zoology lecture 1+2- A Brief History of Life
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
what is the Big Bang Theory?
the theory that the universe expanded from a high density and temperature and formed atoms and subatomic particles as it cooled
how long ago did the Big Bang Theory happen?
13,800 million years ago
what is the Nebular Hypothesis?
the hypothesis that a molecular cloud collapsed due to gravity, most of the mass collected in the center and formed the sun, the rest formed the surrounding planets
when did our solar system form?
4,600 million years ago
when did Earth form according to radiometric dating?
4,100 million years ago
the first atmosphere was formed by___
volcanic gases and storms
what were the first oceans like?
hot and shallow
what does Miller's experiment prove?
the formation of organic macromolecules
when did the first forms of life appear according to radiometric dating?
3,500 million years ago
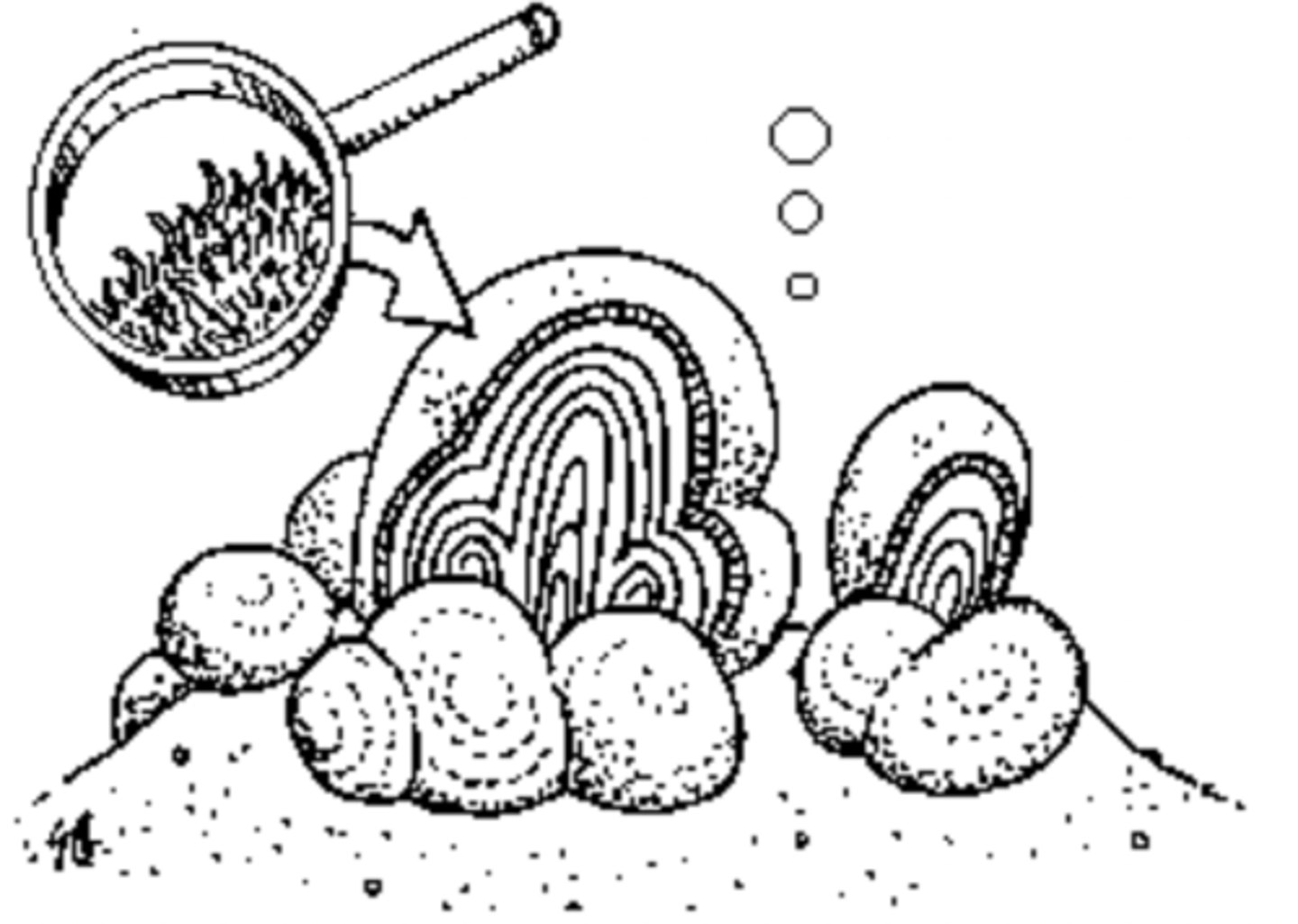
what was the first form of life?
stromatolites
which were the first forms of multicellular organisms?
Ediacara biota
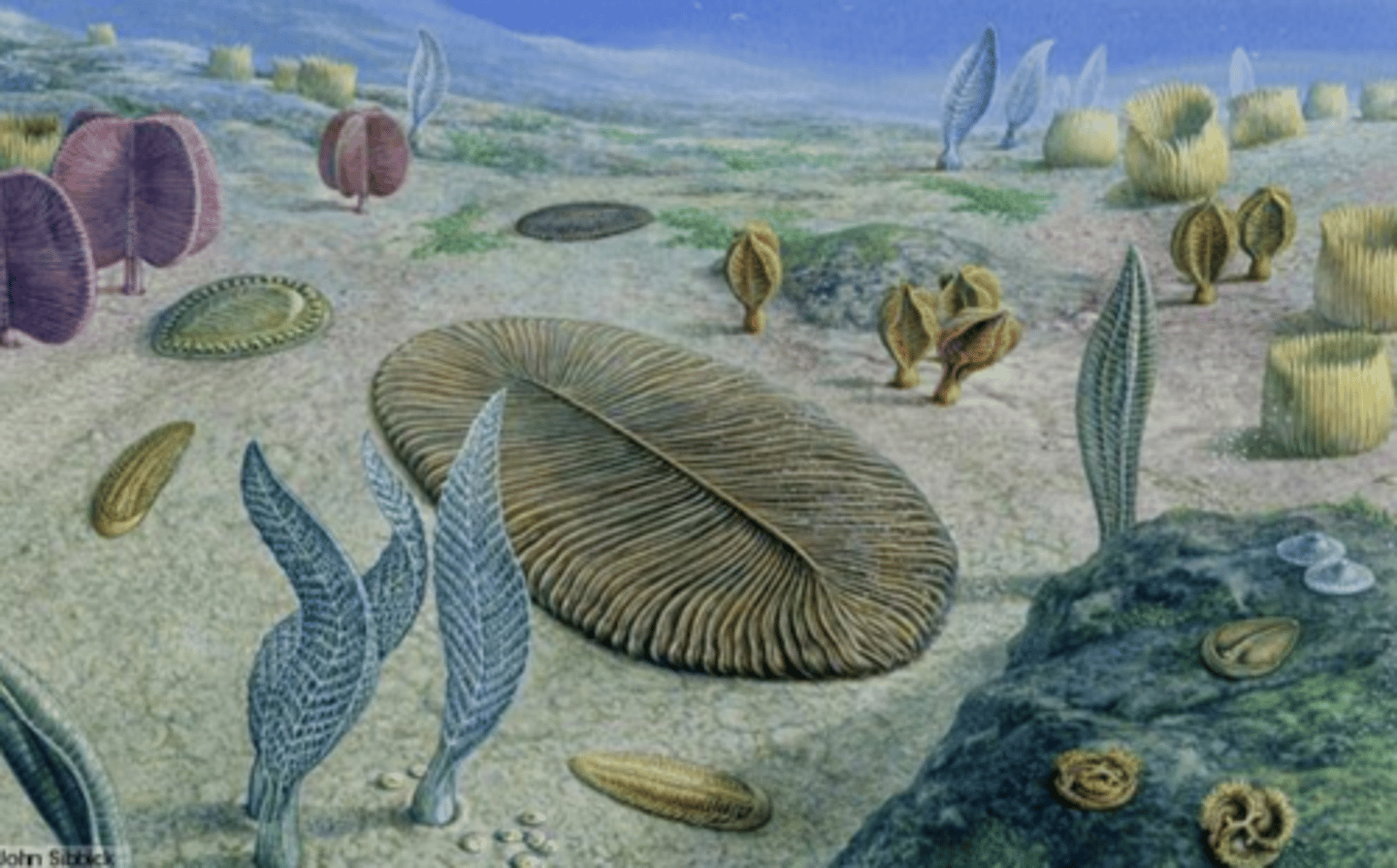

how long ago did the first forms of multicellular organisms appear?
