Chapter 11 (Cell-Cell Interactions)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Order of Organism Process
Atoms - Molecules - Organelles/Cells - Tissues - Organs - Organ Systems - Organism
Plasma Membrane
Made of a phospholipid bilayer (selectively permeability controls the flow) with many integral, peripheral proteins
Function: Create an environment inside the cell different from conditions outside
What is Extracellular Layer?
A protective layer or wall that forms just beyond the membrane
Consists of cross-linked network of long filaments (fibers) surrounded by a stiff ground substance
Extracellular Layer in Animals
Extracellular Matrix
Extracellular Layer in Plants
Cell Wall
Extracellular Layer Function
Filaments (fibers) protect against tension and ground substance protects against compression
When new plant cells form, they secrete a fiber composite called a __________
Primary cell wall
Cell Wall is composed of...
Long strands of cellulose bundled into microfibrils from a crisscross network
Cell Wall is filled with...
Hydrophilic gelatinous polysaccharides such as pectin
Pectin keeps the cell wall moist and jelly like (protection)
The primary cell wall...
Defines the shape of the plant cell and counteracts the turgor pressure it experiences (When the cells volume increases, the plasma membrane gets pushed against the cell wall)
Most animal cells secrete a fiber composite called...
The Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
The ECM consists of...
A ground substance formed of gelatinous polysaccharide and a network of protein fibers (collagen)
Collagen
Most common ECM protein fiber, is more elastic than cellulose, forms a flexible extracellular layer
ECM's most important function is..
Structural support (protection)
ECM is strengthened by connections to transmembrane proteins. These connectors are called...
Integrins
Integrins
ECM connections with transmembrane proteins connected to the cytoskeleton
Direct linkage between the cytoskeleton and ECM
keeps individual cells in place, helps adjacent cells adhere to each other
Breakdown of ECM can lead to
Metastasis of cancerous cells
Unicellular organisms
do not connect to one another
The basis of multicellularity is physical connections between cells
Connections between cells either direct or indirect via the ECM
The extracellular space between adjacent plant cells comprises of three layers:
1. Primary cell wall of one plant cell
2. Middle lamella layer (made up of pectin- gelatinous polysaccharide- jelly-like
3. Primary cell wall of another plant cell
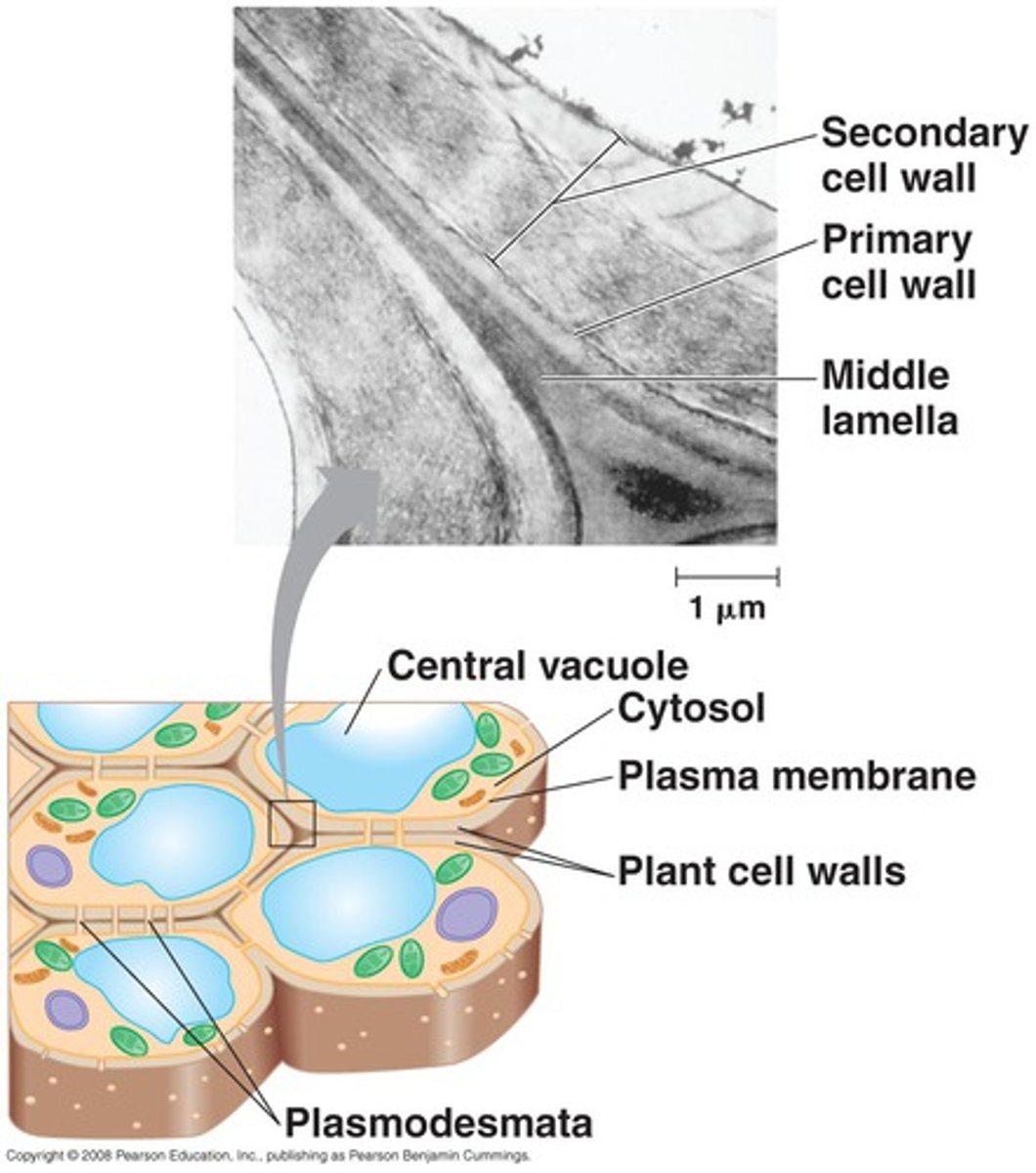
Plant cells are glued together by
