10 [KAYA MO TO, PAPASA KA] Viral Diseases
1/302
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
303 Terms
• Large family of viruses
• Cause latent, recurrent infections
Herpesviridae
Herpesviridae Characterisitics
dsDNA, icosahedral or cubic symmetry, with a spiked envelope
Herpesviridae Examples
• Herpes simplex virus (HSV), types 1 and 2 • Varicella-zoster virus (HHV-3) • Epstein-Barr virus (HHV-4) • Cytomegalovirus (HHV-5) • Human herpesvirus-6 to 8 (HHV-6, HHV-7, HHV-8)
types 1 and 2
Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
(HHV-3)
Varicella-zoster virus
(HHV-4)
Epstein-Barr virus
(HHV-5)
Cytomegalovirus
(HHV-6, HHV-7, HHV-8)
Human herpesvirus-6 to 8
Herpes Causative Agent
HSV-1 (oral) and HSV-2 (genital)
Occurs in childhood
HSV-1
acquired from sexual activity)
HSV -2
Herpes Transmission
direct contact with vesicular discharge
Herpes Mechanism
Virus from active lesions enter through cracks or cuts in the skin or through mucous membranes • Reproduce in epithelial cells • May remain latent in nerve cells » recurrence • Reactivation triggered by a variety of stimuli
fetus is infected in utero / during or after birth
Neonatal herpes
Herpes Manifestations
• Gingivostomatitis
• Painful, itchy skin lesions • Lips (fever blisters or cold sores) • Genitalia
• Flu-like symptoms
• Neonatal herpes: “cigarette burn” lesions
Herpes Complications
Meningitis, Encephalitis, Keratitis (corneal blindness) Eczema herpeticum
Herpes Diagnosis
• Microscopic examination: Tzanck cells • Presence of lesions • Pap smear » cytopathic effects • Antibody testing
Herpes Prevention
• Use of condoms • Abstinence • Mothers with cold sores should be careful in handling newborns
Herpes Treatment
• Acyclovir, Valacyclovir and Famciclovir
Chickenpox
Varicella
Shingles
Herpes Zoster
Chickenpox and Shingles Causative Agent
Varicella zoster virus (VZV or HHV-3)
Chickenpox and Shingles Transmission
respiratory route / transmission through vesicular fluid
Chickenpox and Shingles Mechanism
• Spread through respiratory droplets; close contact with active lesions • Virus enters the respiratory tract, attaches to mucosa and invades the bloodstream » reaches skin • Remain latent in nerve cells • Primary infection: Chickenpox; Reactivation: Shingles
Primary Infection
Chickenpox
Reactivation
Shingles
Chickenpox and Shingles Most often seen in
Children
But Chickenpox and Shingles is typically more severe in
adults
• (IP: 10 – 21 days): lesions on the back and trunk that spread to the face, neck, limbs
Macules » papules » thin-walled, fluid-filled vesicles » vesicles turn cloudy, dry up and crust over (heal without scarring)
Chickenpox
localization of lesions along a band of skin that is innervated by a single sensory nerve; the rash is very painful
Shingles
Chickenpox and Shingles Diagnosis
• Microscopic examination: Tzanck cells • Presence of lesions • Antibody testing
