Range of motion / goniometry of shoulder
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
assessment of 3 things during functional movement and straight plane gross motion
1. quantitative: how much motion exists
2. qualitative: what is the "quality" of the motion
3. symptom response: does the motion reproduce any of the subject's symptoms
pattern of functional movement screening
bilateral
1. hand behind head
2. hand to contralateral scapula
3. reach behind the back
reaching hand behind the head
measure spine level of middle finger to spinal level
assess: shoulder: elevation and external rotation, elbow/forearm: flexion and supination
reaching hand to contralateral scapula
assess how far onto scapula of middle finger
shoulder: flexion, horizontal flexion and internal rotation elbow/forearm: flexion and pronation
reaching hand behind the back
measure level of thumb up the spine
assess: shoulder: extension and internal rotation, elbow/forearm: flexion and pronation
straight plane gross motion assessment
bilateral comparison
shoulder complex flexion/extension
shoulder complex elevation/abductions
internal and external rotation at side
internal and external rotation at 90 degrees (elevation/abduction)
normal values for shoulder flexion
0-180
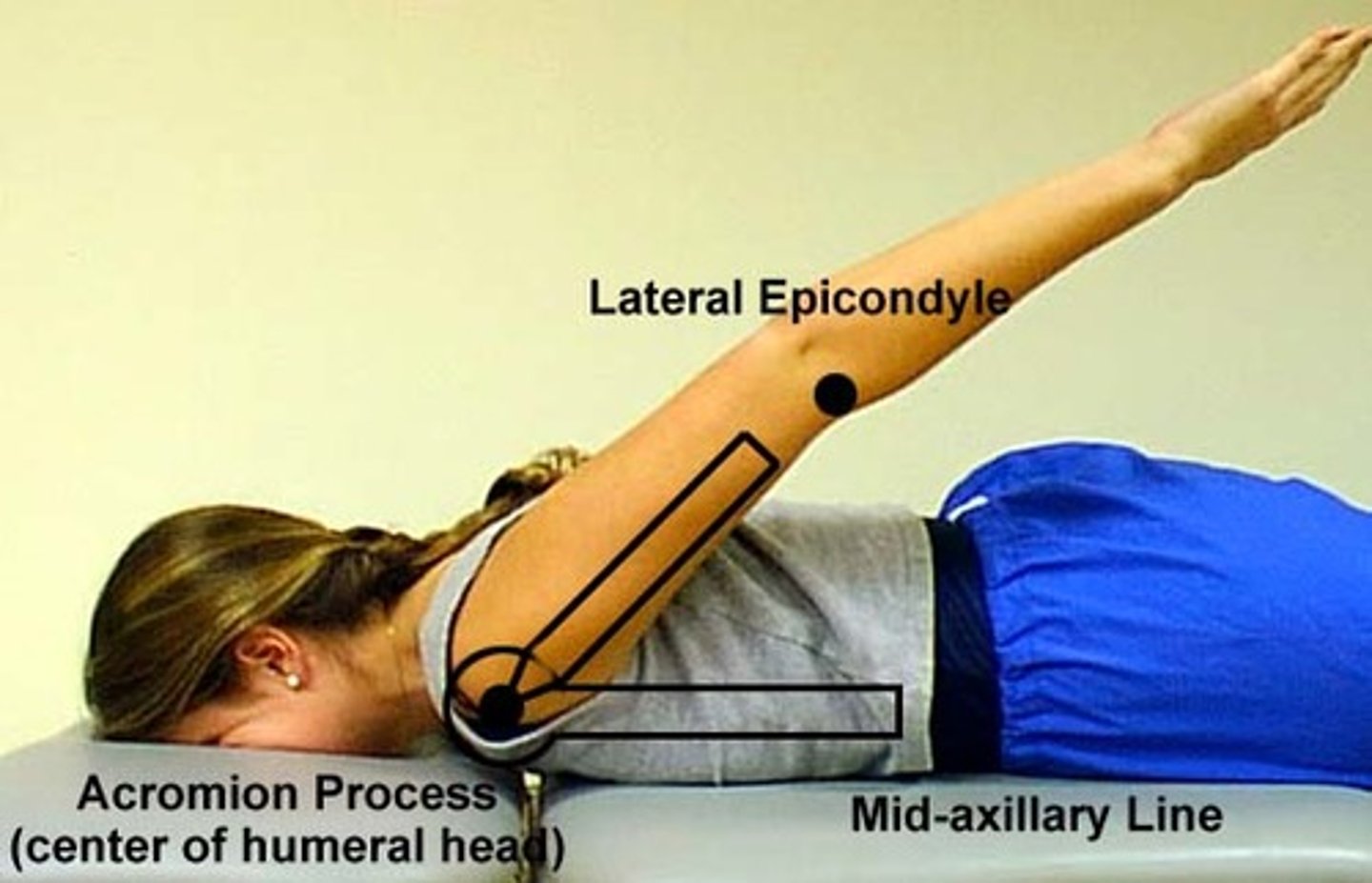
shoulder flexion
subject position: standing/supine
axis: approx. 1-inch distal to lateral acromion
stationary arm: mid axillary arm: rib cage
movable arm: lateral epicondyle of elbow
compensation for shoulder flexion
trunk extension (leaning back)
scapular elevation
normal values for shoulder extension
