Biology Winter Final 23
1/128
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 1, 2, 3 (i didn't include much of T7, so u might wanna check that out)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
energy
the ability to do work, often stored in cells
macromolecules
big arrangements of atoms held together (comes from food) that create energy for survival
protein
CHOPN
maintain life
hormones
immune system
enzymes
protein monomer
✨Whose Monomer?✨
Our Contestant is….
señor amino acid (20)
protein polymer
✨Whose Polymer?✨
Our Contestant is….
señorita polypeptide (amino acid chain)
carbohydrate
CHO
form cell wall
quick ⚡
carbohydrate monomer
✨Whose Monomer?✨
Our Contestant is….
señor saccharide (glucose)
carbohydrate polymer
✨Whose Polymer?✨
Our Contestant is….
señorita polysaccharide (glycogen)
lipid
CHOPN
cell protection
hormones
waterproofing
waxes
lipid monomer
✨Whose Monomer?✨
Our Contestant is….
señor glycerol
lipid polymer
✨Whose Polymer?✨
Our Contestant is….
señorita fatty acids
nucleic acid
AT (Adenine, Theymine)
CG (Cyodine, Guanine)
[sugar + phosphate]
carries genetic information
nucleic acid monomer
✨Whose Monomer?✨
Our Contestant is….
señor nucleotides
nucleic acid polymer
✨Whose Polymer?✨
Our Contestant is….
señorita DNA, RNA
prey
the hunted
predator
the hunter
Genus species
how to write scientific name
niche
the job in an ecosystem
karyotype
a picture of organized chromosomes from individuals
chromosomes
they store genes, 38 in all (but 46 for humans, which is 28 pairs)
male
XY chromosomes gender
female
XX chromosomes gender
genotype
the combination of alleles from each parent
genes
a unit of heredity
alleles
you get one from each parent
aerobic respiration
oxygen must be available for use
anaerobic respiration
occurs in low oxygen environments
fermentation
occurs in the cytoplasm and produces a small amount of ATP; 2 types
lactic acid fermentation
enzymes convert glucose to lactic acid (during strenuous exercise when oxygen is low)
alcohol fermentation
occurs in yeast and some bacteria; used to make beer and wine
producers
1st level on pyramid, get energy from sun, aka autotroph
consumers
>1st level, eat autotrophs and other consumers
primary consumer
herbivore
carnivore
meat-eating
scavenger
carcass-consuming
omnivore
plant and meat-eating
gel
the substance the little DNA fragments swim across
DNA fragments
what are the little lines in this picture called
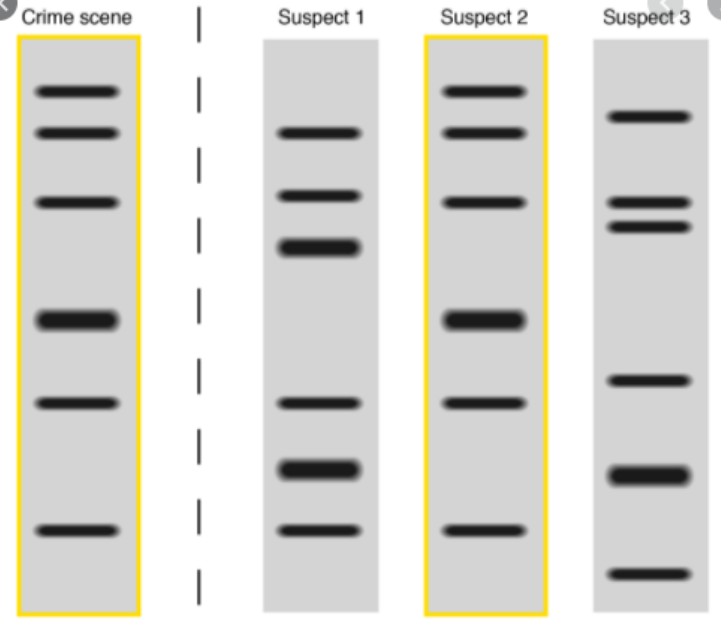
biotic
factors such as algae, trees, grass, fish
abiotic
factors such as water, air, sunlight, rock

limiting
factors such as sunlight available, water, nutrients, food, temperature
blue jays
grasshopper populations before and after blue jays preyed on them
what was the selective pressure?
