Micro Final
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
13-15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Innate Immune System
“born with it,” immediately available; nonspecific, can react against anything
Adaptive Immune System
“Learned/Acquired,” memory, allows immune system to remember “nonself” it’s seen before; specificity; fast response and powerful once memory is established
Antigen
a toxin or other foreign substance which induces an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies; can bind to an antibody or T-call receptor; can be proteins peptides, polysaccharides, etc.
Two molecules used by the innate immune system
TLRs: “toll-like receptors,” are a family of proteins that help in the innate immune system by recognizing pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), which are structures found in pathogens
cytokines: IL-1, IL-6, IL-8…they have different signals they look for and they send messages to the immune system if something is found, and gives directions on what to do
Macrophages
Destroy bacterial, fungal, and protozoan pathogens by phagocytosis; remove virus-infected cells-and tumor cells; present antigen to adaptive immune system
Mast Cells
Produce chemical mediators, recruit effector cells; influence adaptive response
Dendritic Cells
Present antigen to adaptive immune system; perform phagocytosis
Natural Killer Cells
Kill tumor cells and pathogen infected host cells
Two Parts of the Innate Immune System
Physical and Chemical Barriers: Skin, membranes, hair; saliva, stomach acid, enzyme
Cellular Responses: Phagocytosis, inflammation, interferon, complement system, fever
Phagocytosis
ingesting foreign bodies and destroying; goal = remove antigen
Inflammation
Helps destroy infectious agents and signal that the area is damaged and need repair/replacement inflammation includes: swelling, heat, pain, redness chemokines help to mediate/signal inflammation
Fever
Why? availability of iron (important micronutrient for microbes/temperature sensitive microbes, helps lower growth inactivates toxins (proteins) by changing their shape
Complement system
enhances (complements) the innate and adaptive immune system
functions: membrane attack, phagocytosis, and inflammation
c proteins mediate the complement syste
1. classical: antibodies specific to antigen
2. alternative: LPS and other surface antigens
3. lectin: mannose (carb not on human cells)
Interferon
A type of cytokine applies to viral infected cells; viral infected cells produce interferon to “warn” neighboring cells to make anti-viral proteins.
T-cells
2 main kinds:
T cytotoxic cells:
Roles: learn antigen and kill pathogen or learn antigen and become memory T cell
T helper cells
Roles: learn antigen and talk to a B cell or learn antigen and become memory T cell
Learn by being presented with an antigen
MHC: major histocompatibility complex, non-specific proteins, “present” the antigen
B-cells
activate into plasma cells; plasma cells make antibodies
Antibodies
proteins produced by the body’s immune system to help fight off foreign substances, like bacteria and viruses that can cause disease.
Immunoglobulins (Ig)
IgM: 1st antibody to appear in primary response (against polysaccharide)
IgG: “golden one,” most specific; highest affinity for antigen (against peptides)
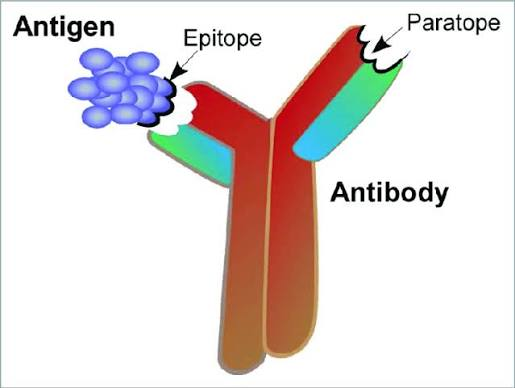
epitope
a part of the antigen to which antibodies bind
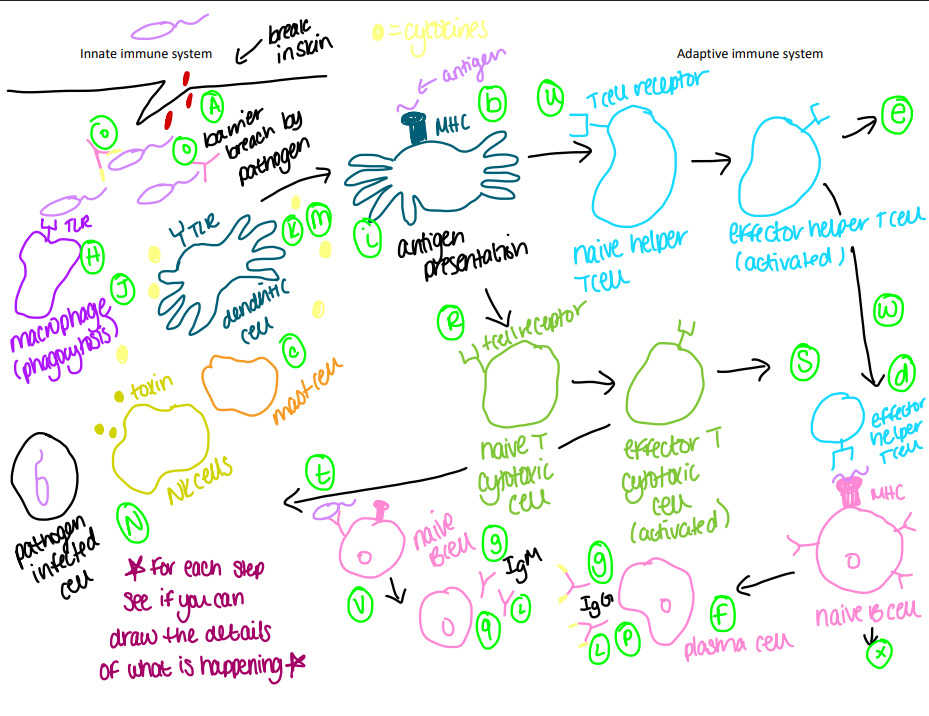
How do the innate and adaptive immune system work together?
The innate system acts first, recognizing broad patterns on pathogens and initiating a rapid inflammatory response. If the innate system fails to clear the infection, it signals to the adaptive system, which then develops a specific response tailored to the pathogen, often involving B cells and T cells.
Sterilization
used on inanimate objects; destruction or removal of all viable organisms
ex: cells, viruses, spores
Disinfection
killing, inhibition, or removal of pathogens-just ones that make people sick
Sanitization
microbial population is decreased to a safe level
ex: laundry, washing dishes, scrubbing into surgery
Antisepsis
preventing infection of living tissue by microbes
Antiseptics
agents used for antiseptics
ex: hand sanitizer
Chemotherapy
chemicals used internally to kill/inhibit of microbes within tissues
Bacterial Cidal
to kill
Bacterial static
inhibit growth
Bacterial lytic
agent that induces cell lysis
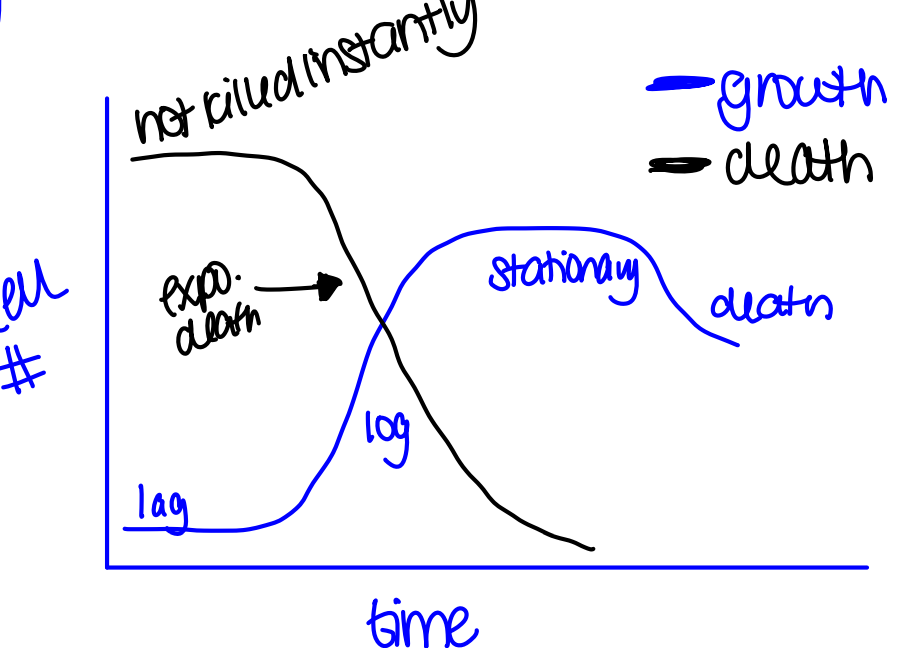
Pattern/measure of microbial death
Conditions that affect effectiveness of antimicrobial agent acitivty
properties of microbe
strength/concentration
population size
temperature
pH
Relative resistance of different microbes

