Chapter 3 - Steps in Civil Litigation
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Process of a Trial
Demand Letter
File Petition/ Complaint
Service of Process
Defendant Files Answer or Counterclaim or Denies/admits
Discovery Process
Pretrial motions
Trial
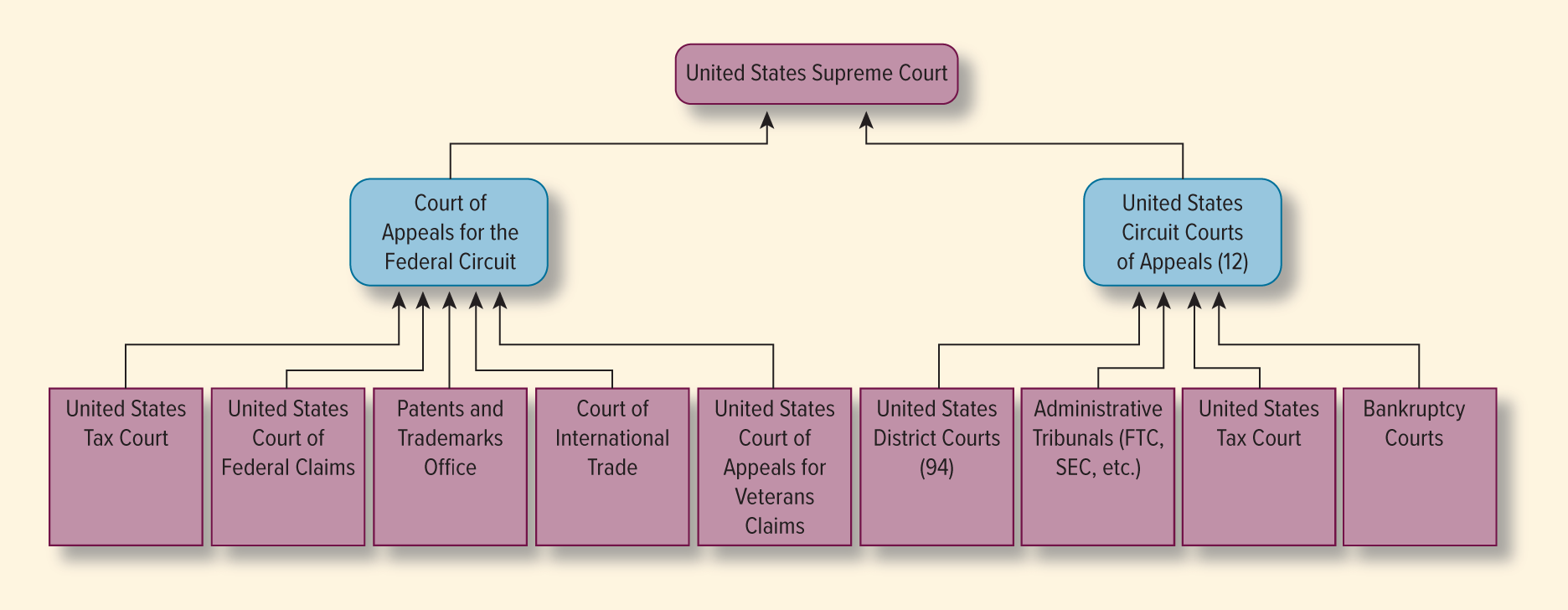
Federal Court System
The U.S. federal court system is a three-tiered structure with trial courts (District Courts), intermediate appeals courts (Circuit Courts of Appeals), and the final authority (the Supreme Court)
State court system
State court systems handle most U.S. legal cases (criminal, civil, family) within a hierarchy of trial courts, intermediate appellate courts, and a state supreme court, all established by state law to interpret state constitutions and statutes, with variations between states but generally covering matters not exclusive to federal courts.
