Campbell Biology Chapter 42
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Small molecules can move between cells and their surroundings by
diffusion
Some animals lack a _______
circulatory system
A gastrovascular cavity
functions in both digestion and distribution of substances throughout the body
A circulatory system has
a circulatory fluid, a set of interconnecting vessels, and a muscular pump called the heart
function of the circulatory system
connects the fluid that surrounds cells with the different organs of the body
Circulatory systems can be ___ or _____ and vary in the number of ____ in the body
open, closed, and circuits
In insect, arthropods, and some molluscs, circulatry fluid called ______ bathes the organs in an _______
hemolymph, open circulatory system
In a _______ circulatory system ____ is confined to vessels and is distinct from the interstitial fluid
closed, blood
Humans and other vertebrates have a closed circulatory system called the
cardiovascular system
Three main types of bloods vessels
arteries, veins, and capillaries
Arteries branch into _____ and carry blood away from the heart to _______
aterioles capillaries
Networks of capillaries called ______ are the sites of chemical exchange between the blood and interstitial fluid
capillary beds
Venules converge into _____ and return blood from the capillaries to the heart
veins
Arteries and veins are distinguished by the direction of blood flow
arteries carry blood away from heart; veins to heart
blood enters through an _____ and is pumped out through a _____
atrium and ventricle
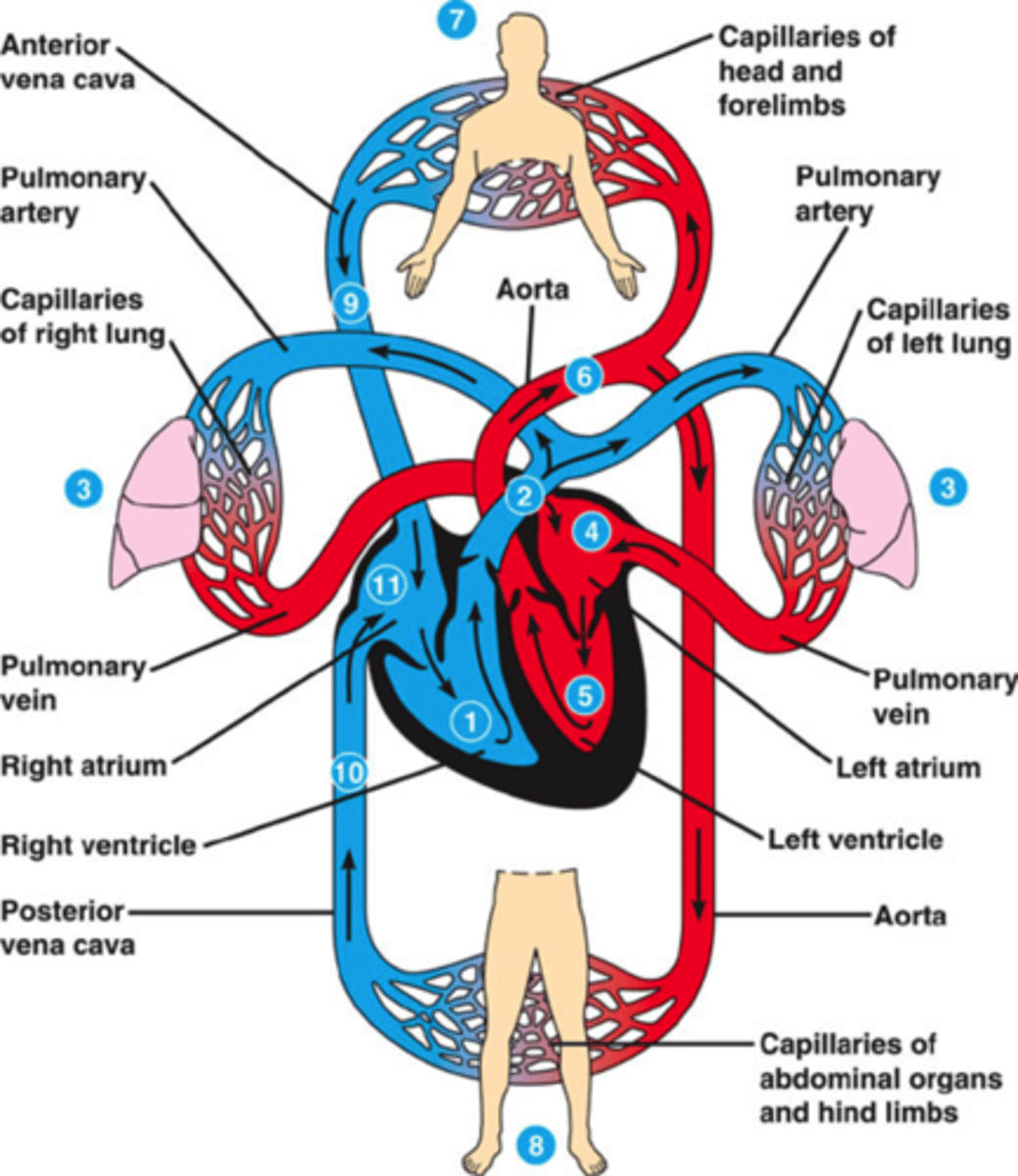
Bony fishes, rays, and sharks have a _____ circulation with a _____ chambered heart
single, two
Single circulation
blood leaving the heart passes through two capillary beds before returning
Amphibians, reptiles, and mammals have _______
double circulation
Oxygen poor and oxygen rich blood are pumped separately from the
right and left sides of the heart
Oxygen rich blood delivers oxygen through the
systemic circuit
frogs and other amphibians have a three chambered heart
two atria and one ventricle
