First Aid USMLE Step 1: Cardiovascular
1/556
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
557 Terms
Truncus arteriosus gives rise to __________.
Ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk
Bulbus cordis gives rise to __________.
Smooth parts (outflow tract) of left and right ventricles
Endocardial cushion gives rise to?
Atrial septum ,membraneous interventricular septum; AV & semilunar valves
Primitive atrium gives rise to __________.
Trabeculated (muscular) portions of the left and right atria
Primitive ventricle gives rise to __________.
Trabeculated (muscular) portions of the left and right ventricles
Primitive pulmonary vein gives rise to __________.
Smooth part of the right atrium
Left horn of sinus venosus gives rise to __________.
Coronary sinus
Right horn of sinus venosus gives rise to __________.
Smooth part of the right atrium (sinus venarum)
Right common cardinal vein and right anterior cardinal vein gives rise to __________.
Superior vena cava (SVC)
When does the heart beat begin to beat spontaneously?
-4 weeks of development
-First functional organ in vertebrate embryos
What is cardiac looping?
-Primary heart tube loops to establish left-right polarity; begins in week 4 of gestation.
Defect in left-right dynein (involved in L/R asymmetry) can lead to___________, as seen in Kartagener syndrome (primary ciliary dyskinesia).
Dextrocardia
What is a foramen/ostium?
opening
What is a septum?
wall
Septation of atria (7 Steps)
1. Septum primum grows toward endocardial cushions, narrowing foramen primum.
2. Foramen secundum forms in septum primum (foramen primum disappears).
3. Septum secundum develops as foramen secundum maintains right-to-left shunt.
4. Septum secundum expands and covers most of the foramen secundum. The residual foramen is the foramen ovale.
5. Remaining portion of septum primum forms valve of foramen ovale.
6. (Not shown) Septum secundum and septum primum fuse to form the atrial septum.
7. (Not shown) Foramen ovale usually closes
soon after birth because of increased LA pressure.
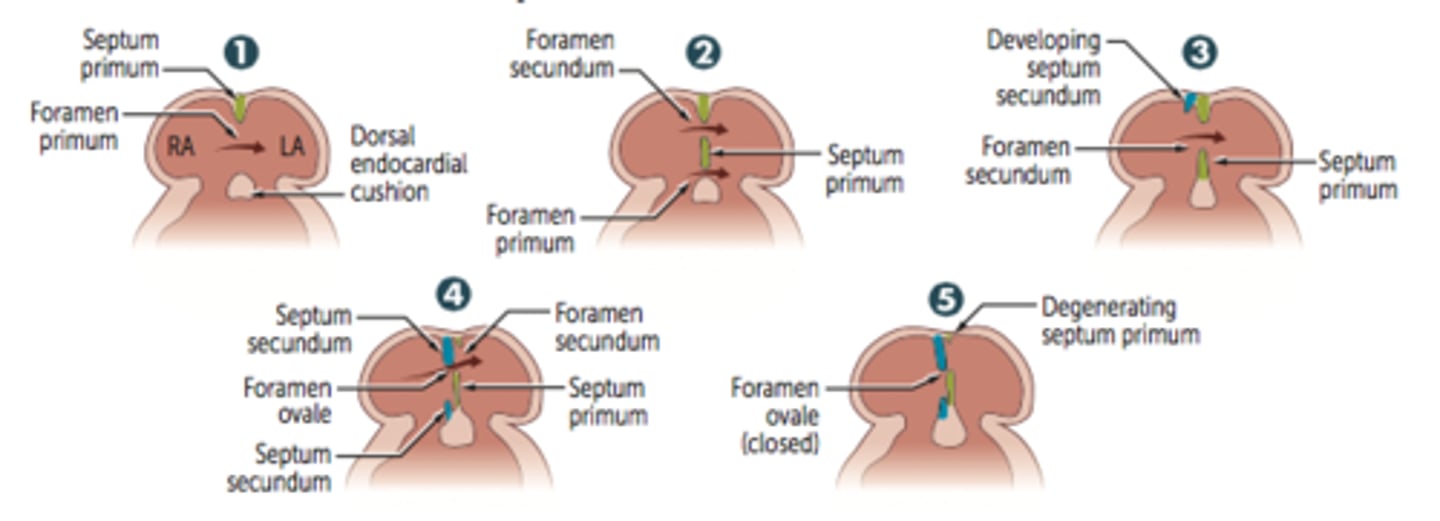
Patent foramen ovale is caused by a failure of __________ and ___________ to fuse after birth. What can this lead to?