600-542 million years ago
what were the first multicellular organisms like?
large, soft bodies, sessile on marine substrate
what was the Cambrian explosion?
The evolutionary event during which most animal phyla appeared. Appearance of hard skeleton.
when was the Cambrian explosion?
580-500 million years ago
what are the main 6 characteristics that are shared by all animals?
1. Basic unit: the cell
2. Eukaryotic cells
3. Multicellular
4. Heterotrophic
5. Digest food in an internal cavity
6. Glycogen and fat as energetic reserve
what is the difference between autotrophy and heterotrophy?
autotrophy- the ability to generate its own organic substances for energy
heterotrophy- not able to generate its own organic substances for energy, thus having to rely on eating organic substances
which is for long term energy storage, lipids or glycogen?
lipids
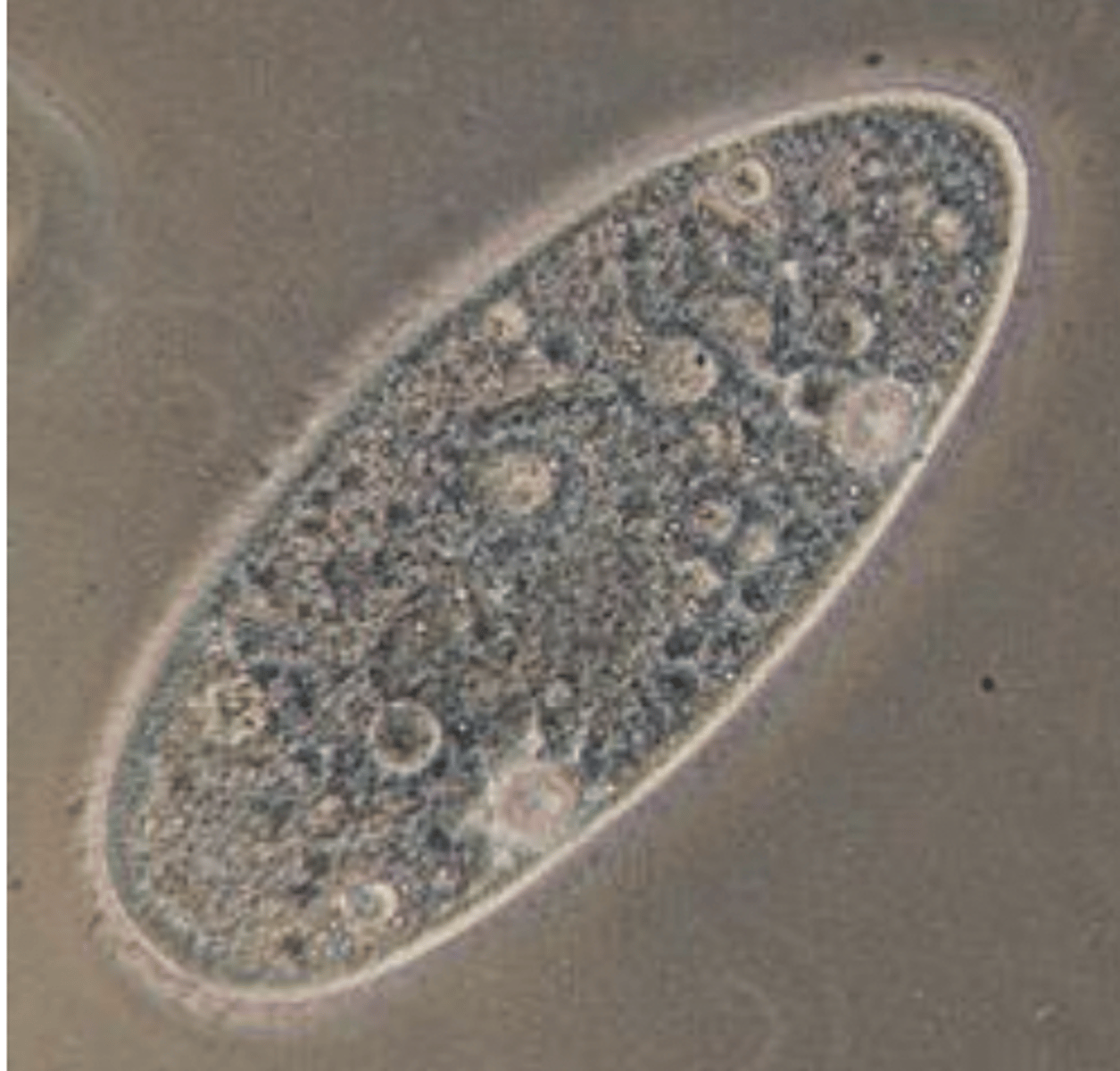
