Immunology intro flash cards 1/6
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Immunology
Study of a host's reactions to foreign substances
Antigens
Foreign substances that induce a host response• Examples: pollen proteins, components of bacterial pathogens
Immunity
condition of being resistant to infection
Attenuation
Pathogens made less virulent through heat, aging, or chemical treatment
Examples of attenuated vaccines
chickenpox, smallpox, MMR, yellow fever
Innate Immunity
Natural immunity, ability to resist infection through normally present body functions, Nonspecific, Prior exposure not required, effect is immediate, memory not generated
Adaptive Immunity
Characterized by specificity for each antigen, memory is generated
Where are leukocytes found, and name all types
Found in peripheral blood
• Neutrophils• Eosinophils• Basophils• Monocytes• Lymphocytes
Where do all WBC originate from?
HSC in the bone marrow
What precursors does HSC give rise to?
Common Myeloid Precursors (CMP) and Common Lymphoid Precursors (CLP)
CMP's develop into WBC's that perform______
Phagocytosis
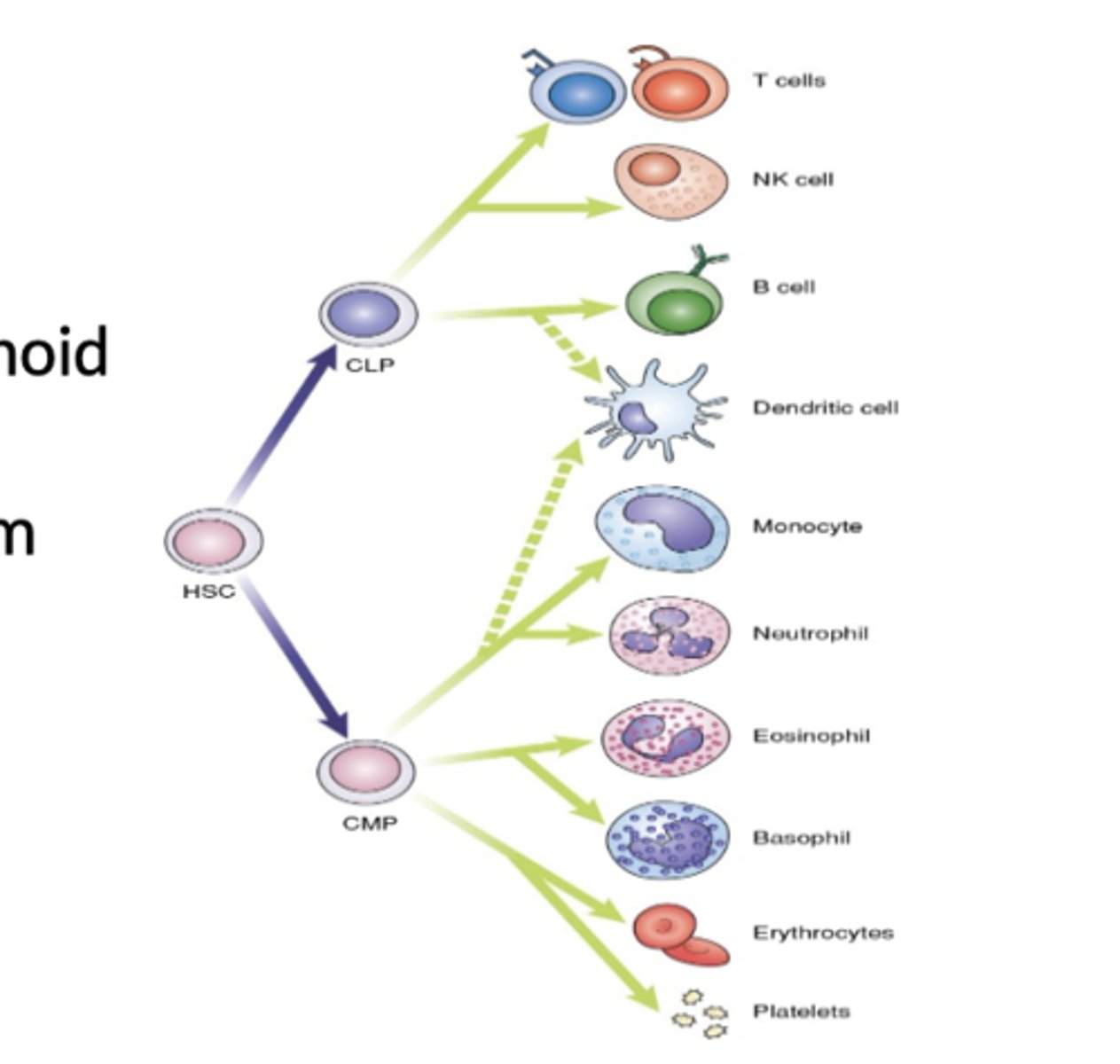
CLP's develop into _______
Lymphocytes
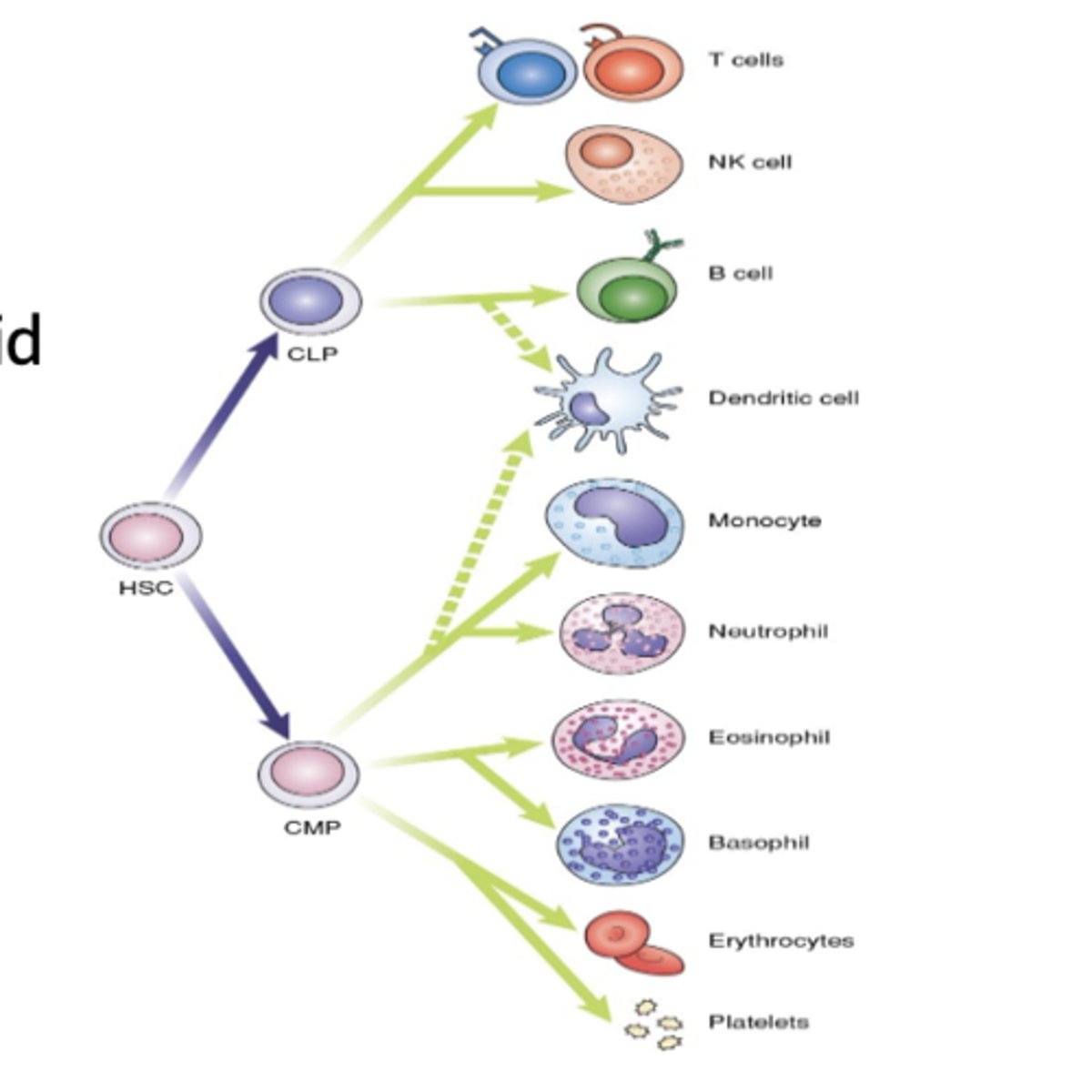
Does dendritic cell come from CMP or CLP?
Both common myeloid and lymphoid precursors
Name Cells of Innate Immune System
PMNs, Monocytes, Macrophages, Mast cells, Dendritic cells.