-Caused by failure of septum primum and septum secundum to fuse after birth; most are left untreated.
-Can lead to paradoxical emboli (venous thromboemboli that enter systemic arterial circulation), similar to those resulting from an ASD.
Septation of the ventricles (3 steps)
1. Muscular ventricular septum forms. Opening is called interventricular foramen.
2. Aorticopulmonary septum rotates and fuses with muscular ventricular septum to form membranous interventricular septum, closing interventricular foramen.
3. Growth of endocardial cushions separates atria from ventricles and contributes to both atrial septation and membranous portion of the interventricular septum.
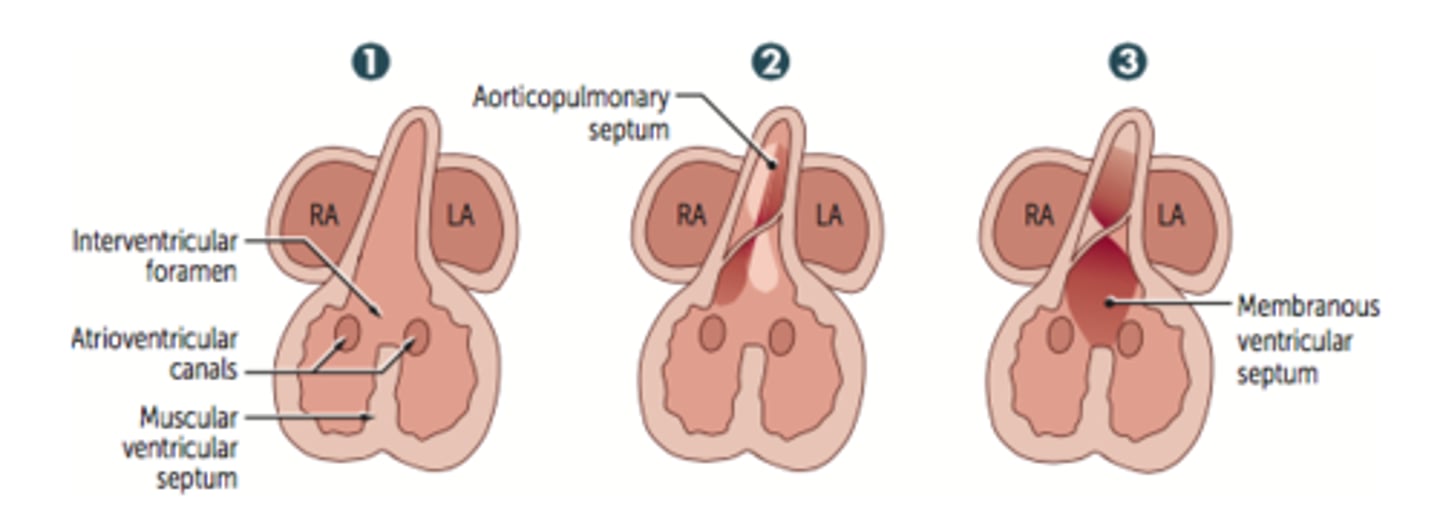
What is the most common congenital cardinal anomaly?
VSD
Most common location of VSD?
The membranous septum
Outflow tract formation
Truncus arteriosus rotates; neural crest and endocardial cell migrations cause truncal and bulbar ridges that spiral and fuse to form aorticopulmonary septum to form ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk.
What are the conotruncal abnormalities associated w/ failure of neural crest cells to migrate?
Transposition of the greta vessels
Tetralogy of Fallot
Persistent truncus arteriosus
Aortic/pulmonary valves are derived from ____________.
The endocardial cushions of outflow tract.
Mitral/tricuspid valves are derived from __________.
Fused endocardial cushions of the AV canal.