what is a protoplasmic organism?
Unicellular organisms with organelles that perform
specialized functions (not animals)
what is an example of a protoplasmic organism?
protozoa
what is the cellular level of organization?
an aggregation of little organized totipotent cells, the ones with similar functions are together
what is the tissue level of organization?
Aggregation of specialized cells (originated from a single cell) into
definite patterns of layers with specialized functions (tissues)
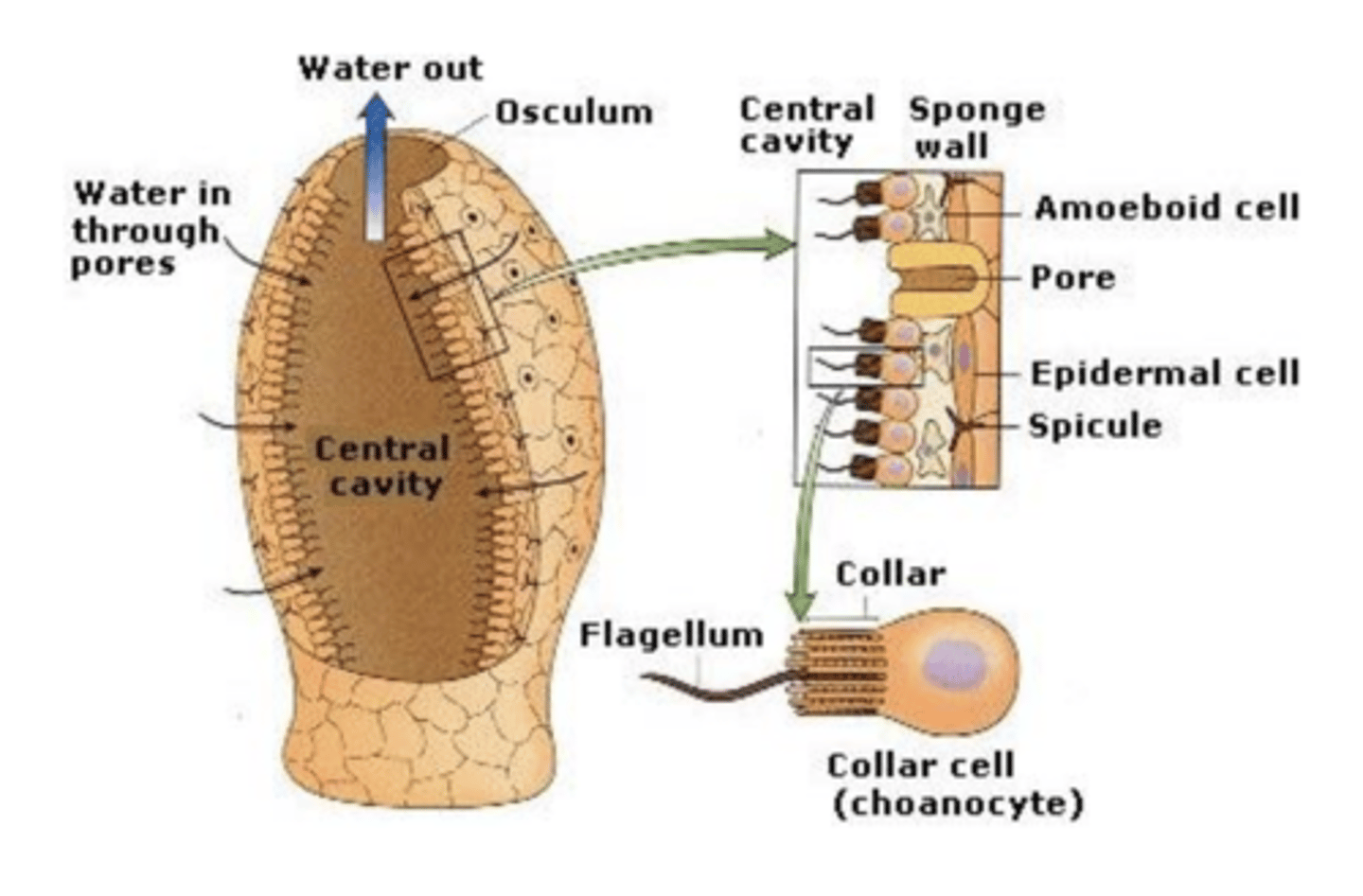
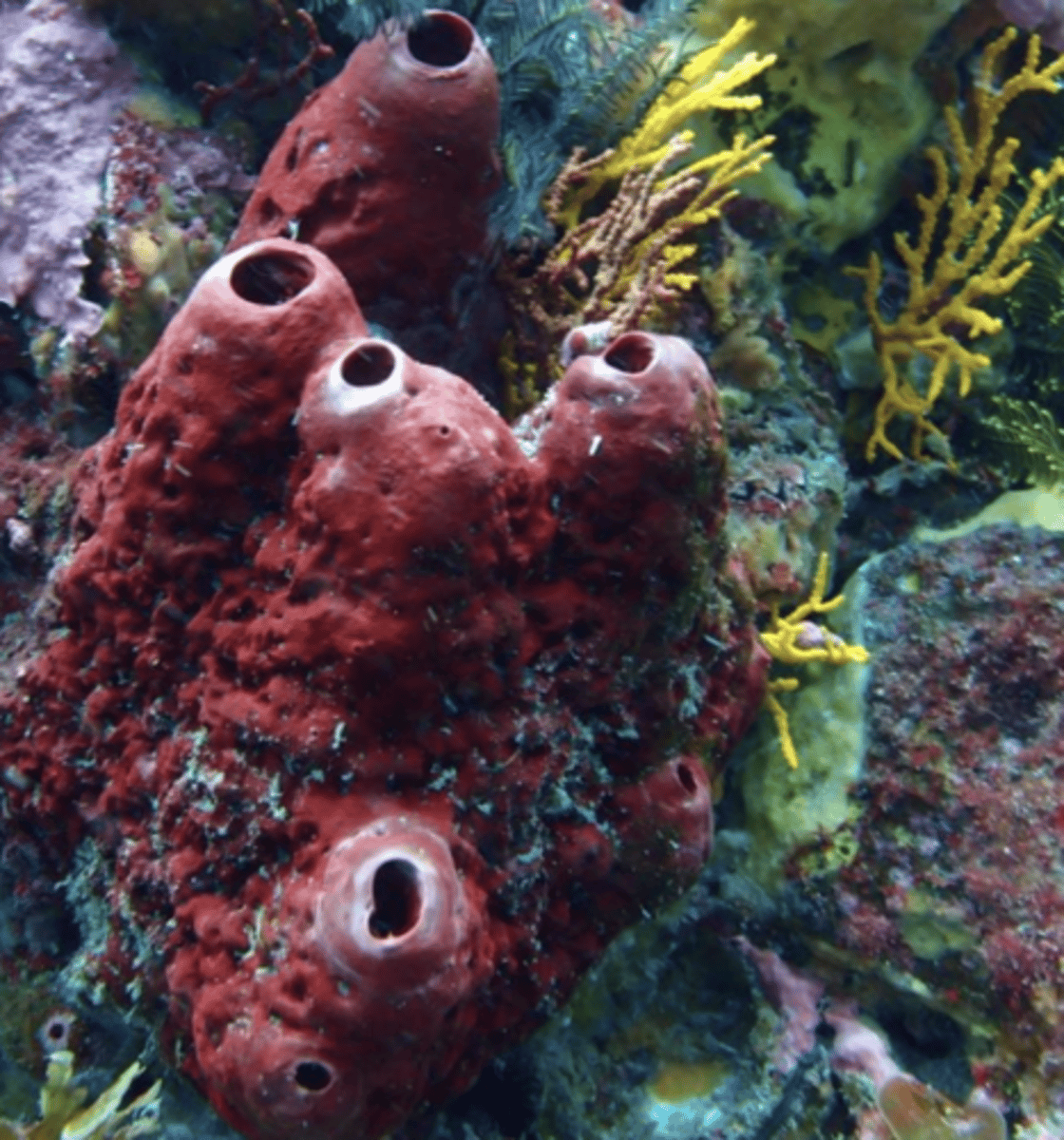
what is an example of an organism at the cellular level of complexity?
porifera (digestive cells)
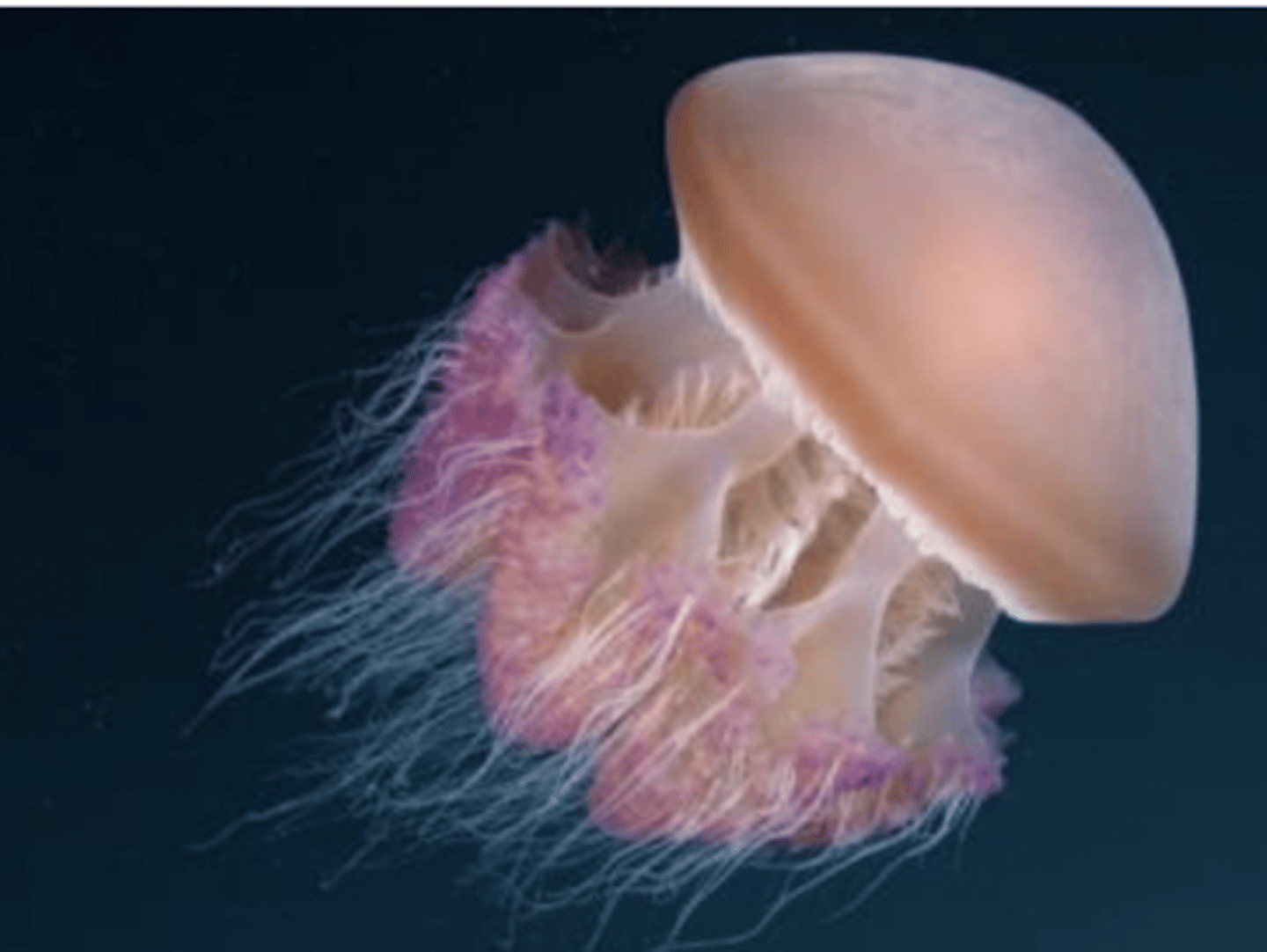
what is an example of an organism at the tissue level of complexity?
cnidaria (nerve net)

what organism has reached the organ level of complexity?
platyhelminthes (eyespots)
what is the organ level of complexity?