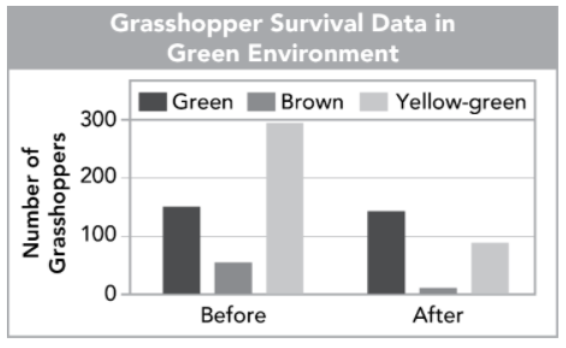
green
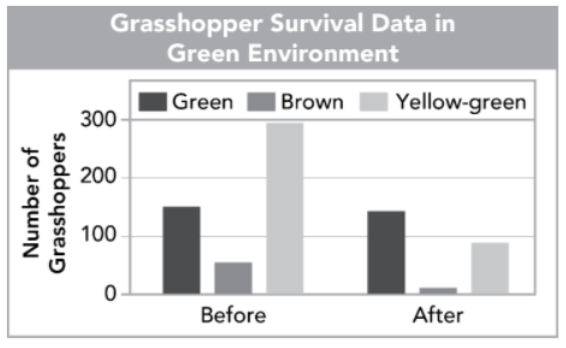
grasshopper populations before and after blue jays preyed on them
which colored hopper was most likely to not unalive themselves
x
which axis represents plant types consumed
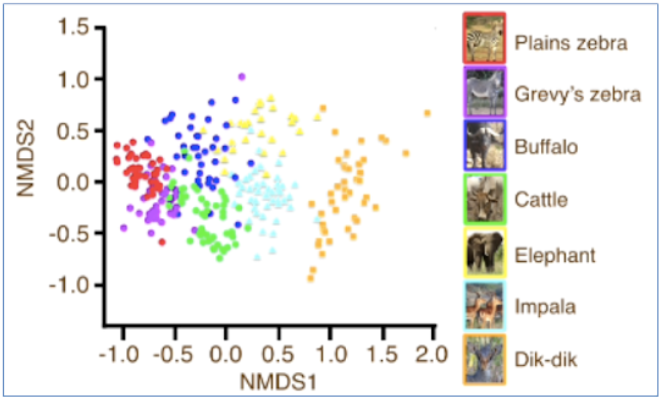
y
which axis represents different species
characteristics of life
cellular organization
reproduction
metabolism
homeostasis
heredity
response to stimuli
growth and development
adaptation through evolution
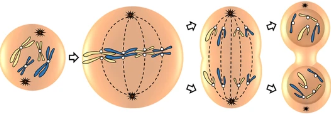
interphase
which stage of mitsosis?

prophase
which stage of mitosis?
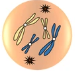
metaphase
which stage of mitosis?
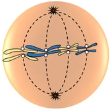
anaphase
which stage of mitosis?
telophase
which stage of mitosis?
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
states of mitosis (without interphase)
cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O + sunlight→ C6H12O6 + 6O2
10% rule
general rule of an energy pyramid
keystone species
animal that an ecosystem couldn’t survive without
carrying capacity
the highest population amount in an ecosystem/enivornment
decrease
did the population increase or decrease?
anaerobic
is glycolysis aerobic or anaerobic
glycolysis
one glucose (6C) turns into two pyruvic acids (3C)
aerobic
is krebs cycle aerobic or anaerobic
krebs cycle
two pyruvic acids (3C) turn into 3 carbon dioxide (C)
cytoplasm
where does the krebs cycle occur
polymer
a large molecule composed of repeating smaller untis or monomers
enzyme
a protein that makes a reaction happen quicker; decreases activation energy of a reaction
active site
part of an enzyme into which a particular substrate fits
catalyst
a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
organic compound
a compound that contains the element of carbon
enzyme-substrate complex
the combination of the enzyme and substrate
activation energy
the minimum amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction
monomer
small chemical that makes up a polymer
hydrolysis
breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
dehydration synthesis
chemical reaction where molecules are connected by loss of a water molecule
leaks in mitochondria
Sea otters stay warm due to their extreme metabolism, which is caused by _____ __ __________ that generate extra heat. This can help scientists understand their evolution and how other mammals stay warm.