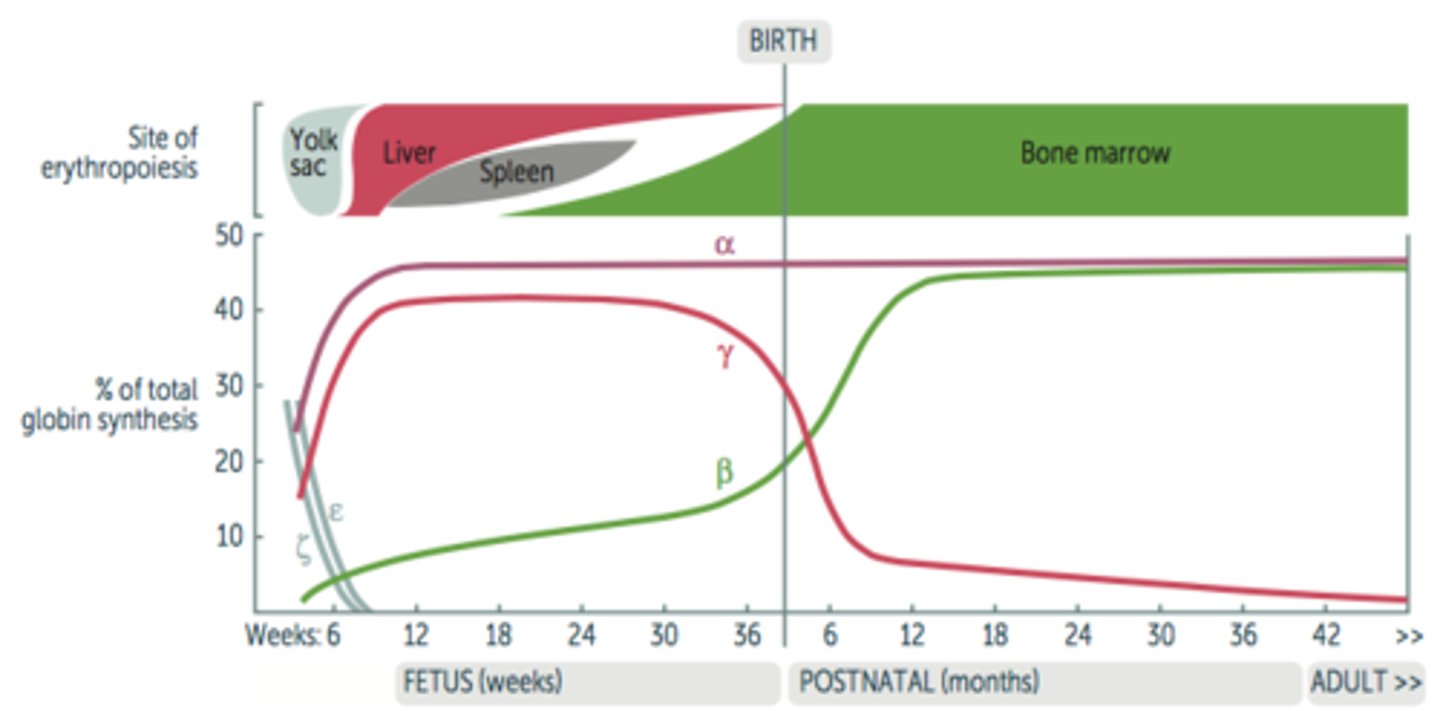
Fetal erythropoiesis occurs in ___________?
-Yolk sac (3-8 weeks)
-Liver (6 weeks-birth)
-Spleen (10-28 weeks)
-Bone marrow (18 weeks to adult)
Hemoglobin development
-Embryonic globins: ζ and ε.
-Fetal hemoglobin (HbF) = α2γ2.
-Adult hemoglobin (HbA1) = α2β2.
-HbF has higher affinity for O2 due to less avid binding of 2,3-BPG, allowing HbF to extract O2 from maternal hemoglobin (HbA1 and HbA2) across the placenta.
Fetal circulation diagram

Blood in umbilical vein has a Po2 of _________ and is ________ saturated with O2.
≈ 30 mmHg, ≈ 80%
Umbilical arteries have _____ O2 saturation.
Low
3 important shunts
1. Ductus venosus
2. Foramen ovale
3. Ductus arteriosus
Ductus venosus
Blood entering fetus via placenta through the umbilical vein is conducted via the ductus venosus into the IVC, bypassing hepatic circulation.
Foramen ovale
Most of the highly oxygenated blood reaching the heart via the IVC is directed through the foramen ovale and pumped into the aorta to supply the head and body.
