neurobiology & structures of the head
1/307
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
308 Terms
rostral
towards the nose
cranial
towards the head
caudal
towards the tail
dorsal
towards the top/spine
ventral
towards the bottom/belly
medial
towards the midline
lateral
away from the midline
proximal
towards the trunk of the body (for limbs)
distal
away from the trunk of the body (for limbs)
palmar
towards the palm of the hand
plantar
towards the sole of te foot
adaxial
toward the longitudinal central axis of the limb
abaxial
away from the longitudinal central axis of the limb
medial plane
divide down the midline
sagittal plane
dive into medial & lateral not at the midline
transverse plane
divide into cranial & caudal (body trunk) or proximal & distal (limbs)
dorsal plane
divide into dorsal & ventral
extension
increase the hinge angle
flexion
decrease the hinge angle
abduction
move limb away from the body
adduction
move limb towards the body
supination
rotate palm upwards
pronation
rotate palm downwards
what comprises the central nervous system?
brain and spinal cord
what does the central nervous system do?
process external stimuli
what are the divisions of the brain?
forebrain
midbrain
hind brain
what are the divisions of the forebrain?
diencephalon & telencephalon
what comprises the diencephalon?
thalamus & hypothalamus
what does the thalamus do?
relay station for vision, taste, & sound sensations
what does the hypothalamus do?
regulate temperature & blood pressure
what are the divisions of the midbrain?
tectum & tegmentum
what does the tectum do?
process visual & auditory information
what does the tegmentum do?
eye movement & reflexes
what are the divisions of the hindbrain?
metencephalon & myelencephalon (medulla)
what comprises the metencephalon?
cerebellum & pons
what does the cerebellum do?
coordinated muscle movement & motor learning
what does the pons do?
facial touching, chewing movement, unconscious functions
what does the medulla do?
sensory input & motor output
what comprises the peripheral nervous system?
autonomic and somatic nervous system
whhat does the peripheral nervous system do?
respond to stimuli
what does the somatic nervous system do?
voluntary sensory & motor control
what does the autonomic nervous system do?
involuntary motor function
divided into sympathetic & parasympathetic systems
what are the classifiations of neurons?
structure or function
what is the structural classifications of neurons?
unipolar
bipolar
multipolar
axonic
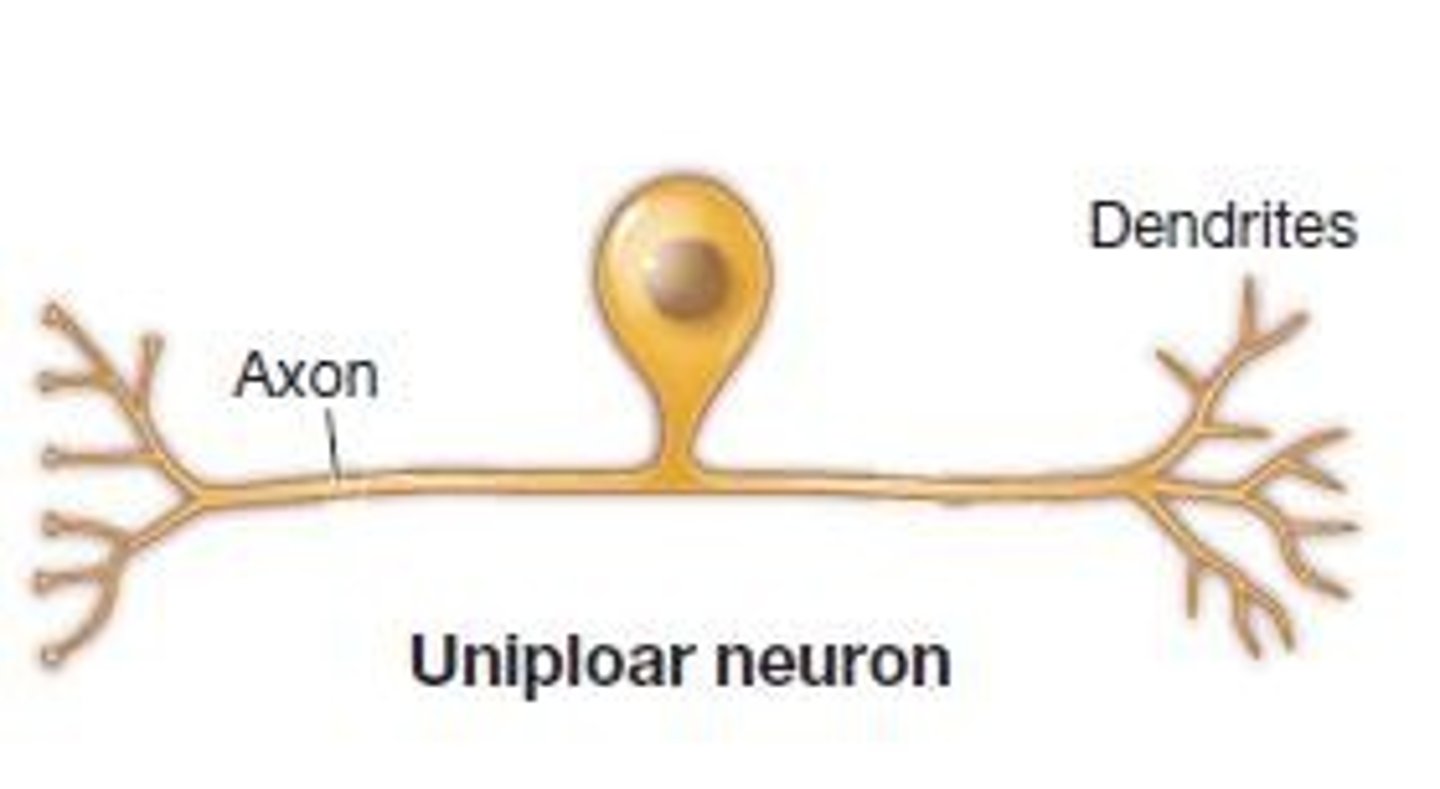
what is a unipolar neuron?
one projection from the cell body
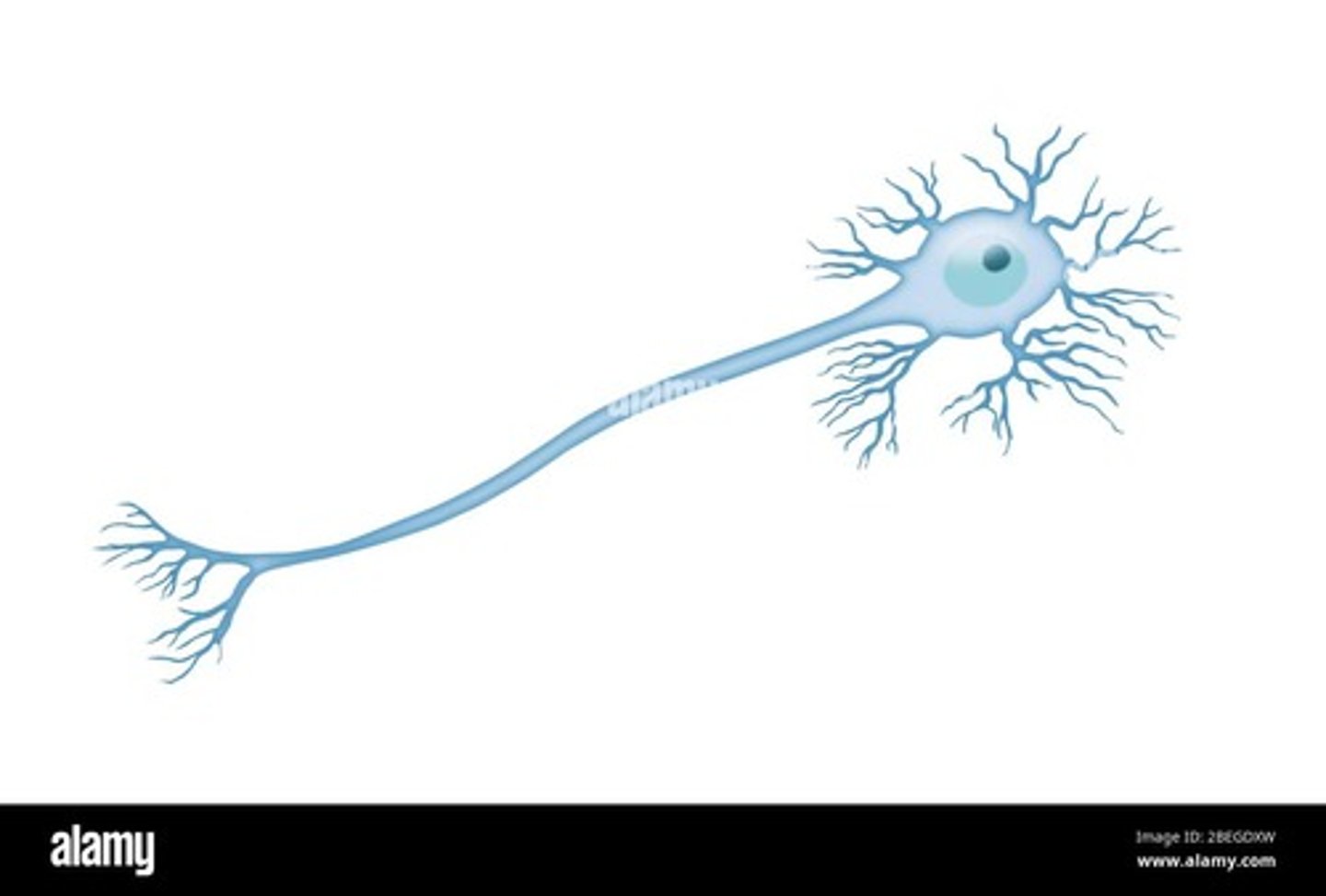
what is a bipolar neuron?
