Chapter 18 - Rates of Reaction
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
rate of reaction
change in concentration of a reactant/product per unit time
equation = change in conc/time
units = mol dm-3 s-1
order of a reactant
the power to which the concentration of a reactant is raised by in rate equation e.g. [A]x
-can only be 0, 1 or 2
rate α [A]x [B]y
zero order with respect to reactant
-changing the concentration of reactant has no effect on rate of reaction e.g. ‘as [A] is doubled, the rate of reaction remains constant’
rate α [A]0
![<p>-changing the concentration of reactant has <strong>no effect on rate</strong> of reaction e.g. ‘as [A] is doubled, the rate of reaction <span style="color: red;">remains constant</span><span>’</span></p><p>rate <strong><span>α </span></strong><span>[A]</span><span style="color: red;"><strong><sup><span>0</span></sup></strong></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e42f6929-6bf3-4661-95af-5320ea53cc03.jpg)
first order with respect to reactant
-the rate of reaction is directly proportional to concentration of reactant e.g. ‘as [A] is doubled, the rate of reaction is doubled’
rate α [A]1
![<p>-the rate of reaction is <strong>directly proportional</strong> to concentration of reactant e.g. ‘as [A] is <span style="color: blue;">doubled</span>, the rate of reaction is <span style="color: blue;">doubled</span><span>’</span></p><p><span>rate </span><strong><span>α </span></strong><span>[A]</span><span style="color: blue;"><strong><sup><span>1</span></sup></strong></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3750360c-1335-4088-94c1-3fb2eded8e29.jpg)