Organization of tissues into organs with specialized functions
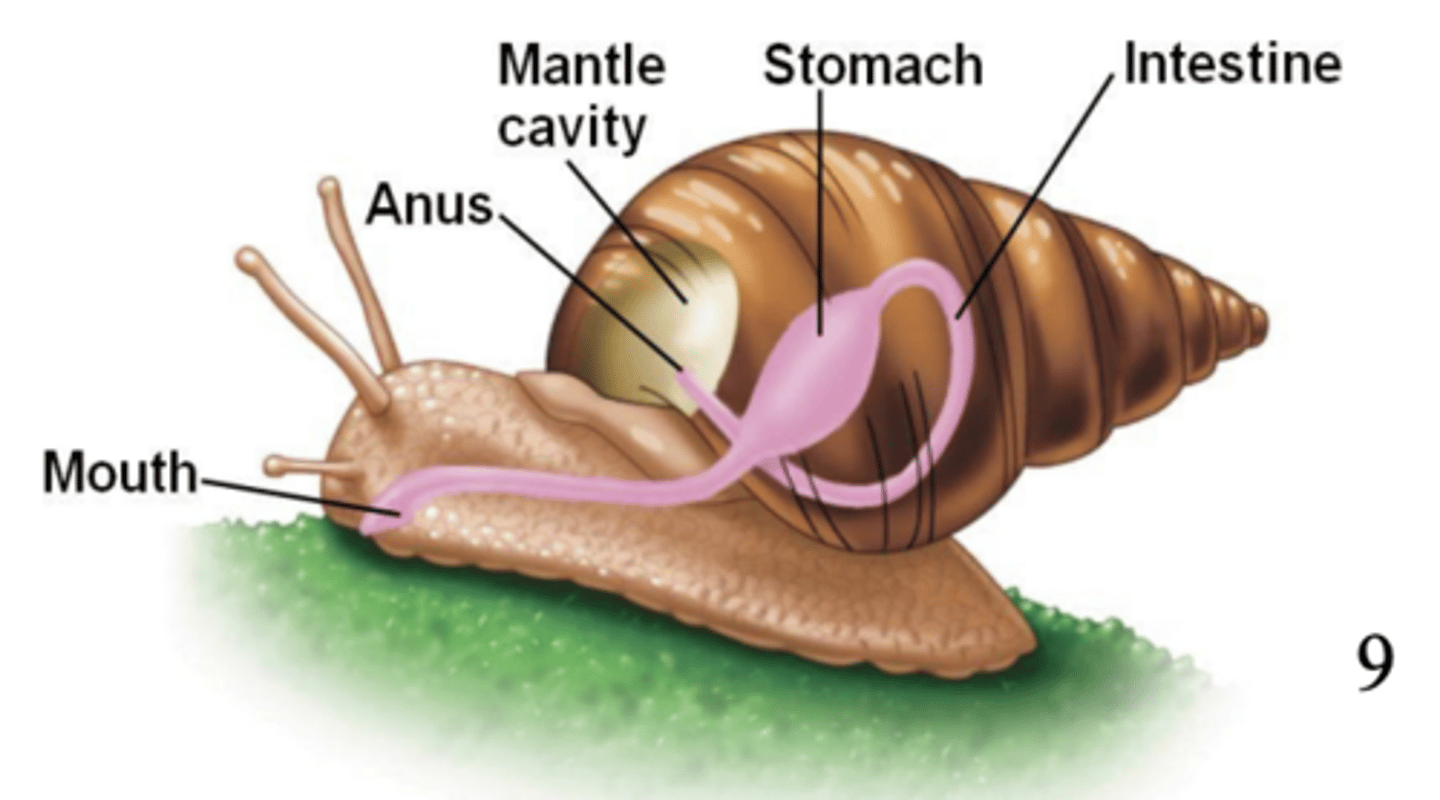
what is the system level of organization?
coordination of organs to perform one function
what is an example of an organism that has reached the system level of complexity?
mollusca (digestive system)
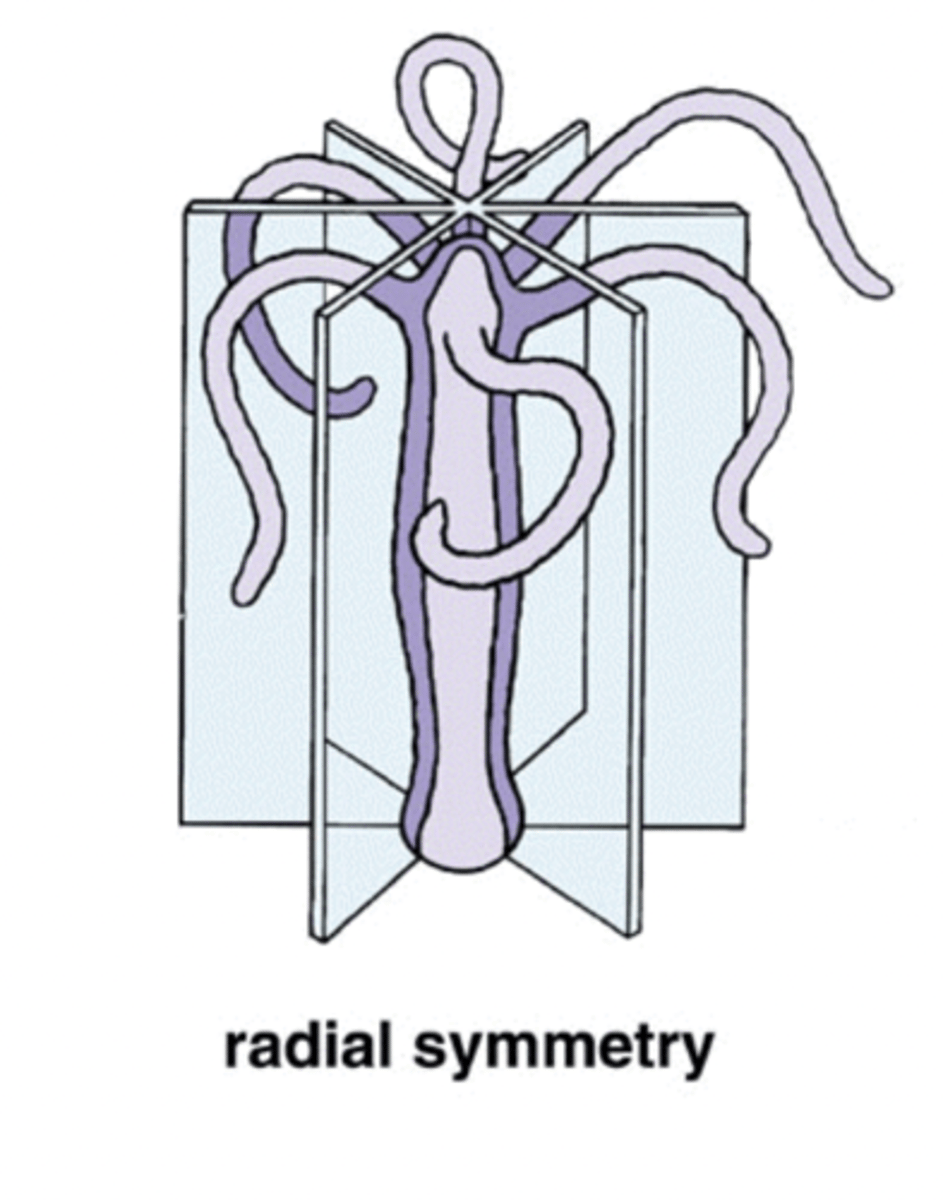
what are the three types of symmetry in organisms?