0-60 degrees
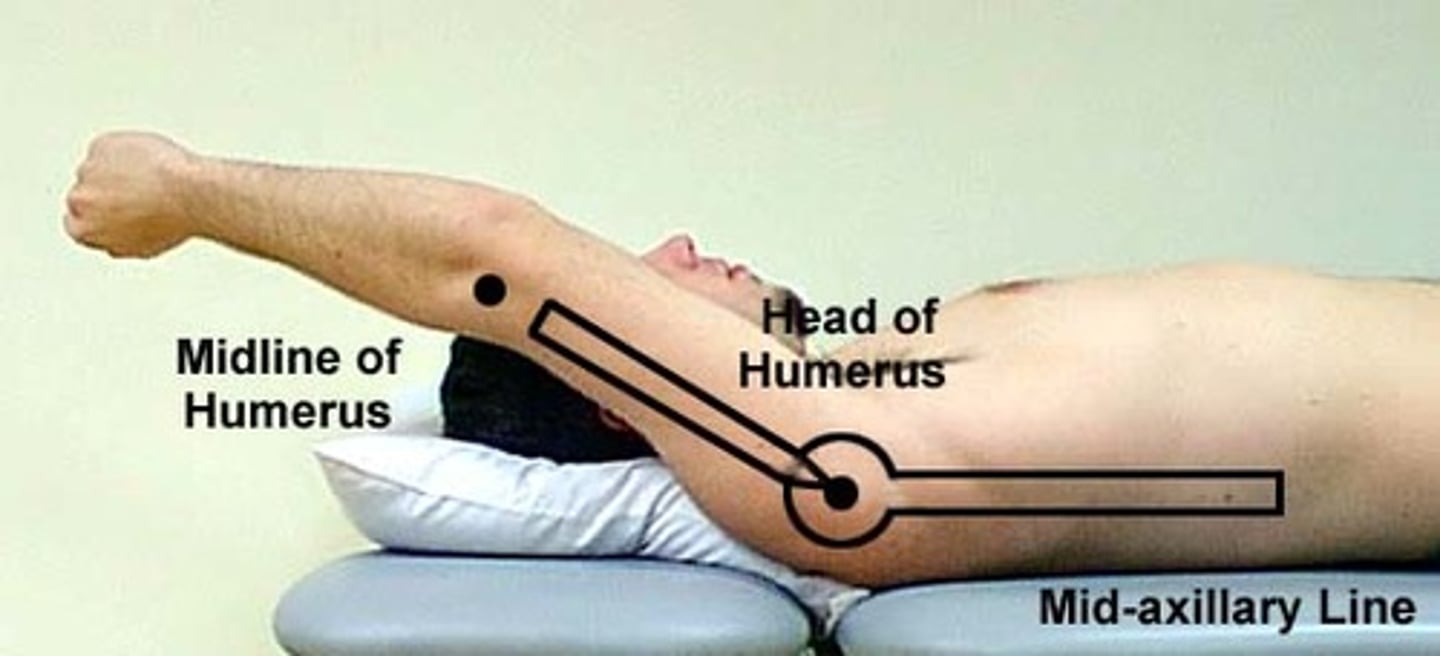
shoulder extension
subject position: standing or supine or prone
axis: approx 1 inch distal to lateral acromion
stationary arm: mid axillary line
moveable arm: lateral epicondyle of elbow
compensations for shoulder extension
may lean forward
normal values for shoulder elevation (abduction)
0-180 degrees
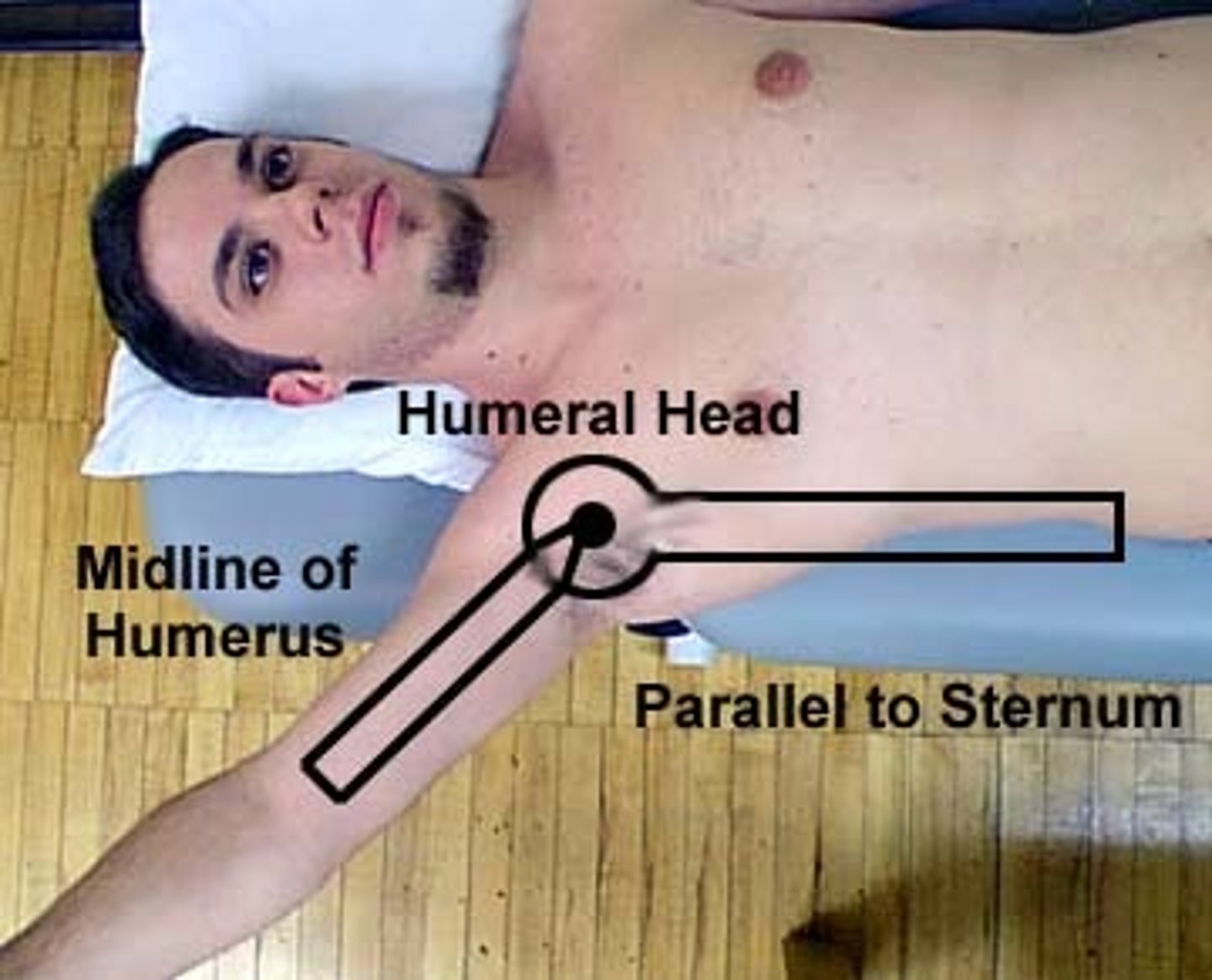
shoulder elevation (abduction)
subject position standing or supine
axis: approx 1 inch inferior to posterior or anterior acromion
stationary arm perpendicular to floor or parallel to sternum
moveable arm: anterior or posterior humerus
compensation for shoulder elevation (abduction)
side bending
scapular elevation (AKA shrug sign)
normal values for shoulder external rotation
0-60
