Economics- 2.5: The UK Economy; Performance and Policies
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:03 PM on 11/9/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
1
New cards
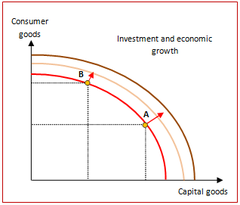
Economic Growth
The increase in productive capacity of an economy (GDP) over a period of time.
2
New cards
Government Growth Targets
2-3%
3
New cards
Unstable Growth concequences
Risk of Recession due to over confidence leading to environmental problems, bottle necks in supply, insifficient infastructure and inequality.
4
New cards
Actual Growth
Economic growth as measured by recorded changes in RGDP over time.
5
New cards
Potential Growth
Economic growth as measured by the changes in the productive potential (capacity) of the economy over time.
6
New cards
Fluctuations of GDP
-Boom = RGDP rise
-Recession = RGDP falls
-Slowdown = RGDP may rise below trend of fall
-Recession = RGDP falls
-Slowdown = RGDP may rise below trend of fall
7
New cards
Factors of Economic Growth
Land, Labour, Capital, Enterpirse. Components of Aggregate Demand
8
New cards
Land Growth
- New Resources: E.g Oil allowing cheaper energy prices and rise production of goods + services. Less reliant on foreign resources.
- Land purchased to build factories (Capital) and new labour demand causes rise in growth.
- Land purchased to build factories (Capital) and new labour demand causes rise in growth.
9
New cards
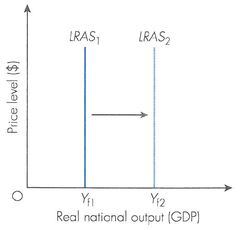
Labour
- Size: Immigration, Age, Participation. = More can be produced
- Quality: Education, Skills = Increased Efficiency
- Quality: Education, Skills = Increased Efficiency
10
New cards
Capital
- Sustained Investment (Foreign or Domestic) = New Technology to improve Productivity
- Improved Technology means lower COP as less labour is needed and more is produced.
- Improved Technology means lower COP as less labour is needed and more is produced.
11
New cards
Enterprise
- Development of jobs and products increases growth. Lead to more investment and more capital, labour or land.
- Lack of Credit or Capital leads to lack of investment. Lowering productivity but costs remain high.
E.g: High Interest rates, Lack of banking.
- Lack of Credit or Capital leads to lack of investment. Lowering productivity but costs remain high.
E.g: High Interest rates, Lack of banking.
12
New cards
Corruption and Instability
- Asymmetric Information in Credit: Lenders charge higher interest to cover risk. (Afforded by corrupt borrowers) = Missing Market, no equilibrium price of credit/ interest
- Incompitent Government = Decreased Investment, War diverts funds
- Fiscal Deficit = Cannot spend to grow
- Unstable Currency
- Incompitent Government = Decreased Investment, War diverts funds
- Fiscal Deficit = Cannot spend to grow
- Unstable Currency
13
New cards
Efficiency
Resources are allocated to serve each person in the best way possible, minimising waste and inefficiency.
14
New cards
Efficiency and Growth Relation
- Competition: Producers forced to lower prices or Increase Quality = Increase output or value
- Solid Credit markets to allow expansion.
- Solid Credit markets to allow expansion.
15
New cards
International Trade
Exchanging goods and services between countries
16
New cards
International Trade Benefits
- Prevents BOP deficit/ poor
- Increases competition = Forces increase in efficiency
- Increases investment into labour or capital to meet demand.
- Increases competition = Forces increase in efficiency
- Increases investment into labour or capital to meet demand.
17
New cards
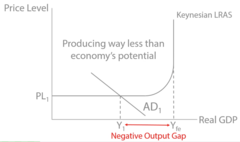
Output Gaps
The difference between actual and potential GDP or growth in GDP.
18
New cards
Positive Output Gap
The level of RGDP in the economy is greater than the Trend output level
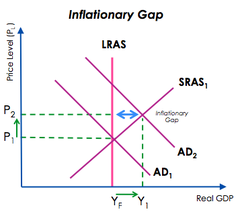
19
New cards
Negative Output Gap
The level of Actual RGDP in the economy is lower than the Trend output level or Potential GDP
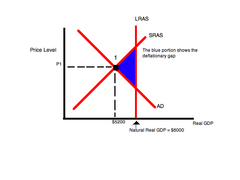
20
New cards
Difficulties of Output Gap
- Very Difficult to measure as exact position of LRAS is unknown.
- RGDP estimates are inaccurate.
- Invalid to use in economic policy due to inaccuracy.
- RGDP estimates are inaccurate.
- Invalid to use in economic policy due to inaccuracy.
21
New cards
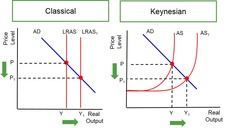
Classical View: Output Gap
Output Gaps cannot occur in the Long-run as Full employment is fixed
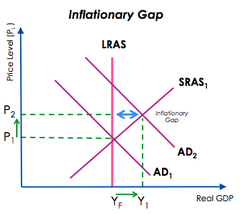
22
New cards
Productivity
Measure of the efficient use of FOP
23
New cards
Productivity effect on Economic Growth
- Increases national output/ GDP
- Inflation increases
-Economic Growth
- Inflation increases
-Economic Growth
24
New cards
Productivity on employment
-Unemployment increases in short- run but decreases in long-run because price levels decrease and exports increase
25
New cards
Productivity gap
Difference between labour productivity in the UK and in other developed economies
26
New cards
Producvitity Gap causes
- Lack of Technology
- Lack of skilled workers
- Entrepreneaurship
- Lack of skilled workers
- Entrepreneaurship
27
New cards
Trade Cycle
The pattern of economic growth which changes from booms or recovery and recessions or slow growth in a fairly regular pattern. Measured by a change in RGDP
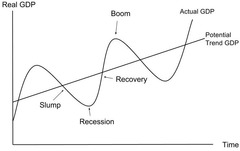
28
New cards
Mild Trade Cycle
RGDP does not fall but growth is lower than the trend
29
New cards
Extreme Trade Cycle
Cycle where RGDP falls.
