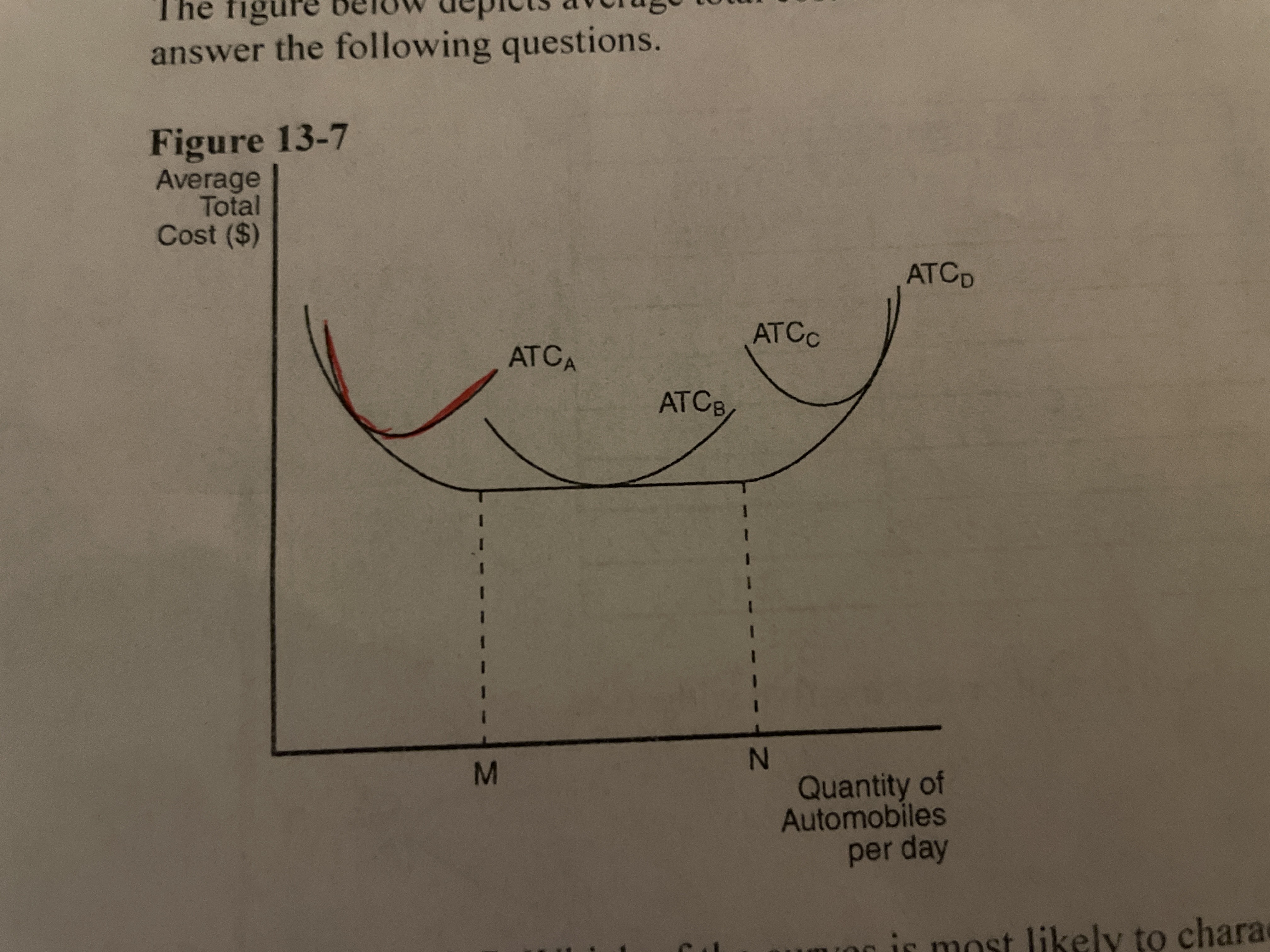
Refer to the image. Which of the curves is most likely to characterize the short-run avergae total cost curve of the smallest factory?
