Unit 5
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Photolysis
light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and splits water into oxygen, H+ and e-
H+ accepted by NADP to form reduced NADPH to be used in light dependent
oxygen used for respiration or diffuses out
Photoionisation of chrorophyll (stg 1 of LDR)
light energy absorbed by chlorophyll
energy results in electrons becoming excited, raising energy level causing them to leave the chlorphyll
some energy released used to make atp and reduced NAD
Chemiosmosis (stage 2 of LDR)
electrons accepted by electron transport chain and are transported along a series of proteins in thylakoid membrane
as they do so they release energy
energy used to pump protons into THYKALOID FROM STROMA by active transport
high concentration of protons in THYKALOID LUMEN so there is an electrochemical gradient
the H+ travel back into the stroma through the only channel protein they can bind to - ATP synthase
on the stroma side of the membrane, the protons combine with NADP to reduce it
Where does the calvin cycle occur?
Chloroplast stroma
Calvin cycle steps
carbon dioxide reacts with ribulose bisphosphate catalysed by rubisco to form 6C molecule
6C molecule splits into two molecules of GP
the GP is REDUCED to form triose phosphate requires energy from ATP
accepts electrons from NADP
Some triose phosphate is used to produce useful organic substances like glucose
the rest of the TP is used to regenerate RuBP using energy from ATP
Role of ATP for light independent
provides energy to reduce GP into TP
provides energy to regenerate RuBP
Limiting factors of photosynthesis- why does each factor limit
Carbon dioxide is a reactant for the light independent stage of photosynthesis calvin cycle
light is needed in photolysis and photoionisation
Glycolysis location
Occurs in cytoplasm
Glycolysis steps
ATP hydrolysis of 2 atp phosphorylates glucose to make it more reactive, unstable so splits into 2
2 Triose phosphate formed
triose phosphate is oxidised to produce pyruvate (3 carbon) this forms 2 molecules of NADH as the electrons are donated to NAD
What are the products of glycolysis
net gain of 2 atp
2 pyruvate
2 reduced NAD
Link reaction location and step
Matrix
pyruvate is oxidised to acetate, loosing hydrogen which is accepted by NAD to become reduced nad
Acetate combines with coenzyme A to produce acetylcoenzyme A
How is NADH and pyruvate transported into the mitochondria from the cytoplasm?
Active transport
What are the products of the link reaction?
2 acetylcoenzyme A molecules
2 co2 released
2 reduced nad produced
Krebs cycle location
Matrix
Krebs cycle steps
AcoA combines with 4C molecule. CoA is released. Produces 6C molecule
Series of redox reactions to reform the 4C molecule which produces:
3 reduced NAD
1 reduced FAD
releases 2 CO2
1 ATP produced by substrate level phosphorylation
Be careful if question is asking for per CYCLE which is this^ or if its per GLUCOSE MOLECULE meaning the cycle two times as two molecules of acetylcoenzyme A are produced
Oxidative phosphorylation steps
in the matrix the reduced co enzymes release protons and electrons
the electrons from this are transported along the electron transport chain, releasing energy
Energy used to actively transport protons into inter membrane space. creates electrochemical gradient, protons move by facilitated diffusion through ATP synthase. adp + pi
OXYGEN is final acceptor of electrons and also accept the hydrogen ions once they pass through, forming water
What is final acceptor of electrons in oxidative phosphorylation?
oxygen, it also picks up hydrogen to form water
How does anaerobic respiration regenerate NAD from pyruvate?
Pyruvate is reduced to form lactate, and NADH is reoxidised to NAD, donating the electrons to pyruvate
this is important as it allows NAD to be used again in glycolysis so it can continue so that some atp is made
What is the downside of anaerobic respiration
-lactate forms lactic acid which can cause muscle fatigue and can denature enzymes/proteins
so cant respire anaerobically for long as the acid will denature the enzymes needed in glycolysis
What are products of anaerobic respiration in microbes?
-ethanol and carbon dioxide
how are other substances used for respiration
ester bionds hydrolysised releasing glycerol and fatty acids
3 carbon glycerol enters glycolysis and is converted into pyruvate
fatty acid molecules are broken down into 2 carbon units, each forms a molecule of AcoA
AcoA then enters the krebs cycle
Protiens
hydrolysed into amino acids in digestion, amino grouo is then removed by damination
Carboxyl group is then processed for example into pyruvate, this varies between amino acids as some can be used as molecules for the krebs cycle
energy levels for proteins are around the same as carbs
how is energy lost between trophic levels
respiration
excretion
GPP and NPP definitions
Gross Primary Production= total chemical energy store in plant biomass
Net primary productivity= chemical energy store in plant after respiratory loss
NPP= GPP- R
Net production of consumers equation
N= I - (F+R)
I= energy in ingested food
f= energy lost in faeces and urine
r= respiratory loss
Which molecules contain nitrogen
Proteins, ATP, nucleic acids
Nitrogen cycle key processes
1) ammonification
nitrification
nitrogen fixation
denitrification
Ammonification (step 1 of nitrogen cycle)
nitrogen fixing bacteria convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium
these live in root nodules or there is free living nitrifying bacteria in the soil
Nitrification (step 2 nitrogen cycle)
nitrifying bacteria oxidise ammonium into nitrites (NO-2) and then further oxidise it into nitrates (NO-3)
Role of decomposers in nitrogen cycle
break down waste produced by animals and organic matter, MUST name the biological molcules- UREA for waste or PROTEINS, DNA for organic matter.
