Eye anatomy
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
what is the function of lateral rectus muscle?
moves eye outward (abduct)
what innervates lateral rectus?
abducens nerve (CN VI)
what is the function of medial rectus?
moves eye inward (adducts)
used for convergence/near
what innervates medial rectus?
oculomotor nerve (CN III)
what is the function of superior rectus?
elevates the eye
upward gaze
tracking objects moving vertically
what innervates superior rectus?
oculomotor nerve (CN III)
what is the function of inferior rectus?
depresses the eye
downward gaze
what innervates inferior rectus?
oculomotor nerve (CN III)
what is the function of superior oblique?
depresses the eye
abducts the eye (outwards)
intorts the eye
what innervates superior oblique?
trochlear nerve (CN IV)
what is the function of inferior oblique?
elevates the eye
abducts the eye
extorts the eye
what innervates inferior oblique?
oculomotor nerve (CN III)
what are the 5 layers of the cornea?
epithelium
bowman’s layer
stroma
descemet’s membrane
endothelium
what is the oily layer of the tear film?
outermost layer
slows evaporation
prevents outflow
lubricates the eye
smooth anterior refracting surface
what is the mucin layer of tear film?
innermost layer of tear film
hydrophilic - wetting agent
uniform spread of tears
stabilises the tear film
what produces the mucin layer of tear film?
conjunctival goblet cells and corneal epithelium
what produces the oily layer of tear film?
meibomian and zeis glands
what is the aqueous layer of tear film?
middle layer of tear film
water-soluble nutrients & oxygen
hydrates
antibacterial and anti-viral
what secretes the aqueous layer of tear film?
the lacrimal glands
where is aqueous humour produced?
ciliary body
what is the function of the olfactory nerve?
sensory nerve
sense of smell
olfactory receptors in the nasal cavity send signals to the olfactory bulb and brain
where does olfactory nerve (CN I) exit?
cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone
what is the function of the optic nerve?
sensory nerve
responsible for vision
carries visual information from retina to the brain
signals are processed by the occipital lobe
what is the exit location of the optic nerve (CN II)?
optic canal (sphenoid bone)
what is the function of oculomotor nerve?
motor nerve
controls most eye movement (IR, SR, MR, IO)
controls pupil constriction (via parasympathetic fibres)
controls eyelid elevation (levator palpebrae superioris)
lens accommodation via parasympathetic fibres
where does oculomotor nerve (CN III) exit?
superior orbital fissure
what is the function of the trochlear nerve?
motor nerve
innervates the superior oblique which allows the eye to move downward and laterally
where does the trochlear nerve (CN IV) exit?
superior orbital fissure
what is the function of the trigeminal nerve?
combination nerve: both sensory and motor
sensory: provides sensation to the face (touch, pain, temperature) and corneal reflex
motor: controls muscles of mastication (chewing)
has 3 branches that serves different areas of the face and head
where does trigeminal nerve (CN V) exit?
there are 3 branches of trigeminal nerve:
V1 (ophthalmic): superior orbital fissure
V2 (maxillary): foramen rotundum
V3 (mandibular): foramen ovale
what is the function of the abducens nerve?
motor nerve
innervates the lateral rectus which abducts the eye
where does the abducens nerve (CN VI) exit?
superior orbital fissure
what is the function of the facial nerve?
combination of sensory and motor function
sensory: taste sensation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue
motor: controls the muscle of facial expression (smile, frown)
parasympathetic: stimulates lacrimal (tear) and salivary glands (submandibular/sublingual)
where does the facial nerve (CN VII) exit?
internal acoustic meatus (enters temporal bone)
what are the divisions of the facial nerve?
temporal branch: to forehead and eyes
zygomatic branch: to cheek muscles
buccal branch: muscles of the cheek
mandibular branch: lower lip and chin
cervical branch: platysma and neck
what is the function of the vestibulocochlear nerve?
sensory nerve
responsible for hearing (cochlear part)
responsible for balance (vestibular part)
sends auditory information from the cochlear and equilibrium data from the vestibule to the brain
where does the vestibulocochlear nerve exit (CN VIII)
internal acoustic meatus
what is the function of the glossopharyngeal nerve?