asymmetry, radial symmetry, bilateral symmetry
what does it mean if an organism is radially symmetrical?
the organism has at least two cutting planes that produce roughly identical pieces
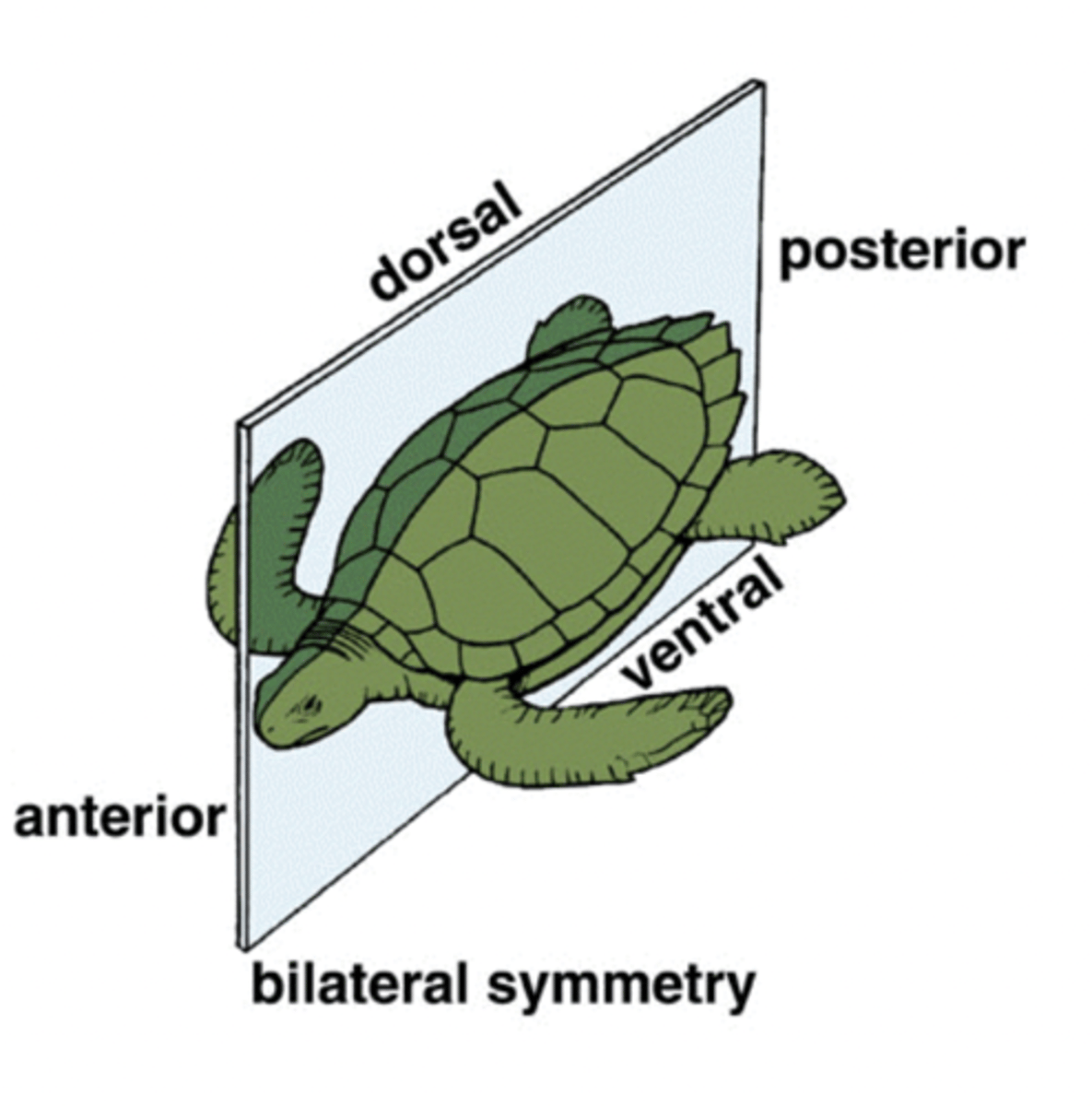
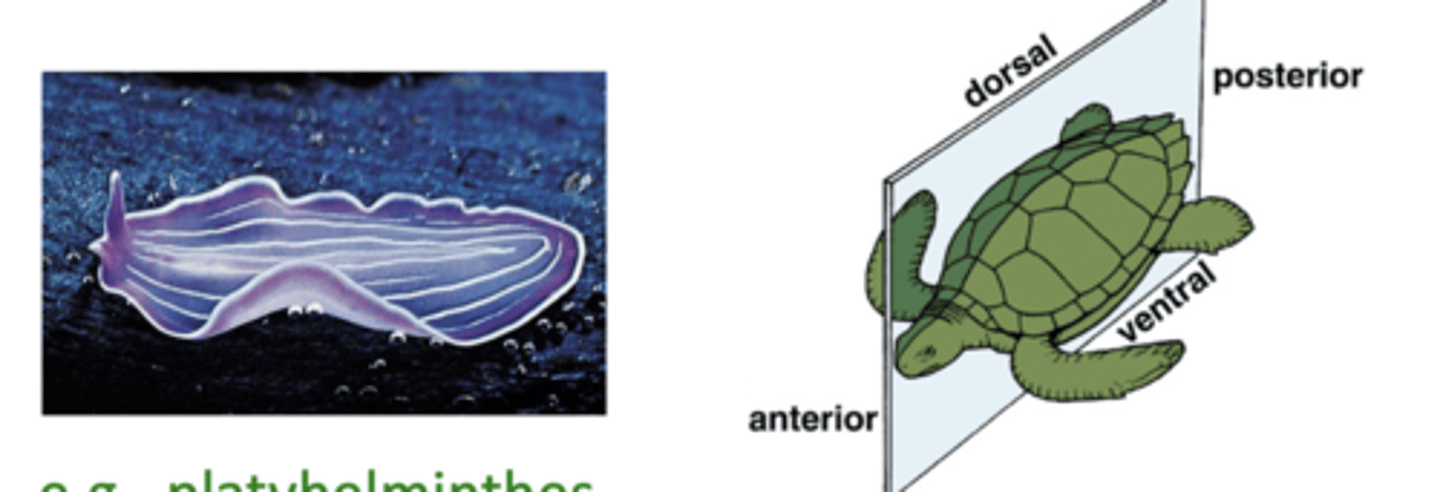
what does it mean if an organism is bilaterally symmetrical?
the organism has only one plane, the saggital plane, that divides
them into roughly mirror image halves
what does it mean if an organism is asymmetrical?
the organism has no plane that would produce mirror images
what type of organism is asymmetrical?
porifera

what type of animal is radially symmetric?
