Pregnancy & Embryonic Development
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
FHA Final Exam Review // Spring 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What does prenatal mean?
Prior to birth
Pre-embryonic development
Fertilization to implantation
Approx 2 weeks
Embryonic development
Implantation to the end of the 8th week of pregnancy
Fetal development
9th week of pregnancy to birth
Prenatal development is known as?
Gestation period (nine lunar months or 40 weeks)
Prenatal development is divided into…
Three, 3-month trimesters:
First trimester
Second trimester
Third trimester
First trimester
Rudiments of all organs appear
Most dangerous period in prenatal life
Only 40% of conceptions survive
1 to 12 weeks
Second trimester
Further development of organs and organ systems
Fetus looks like a human
Fetus is covered by the amnion
Fetus grows faster than the placenta
Third trimester
Phase of rapid growth
Much growth in size and weight
Most organ systems become functional
Most organs are formed but still maturing
Lungs are last to develop
Four events within the 1st trimester:
Cleavage (sequence of cell divisions)
A blastocyst forms
Implantation (implantation into endometrial lining)
Placentation (formation of the placenta)
Embryogenesis (development of the embryo)
First trimester - Implantation
Gastrulation and germ layer formation
The ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm are collectively known as the germ layers
Each layer will form specific tissues and organs of the body
First trimester - Placentation
Placenta develops
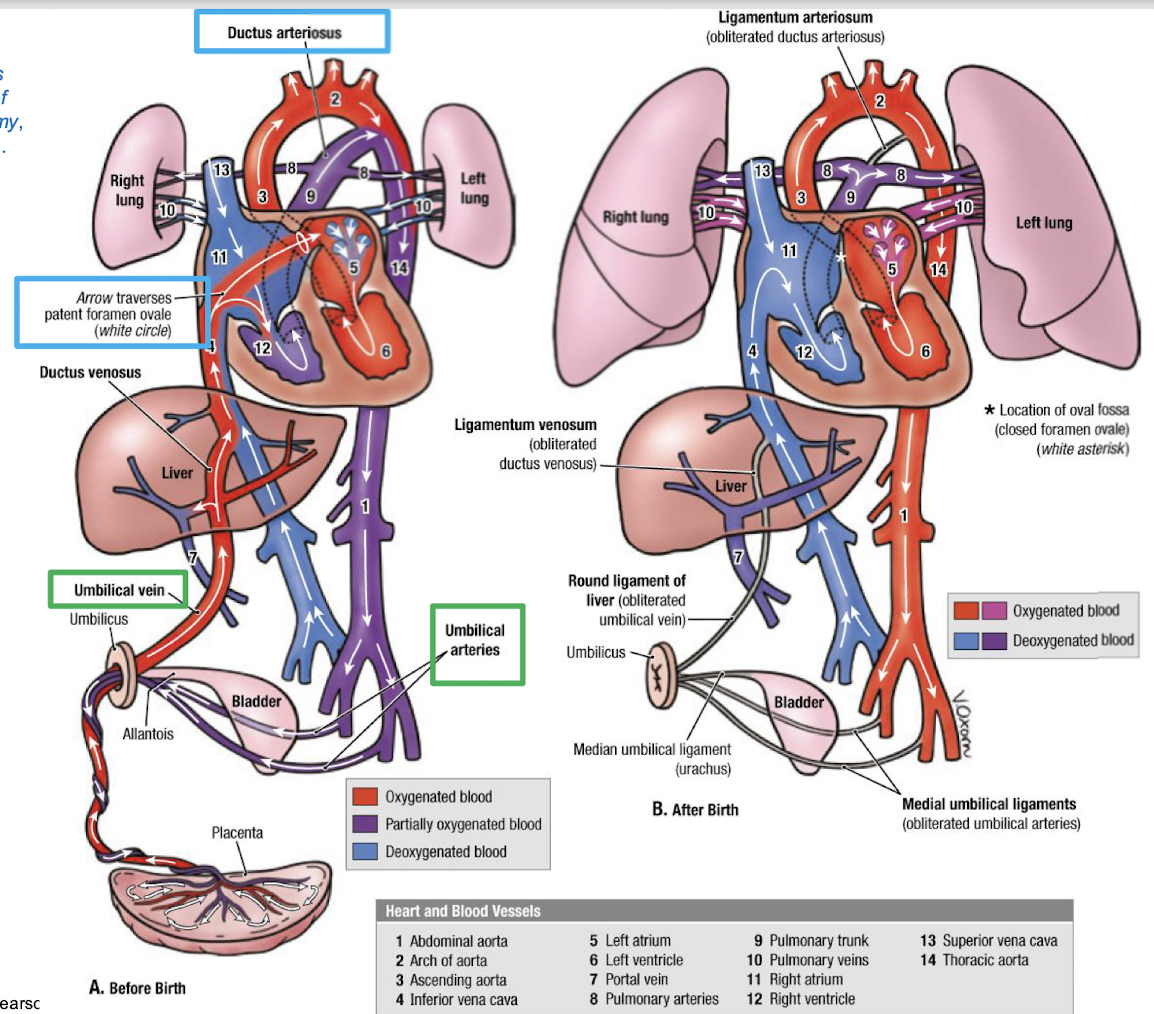
Placental circulation
Blood flows from the fetus to the placenta in the paired umbilical arteries (away from the fetal heart)
Blood returns via a single umbilical vein (fresh oxygenated blood to fetus)
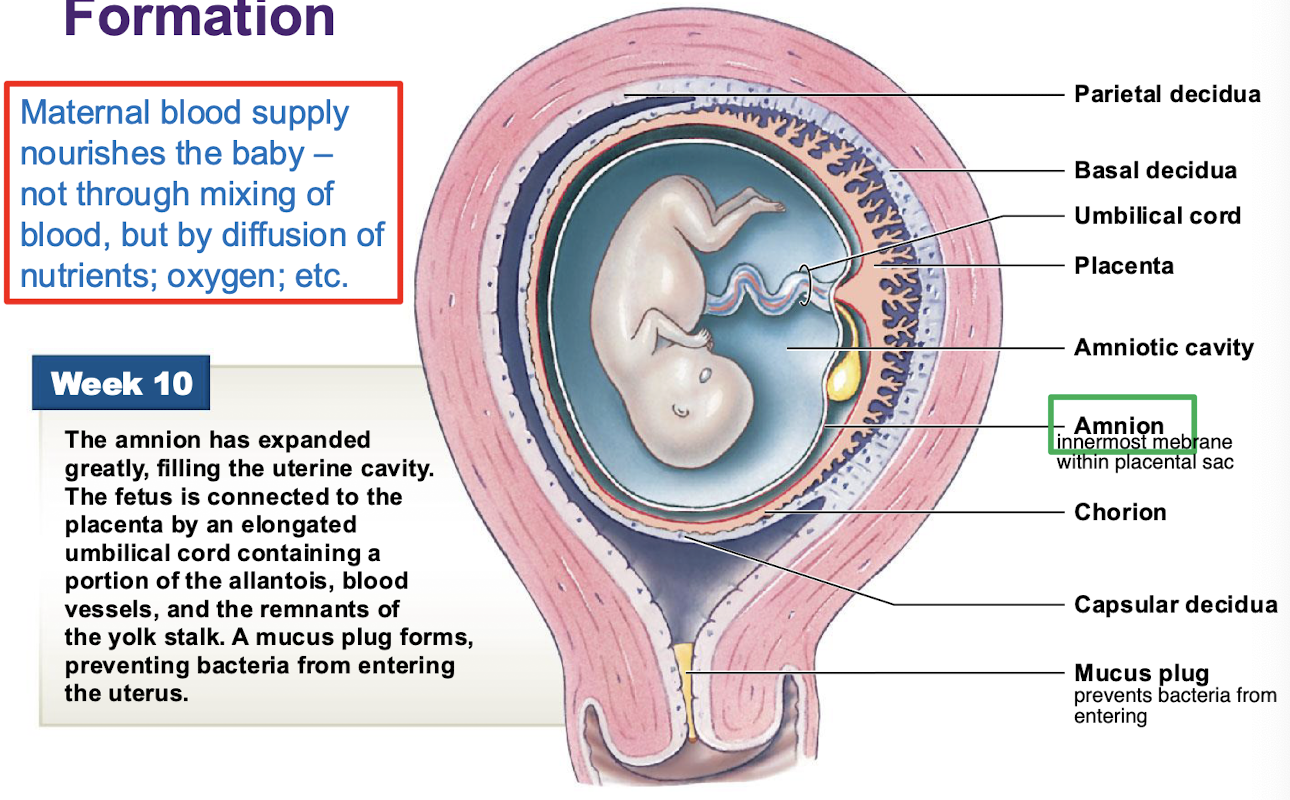
How does the maternal blood supply nourish the baby?