ATC A
Economies of scale arise when
workers are able to specialize in a particular task
The marginal product of labor can be defined as
change in output/change in labor
T/F: When economists speak of a firms costs, they are usually excluding the opportunity costs
false
T/F: Diminishing marginal product exists when the total cost curve becomes flatter as outputs increases
false
T/F: Average total cost reveals how much total cost will change as the firm alters its level of production
False
T/F: Fixed costs are those costs that remain fixed no matter how long the time horizon is
false
T/F: Accountants often ignore implicit costs
true
T/F: If the marginal cost curve is rising, so is the average total cost curve
false
T/F: Diseconomies of scale often arise because higher production levels allow specialization among workers
false
For a competitive
average revenue, marginal revenue, and the price of the goodare all equal to one another
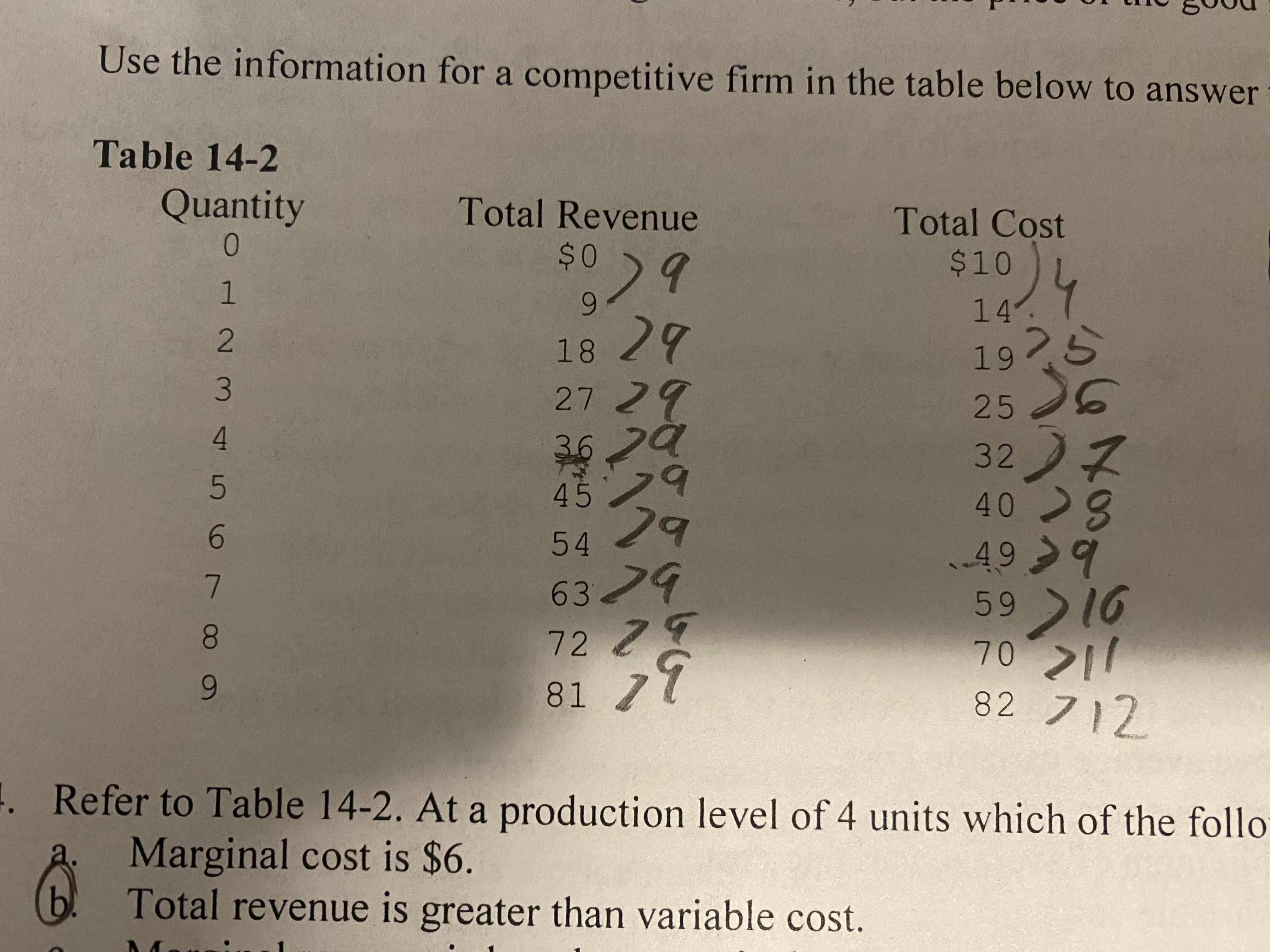
Refer to table 14-2. If this firm chooses to maximize profit it will choose a level of output where marginal cost is equal to
9
when a perfectly competitive firm makes a decision to shut down, it is most likely that
price is below the minimum of average variable cost
