Viruses, Viroids, Prions: Structure and Multiplication
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Virus
Microbe requiring a host cell to reproduce.
Capsid
Protein coat surrounding a virus's nucleic acid.
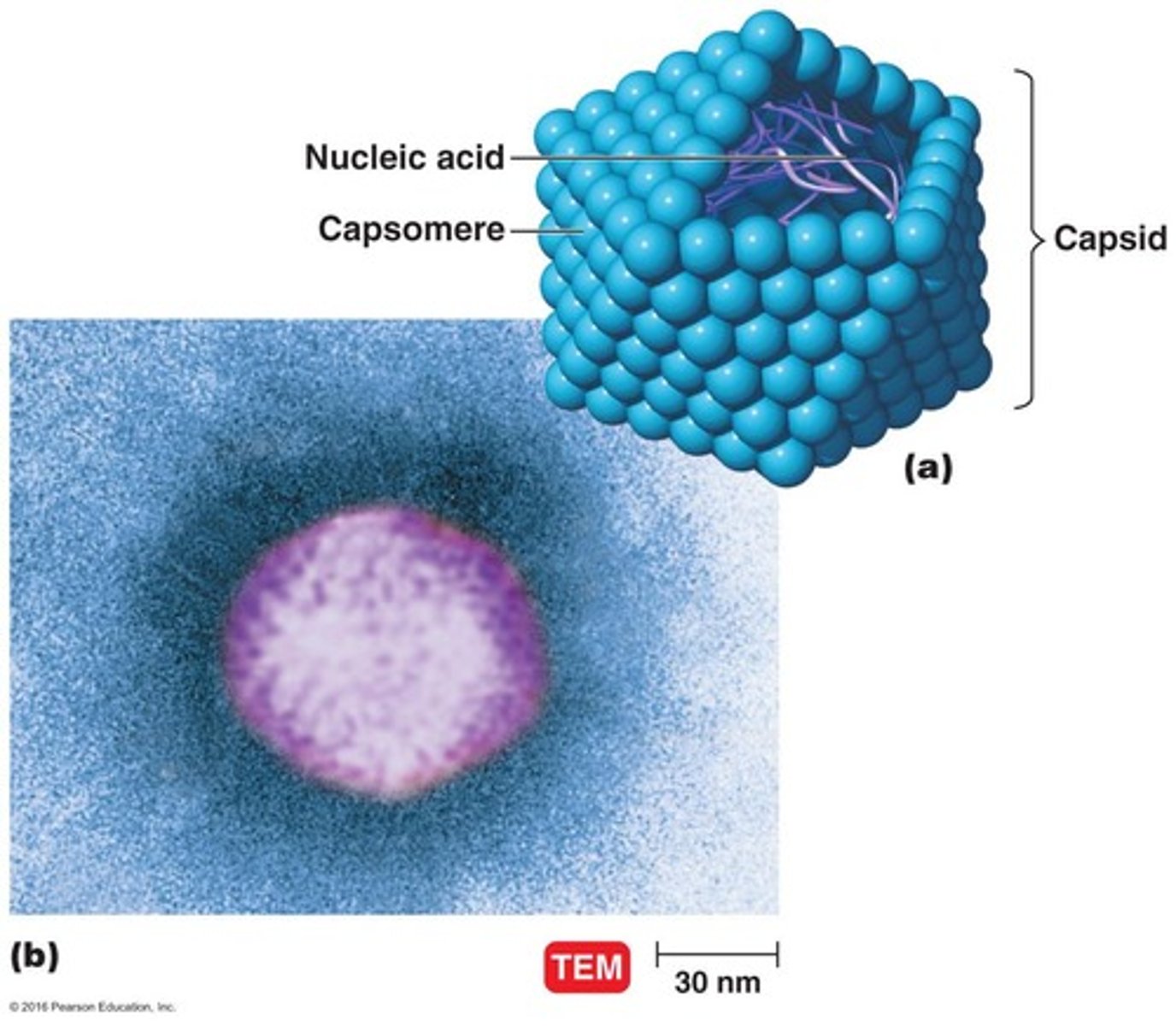
Capsomere
Protein units that make up the capsid.
Viroid
Short RNA sequences without a capsid, found in plants.
Morphology
Form and structure of a virus.