Chickenpox and Shingles Prevention
• Immunization for all children (live, attenuated vaccine for chickenpox is recommended for all children, starting at 1 year of age) • More potent form of the vaccine » people older than 19
Chickenpox and Shingles Treatment
• Typically self-limiting
• Relief of symptoms with paracetamol, antihistamines
• Acyclovir: used in severe cases; may provide relief for shingles
Why is Aspirin NOT given to children/adolescents
Aspirin should NOT be given to children/adolescents Reye’s syndrome
Mono, Kissing disease
Infectious Mononucleosis
Infectious Mononucleosis CA
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV or HHV-4),
Type of herpesvirus of EBV
a gamma herpesvirus
Infectious Mononucleosis Transmission
respiratory route
Infectious Mononucleosis Mechanism
• Spread through direct oral contact; contamination with saliva • Infects epithelial cells of the throat or salivary glands • Enters the blood, invades B lymphocytes » latency (incorporates in cell DNA) • Suppresses apoptosis of B cells » immortal B cells
• Age at the time of infection is a determining factor: adolescent (teens) develop symptomatic disease
Infectious Mononucleosis Manifestations
• Seldom result to disease • Aggressive cellular immunity: Infectious Mononucleosis (severe sore throat and fever, disseminated lymphadenopathy, pharyngitis, splenomegaly, rash) • Poor immunity: Cancer of the lymphatic system (Burkitt’s lymphoma, Hodgkin lymphoma)
Infectious Mononucleosis Diagnosis
• Blood work: Large, lobed B lymphocytes with atypical nuclei • Monospot test – based on the detection of cross-reactive, heterophile antibodies
Infectious Mononucleosis Treatment
• Relief of symptoms • Chemotherapy
Cytomegalovirus Disease CA
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Type of herpesvirus Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
a beta herpesvirus
Cytomegalovirus Disease Transmission
• Carried in bodily secretions (saliva, semen, breastmilk) • Sexual contact, in utero, vaginal birth, blood transfusion, organ transplants • Congenital transmission • Achieve latency in leukocytes
Cytomegalovirus Disease Manifestations
• Most are asymptomatic • Fetuses, newborns: Enlarged liver, spleen, jaundice, anemia, birth defects • Immunocompromised: pneumonia, CMV retinitis, CMV mononucleosis
Cytomegalovirus Disease Diagnosis
• Microscopic examination of kidney biopsy tissue abnormally enlarged cells and inclusions within nuclei (“owl’s eyes”) • Serology (IgM)
Cytomegalovirus Disease Treatment
• Ganciclovir OR Valganciclovir • Foscarnet OR Cidofovir for the resistant CMV • CMV immune globulin for prophylaxis of CMV associated with organ transplantation
Roseola Other name
aka Roseola infantum, Exanthem Subitum, or Sixth disease
Roseola CA
HHV-6, sometimes HHV7
HHV-6, sometimes HHV7 herpesvirus type
beta herpesvirus
Roseola Transmission