homeostasis
when the population trend never changes, it appears to be in __________
immigration
moving into a population
emigration
leaving a population
population density
# number of individuals in an area
unit of area
density independent
factors that limit growth regardless of density of population
density dependent
factors effected by density of population
density independent factors
climate/weather, natural disasters, human activities
density dependent factors
predation, disease, parasites, competition
R-strategist
small organism
short life span
many offspring
populations controlled by independent factors
K-strategists
large organism
longer life span
few offspring, lots of care
populations controlled by dependent factors
color
On what variation do sea otters select urchin prey? 🤨🧐🥸
8
What pH should ocean water be at? 🤨🧐🥸
increase
over time, there has been a steady ________ of CO2 in the atmosphere
decreased, more
over time, the pH of the ocean has _________, making it ____ acidic
hydrogen
the increase of ________ ions decreases pH level
i understand, my lord
me: please just understand that this image exists idk how to explain it, which doesn’t really help any of our cases, but if you want a link to it, it’s on page 3.19 in ur nb
you: I understand, my lord
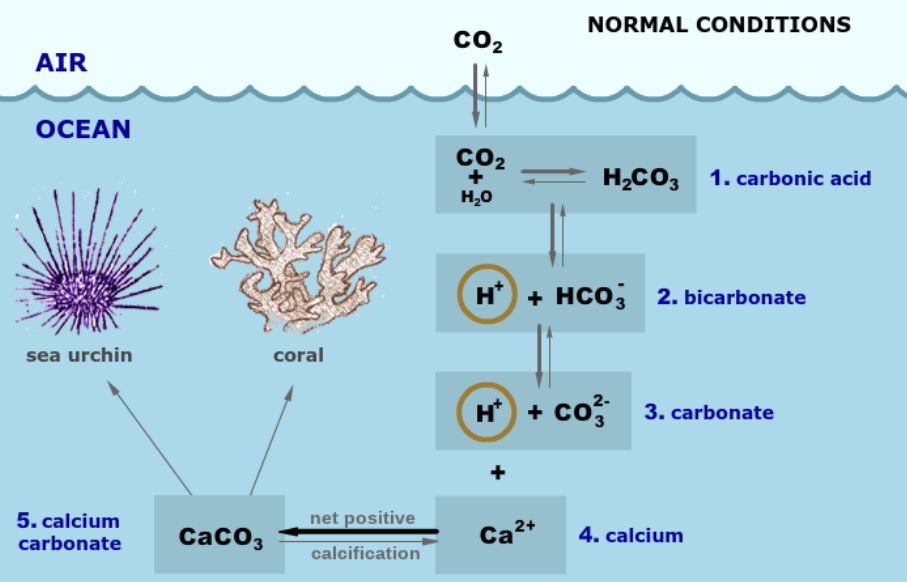
calcifiers
crab, urchin, tube worm, pteropod, coccdiphophore, coral, alga
non-calcifiers
jellyfish, brown alga, octopus, sea anenome, sea squirt (lol), sea slug, fish, polychaete worm
test
pictured in purple
outer layer of sea urchin
internal skeleton w/ infused plates
aka the shell
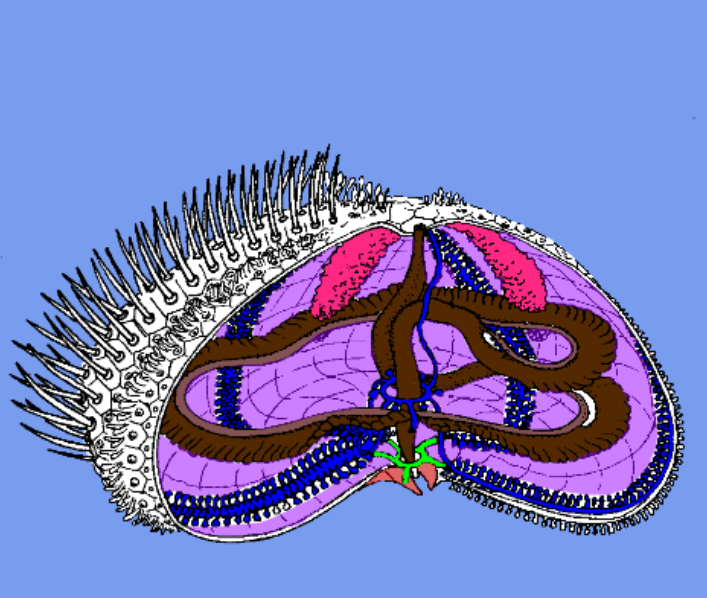
