Unit 2- Cell Structures and Processes AP BIO
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
if ur in Mr Doziers class, good luck ❤️ NOT DONE YET
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Which are larger Eukaryotic Cells or Prokaryotic Cells?
Eukaryotic Cells
What structures do ALL cells have?
Plasma Membrane (made up of phospholipids)
Cytosol (semi-fluid layer and has ribosomes)
Cytoplasm
Organelles
Chromosomes
Ribosomes
Where is most of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell?
The Nucleus
What encloses the nucleus, separating it from cytoplasm?
The Nuclear Envelope
What is the nuclear envelope made out of?
Phospholipid bilayer, and protein complexes
What is inside the nucleus?
The nucleolus
What does the nucleolus do?
Involved in synthesis of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and assembly of ribsomes
What are ribosomes made out of?
Ribosomes are complexes made of ribosomal RNA and protein
What is the structure of a ribosome?
A large subunit and a smaller subunit

How do ribosomes synthesis proteins?
The ribosomes use the information give by DNA to make proteins
Where to ribosomes carry protein synthesis?
2 places
- In the Cytosol with free ribosomes
-On the outside of Endoplasmic reticulum or the nuclear envelope
Where is the Endoplasmic Reticulum?
Near the cell’s nucleus, along the nuclear envelope
What is the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
A large, interconnected networks of membranes (accounts for most membranes in the cell) that is involved in synthesizing proteins, lipids, and distributing other molecules
What is the difference between Smooth ER and Rough ER
Smooth ER has NO ribosomes, while Rough ER has bound ribosomes, differs in what the ribosome produces
What does the Smooth ER control?
Synthesizes lipids
Metabolizes carbohydrates
Stores calcium
Detoxifies poison
What does the Rough ER control?
Produces proteins and membranes
What does Golgi Apparatus do?
A cell organelle that modifies, sorts, and packages, proteins and lipids into vesicles for transport to other parts of the cell or outside the cell (think of it as a shipping center)
What are transport vesicles and where can you find them?
Transport vesicles are sacs that transport different molecules to different places, you can find them in the ER and Golgi.
What do the modifications given by the Golgi proteins determine?
Function such as (Folding, and Stability)
Target
What is glycosylation?
Carbohydrate is attached to a functional group on the protein.
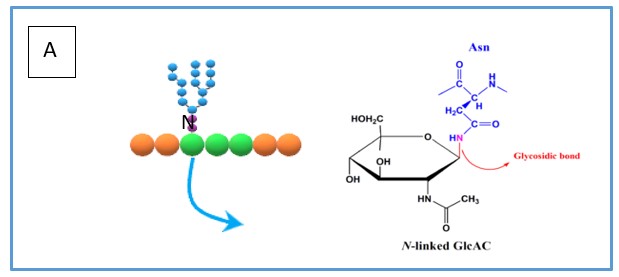
What are Lysosomes?
Membranous sacs of hydrolytic enzymes
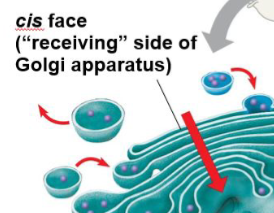
What is the “cis face” of the Golgi apparatus?
The cis face is the receiving side of Golgi apparatus
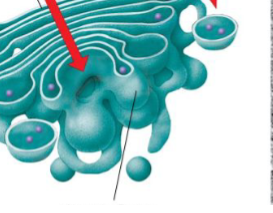
What is the trans face of the Golgi apparatus?
“shipping” side of Golgi Apparatus
What is autophagy?
Autophagy is a cellular process in which the body breaks down and recycles its own damaged or unnecessary components such as old cell compenents like proteins and organelles.
What are vacuoles?
membrane-bound sacs with varied functions
What are the various functions of the vacuoles?
Food vacuoles
Contractile vacuoles
Central vacuoles
What are food vacuoles and how are the formed?
Food vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles found in some eukaryotic cells, such as protists, that hold food particles for digestion. These formed by autophagy when a cell consumes a food molecules and the cell membrane bends inwards and pinches off to form a vacuole.
Difference between flagella and cillia?
Cillia are short anchored, numerous, hairlike
What do plants cells have ONLY?
Cell Walls
Chloroplasts
How does Cytoplasmic Streaming work?
Movement proteins move cytoplasm around cell
What are contractile vacuoles do?
A contractile vacuoles expel water from the cell
What are vesicles?