Control Methods
physical agents: 1. heat 2. radiation
chemical agents: 1. gas 2. liquid
mechanical removal: filtration
biological agents: 1. phage 2. Bdelloubrio
Chemotherapeutic agents
Chemicals used to treat disease; destroy microbes or inhibit growth within a host
Penicillin
Alexander Fleming stole the work of Ernest Duchesne; discovered the antibiotic properties of penicillin cause he had a nasty work space and it got discovered on accident
Characteristics of antimicrobials
narrow spectrum: “attack” only a few types of bacteria
broad spectrum: “attack” a large #/types of bacteria
bacteriocidal: kill bacteria
bacteriostatic: prevent growth
How is effectiveness of an antimicrobial measured?
MIC: minimum inhibitory concentration; minimum concentration of antibodies required to inhibit growth
MLC: minimum lethal concentration; minimum concentration of antibodies required to kill growth
How to we determine level of antimicrobial activity?
Kirby Bauer
Dilution
Level of turbidity
Categories of Antimicrobials
antibodies
antivirals
antifungals
antiparasitics
antiprotozoans
Antibiotic Mechanisms of Action
Cell Wall
Nucleic acid synthesis
protein synthesis
metabolism
Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors

Protein Synthesis Inhibitors

Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors

Metabolism
folate synthesis inhibition; ex: sulfonamides, quinolones- associated with ligament damages
Factors that affect effectiveness of drugs
ability of drug to reach the site of infection
susceptibility to drug
ability of drug to reach/exceed MIC/MLC in body
depends on: amount (dose), route of administration, rate of clearing, rate of uptake, pharmacology
Antibiotic resistance mechanisms comes from where?
Mutation
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Antibiotic resistance mechanisms
Modification of target
Enzymatic inactivation
Removal from cell
Metabolic bypass
Persister cells
not resistant to antibiotics
dormant cells so antibiotics don’t bother them as antibiotics only work on actively growing cells
when antibiotic is removed, persister cell start growing again
Gut microbiome→brain interaction
The gut microbiome influences brain function and vice versa
plays a role in cognition and neurological disorders
C. sphaerosperum
a type of fungus that helps prevent from radiation poisoning-uses melanin to absorb radiation; used for the site around Chernobyl
Using microbes for our benefit
radiation shielding
radioprotective drugs
speed up rate of plant growth
bioremediation- microbial cleanup of oil, toxic chemicals, etc.
biodegradation- disintegration of materials by bacterial, fungi, or other microbes
Microbes in space
Microbes in space become more virulent and have higher antibiotic resistance; biofilms are able to form in space