NOT through mixing of blood, but by diffusion of nutrients; oxygen, etc.
Amnion
Innermost membrane within placental sac
First trimester - Embryogenesis
At about 4-8 weeks post-fertilization, organs begin to form
This is called organogenesis
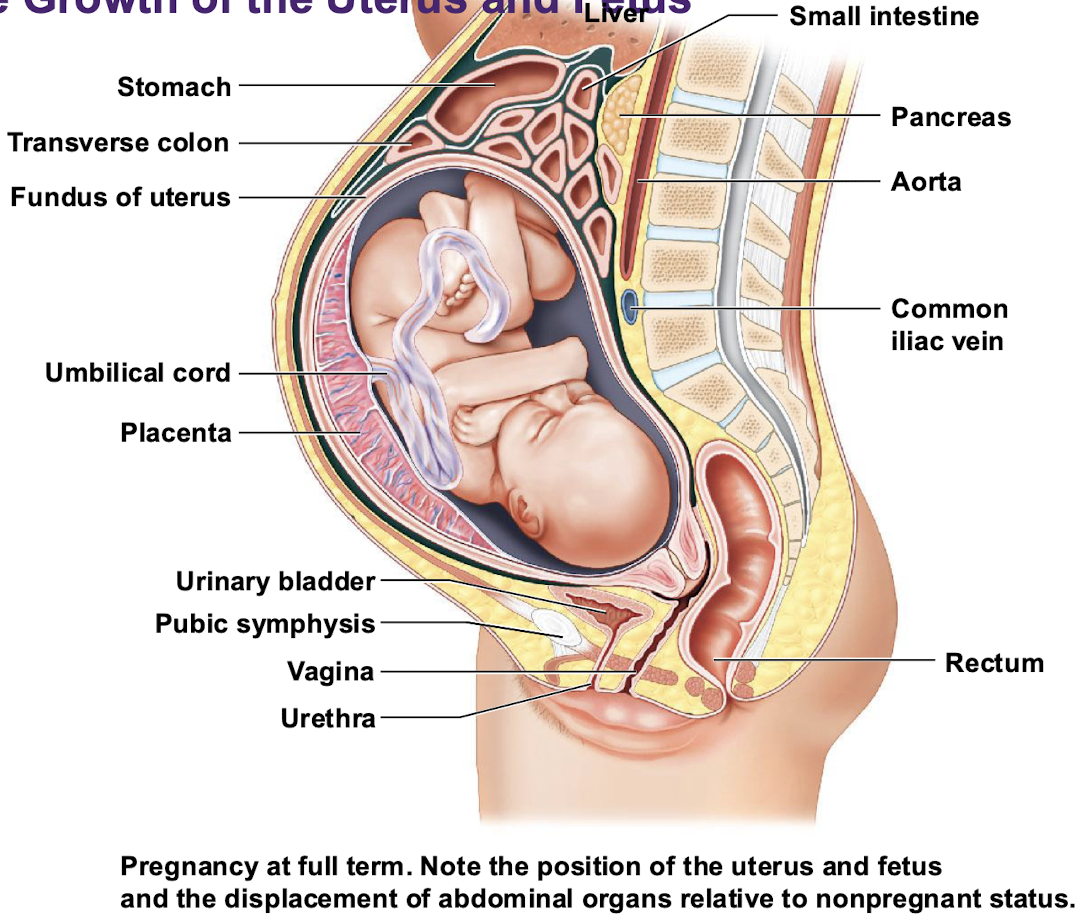
Changes in the uterus during gestation
Uterus will increase in length from 7.5 cm to 30 cm
Contains almost 5 L of fluid
the uterus and contents weigh about 22 pounds
Maternal abdominal organs are pushed out of their normal positions — these organs remain functional but are displaced
What is labor?