this is known as saprobionic nutrition
converts it into ammonium
What is the effect of lack of oxygen on bateria in nitrogen cycle
anaerobic denitrifying bacteria convert nitrates back into nitrogen gas by denitrification
Where in the phosphorous cycle is phosphate found?
as phosphate ion
in mineral form in sedimentary rocks
What are the role of mycorrhizae in phosphate and N cycle
the fungi increase surface area for water and mineral absorbtion
acts like a sponge for water/minerals around roots
makes plants more drought resistant and can take up more ions
What type of relationship do fungi and plants have for in mycorrizae
Mutualistic.
the plant provides the fungi with carbohydrates
Describe the phosphate cycle
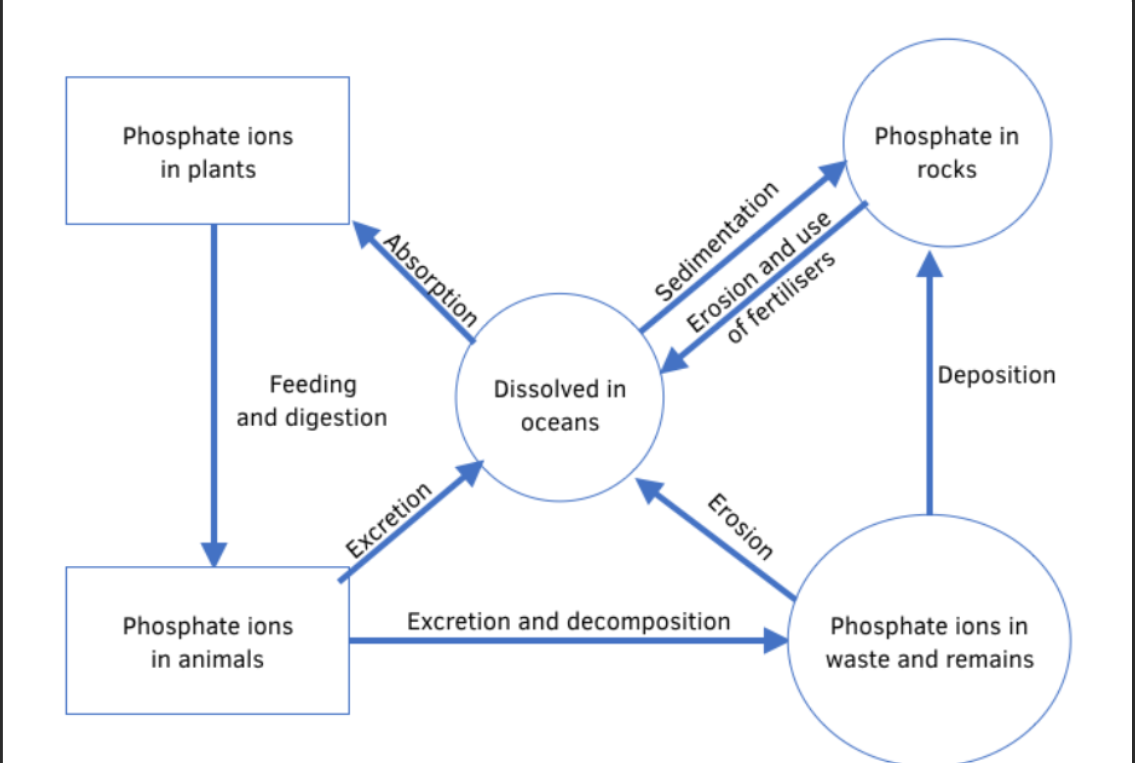
Compare natural fertilisers and
Natural
cheaper, often free as it is animal manure
however doesnt necesserily contain exact minerals needed by that plant
Artificial
Created to contain exact proportions that the plant needs
however inorganic substances are more water soluble- an advantage to the plant absorbing it, but leads to leaching with rainfall
this causes eutrophication if the nitrates enter the ponds or rivers
Explain eutrophicaton
nitrates leached from farming stimulates the growth of algae in pond
created blanket on surface blocking light
plants blow can not photosynthesise and die
bacteria feed and respire on dead plant matter
increase in bacteria using up oxygen in water
eventually other fish and organisms die due to the lack of dissolved oxygen in the water