Chapter 3 Cell Types, Membranes, and Tissue Structures Quizlet
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
What are the two main types of cells discussed in Chapter 3?
Eukaryotic (animal and plant) and prokaryotic.
What are the two types of body fluids mentioned in the study guide?
Intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF).
What is the concept of lumen in biological terms?
Lumen refers to the inside space of a tubular structure, such as a blood vessel or an organ.
What are the primary functions of biological membranes?
Biological membranes serve as barriers, facilitate communication, and regulate the transport of substances.
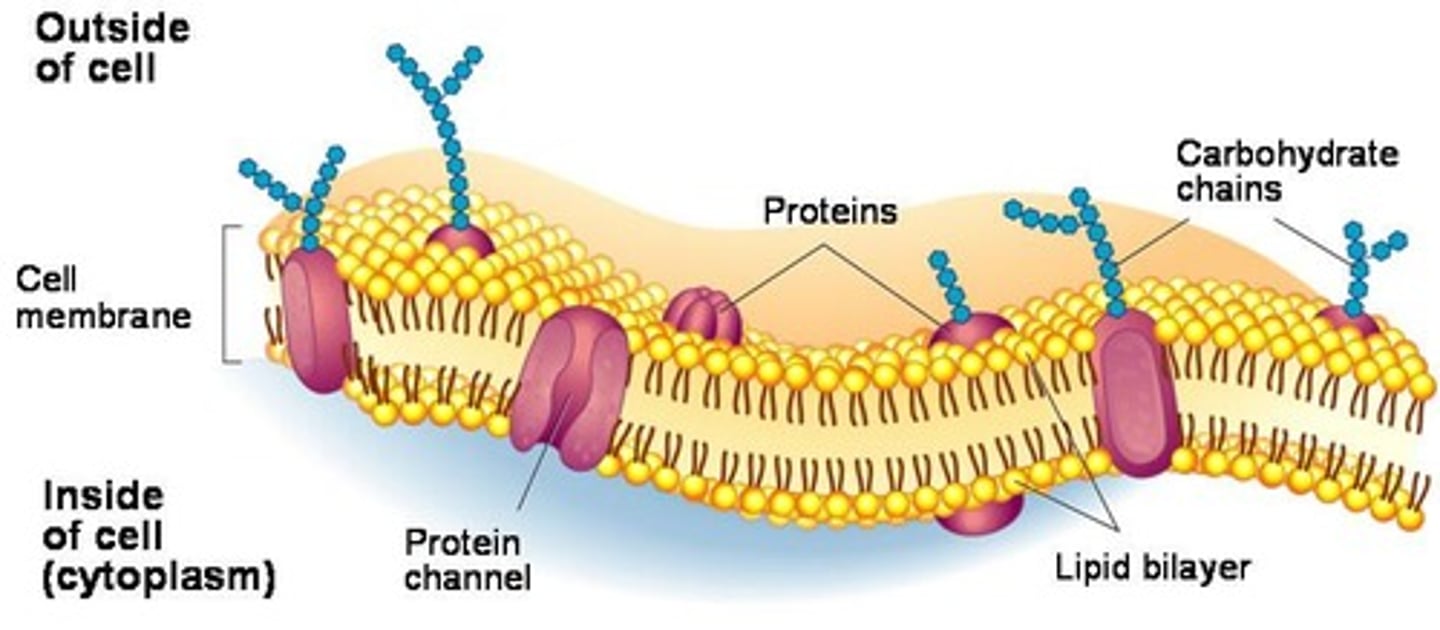
What are the major organelles in cell anatomy and their characteristics?
Major organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes, each with specific functions and localization.
What is the structure and function of the cytoskeleton?
The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that provides structural support, aids in cell movement, and facilitates intracellular transport through motor proteins.
What are the four primary tissue types in the body?
Epithelial, connective, muscle, and neural tissues.
What are the characteristics and functions of epithelial tissue?
Epithelial tissue covers body surfaces, lines cavities, and forms glands; it is characterized by closely packed cells and minimal extracellular matrix.
What is the role of the extracellular matrix?
The extracellular matrix provides structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells, influencing their behavior and function.
What are cell junctions and their importance?
Cell junctions are structures that connect cells to each other, facilitating communication and maintaining tissue integrity.
What should students not overlook in their preparation for the test according to the study guide?
Students should not overlook the Questions Section at the end of the chapter and the Concept Check questions, as they may appear on the exam.