Ductus arteriosus
Deoxygenated blood from the SVC passes through the RA -> RV -> main pulmonary artery through patent ductus arterioles -> patent descending aorta; shunt is due to high fetal pulmonary artery resistance (due partly to low O2 tension).
Closure of foramen ovale
At birth, infant takes a breath; decreased resistance
in pulmonary vasculature (d/t a decrease in intra-thoracic pressure from the baby taking a breath) -> increased left atrial pressure vs. right atrial pressure (d/t increase in blood entering the pulmonary artery & more blood returning to the LA); foramen ovale closes (now called fossa ovalis);
Closure of ductus arteriosus
Increase in O2 (from respiration) and decreaese in prostaglandins (from placental separation) causes closure of ductus arteriosus.
________ helps close a PDA
Indomethacin
__________ keeps the PDA open.
PGE1 and PGE2
**Prostaglandins dilate vessels
"E1 & E2 kEEp PDA open"
What is the remnant of the ductus arteriosus called
ligamentum arteriosum
What becomes of the allaNtois-> urachus
MediaN umbilical ligament
Urachus is part of what?
Urachus is part of allantoic duct between bladder and umbilicus
What is the adult remnant of the ductus arteriosus?
Ligamentum arteriosum
What is the adult remnant of the ductus venosus?
Ligamentum venosum
What is the adult remnant of the foramen ovale?
Fossa ovale
What is the adult remnant of the Notochord?
Nucleus pulposus
What is the adult remnant of the umbiLical arteries?
MediaL umbilical ligaments
What is the adult remnant of the umbilical vein?
Ligamentum teres hepatis
Tunica intima
-Innermost layer of the wall of a blood vessel
-In contact with blood
-Composed of endothelium (simple squamous epithelium), subendothelium (loose connective tissue), and (maybe) an internal elastic lamina (IEL)
-Endothelium provides very smooth surface
-Subendothelium is the "glue"
-Where the fat/cholesterol deposits in atherosclerosis
Tunica media
-Middle layer of blood vessel wall
-Primarily contains circularly arranged smooth muscle cells (*except in elastic artery where elastic lamina/fibers dominates)
-Contraction of smooth muscle cells changes the diameter of the vessel and affect the blood pressure
Tunica adventitia
-Outer layer of blood vessel wall
-A layer of c.t. containing collagen and elastic fibers
-In large and medium veins it contains longitudinal smooth muscle fibers
-Small blood vessels called vasa vasorum may be present
Internal elastic lamina