through saliva
Roseola Manifestations
• Abrupt fever, sore throat, lymphadenopathy • Pink rash on the face, neck, trunk, thighs • Self-limiting
Roseola causes what in young children
Febrile seizures
Does Roseola Reactivate frequently in highly immunocompromised hosts?
Yes
Roseola Treatment
No therapy has been shown to be effective for HHV-6 or HHV-7, but both viruses are sensitive to Ganciclovir, Foscarnet and Cidofovir in vitro
Kaposi’s Sarcoma CA
HHV-8, aka Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)
Persisting in latently infected B lymphocytes
Kaposi’s Sarcoma
Kaposi’s Sarcoma Transmission
Sexual contact; contact with infected blood
Kaposi’s Sarcoma Manifestation
Tumors under the skin with or without organ involvement (for PLHIV)
• Largest animal viruses
Poxviridae
Poxviridae Characteristics
dsDNA, brick-shaped, multilayered capsid, with envelope
Poxviridae Replication
Replication occurs in the cytoplasm
Poxviridae Examples
• Variola virus (25 to 50% mortality rate) • Vaccinia virus
• First human disease to be eradicated globally in nature (WHO, 1980)
Smallpox
Smallpox CA
Variola virus aka Human poxvirus
Smallpox Transmission
similar to Chickenpox virus (IP: 12 to 16 days)
Smallpox Manifestations
Chills, fevers, headache, back pains; skin lesions filled with pus and often a dimple in the center
Smallpox Prevention
Vaccination based on the Vaccinia virus (cowpox, monkeypox)
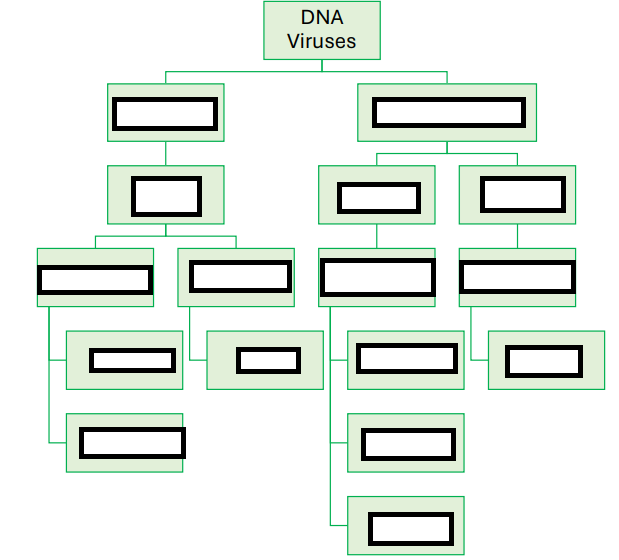
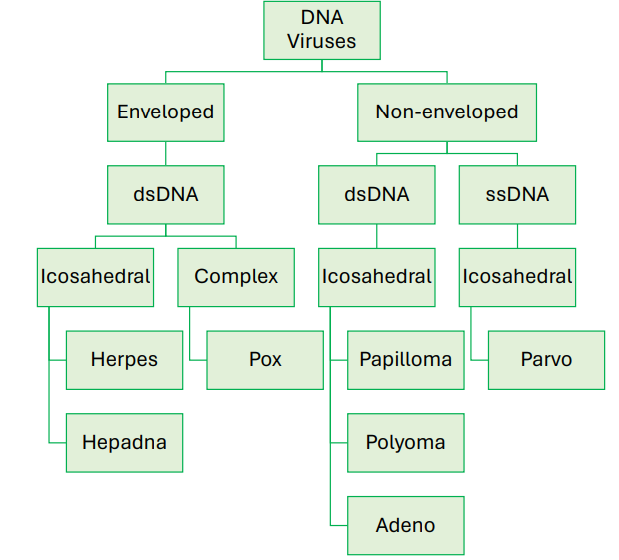
Hepatotropic DNA viruses
Hepadnaviridae
Hepadnaviridae Characteristics
dsDNA, icosahedral virus with envelope
Hepadnaviridae Examples
Hepatitis B virus
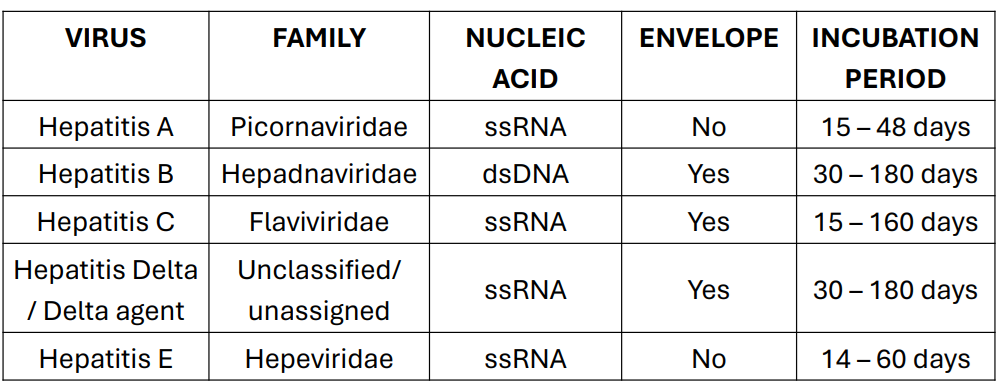
Viral Hepatitis Manifestations
• Jaundice, abdominal pain and distention, dark urine, light-colored stools • Loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, fever, weight loss • Chronic hepatitis: liver cirrhosis, liver failure, liver cancer
fulminant hepatitis; may cause meningitis or relapse (15%)
Hepatits A
acute and chronic hepatitis; hepatocarcinoma and cirrhosis
Hepatitis B and C
superinfection or coinfection with HBV
Hepatitis D
protracted and chronic hepatitis only in immunosuppressed patients
Hepatitis E
Hepatitis A (Infectious Hepatitis)
• Can survive on fomites
Typically causes an acute, self-limited illness, more often symptomatic in adults
Hepa A Transmission
Fecal-oral route, sexual contact
Hepa A Virulence
Generally, of low virulence; does not cause chronic infection
Hepa A Diagnosis
IgM anti-HAV antibodies, HA antigen or virus in stool samples
Hepa A Prevention
Inactivated viral vaccine (Havris®); Passive immune globulin (IM) for short term immunity
• The growth of the virus first results in systemic symptoms • One to two weeks later, the patient may develop jaundice (since bilirubin increases) • As the virus grows in the hepatocytes, the liver cells die.