shoulder external rotation
subject position: standing
axis: olecranon process
stationary arm: in sagittal plane
moveable arm: ulnar surface of forearm to the ulnar syloid process
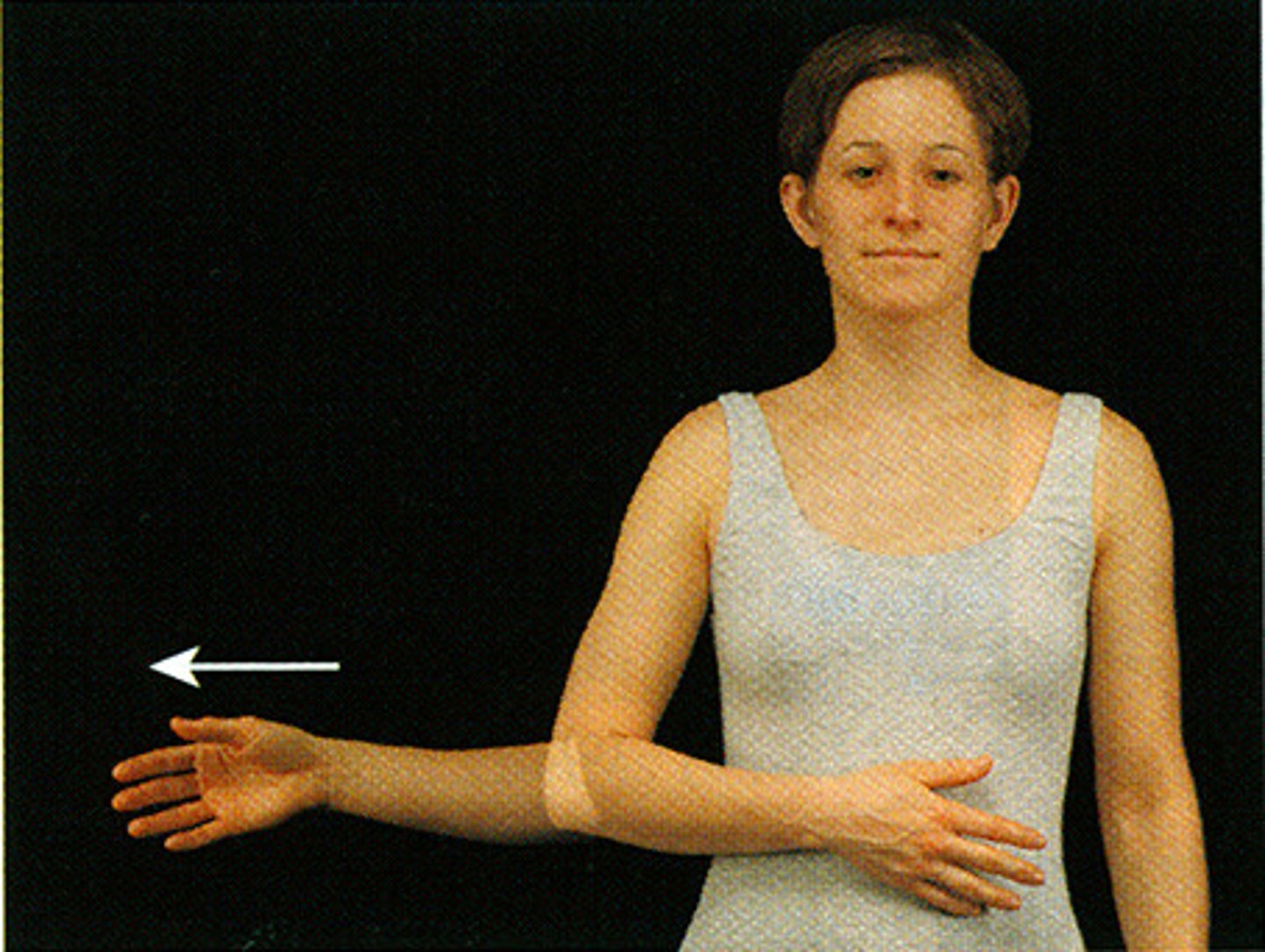
compensations for external rotation
trunk rotation
external rotation at 90 degrees
subject position : supine with shoulder at 90
axis: olecranon process of elbow
stationary arm: perpendicular to floor
moveable arm: ulnar surface of forearm
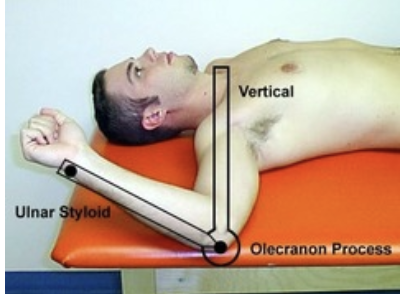
normal values for external rotation at 90 degrees
0-90
normal values shoulder internal rotation at 90
composite: 0-70
limited: 0-45
internal rotation
subject position: supine with shoulder at 90 degrees
axis: olecranon process of elbow
stationary arm: perpendicular to floor