-A layer of elastic tissue that forms the outermost part of the tunica intima of blood vessels. It separates tunica intima from tunica media
External elastic lamina
A layer of elastic connective tissue lying immediately outside the smooth muscle of the tunica media of an artery
Coronary Artery Anatomy (Pic!)
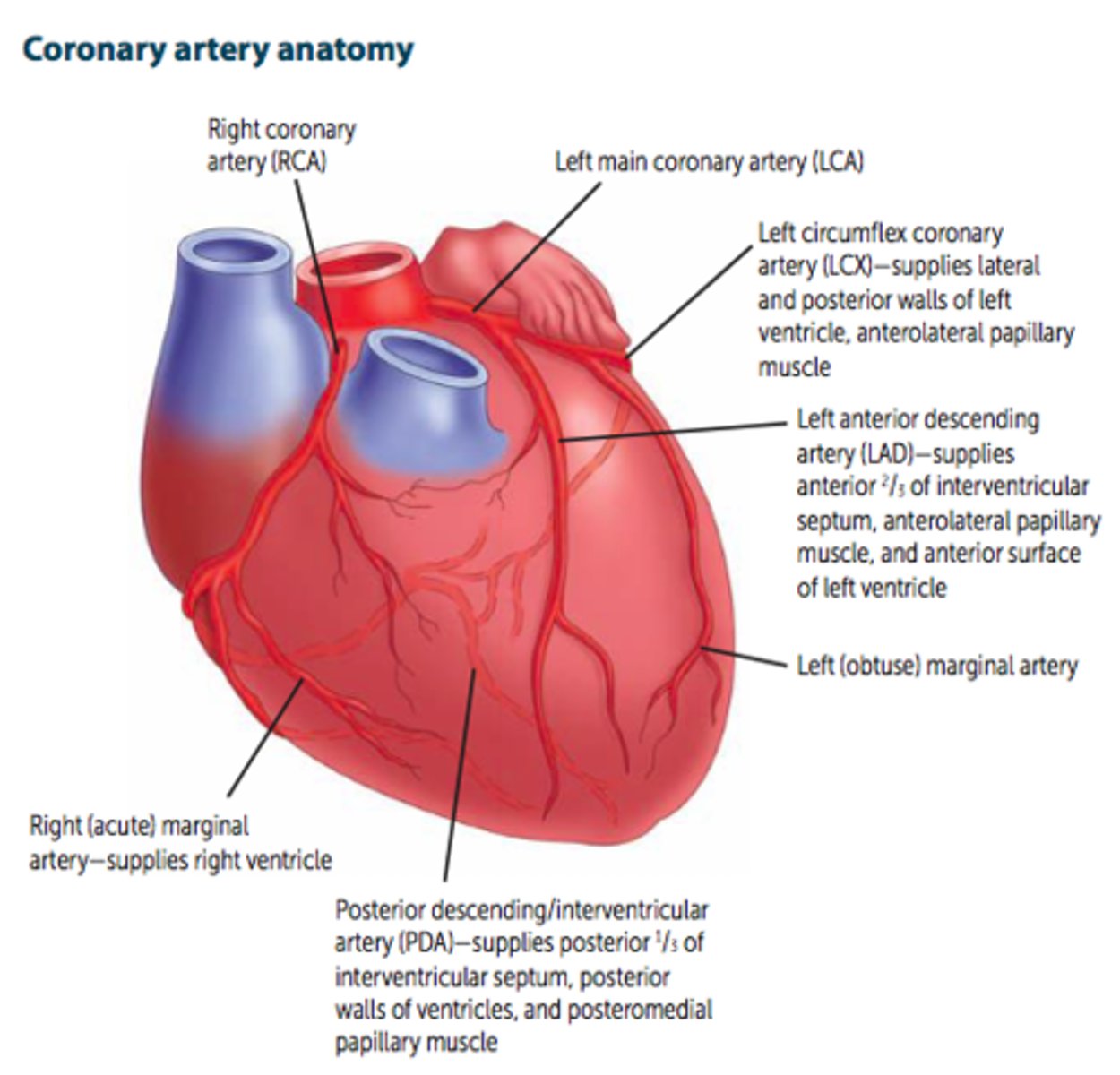
SA and AV nodes are usually supplied by _____.
RCA
Infarct of blood supply to SA and AV nodes may cause _____________.
Nodal dysfunction (bradycardia or heart block).
The coronary arteries arise from _________.
The aorta
3 main branches of the left main coronary artery (LCA)
Left circumflex artery (LCX), left anterior descending artery (LAD), & Left (obtuse) marginal artery
The left circumflex artery (LCX) supplies what?
Lateral and posterior walls of left ventricle, anterolateral papillary muscle
The left anterior descending artery (LAD) supplies what?
The anterior 2/3 of the interventricular septum, anterolateral papillary muscle, and anterior surface of the left ventricle
"Widow-Maker"
Branches of the Right Coronary Artery (RCA)?
Right (acute) marginal artery and the posterior descending/interventricular artery (PDA)
What does the right (acute) marginal artery supply?
Right ventricle
What does the posterior descending/interventricular (PDA) artery supply?
The posterior 1/3 of the IV septum, posterior walls of the ventricles, and the posteromedial papillary muscle
What is right-dominant circulation?
PDA arises from RCA (occurs 85% of the time)
"most people are right-handed"
What is left-dominant circulation?
PDA arises from LCX (occurs 8% of the time)
What is co-dominant circulation?
PDA arises from both RCA & LCX (occurs 7% of the time)
Coronary artery occlusion most commonly occurs in the ____.
LAD
Coronary blood flow peaks in ________.
Early diastole
What is the most posterior part of the heart?
Left atrium
Enlargement of the left atrium can cause?
Dysphagia due to compression of the esophagus and/or hoarseness due to compression of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve (a branch of the vagus)
What are the 3 layers of the heart?
1) endocardium (lines chambers of heart)
2) myocardium (muscle-layer)
3) pericardium (outside-layer of heart)
What are the 3 layers of the pericardium (from outer to inner)?
Fibrous pericardium
Parietal layer of serous pericardium
Visceral layer of serous pericardium
Where is the pericardial cavity located?
Between the parietal & visceral layers
What is the Transverse Pericardial Sinus?