- Normally caused by demand and supply shock.
- Normally caused by demand and supply shock.
30
New cards
Trend Explanation
Keynes: Due to 'Animal Spirit'- speculative action from rise and fall in output or asset prices
- Change in capital which exacerbate change in output
- Change in capital which exacerbate change in output
31
New cards
Characteristics of Boom
-High rates of economic growth
-Near full capacity or positive output gaps
-Unemployment Falls
-Demand pull inflation
-High consumer/firm confidence
-Government budget improves (more tax revenue and less spending on welfare)
-Interest Rates Increase
-Imports increase
-Standard of Living Increases
-Near full capacity or positive output gaps
-Unemployment Falls
-Demand pull inflation
-High consumer/firm confidence
-Government budget improves (more tax revenue and less spending on welfare)
-Interest Rates Increase
-Imports increase
-Standard of Living Increases
32
New cards
Characteristics of Recession
-Negative economic growth
-Spare capacity and negative output gaps
-Demand-deficient unemployment
-Low inflation rates
-Government budgets worsen due to more spending on welfare payments and lower tax revenues
-Less confidence amongst consumers and firms, which leads to less spending and investment
-Interest Rates decrease: to increase investment.
-Imports decrease.
-Standard of Living Falls
-Spare capacity and negative output gaps
-Demand-deficient unemployment
-Low inflation rates
-Government budgets worsen due to more spending on welfare payments and lower tax revenues
-Less confidence amongst consumers and firms, which leads to less spending and investment
-Interest Rates decrease: to increase investment.
-Imports decrease.
-Standard of Living Falls
33
New cards
Benefits of Economic Growth: Consumers
-Income and Wealth rise
-Increase saving for future consumption
-Increased Confidence = More spending on consumer durables
-Increased Employment and opportunities
-Increase saving for future consumption
-Increased Confidence = More spending on consumer durables
-Increased Employment and opportunities
34
New cards
Costs of Economic Growth: Consumers
-Increased inequality: Unwaged and Unskilled less likely to benefit from growth, Incomes of some accelerate faster those on low wages affected by inflation + tax.
-Long term Unemployment with inflexible labour markets.
-Long term Unemployment with inflexible labour markets.
35
New cards
Benefits of Economic Growth: Firms
-Increased Profit
-Increased sales due to increased consumption
-More workers and Investments = Future growth
-FDI increases
-Multiplier and Accelerator effect
-Invest into cleaner technology to boost brand image.
-Increased sales due to increased consumption
-More workers and Investments = Future growth
-FDI increases
-Multiplier and Accelerator effect
-Invest into cleaner technology to boost brand image.
36
New cards
Costs of Economic Growth: Firms
-Environmental problems/ Negative externalities
-Depletion of natural resources and external costs
-May have tight labour markets = Less suitable workers available and higher skilled more competitive.
-Inflation
-Depletion of natural resources and external costs
-May have tight labour markets = Less suitable workers available and higher skilled more competitive.
-Inflation
37
New cards
Benefits of Economic Growth: Government
-Increased tax revenue from: VAT, Income, Corporation
-Fewer demands to pay welfare = better fiscal position. (Gov Spending decreases)
-Standard of Living rises and total incomes rise as long as Cost of living does not rise at same rate
-More Gov Spending on areas to increase SOL
-Wealth/ Asset increases.
-Fewer demands to pay welfare = better fiscal position. (Gov Spending decreases)
-Standard of Living rises and total incomes rise as long as Cost of living does not rise at same rate
-More Gov Spending on areas to increase SOL
-Wealth/ Asset increases.
38
New cards
Costs of Economic Growth: Government
-Balance of Payments deficit/ decrease: Consumers have higher incomes and spend more on imports and less incentive for firms to export
-Bottleneck: Little spare capacity = Increase price for energy, skilled labour = COP increases
-Monopoly power develops = Barrier to entry developed
-Social Dislocation and Stress = Increase spending and social pressure may result in more household debt
-Decreased Productivity: More travels, less hours worked due to high income, retire
-Bottleneck: Little spare capacity = Increase price for energy, skilled labour = COP increases
-Monopoly power develops = Barrier to entry developed
-Social Dislocation and Stress = Increase spending and social pressure may result in more household debt
-Decreased Productivity: More travels, less hours worked due to high income, retire
39
New cards
Rapid Growth Problems
-Short term spikes/ inflation
-Bad planning/ Corner Cutting
-Poor income distribution
-Volatility in economic cycle (deeper recession)
-Bad planning/ Corner Cutting
-Poor income distribution
-Volatility in economic cycle (deeper recession)
40
New cards
Growth pessimists
Those who question long-term sustainability of growth.
-Renewable energy will be depleted due to concept of the Tragedy of the Commons: public good means no one will look after it and quality decreases.
-Increased environmental threats putting pressure on scarce land and over-population.
-Renewable energy will be depleted due to concept of the Tragedy of the Commons: public good means no one will look after it and quality decreases.
-Increased environmental threats putting pressure on scarce land and over-population.