Host Range
Organisms a virus can infect.
Bacteriophage
Virus that specifically infects bacteria.
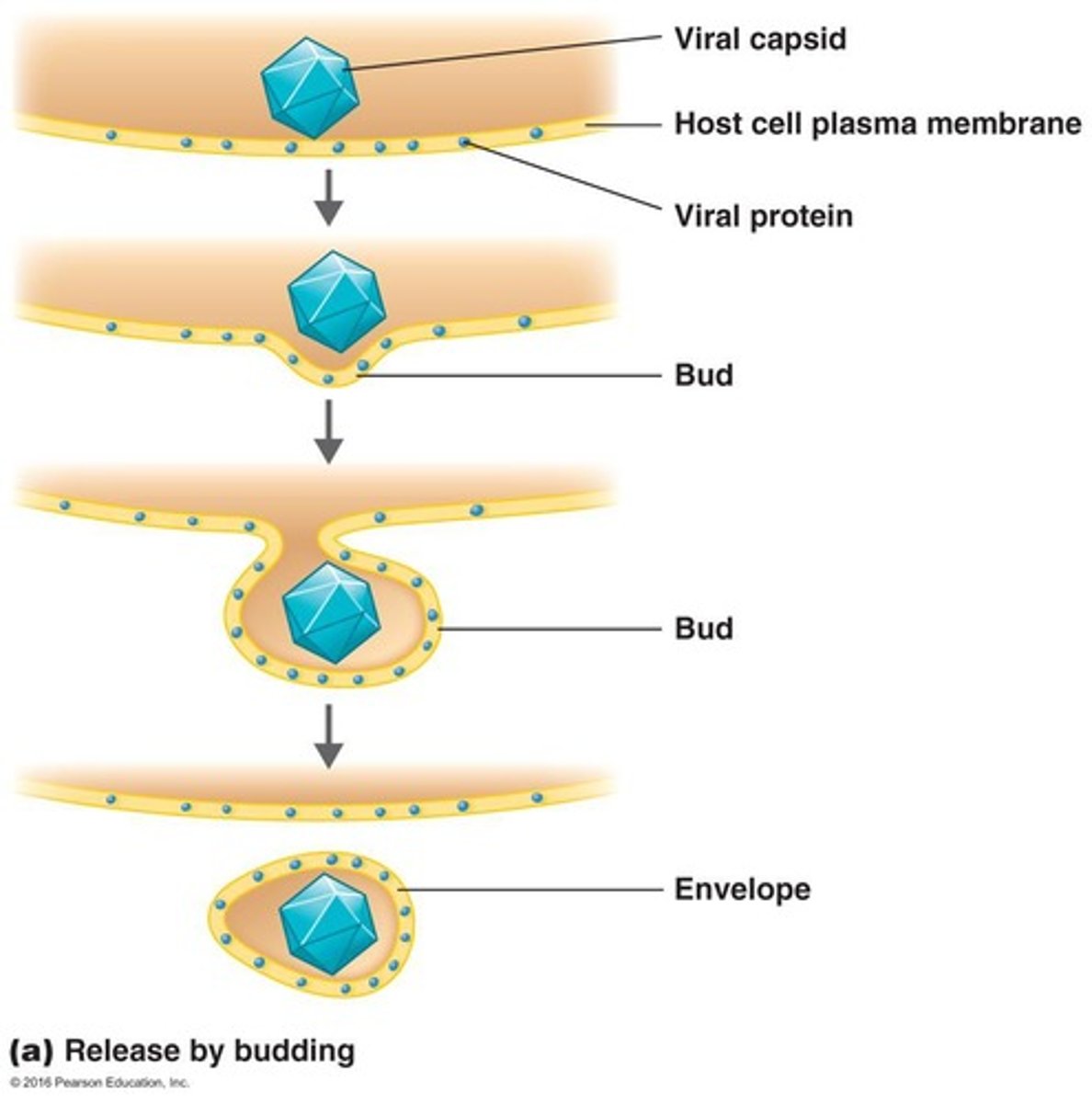
Envelope
Lipid layer surrounding some viruses' capsids.
Spikes
Carbohydrate-protein complexes aiding virus attachment.
Helical Virus
Long rods, can be rigid or flexible.
Polyhedral Virus
Common eicosahedron structure with twenty sides.