Spot in body where finger can be passed through posterior to the aorta & pulmonary trunk & anterior to the SVC.
Cardiac output using Fick principle
rate of O2 consumption/(arterial O2 content - venous O2 content)
Cardiac output (CO) =
stroke volume (SV) × heart rate (HR).
Definition of CO?
Volume of blood pumped put out of heart in 1 minute
Definition of SV?
Amount of blood pumped out of heart w/ each heart beat
Features of lymphatic vessel system
-Function: collect and drain interstitial fluid from the tissue into the large veins (subclavian veins) of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic vessels, and lymphatic ducts
-Lymphatic vessels can be found in most of the tissues of the body except the CNS, the bone marrow, and the hard tissues (cartilages, bones, and the hard tissues of the teeth)
Mean arterial pressure (MAP) =
1) CO x total peripheral resistance (TPR) AKA (P=Q*R)
2) 2/3 diastolic Pressure + 1/3 systolic Pressure
"MAP is mainly used to find Diamonds"
Pulse pressure =
systolic - diastolic pressure
Pulse pressure is proportional to ____, inversely to __________.
SV, compliance of aorta
**If the aorta becomes rigid (decreased compliance) in conditions such as arteriosclerosis or atherosclerosis, the pulse pressure would be very high
Another formula for SV?
EDV - ESV
What is EDV?
volume of blood in heart at its fullest
What is ESV?
volume of blood left in ventricle after heart pumps
During the early stages of exercise, CO is maintained by _____ and _____?
Increase HR, increased SV
During late exercise, CO is maintained by ________.
HR only
SV plateaus
What stage of the cardiac cycle is altered most with increased HR? Why is this?
Diastole
Less filling time -> decreased CO (i.e. ventricular tachycardia & A-fib)
Conditions that cause an increased Pulse Pressure
hyperthyroidism, aortic regurgitation, aortic stiffening (isolated systolic HTN in elderly), obstructive sleep apnea (increases sympathetic tone), exercise (transient)
Conditions causing decreased pulse pressure
Aortic stenosis, cardiogenic shock, cardiac tamponade, advanced heart failure (HF)
What causes an increase SV?
-Increased contractility (e.g., anxiety, exercise)
-Increased preload (i.e. early pregnancy, exercise-> d/t muscle contraction pushing more blood up to the heart, increased blood volume)
-Decreased afterload
"SV CAP"-> Stroke Volume affected by Contractility, Afterload & Preload
A failing heart has _____ SV.
Decreased
Contractility (and SV) increase with?
-Catecholamines (inhibition of phospholamban (inhibitor of cardiac muscle SR ATPase-> increased activity of Ca2+ pump in SR)
-Increased intracellular Ca2+
-Decreased extracellular Na+ (decreased activity of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger)
-Digitalis (blocks Na+/K+ pump -> increased intracellular Na+ -> decreased Na+/Ca2+ exchanger activity -> increased intracellular Ca2+)
Contractility (and SV) decrease with?
-β1-blockade (decrease cAMP)
-HF with systolic dysfunction
-Acidosis
-Hypoxia/hypercapnia (decrease Po2/ increase Pco2)
-Non-dihydropyridine Ca2+ channel blockers
What increases myocardial oxygen demand?
-Increased Contractility
-Increased Afterload
-Increased heart Rate
-Increased Diameter of ventricle (increased wall tension)
"myoCARDial"
Wall tension follows Laplace's law. What is Laplace's Law?
Wall tension = (pressure x radius)/ (2 x wall thickness)
What is Preload
amount of blood you are pushing into your ventricles
What is Preload approximated by?
Preload approximated by ventricular EDV; depends on venous tone and circulating blood volume.
What decreases preload?
VEnodilators (e.g., nitroglycerin)= decrease prEload
**This is because the dilation of the veins causes a pooling of blood in the venous system instead of reaching the heart
What is Afterload?
Pressure coming back at the heart
What is Afterload approximated by
-Afterload is approximated by MAP
-Increased afterload -> increased pressure -> increased wall tension per Laplace's law
_____ compensates for increased afterload by ________ in order to decrease wall tension.
LV, hypertrophy (thickening)
What decreases afterload?
VAsodilators (e.g., hydrAlAzine) decreases Afterload (Arterial)
**This decreases pressure back on the aorta