A series of strong, rhythmic uterine contractions
What is the goal of labor?
Parturition (expulsion of the fetus)
What are the 3 stages of labor?
Dilation stage
Expulsion stage
Placental stage
What hormone stimulates contraction of the uterus?
Oxytocin
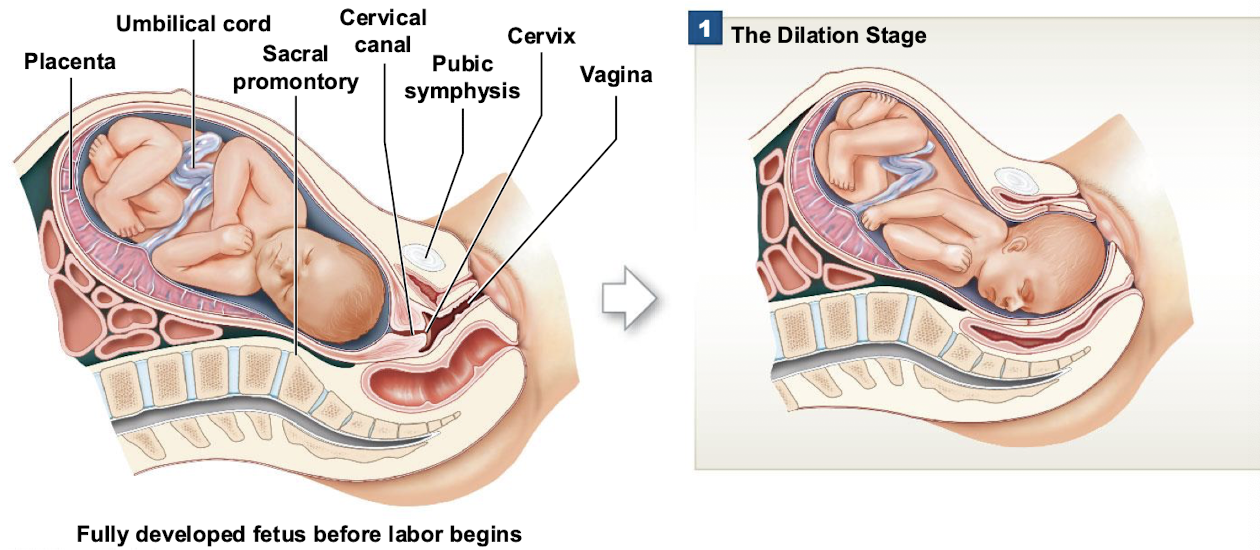
Labor - Dilation Stage
Cervix dilates, the fetus is pushed by muscular contractions into the cervical canal, and the amnion ruptures — water breaking
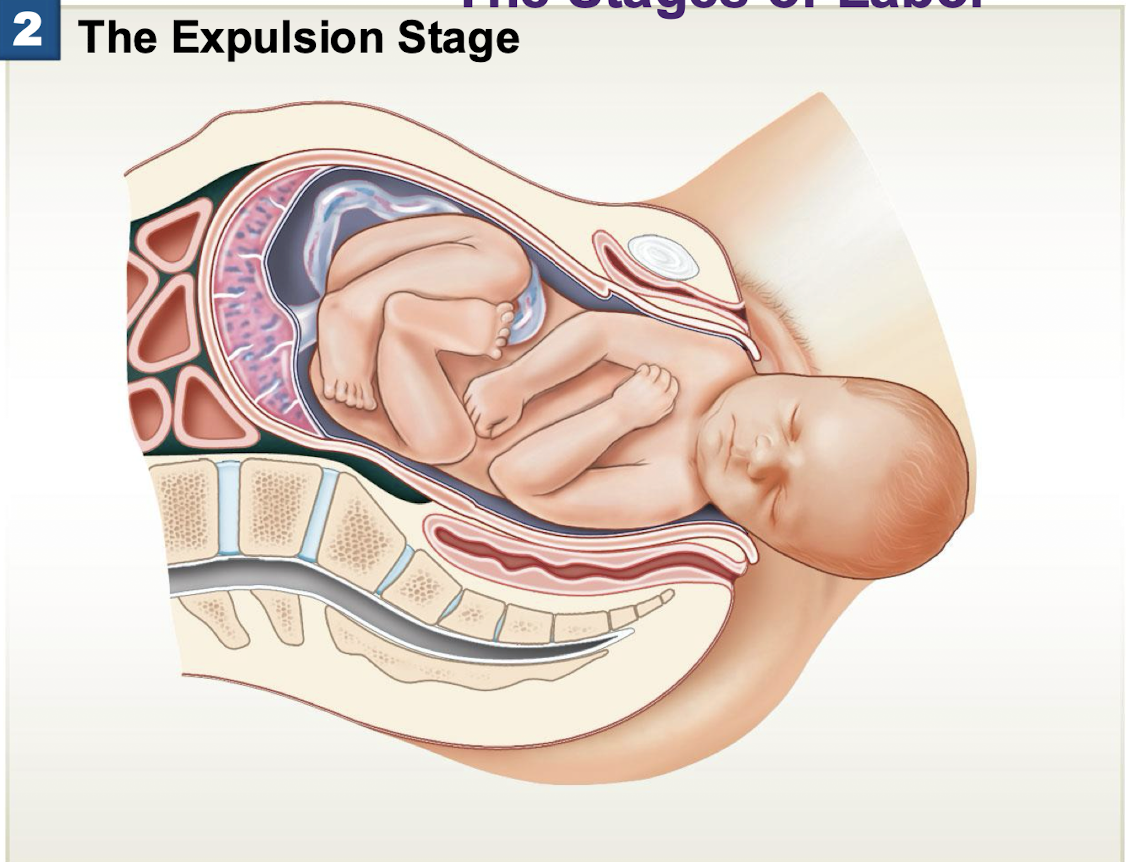
Labor - Expulsion Stage
the movement of the fetus through the cervical canal and vagina
Delivery can be helped by episiotomy (cut between vagina and anus) or cesarian section
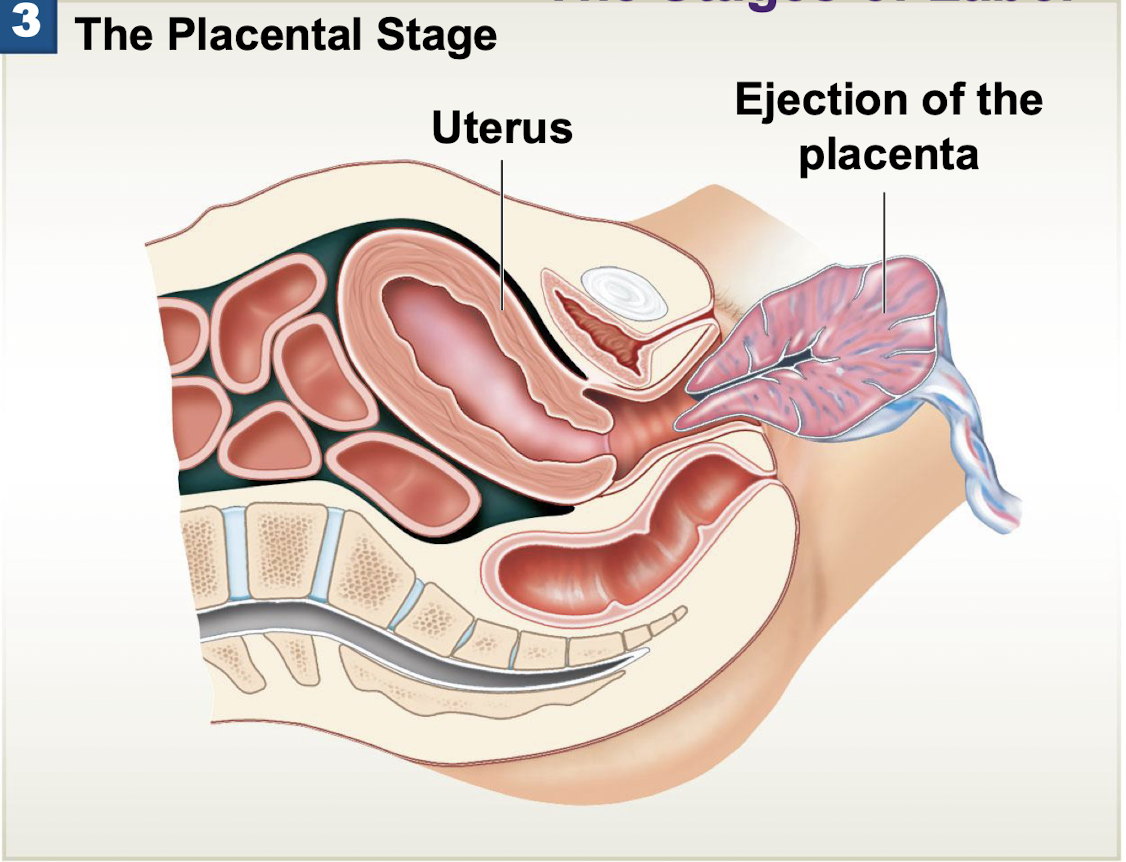
Labor - Placental Stage
Ejection of the placenta (afterbirth)
Placenta previa
A condition in which the placenta attaches low in the uterus and partially or completely covers the cervix, the opening of the uterus