two projections from the cell body

what is a multipolar neuron?
more than 2 projections from the cell body
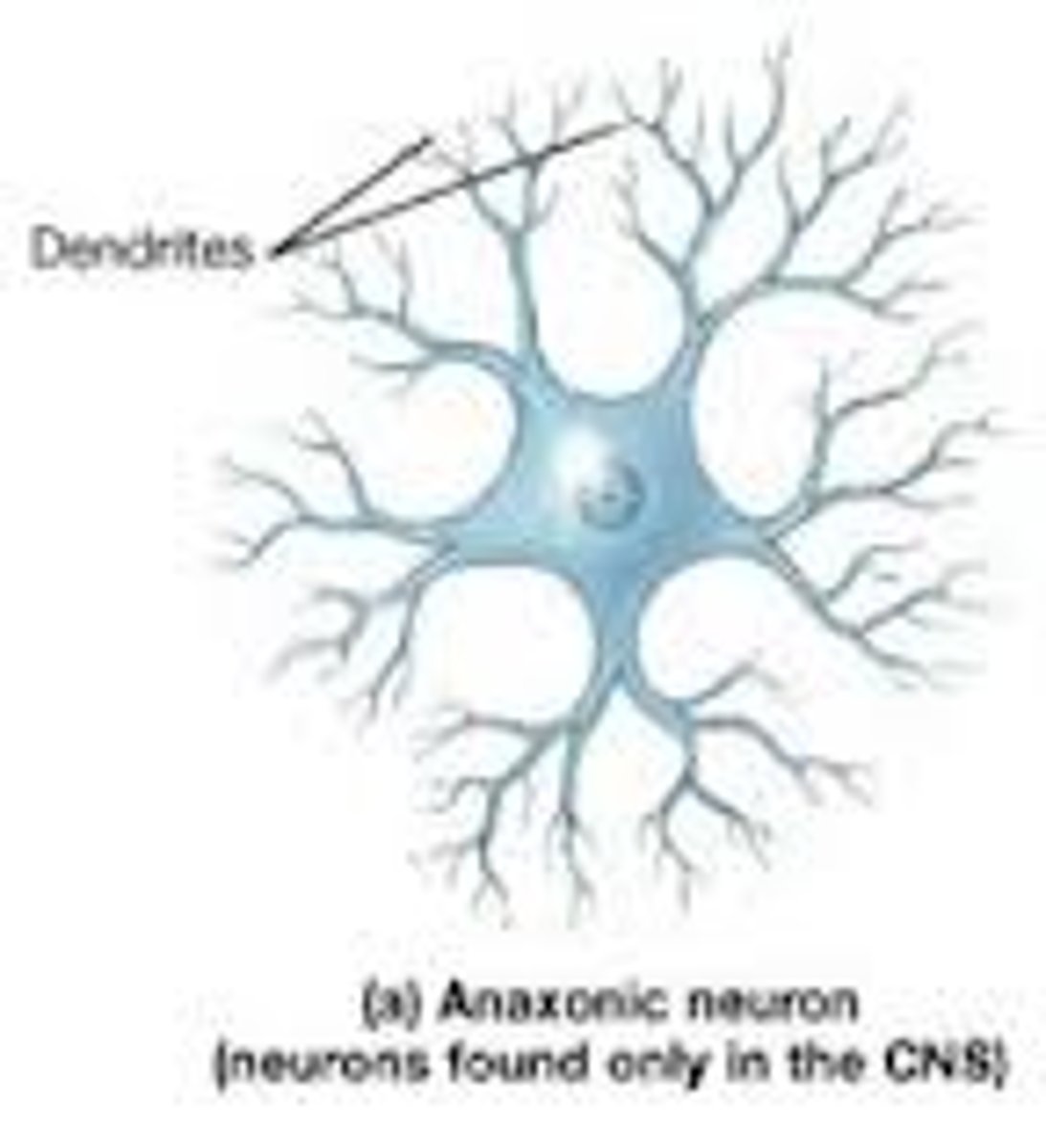
what is an anaxonic neuron?