Turtles snakes and lizards have a three chambered heart
two atria and one ventricle, partially divided by an incomplete septum
mammals and birds have a four chambered heart
two atria and two ventricles
the left side of the heart pumps and receives
oxygen rich blood
the right side receives and pumps
oxygen poor blood
Cardiovascular system
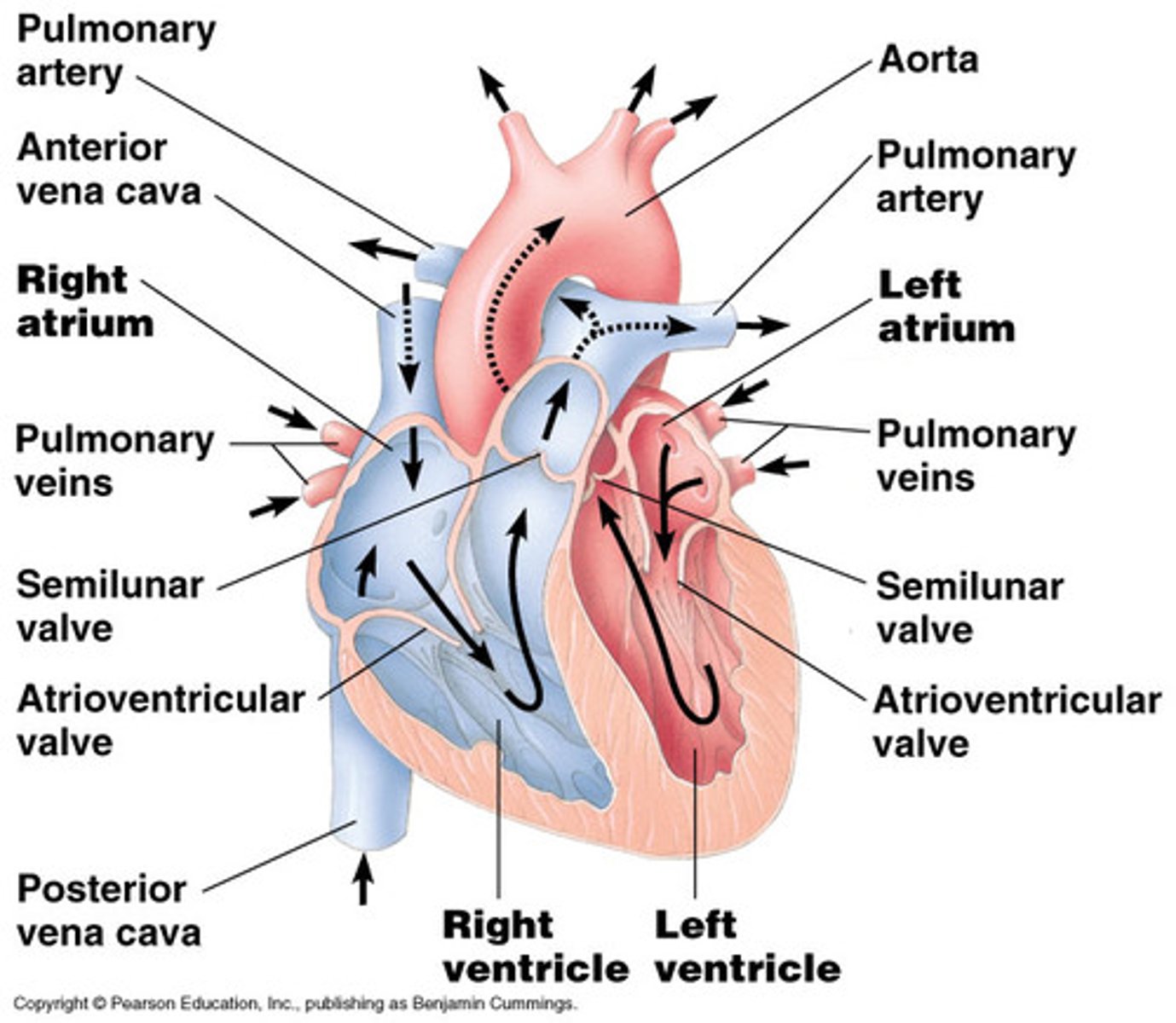
Mammalian heart
The heart contracts and relaxes in a rhythmic cycle called the
cardiac cycle
the contraction or pumping phase is called
systole
the relaxation or filling phase is called
diastole
The number of beats per minute is called the
heart rate
the amount of blood pumped in a single contraction is called the
stroke volume
The volume of blood pumped into the systemic circulation, it depends on both the heart rate and stroke volume
cardiac output
atrioventricular valves
separate each atrium and ventricleg
semilunar valves
control blood flow to the aorta and pulmonary artery
"lub dup" sound of a heart beat is caused by the recoil of blood against the ____ valves then against the _____ valves
AV, semilunar
Backflow of blood through a defective valve causes a
heart murmur
Autorhythmic
contraction without signal from the nervous system
sinoatrial (SA) node or pacemaker sets
the rate and timing at which cardiac muscle cells contract
impulses that travel during the cardiac cycle can be recorded as an
electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
Impulses from the SA node travel to the
atrioventricular (AV) node
at the av node the impulses are delayed and then travel to the
purkinje fibers that make the ventricles contract
the pacemaker is regulated by two portions of the nervous system
the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
the sympathetic division speeds up the
pacemaker
the parasympathetic division slows down
the pacemaker
the pacemaker is also regulated by
hormones and temperature
A blood vessels cavity is called the
central lumen
the epithelial layer that lines blood vessels is called the
endothelium
the endothelium is
smooth and minimizes resistance
Which has thicker walls, arteries or veins