Acute Viral Hepatitis
In acute viral hepatitis
The concentration of liver-function enzymes increases:
• Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) • Alanine aminotransferase (ALR) • Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) • Alkaline phosphatase
• Dane particles – intact viruses
Hepatitis B (Serum Hepatitis)
Hepatitis B (Serum Hepatitis) Transmission
virions shed in saliva, semen, vaginal secretions
Hepatitis B (Serum Hepatitis) Transmission
• Sexual transmission, contaminated needles, childbirth
T/F Hepa B May enter latency in some patients
T
Hepatitis B (Serum Hepatitis) Diagnosis
Detection of anti-HBV antibodies
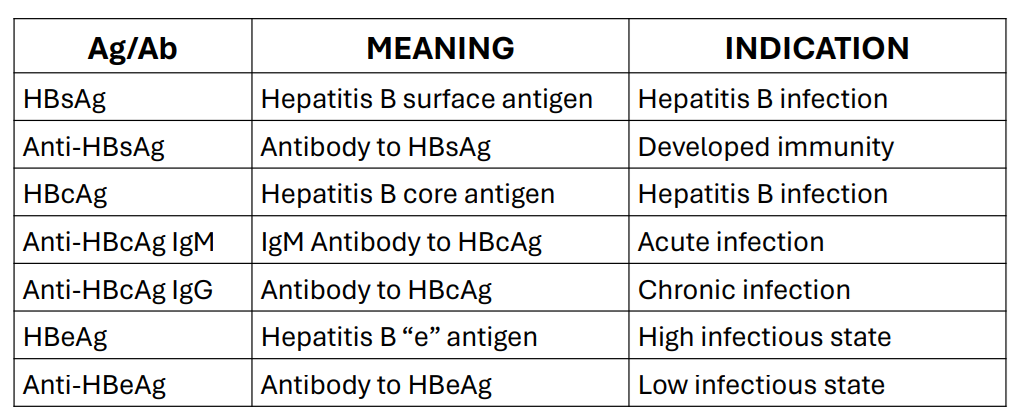
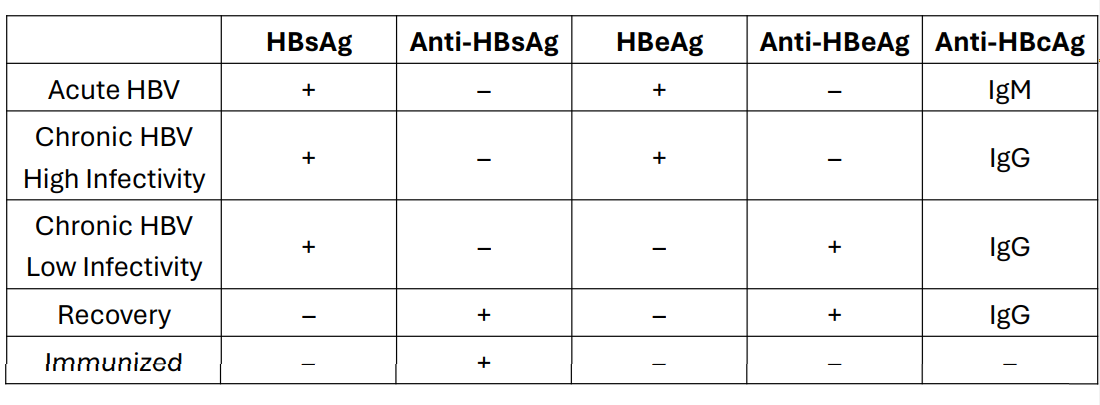
Viral Hepatitis Treatment and Prevention
• Vaccination with recombinant vaccines (Recombivax B®, Engerix B®) • Passive immunization with Hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) • Interferon, Lamivudine, Adefovir, Entecavir
Hepatitis C (Non-A, Non-B Hepatitis; Chronic Hepatitis) Transmission
Sexual transmission, via contaminated needles
Hepa C other name
Chronic hepatitis
– large percentage of the population is affected with no symptoms
“Silent Epidemic”
Hepa C Diagnosis
Serology to test for antibodies to the virus
Hepa C Treatment
• No vaccine available • Pegylated interferon, Ribavirin
Utilizes Hepatitis B capsomeres
• Coinfection with HBV or Superinfection of HBV carrier
• More severe acute disease
Hepatitis D