The umbilical cord physically connects what?
The embryonic/fetal body with the placenta
Where is the placenta located?
Physically adjacent to the uterine wall in the mother’s body
The umbilical blood vessels enter and exit the fetal body at the…
Umbilicus (belly button)
Fetal bypasses that exist in the fetal heart and liver
In the fetal heart, the blood largely bypasses the fetal lungs. Remember that the fetus is in a liquid environment. There is no mechanical breathing taking
place in the fetal lungs. Gas and nutrient exchange is taking place at the interface between the uterine wall and the placenta. It is not necessary in the fetal body to send a significant amount of blood towards the lungs. That is why these bypasses exist. After birth, however, these bypasses should seal off. This then forces blood to enter into the newborn’s lungs
Premature Labor
Labor that begins before the fetus has completed normal development
Fetuses born <36 wks (birth wt > 1 kg) are considered premature
Generally survive with care
Fetuses born <24 wks (birth wt below 600 g) generally die
Respiratory/cardiovascular/urinary systems have not developed enough to support life
Neonatal period
Period from birth to 1 month
Events that occur in the neonate during the neonatal period:
Lungs fill with air
Blood circulation changes with the closing of the ductus arterioles and the foramen ovals of the heart
Heart rate drops from 110-190 bpm to about 80-130
Breathing rate commences at 30-60 breaths per minute
Kidney’s filter the infant’s own blood
Digestive system becomes active
Metabolic rate is increased to maintain warmth for a few days after birth