Arteries, to accommodate the high pressure of blood pumped from the heart
Velocity of blood flow is slowest where
the capillary beds, as a result of the high resistance and large total cross sectional area
Blood flow in capillaries is necessarily ____ for exchange materials
slow
T or F Blood flows from areas of lower pressure to higher pressure
FALSE, blood flows from high to low
Systolic pressure
the pressure in the arteries during ventricular systole; it is the highest pressure in the arteries
diastolic pressure
the pressure in the arteries during diastole; it is lower than systolic pressure
Pulse
the rhythmic bulging of artery walls with each heartbeat
Vasoconstriction
the contraction of smooth muscle in arteriole walls; it increases blood pressure
Vasodilation
the relaxation of smooth muscles in the arterioles; it causes blood pressure to fall
_____ is a major inducer of vasodilation
Nitric oxide
The peptide _____ is a strong inducer of vasoconstriction
endothelin
The system that returns fluid that leaks out from the capillary beds
lymphatic
fluid lost by capillaries is called
lymph
Edema
swelling caused by disruptions in the flow of lymph
Lymph nodes are
organs that filter lymph and play an important role in the body's defense
Blood in vertebrates is a connective tissue consisting of several kinds of cells suspended in a liquid matrix called
plasma
The composition of mammalian blood
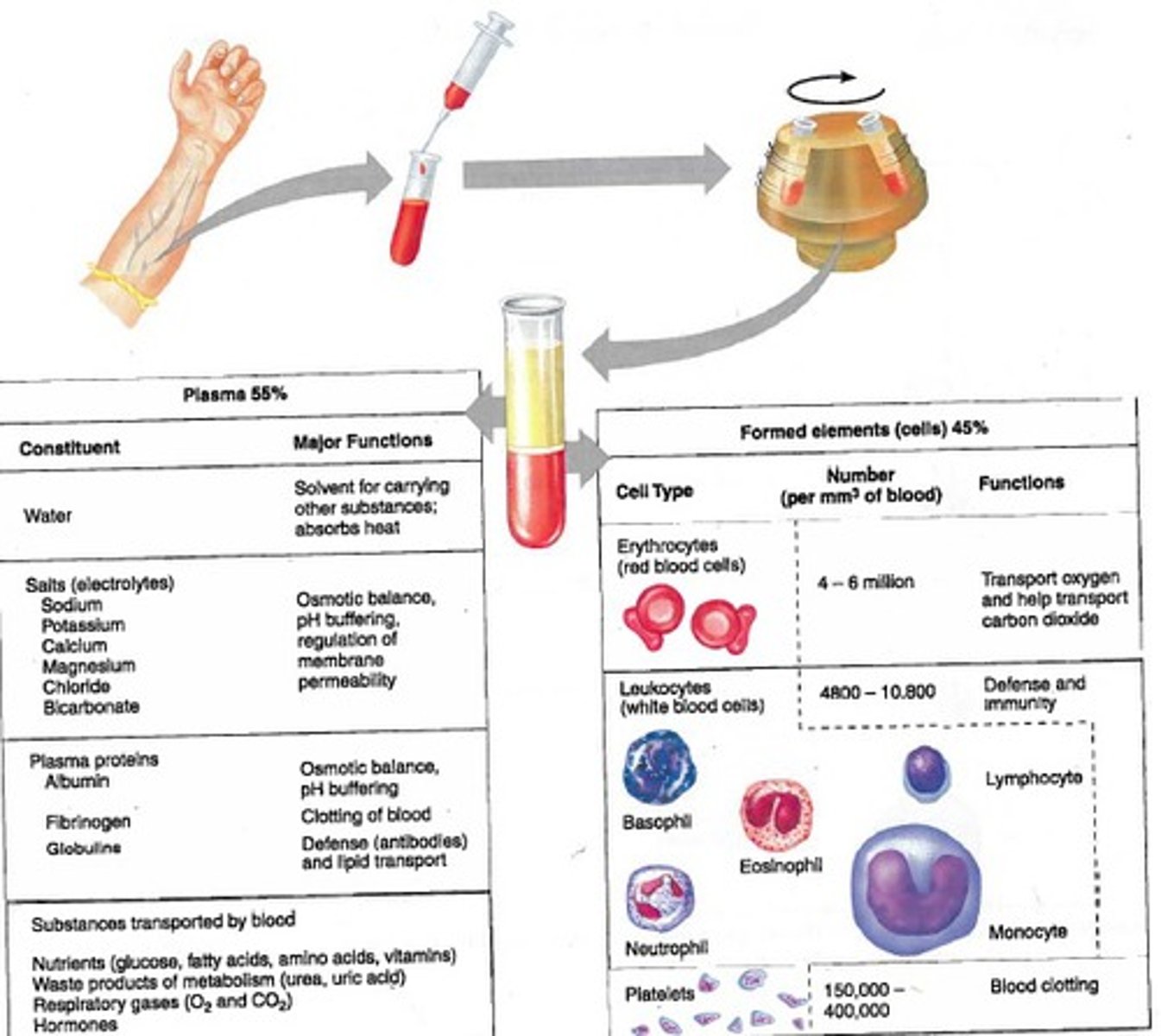
Platelets
fragments of cells that are involved in clotting
Erythrocytes
the most numerous blood cells
hemoglobin
iron containing protein that transports O2
Sickle cell disease is caused by
abnormal hemoglobin proteins that form aggregates
5 major types of white blood cells or leukocytes
monocytes, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, and lymphocytes
They function in defense either by _______ bacteria or mounting immune responses
phagocytizing
Platelets are fragments of cells and function in
blood clotting
Erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets all develop from a common source of
stem cells in the red marrow of bones
The hormone erythropoietin