Profit-maximizing firms enter a competitive market when, for existing firms in that market,
Price exceeds average total cost
If a profit - maximizing monopolist faces a downward-sloping market demand curve, its
marginal revenue is less than the price of the product
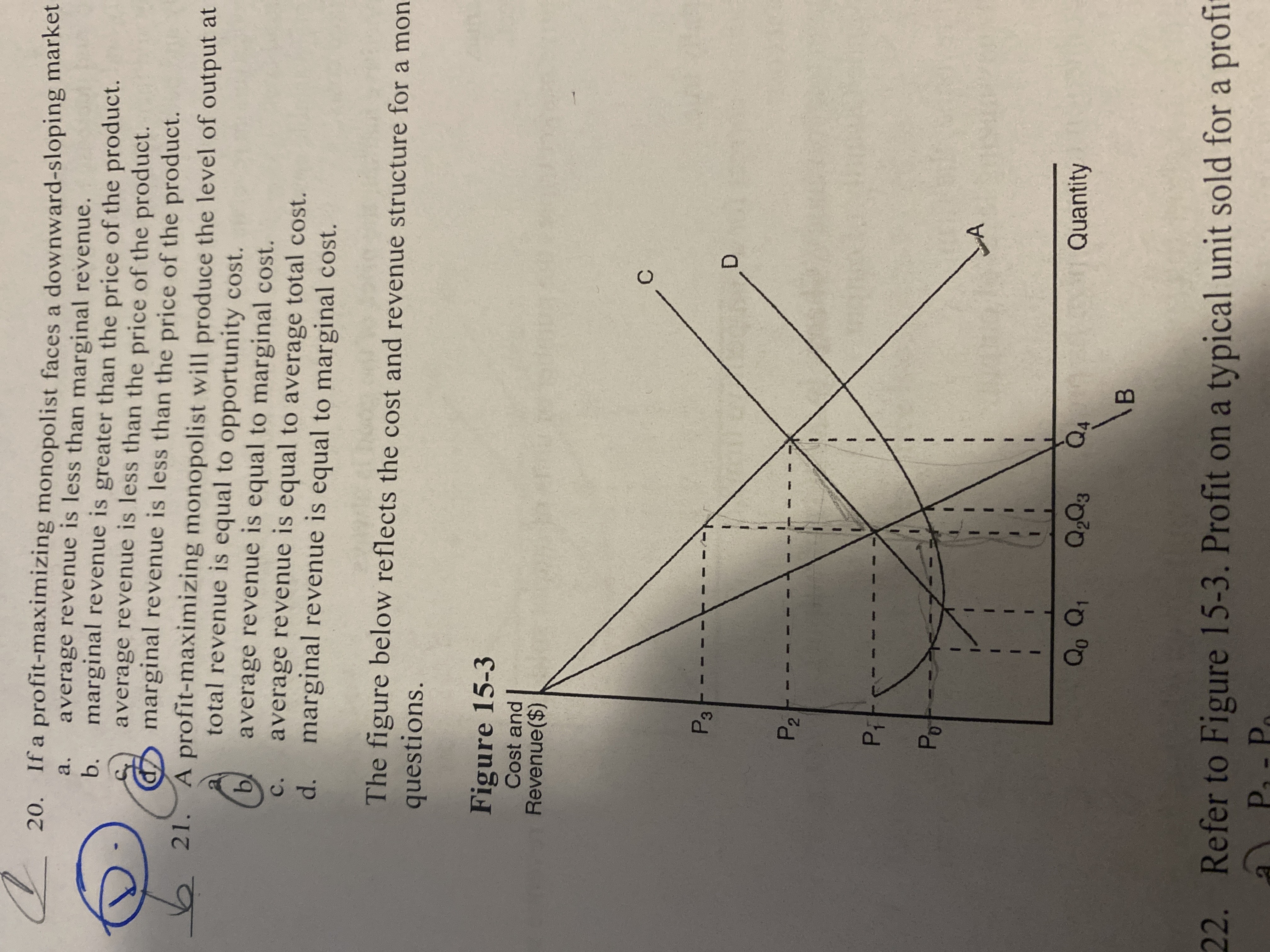
Refer to Figure 15-3. At the Profit-maximizing level of output,
Average revenue is equal to P3
For a firm in a competitive market, marginal revenue is always equal to average revenue
True
When a Profit-maximizing firm in a competitive market experiences rising prices, it will respond with an increase production
True
When a firm experiences zero-profit equilibrium, the firms revenue must be sufficient to cover all opportunity costs.
True
A firm will shut down in the short run if revenue is not sufficient to cover all of its fixed costs of production.
False
The De Beers Diamond company advertises heavily to promote the sale of all diamonds, not just its own. This is evidence that they have a monopoly position to some degree
True
Declining average total cost with increased production is one of the defining characteristics of a natural monopoly
True
For a monopoly, marginal revenue is often greater than the price they charge for their good
False