Fertility Testing- FINALS L8
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
MALE FERTILITY TESTING
Semenalysis
Ultrasound
Testicular Biopsy
Vasography
Panleukocyte Immunocytochemical staining
MACROSCOPIC EXAMINATION
Performed after liquefaction (30-60 minutes)
VISCOCITY- consistency of the fluid
VOLUME- 2-5 mL
SEMEN PH- measured within 1 hour (7.2-8.0)
SPERM CONCENTRATION
Normal: 20-160 mil./mL
SPERM MOTILITY
>50% shows moderate to strong forward motion
SPERM MORPHOLOGY
>50% normal forms
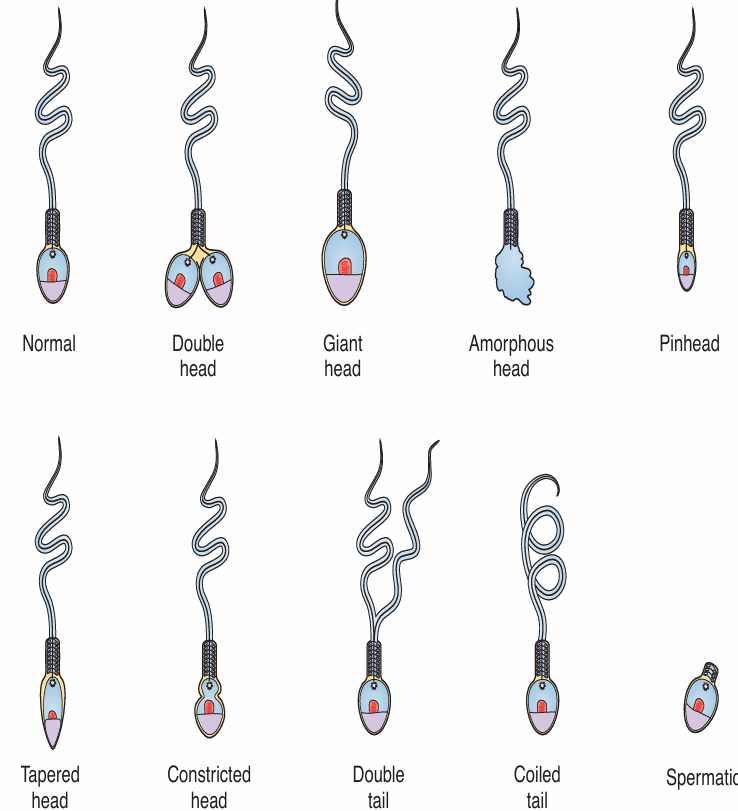
TERATOAZOOSPERMIC INDEX (TZI)
Average number of defects per sperm
SPERM AGGLUTINATION
DIRECT OR INDIRECT MIXED AGGLUTINATION REACTION (MAR)- for IgG or IgA
IMMUNOBEAD ASSAY- detect all three Ig classes when beads are coated with monospecific antisera to each class
ULTRASOUND
Cost-effective & non-invasive
Assess testicular anatomy & vascularity
SCROTAL ULTRASOUND
Epididymis
Cysts
Infections
Masses
Obstructions
Testicles Infections
Truma
EPIDIDYMIS (SU)
Normal caput diameter 7-8 mm
CYSTS (SU)
Hypo-/anechoic, well circumscribed, commonly located at head
Simple cysts (no sperm) & spermatoceles (sperm present) not associated with infertility
INFECTIONS (SU)
Enlarged, thickened, decreased echogenicity
MAGI associated with decreased motility, increased sperm DNA fragmentation, abnormal sperm morphology
MASSES (SU)
Presence of vascularity, varied echotexture
Most commonly adenomatoid tumors; others include cystadenomas, mesotheliomas, sarcomas
OBSTRUCTION (SU)
Epididymal enlargement, prominence of rete testis, hypoechoic appearance
Normal volume ejaculate with oligo-/azoospermia
TESTICLES INFECTIONS (SU)
EARLY: Decreased echogenicity, increased heterogeneity, enlargement
LATE: Atrophy, increased echogenicity
Associated with subsequent infertility, particularly with post pubertal mumps
TRAUMA (SU)
May visualize seminiferous tubules, hematomas
May lead to secondary infertility, antisperm antibodies
TRANSRECTAL ULTRASOUND
PROSTATE- Cysts
SEMINAL VESICLES- EDOa
CYSTS (PROSTATE)
May be located peripherally, midline, paramedian, hypo-/anechoic, thin wall
May result in obstruction, rare malignant processes
EDOA (SEMINAL VESICLES)
Dilated ejaculatory duct & SVs, may have calcification
Low volume ejaculate, oligo-/azoospermia, decreased fructose & semen pH, requires confirmatory aspiration demonstrating sperm
TESTICULAR BIOPSY- PURPOSE
Check the location & condition of a lump in the testes
Diagnose causes of male infertility
Obtain sperm for in vitro fertilization (IVF)
OPEN BIOPSY
Surgical biopsy
Small tissue sample is taken from both testicles
PERCUTAENOUS BIOPSY
Fine needle biopsy
Tissue sample is aspirated
Also performed on both testicles
VASOGRAPHY
Used to evaluate the condition of vas deferens & ejaculatory ducts
Uses radiologic dye
X-ray is taken as dye flows through the ejaculatory ducts
Only performed when there’s abnormal findings in biopsy & when the ultrasound is uncertain
PANLEUKOCYTE (CD45) IMMUNOCYTOCHEMICAL STAINING
Detects peroxidase negative polymorphonuclear leukocytes which can only be detected thru immunocytochemical
Helps in differentiating leukocytes & germ cells
1.0 x 10^6 cells/mL
Consensus threshold value for peroxidase positive cells
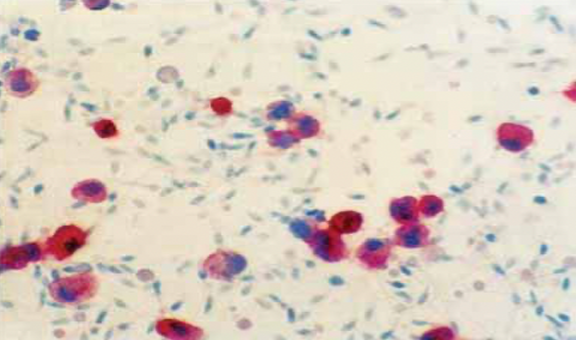
LEUKOCYTE IN SEMEN; CD45- BEARING CELLS ARE STAINED RED
If there are fewer CD45-positive cells than spermatozoa in the sample (i.e., <400), the sampling error will exceed 5%, in this case, the sampling error for the number of cells counted
If fewer than 25 C45-positive cells are counted, report the number of CD45-positive cells observed with the comment “too few for accurate determination of concentration”
CAUSES OF MALE INFERTILITY
Sperm abnormalities
Low sperm count or lack of sperm
Ejaculation problems
Other causes
SPERM ABNORMALITIES MAY BE CAUSED BY
Inflammation of the testicles