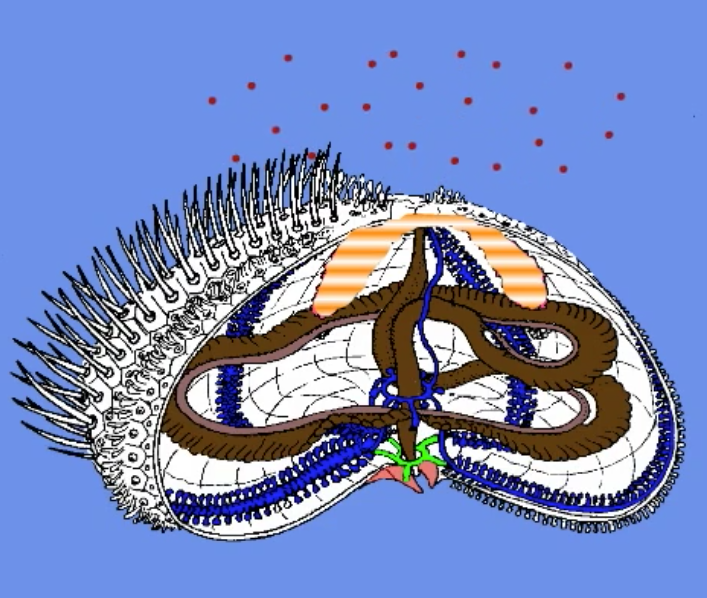
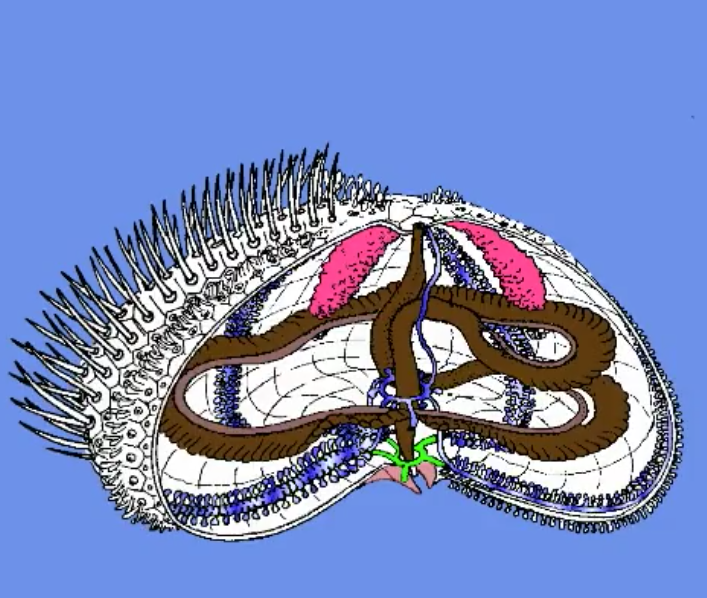
gonads
reproductive organ
usually 5
feels like jelly
looks like a tongue
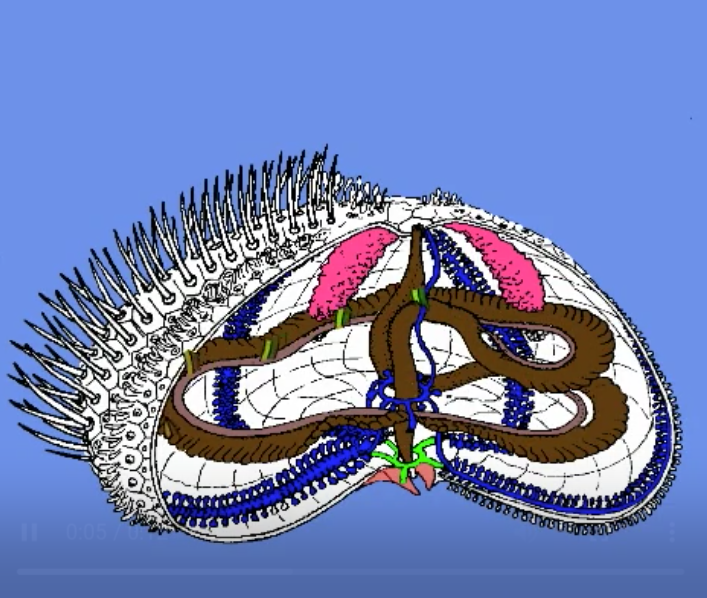
water vascular system
pictured in blue
goes all around the inside of the urchin
responsible for circulation and movement
digestive system
pictured in brown
takes up the most space
waste expelled through top
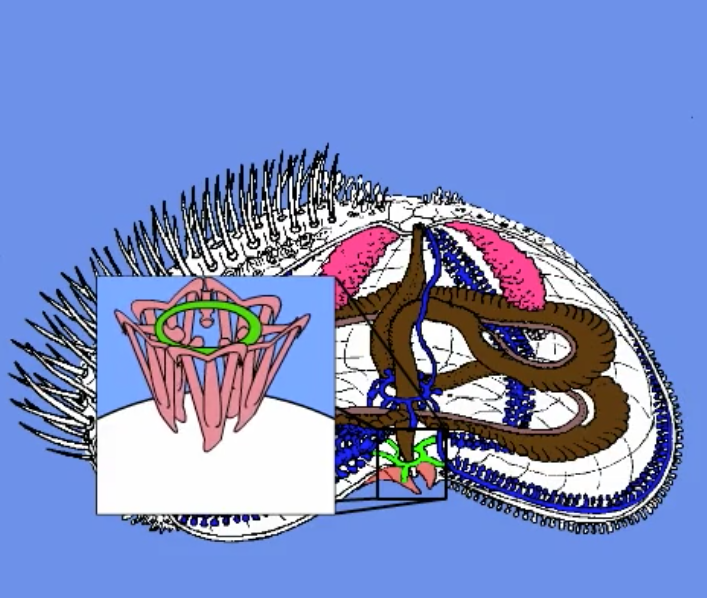
aristotle’s lantern
person who named this was definitely on something weird
the mouthparts
five bony plates used to scrape (teeth)
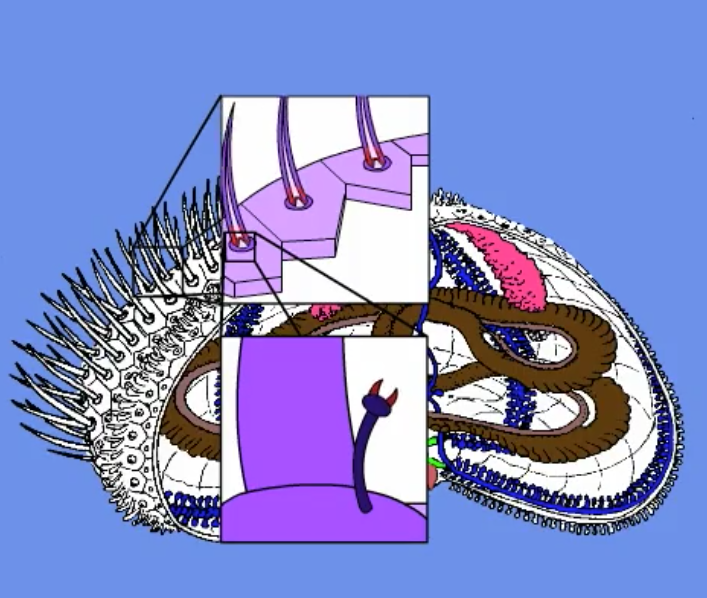
spines and pedicellaria
primary mode of defense
covered with a layer of epithelium
tube feet
movement
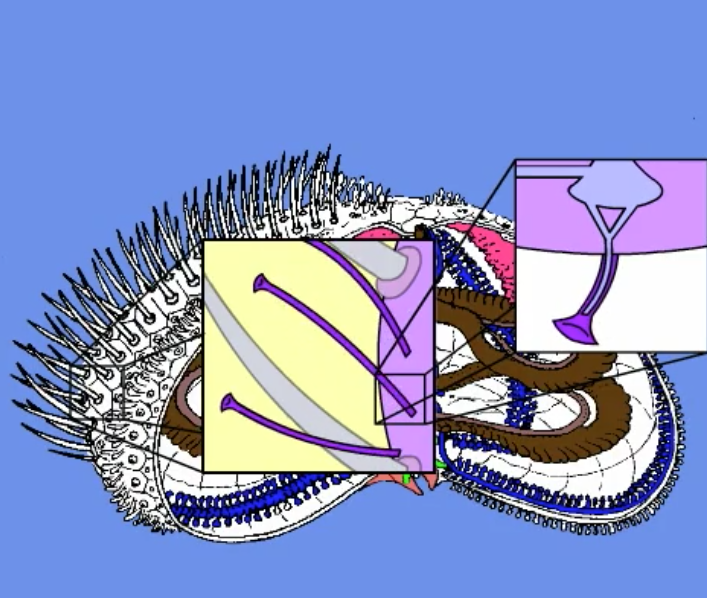
aboral
side of the urchin with
bottom
rectum
anus