Enveloped Virus
Roughly spherical due to its lipid envelope.
Complex Virus
Viruses with multiple conjoined shapes.
Baltimore Classification
Sorts viruses by nucleic acid type and strands.
Viral Species
Group of viruses sharing genetic info and host range.
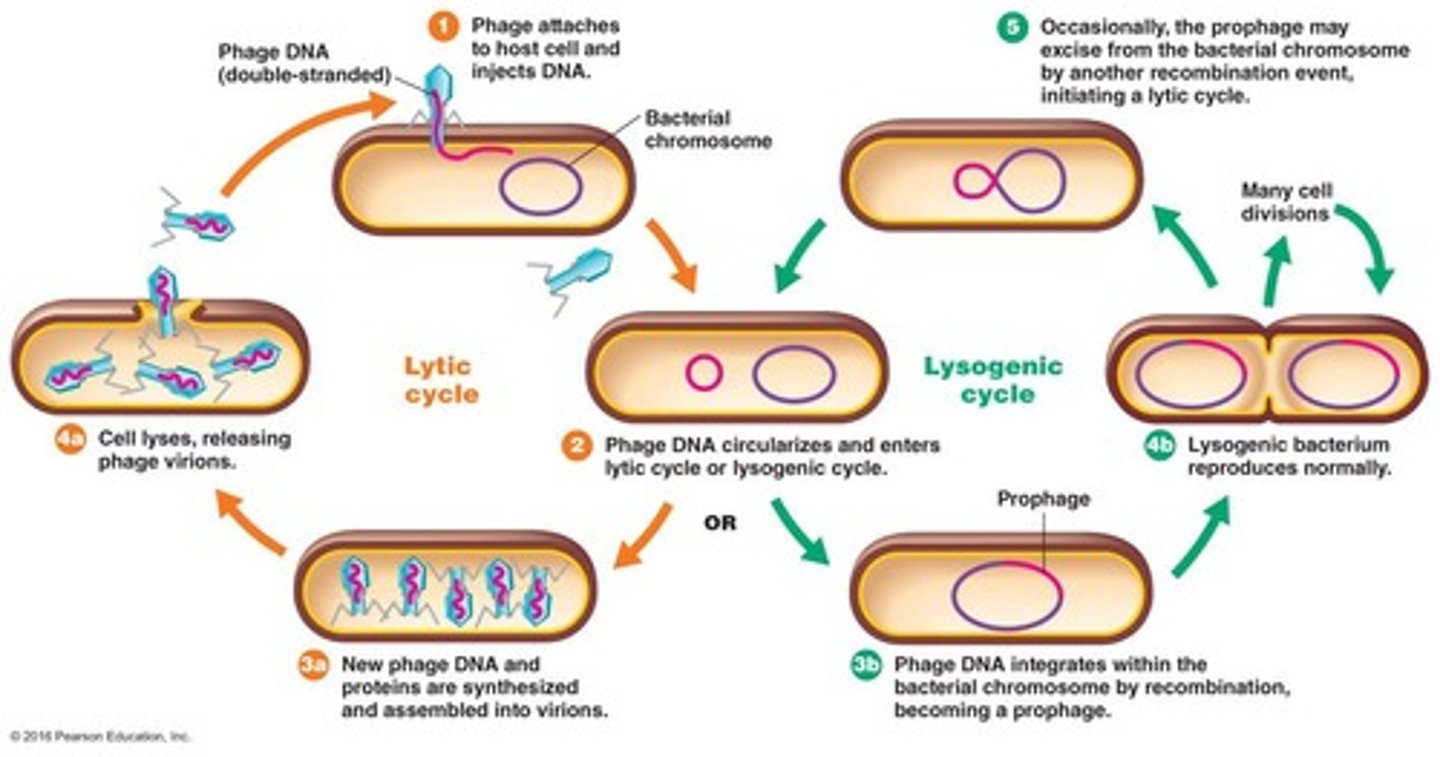
Lytic Cycle
Virus hijacks host cell, producing new virions.
Lysogenic Cycle
Viral DNA integrates into bacterial chromosome.