Swollen veins in the scrotum
Abnormally developed testicles
LOW SPERM COUNT OR LACK OF SPERM
A pre-existing genetic condition
Use of alcohol, tobacco, or other drugs
Severe mumps infection after puberty
Hernia repairs
Hormone disorder
Exposure to poisonous chemicals
Exposure to radiation
Blockage caused by a previous infection
Wearing restrictive or tight underwear
Injury to the groin area
EJACULATION PROBLEMS
Premature ejaculation
Retrograde ejaculation
Erection dysfunctions
Complications from radiation therapy or surgery
OTHER CAUSES OF MALE INFERTILITY
History of STDs
Urinary tract infection (UTI)
Use of certain types of medications (steroids)
MANAGEMENT OF MALE INFERTILITY
Lifestyle Change
Artificial Insemination
Hormone Treatment
IVF
LIFESTYLE CHANGE
Avoid heat sources, radiation, chemicals, alcohol, drugs, tobacco
ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION
Sperm is collected through multiple ejaculations; manually placed in female’s uterus or fallopian tubes
HORMONE TREATMENT
Clomid or testosterone may increase sperm count
IVF
Fertilization of mature ovum in lab & reimplantation of zygotes into uterus via laparoscopy
FEMALE FERTILITY TESTING
Hormone Testing
Other infertility tests
AMENORRHEA
Absence of menstrual flow which could be genetic and/or anatomic abnormality or endocrine abnormality

STEPWISE APPROACH TO EVALUATING AMENORRHEA
Step 1: HCG is measured to exclude pregnancy. Although a result > 5 mIU/mL is typically indicative of pregnancy, or other conditions.
Step 2: PRL, TSH, and FT4 are measured to exclude a prolactinoma and thyroid disease.
Step 3: If HCG, PRL, TSH, and FT4 are all normal, then endogenous estrogen status is evaluated with the progestin withdrawal test
Step 4: Serum FSH and LH levels determined
Step 5: Serum androgens measured
INFERTILITY TESTS FOR WOMEN
Pelvic ultrasound
Hysterosalpingogram (HSG)
Sonohysterogram
Laparoscopy
Pap Smear
Colposcopy
PELVIC ULTRASOUND
Helps to see the size & position of vagina, cervix, uterus & ovary
HYSTEROSALPINGOGRAM (HSG)
Looks inside of uterus & fallopian tubes & area around them
SONOHYSTEROGRAM
Utilizes saline & ultrasound to look at female reproductive organs
LAPAROSCOPY
Used to asses woman’s pelvic organs (uterus, fallopian tubes, & ovaries) using a thin, lighted scope that’s put through a small cut (incision) in the belly
PAP SMEAR
Routine physical exam for women, collects a small sample of cells from the cervix
COLPOSCOPY
Test to look at vagina & cervix through lighted magnifying tool (colposcope)
CAUSES OF FEMALE INFERTILITY
Ovulation Disorders
Tubal Infertility
Endometriosis
Uterine or Cervical Causes
OVULATION DISORDER
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
Hypothalamic dysfunction
Premature ovarian failure
Too much PRL
TUBAL INFERTILITY
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Previous surgery in the abdomen or pelvis
Pelvic tuberculosis
ENDOMETRIOSIS
Extra tissue growth outside the uterus
Affects the lining of the uterus
UTERINE OR CERVICAL CAUSES
Benign polyps or tumors
Endometriosis scarring
Uterine abnormalities present from birth
Cervical stenosis
MANAGEMENT OF FEMALE INFERTILITY
Infection
Endometriosis
Cervical Problems
Endocrine Problems
Fallopian Tube Problems
INFECTION
Terazol- for yeast infection
Metronidazole- for bacterial vaginosis/trichomoniasis
ENDOMETRIOSIS
Danazole (Danocrine)
Oral Contraceptives- continuously to suppress ovulation & treatment for endometriosis
Surgical Removal- for moderate to severe disease [laparoscopy]
CERVICAL PROBLEMS
Estrogen Therapy
Cryosurgery- freezes the surface of the cervix if there’s recurrent cervicitis
ENDOCRINE PROBLEMS
Hypothyroid- replacement therapy (Synthroid)
Hyperthyroid / Hyperthyroidism- surgery, radioiodine, medicines
FALLOPIAN TUBE PROBLEMS
Treatment for Infections- terazol, metronidazole
Lysis & Excision of Adhesions- with microsurgery