cnidaria
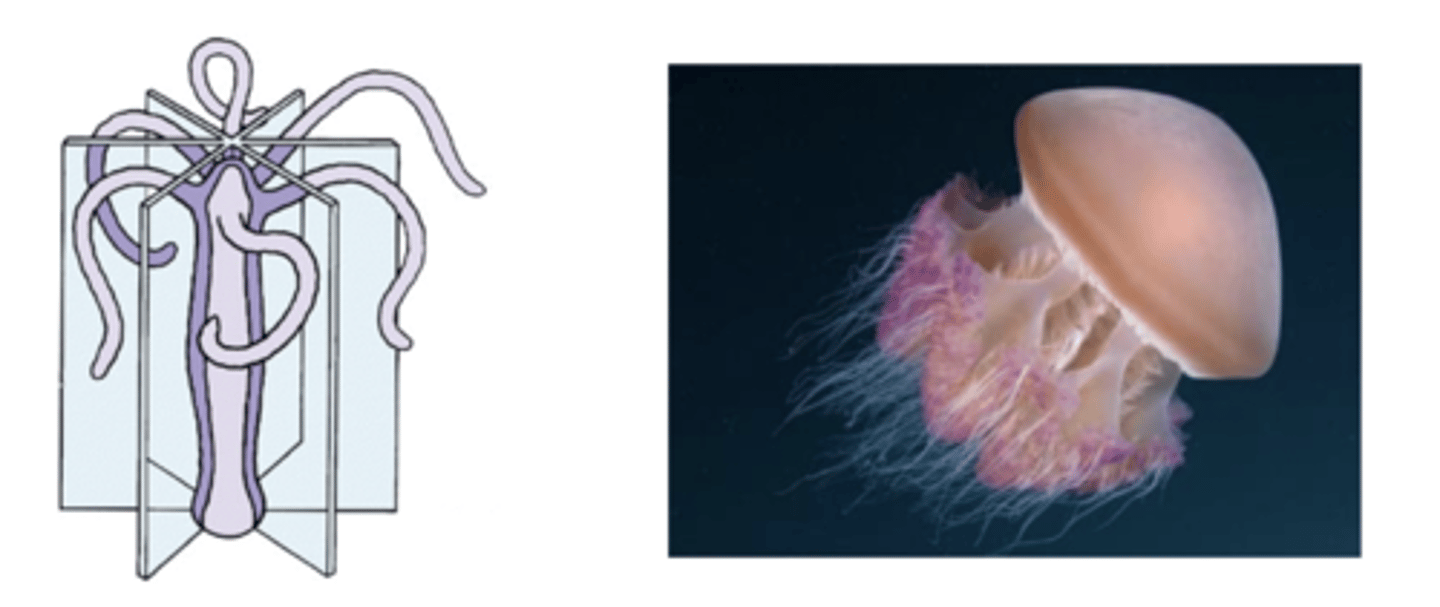
what type of animal is bilaterally symmetric?
platyhelminthes
depending on the coelem, the organism can be _____
coelomate, pseudocoelomate, or acoelomate
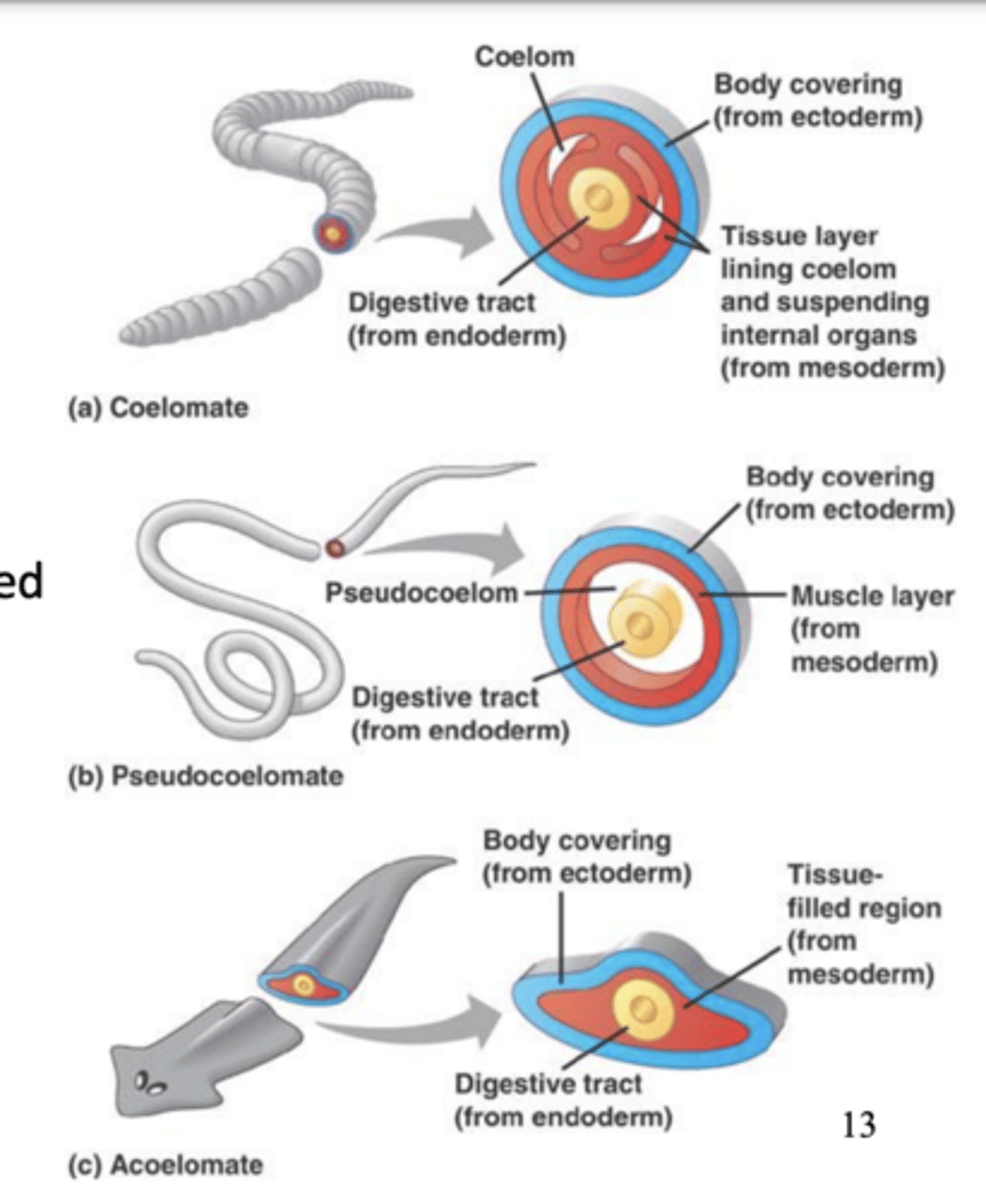
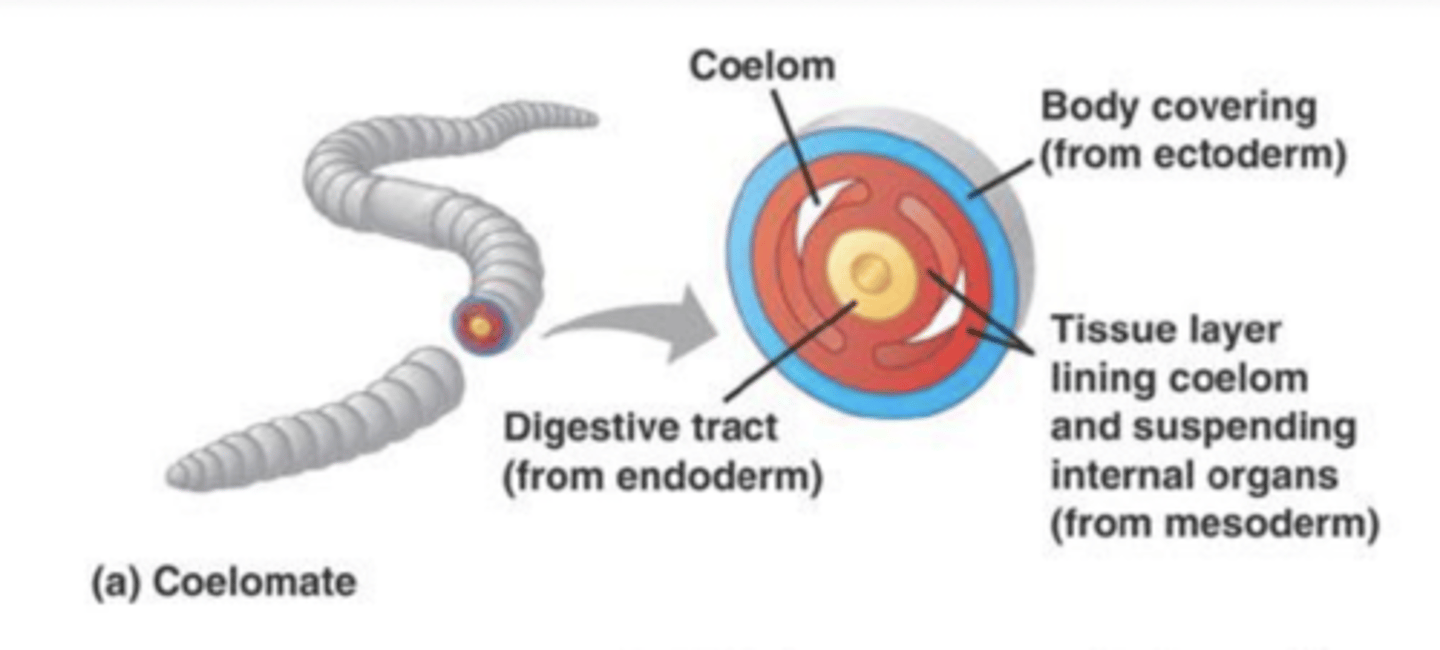
what does coelomate mean?