What are the Polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) and what does PMNs means?
Neutrophils, Eosinophils, and Basophils
Multi-lobed and granular cytoplasm

What are the tissue cells of the innate immune system ?
• Macrophages• Mast cells• Dendritic cells

What compromises 50-70% of WBC in peripheral blood?
Neutrophils
What is the primary function of Neutrophils
Phagocytosis and destruction of foreign particles
What are the nucleus and granules like for neutrophils?
Multi-lobed nucleus and neutral staining granules in cytoplasm
What compromises 1-4% of WBC in peripheral blood
Eosinophils
What are the functions of eosinophils?
• Phagocytosis
• Neutralization of products released in allergic reactions
• Killing of parasites
• Release of cytokines
What are the nucleus and granules like for eosinophils?
Contain a bilobed or ellipsoidal nucleus and red-orange cytoplasmic granules
What is the least abundant WBC
Basophils
What are the functions of basophils?
Release histamine and other granular contents, which induce and maintain allergic reactions
What are the nucleus and granules like for basophils?
Contain a bilobed nucleus and deep blue-purple cytoplasmic granules
What compromises 2-10% of circulating WBC
Monocytes
Where are Monocytes located?
Peripheral blood
What is a macrophage?
Originate from monocytes that have migrated to the tissues
What are the nucleus and granules like for monocytes ( and macrophages) ?
Large cells with a horseshoe-shaped nucleus, dull grayish blue cytoplasm ,and fine granules
What are the Macrophages innate immune functions?
• Phagocytosis and microbial killing
• Anti-tumor cell activity
• Intracellular parasite eradication
• Secretion of cell mediators
What are the Macrophages adaptive immune functions?
• Process and present antigens to T cells
• Produce cytokines that regulate immune responses
What do Mast Cells resemble ?
Basophils, but come from a different lineage
Where is Mast Cells present and what are the functions?
Tissues
Induce and maintain allergic reaction
Is dendritic cell adaptive or innate immunity?
Both adaptive and innate immunity
What is the most potent phagocytic cell
Dendritic cell
What is the most effective antigen presenting cell?
Dendritic cell
What are the cells of adaptive immune system
Lymphocytes
What represents 20-40% of circulating WBC
Lymphocytes
What are the types of Lymphocytes
T cells, B cells, NK cells
What are the nucleus and granules like for lymphocytes?
Small cells with a large, round nucleus, and sparse, light blue cytoplasm
Where do B cells mature?
Bone Marrow
When do B cells differentiate into plasma cells?
After contacting antigen
Where do T cells mature?
Thymus and all are CD3+
What do plasma cells secrete?
Antibodies (immunoglobulins)
What are the different subtypes of T Cells and Functions?
Helper T (CD4+)- produce cytokines that stimulate B cells in antibody production, and assist other T cells in cell mediated immunity
Regulatory T cells(CD4+) - inhibit immune response ( helps prevent auto-immune disease)
Cytotoxic T cells(CD8+) - destroy tumor cells and virus infected cells
What is a major type of innate immune cell (ILC) ?
NK cell
What are the features and functions of NK cells?
Large cells with kidney shaped nuclei and granular cytoplasm
Kill virus infected cells and tumor cells without needing prior exposure
Destroys antibody coated target cell
Positive for CD16 and CD56
What are the primary lymphoid organs?
Bone marrow and Thymus
What are the secondary lymphoid organs?
• Spleen
• Lymph nodes
• Mucosal associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)
• Cutaneous associated lymphoid tissue (CALT)
What do the secondary lymphoid organs function as?
Sites for contact with foreign antigens
What is the largest secondary lymphoid organ and what pulps does it have ?
Spleen has white pulp and red pulp
What is the red pulp
Rich with macrophages and destroys old RBC
What is white pulp?
• 20% total weight of spleen
• Contains lymphoid tissue arranged around arterioles in a periarteriolar lymphoid sheath containing T cells
• B cells are in follicles attached to the sheath
Where are lymph nodes located and what do they do ?
• Along lymphatic ducts, especially near joints and where arms and legs join the body
• Collect lymph from adjacent tissues
Where do lymphocytes and foreign antigens enter
Via afferent lymphatic vessels
Where are B lymphocytes and T cells located in a lymph node
• B lymphocytes are located in follicles within cortex
• T cells are mainly in the paracortex
Where is MALT found?
• Found on mucosal surfaces of the gastrointestinal, respiratory, and urogenital tracks
CALT is for ?
T cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells found on skin