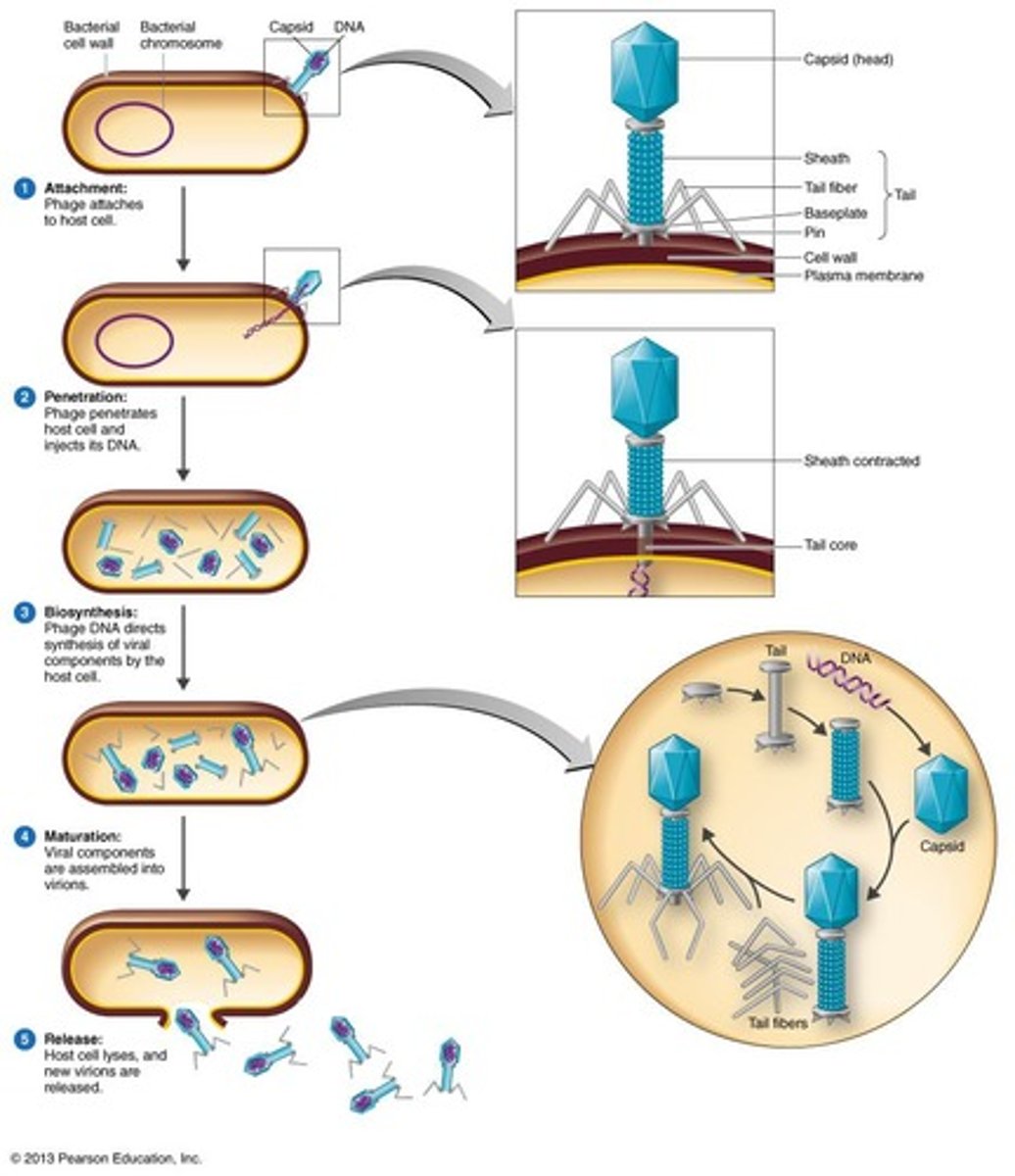
Attachment (Lytic Cycle)
Phage attaches to host cell's wall.
Penetration (Lytic Cycle)
Phage injects genetic material into host cell.
Biosynthesis (Lytic Cycle)
Host cell duplicates phage genetic material.
Maturation (Lytic Cycle)
Assembly of viral proteins and genetic material.
Release (Lytic Cycle)
Host cell lyses, releasing new virions.
Oncogene
Gene inducing uncontrolled growth, leading to cancer.
Prion
Infectious particle made of misfolded proteins.