Demand Letter
statement of what happened, under what law is why there is a lawsuit, amount to accept within a certain number of days - defendant can:
try to negotiate
respond with new info / not pay
no response
File Petition
pleading stage - complaint states the names of the parties to the action, the basis for the court’s subject-matter jurisdiction, the facts that form, and the relief that plaintiff seeks
Service of Process
when defendant is given a copy of the complaint and summons by a process sever or by a certified or ordinary mail, defendant can:
counterclaim, steps start over
answer, admit, deny, or say not enough info
Defendant’s response
Motion to dismiss: a request by the defendant that asks a judge or a court to dismiss the case because even if all the allegations are true, the plaintiff is not entitled to any legal relief
Discovery Process
The pretrial phase in a lawsuit during which each party requests relevant documents and other evidence from the other side in an attempt to “discover” pertinent facts and to avoid any surprises in the courtroom during the trial. Discovery tools include requests for admissions, interrogatories, depositions, requests for inspection, and document production requests.
Request for admission
request for production
interrogatories
depositions
Request for admission
a way for parties in a legal dispute to focus only on the issues about which they disagree.
There are two types: one asks the opposing party to admit to or deny certain facts; the second asks the opposing party to admit or deny certain documents or electronically stored information.
Request for production
forces the opposing party to produce certain information unless it is privileged or irrelevant to the case.
Interrogatories
A formal set of written questions that one party to a lawsuit asks the opposing party during the pretrial discovery process to clarify matters of evidence and help determine what facts will be presented at a trial in the case. The questions must be answered in writing under oath or under penalty of perjury within a specified time.
Hearsay
a testimony about a what a witness heard another person say
Depositions
A pretrial sworn and recorded testimony of a witness that is acquired out of court with no judge present.
Pretrial Motions
A meeting of the judge and the attorneys for both sides to narrow the issues for trial and identify witnesses for trial and goes like:
there is not material dispute → trial SKIPPED and can appeal
defense wins → trial SKIPPED and can appeal
there is material dispute → TRIAL
Trial
*most try to settle because trial is expensive
1. jury selection
opening statement
defendants case
closing statements
Jury selection
voir dire - The process of questioning potential jurors to ensure that the jury will be made up of nonbiased individuals.
Opening statements
each party explains to the judge and jury which facts he or she intends to prove
Plaintiff’s case
evidence is put forth
cross examination
directed verdict - A ruling by the judge, after the plaintiff has presented her case but before any evidence is put forward by the defendant, in favor of the defendant because the plaintiff has failed to present the minimum amount of evidence necessary to establish his claim.
Defendants Case
witness is called
rarely cross examined
Writ of Certiorari
A Supreme Court order, issued after the Court decides to hear an appeal, mandating that the lower court send to the Supreme Court the record of the appealed case.
Jurisdiction
The power of a court to hear cases and resolve disputes.
In-personam jurisdiction
The power of a court to require that a party (usually the defendant) or a witness come before the court; extends to the state’s borders in the state court system and across the court’s geographic district in the federal system.
ex: Oklahoma has jurisdiction over a case in Oklahoma
Minimum contacts rule:
A statute that enables a court to obtain jurisdiction against an out-of-state defendant as long as the defendant has sufficient minimum contacts within the state, such as committing a tort or doing business in the state.
In rem jurisdiction
The power of a court over the property or status of an out-of-state defendant located within the court’s jurisdiction area.
Subject-matter jurisdiction
The power of a court over the type of case presented to it.