only a cell body & dendrites
no axon
what are the functional classifications of neurons?
motor (efferent)
sensory (afferent)
interneurons
what are motor neurons?
deliver a physical response to target tissues from CNS
what are sensory neurons
receive sensory information from a stimulus to send to CNS
what are interneurons?
neurons only in the CNS that connect functional neurons
what do dendrites do?
receive signals from other cells
what does the cell body do?
process received signals
what does the axon do?
respond to the processed signal
what do telodendria do?
send the signal to other neurons
what are glial cells?
cells that bind to axons
what are the types of glial cells
schwann cells & oligodendrocytes
where are schwann cells found?
in the ganglia of the peripheral nervous system
where are oligodendrocytes found?
in the nuclei of the central nervous system
what do glial cells do?
form myelin sheaths & provide structural support
regulate paracrine communication
what is a myelin sheath?
a lipid membrane that insulates & stabilizes the axon
how does myelination effect information relay?
thicker nodes = faster because of increased electrical reistance
longer nodes = faster because length to jump is shorter
what is neuronal convergence?
when many neurons feed signal into one neuron
what is neuronal divergence?
when one neuron sends signal to many neurons
cranial nerve 1
olfactory
sensory
smell
cranial nerve 2
optic
sensory
vision
cranial nerve 3
oculomotor
motor
eye movement & pupil reflex
cranial nerve 4
trochlear
motor
eye movement
cranial nerve 5
trigeminal
mixed
facial sensation & movement
what are the branches of the trigeminal nerve?
opthalamic branch
maxillary branch
mandibular branch
what does the opthalamic branch do?
sensory
vision & forehead sensation
what does the maxillary branch do?
sensory
teeth, gums, upper jaw, sinuses, lips
what does the mandibular branch do?
sensory & motor
close lower jaw & sensation
cranial nerve 6
abducens
motor
eye movement
cranial nerve 7
facial
mixed
taste, movement of face, ear, neck
what are the branches of the facial nerve?
auriculopalpebral branch
dorsal buccal branch
ventral buccal branch
what does the auricopalpebral branch do?
motor
external ear muscles, orbicularis oculi, upper eyelid
what do the dorsal & ventral buccal branches do?
motor
lip, nose, & cheek movement
cranial nerve 8
vestibulocochlear
sensory
hearing & balance
cranial nerve 9
glossopharyngel
mixed
taste & throat sensation
swallowing movement via pharyngeal muscles
cranial nerve 10
vagus
mixed
regulate PNS
glottis closure via pharyngeal muscles
innervate pharynx, larynx, soft palate muscles
cranial nerve 11
accessory
motor
neck movement
cranial nerve 12
hypoglossal
motor
tongue movement
what is neuronal resting membrane potential?
the charge difference between the inside and the outside of the cell
how is resting membrane potential determined?
dynamic equilibrium of unequal charge distribution
Na+/K+ pumping & permeability
how is resting membrane potential created?
movement of 2 K+ ions inside of the cell
movement of 3 Na+ ions outside of the cell
create electrochemical gradient
inside the cell is more negatively charged
outside the cell is more positively charged
what is an action potential?
an electrical impulse causes the depolarization and repolarization of a cell to transmit a signal
what is depolarization?
when the internal charge of a cell becomes more positive
step 1 of an action potential
cell is at resting membrane potential (-70 mV)
step 2 of an action potential
stimulus causes depolarization to start (-70 to -50 mV)
step 3 of an action potential
membrane depolarizes to threshold levels (-50 mV)
Na+ voltage-gated channels open & Na+ enters
step 4 of an action potential
rapid Na+ entry depolarizes inside cell after membrane is depolarized (-50 mV to 30 mV)
step 5 of an action potential
repolarization starts
Na+ channels close & K+ channels open slowly (30 to -50 mV)
step 6 of an action potential
repolarization
K+ moves out of the cell (-50 to -80 mV)
step 7 of an action potential
hyperpolarization
K+ voltage-gated channels close (-80 mV)
step 8 of an action potential
Na+ ions, K+ ions, and ATPase return cell to resting membrane potential (-80 to -70 mV)
what is axon conduction?
the process when an axon transmits an action potential from the cell body to synapses for nerve transmission
what is nerve transmission?
the process of sending an electrical impulse across the synaptic cleft from one axon to the dendrites of another
what is synaptic signalling?
the process of releasing neurotransmitters from the synaptic vesicles of the pre-synaptic cells to bind to the receptors of the post-synaptic cell