second order with respect to reactant
-the rate of reaction will equal to concentration of reactant squared e.g. ‘as [A] is doubled, the rate of reaction is quadrupled’
rate α [A]2
![<p>-the rate of reaction will equal to <strong>concentration </strong>of reactant <strong>squared </strong>e.g. ‘as [A] is <span style="color: green;">doubled</span>, the rate of reaction is <span style="color: green;">quadrupled</span><span>’</span><span style="color: green;"> </span></p><p><span>rate </span><strong><span>α </span></strong><span>[A]</span><span style="color: green;"><strong><sup><span>2</span></sup></strong></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7492c09f-c0ec-4f82-9f29-f5111c5cebdd.jpg)
rate equation + constant
rate = k [A]x [B]y [C]z
k = constant that links rate of reaction with order of reactants
overall order
-sum of individual orders in reaction equation
e.g. x + y + z
calculating k and units
-rearrange rate equation to work out k
-work out units the same as Kc, mol dm-3 s-1
measuring rate of reactions
-measuring pH changes in titrations
-measure volume of gaseous product with gas syringe
-monitor colour changes using colorimeter
half life t1/2
the time taken for the concentration of a reactant to decrease by half
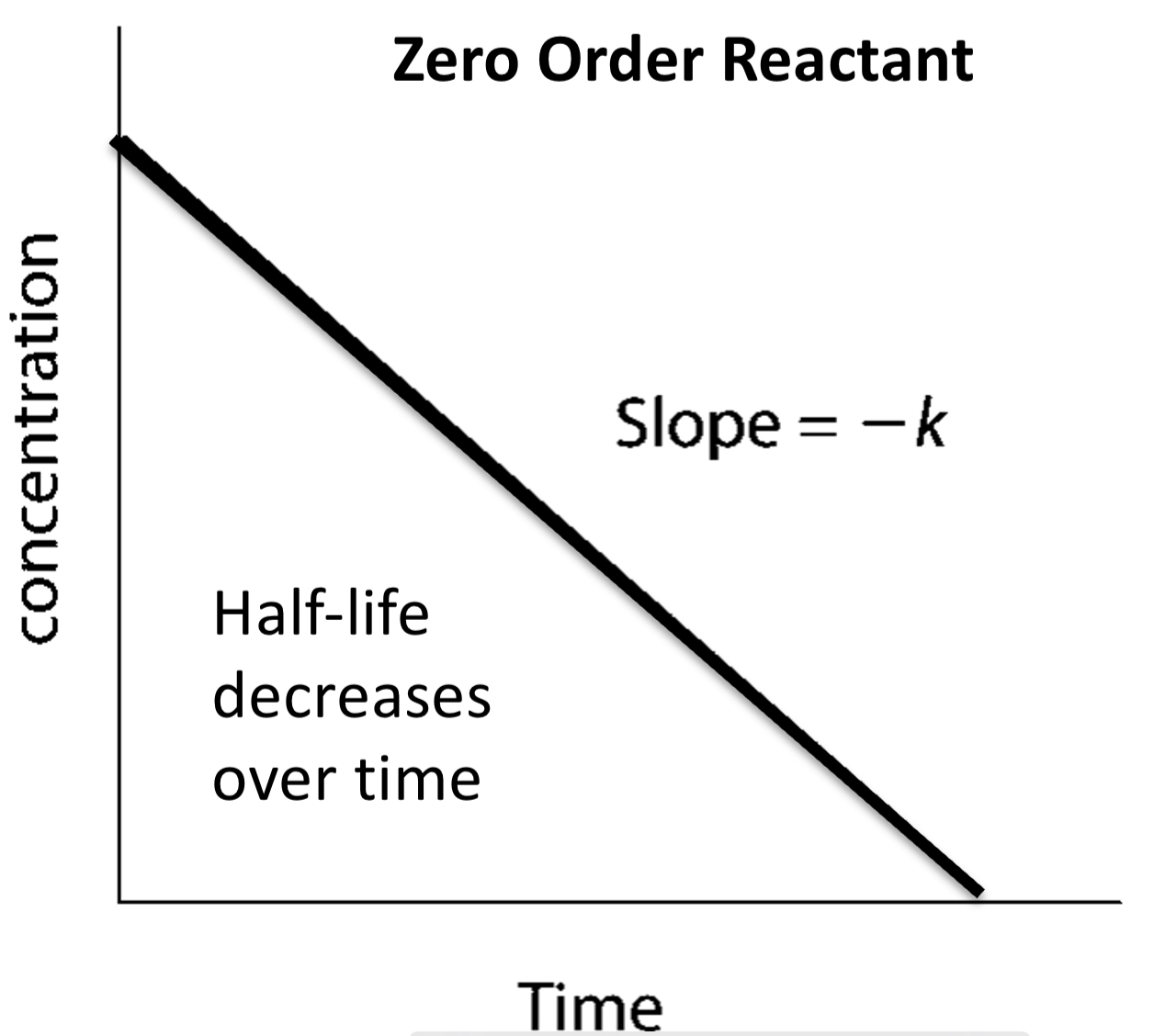
concentration-time graph for ZERO ORDER (draw graph)
has no effect on rate so also no effect on half life
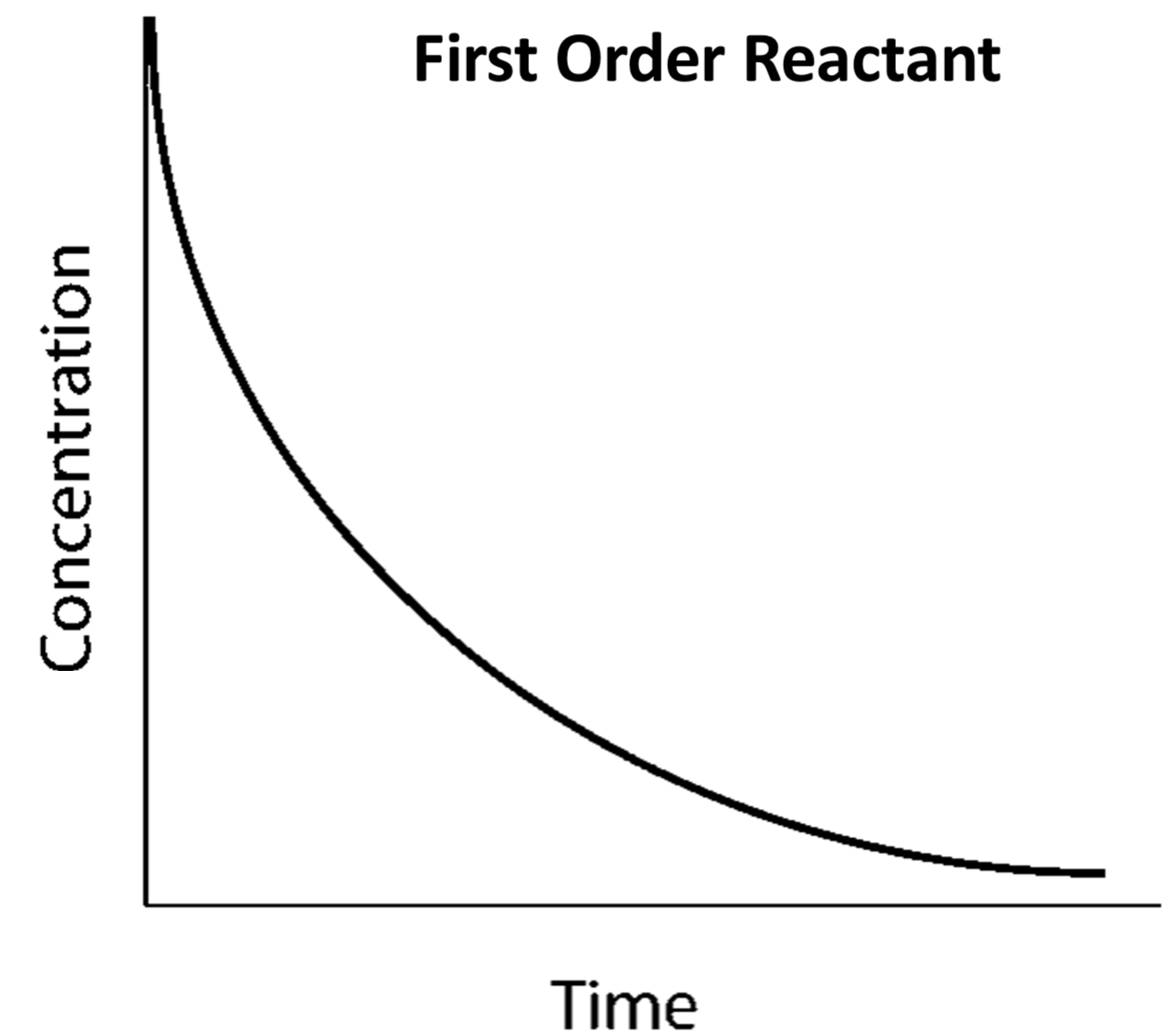
concentration-time graph for FIRST ORDER (draw graph)
half life remains constant/the same over time
equation for k using HALF LIFE
k = ln2 / t1/2
plotting RATE-CONCENTRATION graphs
x-axis = concentration, y-axis = rate
gradient = rate constant k
clock reaction
-method to measure initial rate of reaction
initial rate α 1/t
examples = visual colour change, formation of ppt increases over time, time taken for ppt depends on conc of reactants
rate determining step
the slowest step in a reaction mechanism
-determines the rate as it is the slowest
how to work out rate determining step
-given overall chemical equation
-then given rate equation - reactant in equation is the only species present in rate determining step
-first equation uses reactant and forms products then used in second equation
-then cancel out species present on both sides to gain chemical equation
example of rate determining step
CH3Br + OH- → CH3OH + Br-
rate = k [CH3Br]
1) CH3Br → CH3+ + Br-
2) CH3+ + OH → CH3OH
then cancel out CH3+
Arrhenius equation - taking logs
k = Ae-Ea/RT
k = rate constant, Ea = activation energy, T = temp in Klevin, A = pre-exponential factor, R= gas constant,
ln k = (-Ea/R x 1/T) + ln A
y = m x + c - y = ln k, m = -Ea/R, x = 1/T, c = ln A