the organism has a fluid-filled body cavity lined by mesodermal cells
what does pseudocoelomate mean?
the organism has a fluid-filled body cavity, not fully lined by mesodermal cells
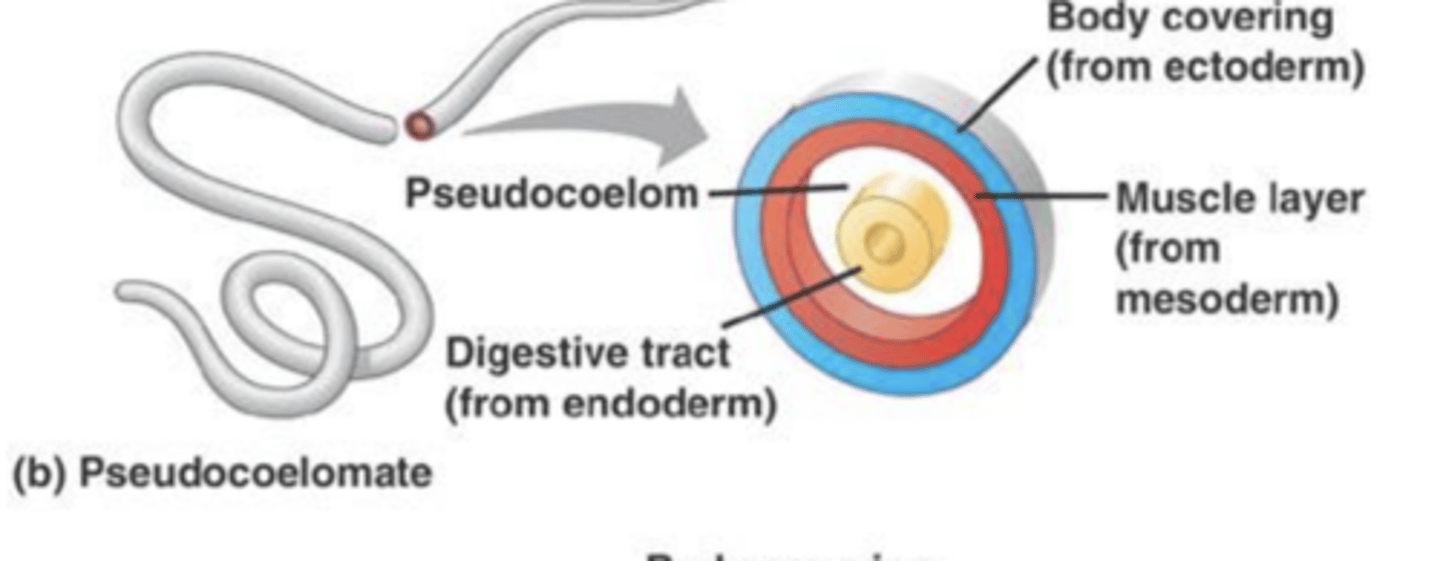
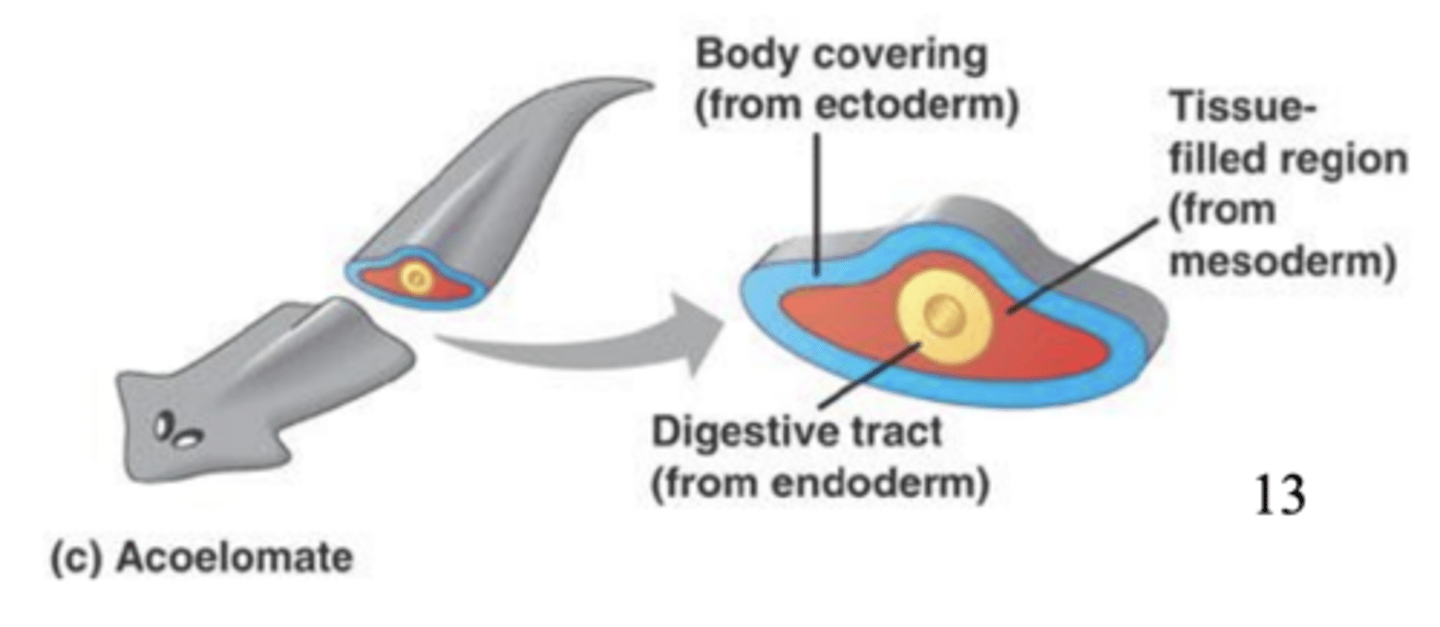
what does acoelomate mean?
no internal cavity but compact body
what are the two words for the different ways a coelom can form?