stimulates erythrocyte production when O2 delivery is low
Coagulation
the formation of a solid clot from liquid blood
A blood clot formed within a blood vessel is called a ____ and can block blood flow
thrombus
Atherosclerosis
caused by the buildup of fatty deposits (plaque) within arteries
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
delivers cholesterol to cells for membrane production
High density lipoprotein (HDL)
scavenges excess cholesterol for return to the liver
Heart attack or myocardial infarction
the damage or death of cardiac muscle tissue resulting from blockage of one or more coronary arteries
stroke
nervous tissue in the brain usually resulting from rupture or blockage of arteries in the head
Angina pectoris
chest pain caused by partial blockage of the coronary arteries
Gas exchange supplies O2 for ________ and disposes of CO2
cellular respiration
Partial pressure is the pressure exerted by a _____ in a mixture of gases
particular gas
Ventilation moves the respiratory medium over the
respiratory surface
Lungs
an infolding of the body surface
Swallowing moves the ____ upward and tips the epiglottis over the glottis in the pharynx to prevent food from entering the ______
larynx and trachea
Air passes through the
pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles to the alveoli, where gas exchange occurs
Cilia and mucus line the epithelium of the air ducts to
move particles up to the pharynx
Gas exchange takes place in
alveoli, air sacs at the tips of bronchioles
surfactants
secretions that coat the surface of the alveoli
Breathing
the process that vetilates the lungs, the alternate inhalation and exhalation of air
Positive pressure breathing
ventilation by forcing air down the trachea
Negative Pressure breathing
pulls air into the lungs
Lung volume increases as the rib muscles and ______ contract
diaphragm
Tidal volume
is the volume air inhaled with each breath
vital capacity
maximum tidal volume
after exhalation a _______ of air remains in the lungs
residual volume
respiratory pigments
proteins that transport oxygen, greatly increase the amount of oxygen that blood can carry