combination of sensory and motor
sensory: taste from the posterior one-third part , sensation from the pharynx
motor: controls the muscle involved in swallowing
parasympathetic: salivation (parotid gland)
where does the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) exit?
jugular foramen
what is the function of the vagus nerve?
combination of sensory and motor
sensory: taste from the epiglottis and pharynx
motor: muscles of the larynx and pharynx involved in swallowing and phonation
parasympathetic: controls the heart, lungs and digestive tract
where does the vagus nerve (CN X) exit?
jugular foramen
what is the function of the accessory nerve?
motor nerve
controls the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles to turn the head and shrug the shoulders
where does the accessory nerve (CN XI) exit?
jugular foramen (spinal root enters via the foramen magnum)
what is the function of the hypoglossal nerve?
motor nerve
controls the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue involved in speech, swallowing and food manipulation
where does the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) exit?
hypoglossal canal
what is the function and origin of the orbital part of the orbicularis oculi?
originates from medial palpebral ligament
deep insertions into the lacrimal sac
innervated by the facial nerve (CN 7)
holds the lower lid against the eye
largest part of the orbicularis oculi
function: closes the eyes tightly
voluntary: crying, excessive laughing, sneezing
additional protection (increased thickness)
prevents tears flowing into punctum
what is the function of the palpebral part of the orbicularis oculi?
closes the eye without effort
used for blinking
can blink involuntarily e.g. blink reflex to a threat, spread tears over dry cornea, pump away excess tears
how does the lower eyelid move?
it does not have a muscle like the levator palpebrae
even when looking down, it does not move
what is the function and origin of levator palpebrae?
function: lifts the upper lid
origin: sphenoid bone (lesser wing)
it runs forward to superior tarsal plate
lies between the superior rectus and the roof of the orbit
a sheath encloses the superior rectus and levator muscle to each other —> allows for coordinated eye movements with eyelid position (elevation of eyelid with upgaze)
what is the function of retinal ganglion cells?
what are bipolar cells in the retina?
what are amacrine cells in the retina?
what are horizontal cells in the retina?
what are rod cells in the retina?
what are cone cells in the retina?
what is the function of the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)?
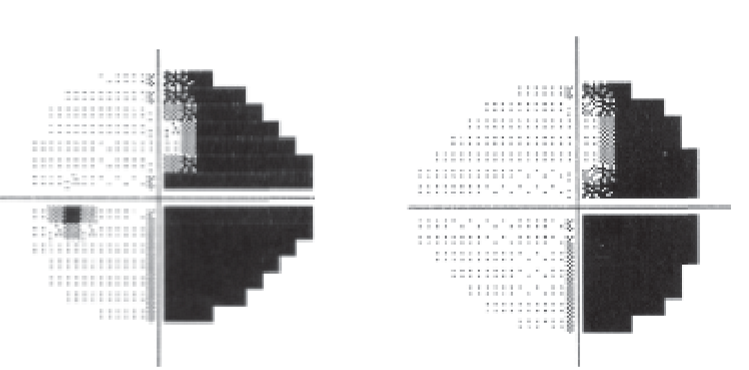
what is this VF defect called?
right incongruous homonymous hemianopia
function of internal limiting membrane
basement membrane formed by Muller glial cells
separates retina from vitreous humour
function of nerve fibre layer
contains axons of ganglion cells that converge to form the optic nerve (CN II)
function of ganglion cell layer
contains cell bodies of ganglion cells
function of inner plexiform layer
synapses between bipolar, ganglion, and amacrine cells
function of inner nuclear layer
contains bipolar, amacrine, horizontal, and Muller cells
function of outer plexiform layer
synapses between bipolar cells and photoreceptors
function of outer nuclear layer
contains cell bodies of rods and cones (photoreceptors)
function of external limiting membrane
tight junctions between photoreceptors and Muller cells
function of photoreceptor layer
contains outer and inner segments of rods and cones
function of retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)
nourishes photoreceptors
absorbs stray light
forms blood-retina barrier