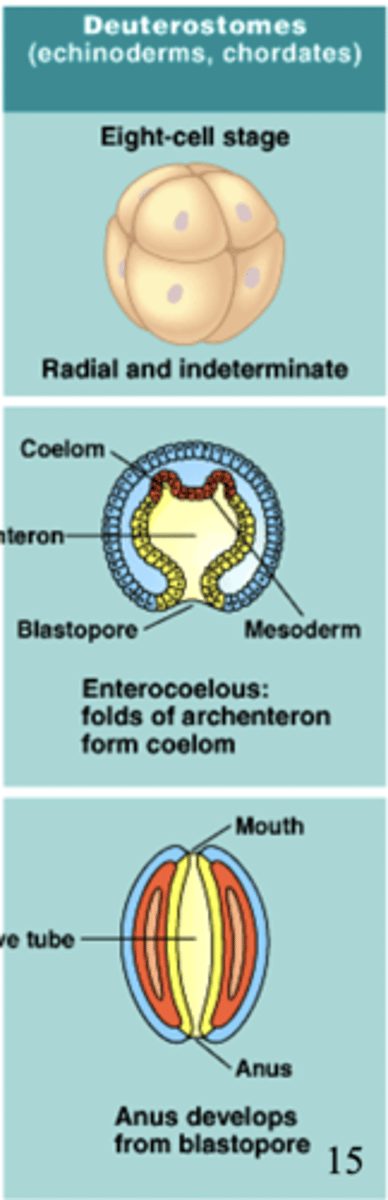
protostomes, deuterostomes
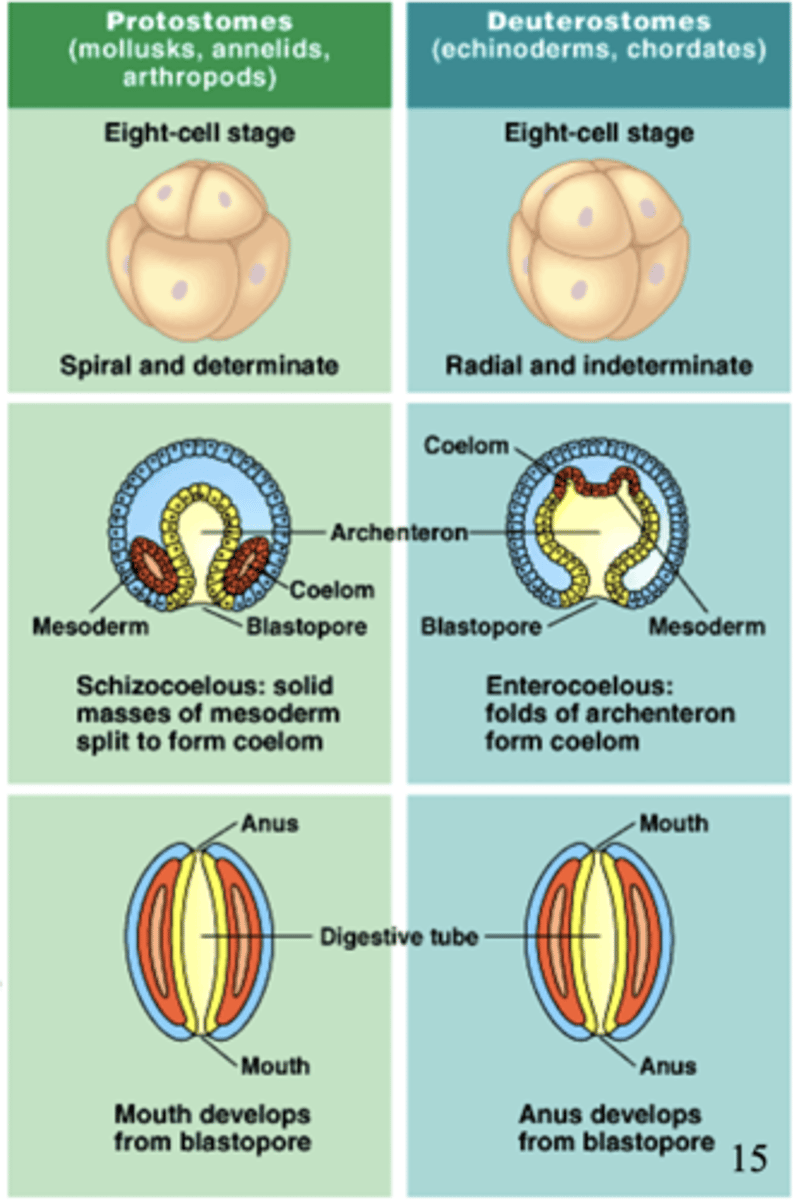
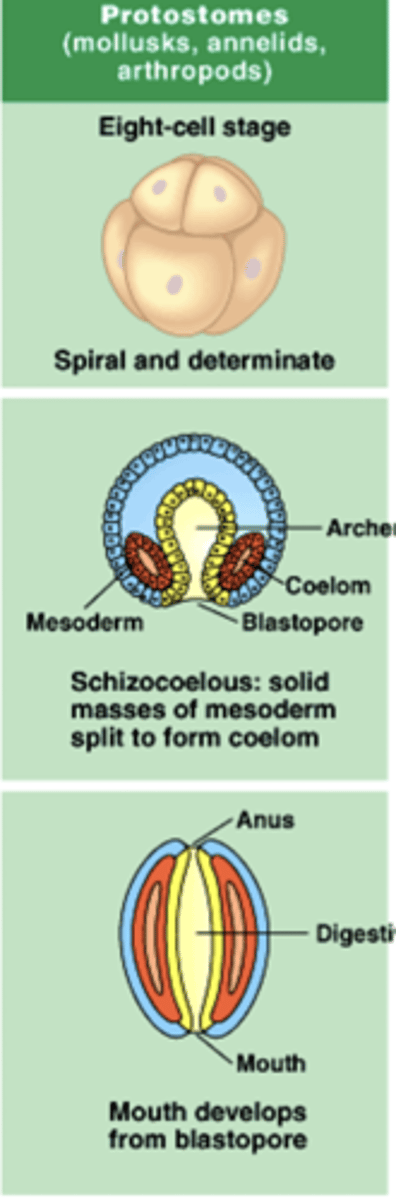
what does protostome mean?
an organism that has mouth development before anus development
what does deuterostome mean?
an organism that has anus development prior to mouth development
which organisms are protostomes?
molluscs, annelids, arthropods
which organisms are deuterostomes?
echinoderms, chordates
what does it mean when an organism is segmented (metamerism)?
parts repeat
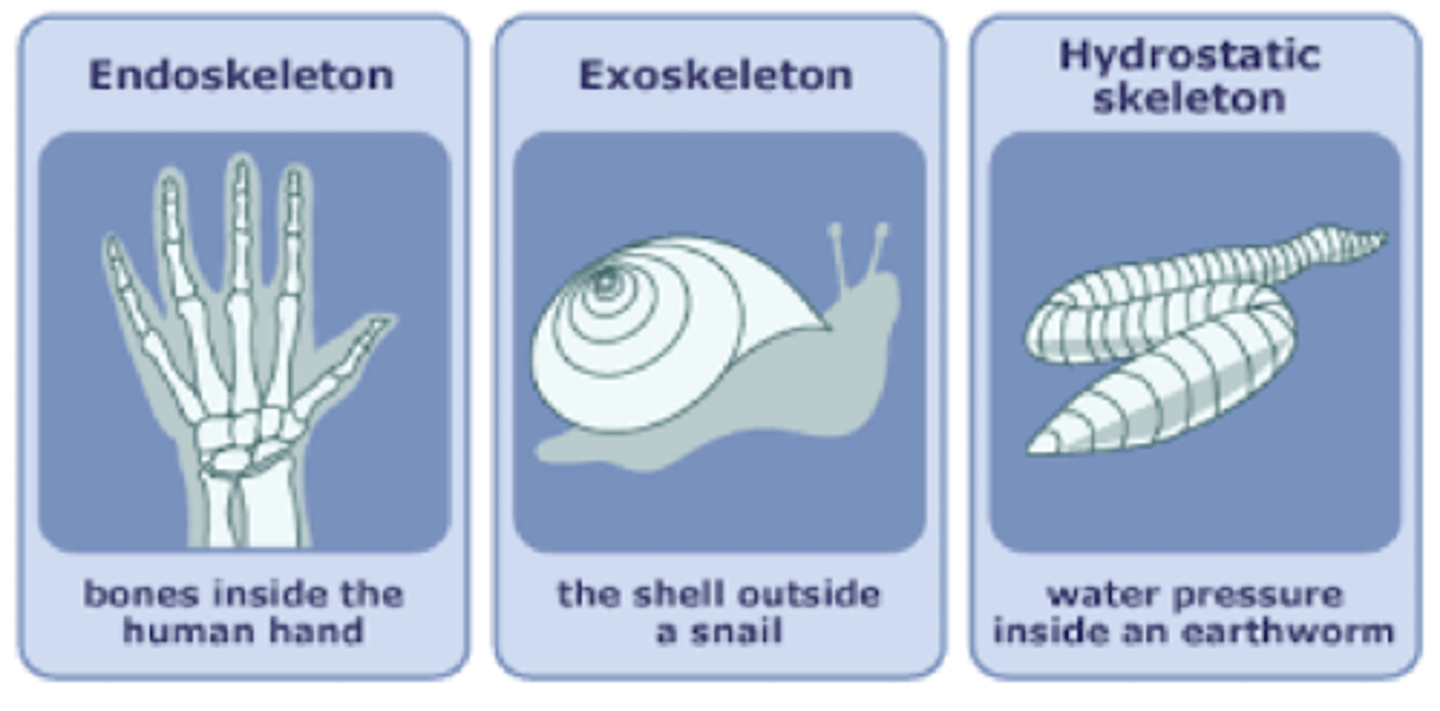
what are the three types of skeletons?
exoskeleton, endoskeleton, hydrostatic skeleton