moveable arm: ulnar surface of forearm to the ulnar styloid process
compensation for internal rotation
scapular elevation
normal values for horizontal adduction/flexion
0-135 degrees
horizontal adduction/flexion
subject position: sitting with shoulder abducted to 90 degrees with palm down
axis: superior acromion
stationary arm: in frontal plane of body
moveable arm: superior humerus, lined up with lateral epicondyle
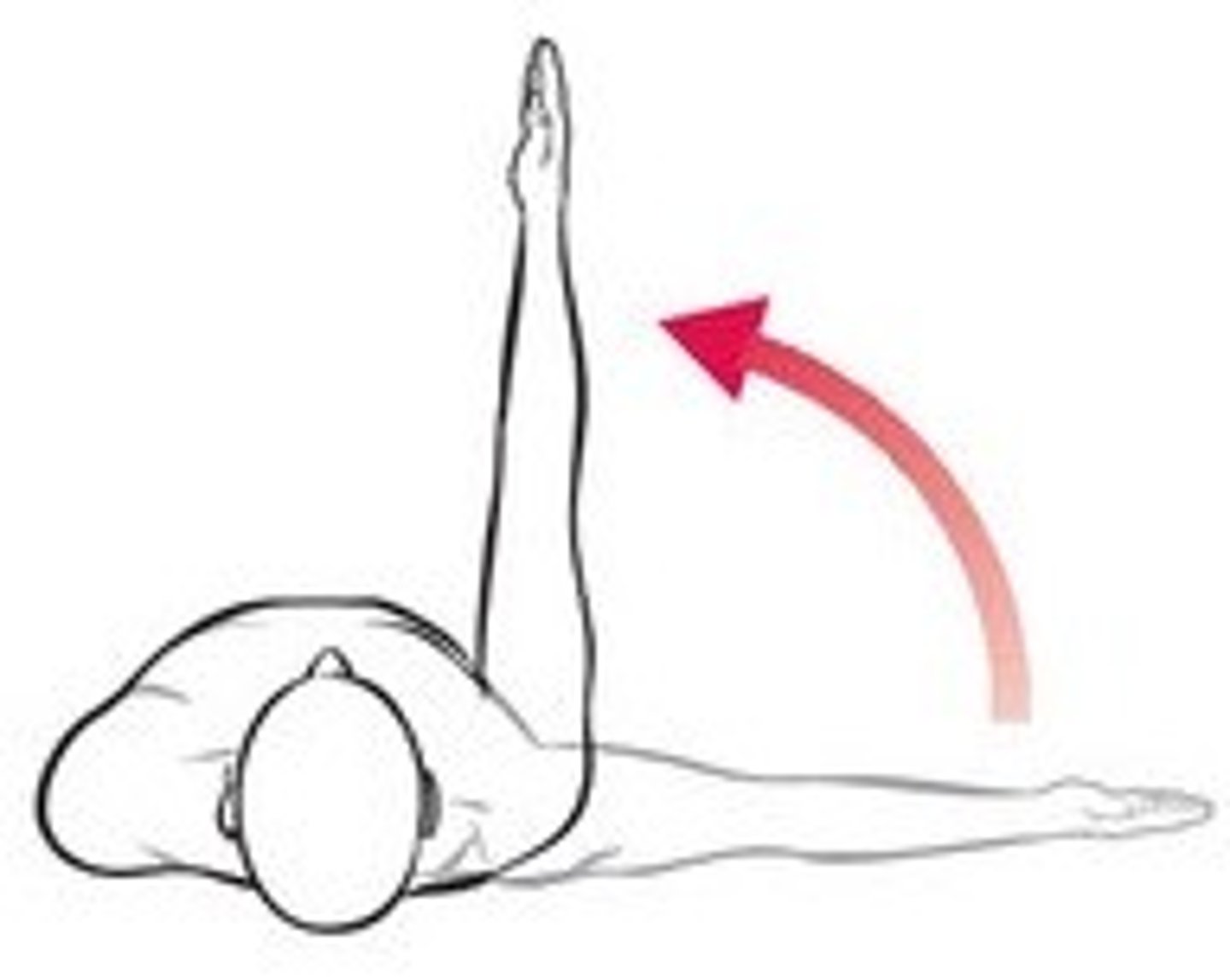
compensation for horizontal adduction
trunk rotation
normal values for horizontal abduction/extension
0-60 degrees
horizontal abduction/extension
subject position: sitting with shoulder abducted to 90 degrees making a fist with palm down
axis: superior acromion
stationary arm: in frontal plane of body
moveable arm: superior humerus, lined up with lateral epicondyle