Exclusive Fed vs. State Fed
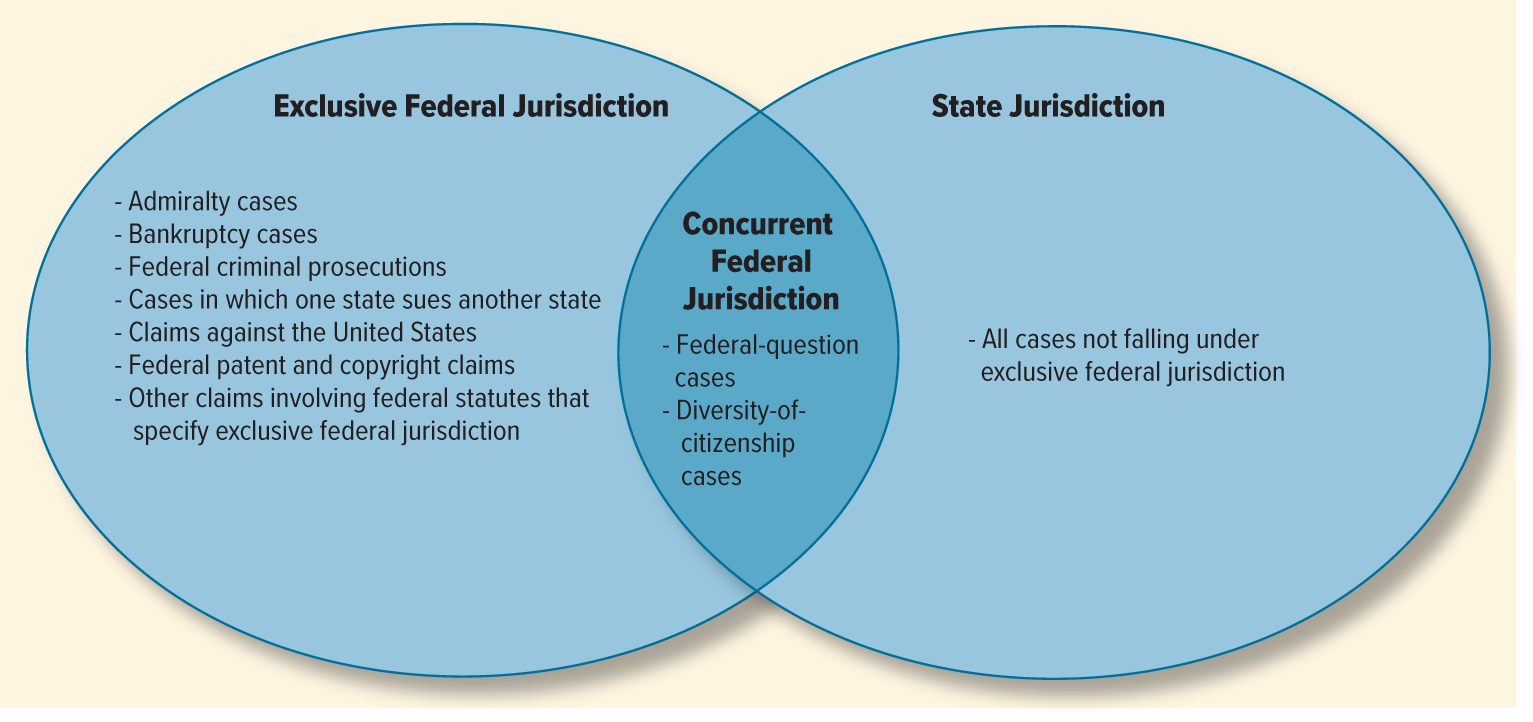
Diversity of citizenship
parties are from different states
the controversy concerns an amount in excess of $75,000
Threshold Requirements:
standing
case or controversy
ripeness
Standing
The legal right of a party to bring a lawsuit by demonstrating to the court sufficient connection to and harm from the law or action challenged
plaintiff must have injury in fact that is concrete and actual
injury must be fairly traceable to the challenged action of defendant
must be likely that the injury will be redressed by a favorable decision
Case or controversy
requires an actual dispute between parties over their legal rights that remains in conflict at the time the case is presented and that is a proper matter for judicial determination.
relationship between the plaintiff and the defendant must be adverse
actual or threatened actions of at least one of the parties must give rise to an actual legal dispute
courts must have the ability to render a decision that will resolve the dispute
Ripeness
A measure of the readiness of a case for a decision to be made; designed to prevent premature litigation for a dispute that is insufficiently developed. A claim is not ripe for litigation if it rests on contingent future events that may not occur as anticipated or may not occur at all.