the middle lamella, which is continuous with adjacent plant cells' primary cell walls and is comprised of gelatinous pectins (glue primary cell walls)
Epithelial tissue
composed of sheets of cells which cover organs, line body cavities
Function: Epithelia function as barriers between the external and internal environments (separate organs, preventing mixing of solutions between adjacent organs or structures)
Many types of structures connect neighboring epithelial cells
Tight Junctions and Desmosomes
Tight Juctions
Composed of specialized proteins, in the plasma membrane of adjacent animal cells, is found between cells in tissues that form a barrier (tissue lining the stomach or bladder)
These proteins line up and bind to each other to form a watertight seal between the two plasma membranes
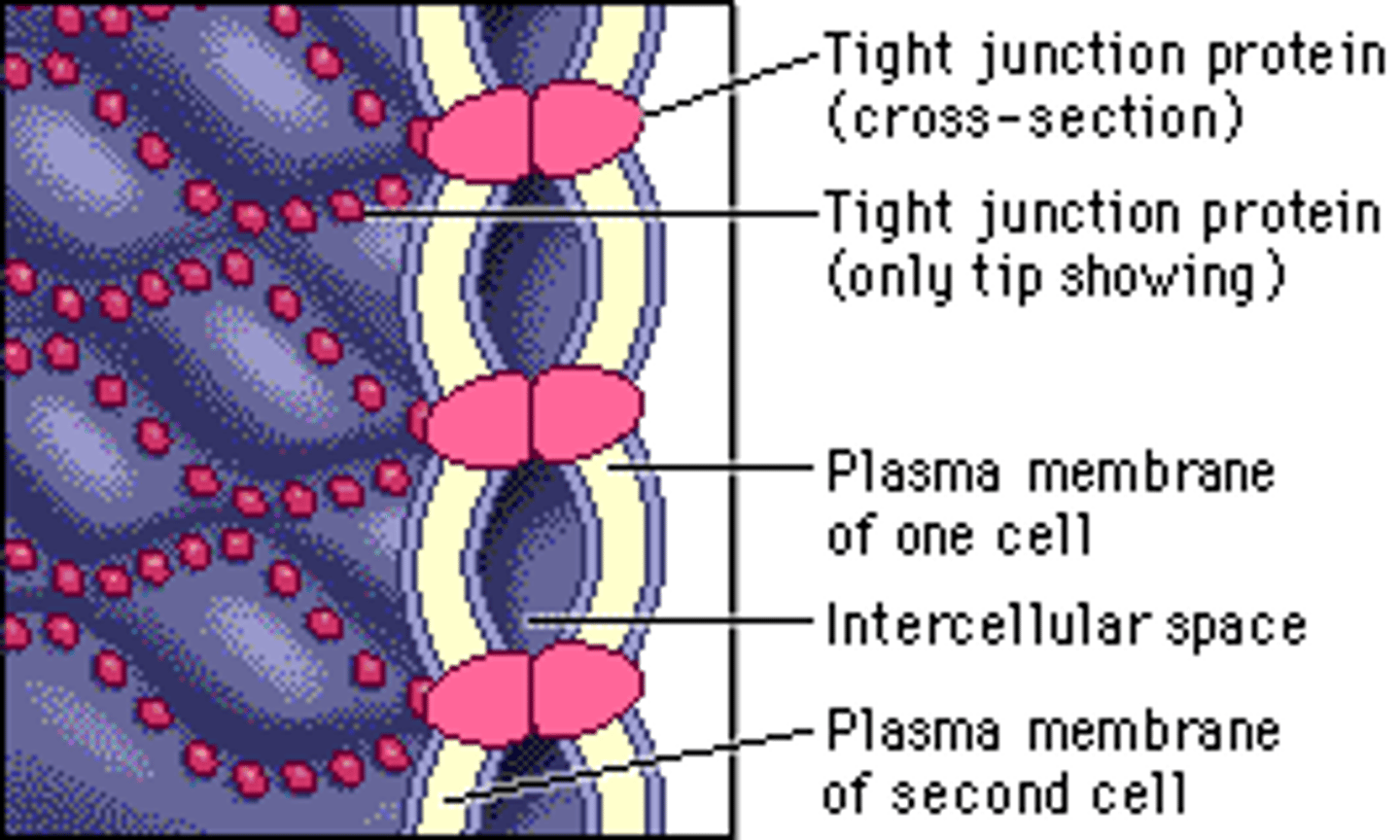
Tight Junctions are dynamic and variable
Open and close in response to changes in environmental conditions (Hold cells together)
Desmosomes
Are made of proteins that link the cytoskeletons of adjacent cells, are common in epithelial and muscle tissue
These proteins bind to each other, to the proteins that anchor cytoskeletal intermediate filaments
Come together below tight junctions
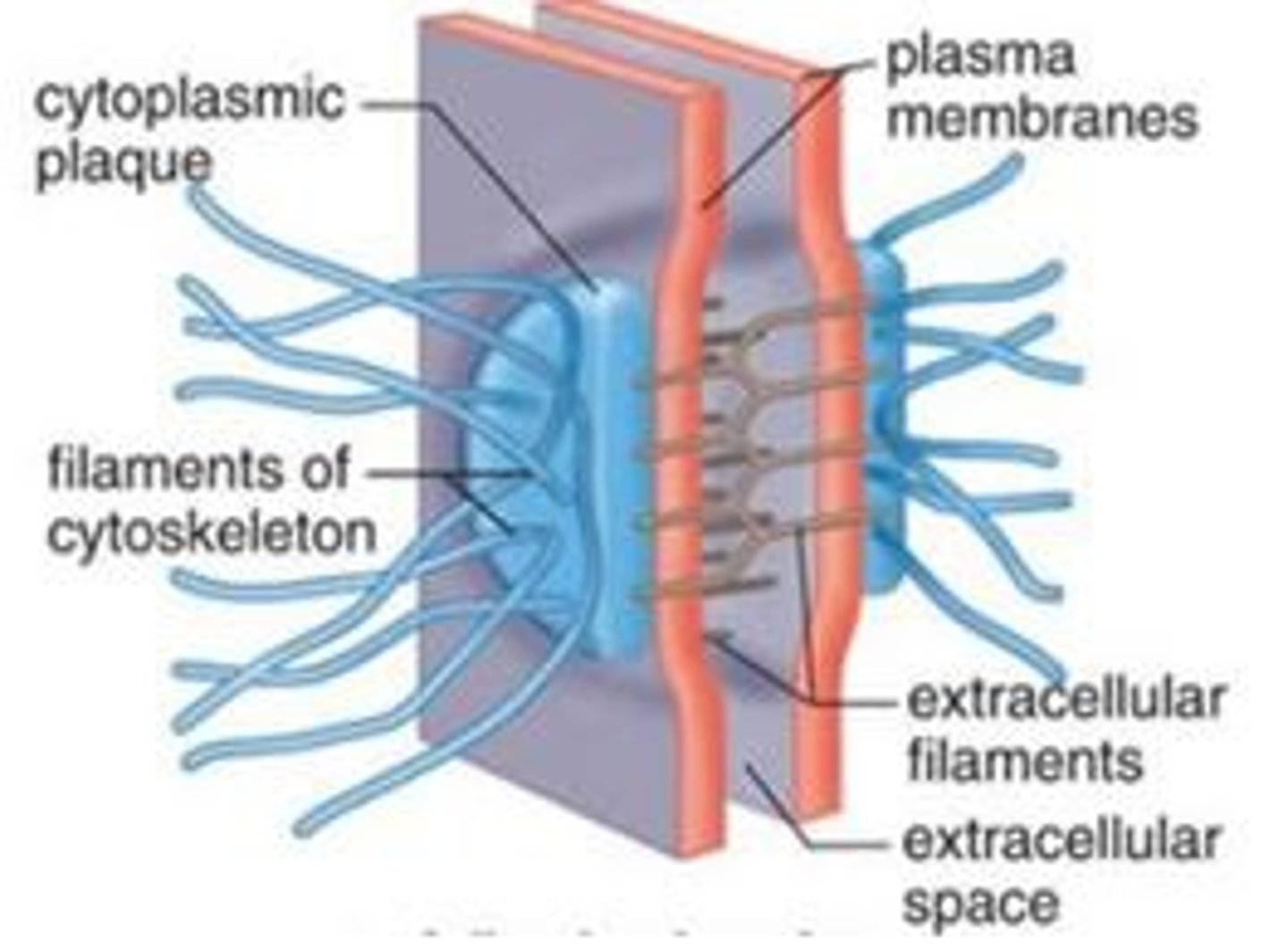
Direct connections between cells in the same tissue
Allow cells to communicate and work together in a coordinated fashion
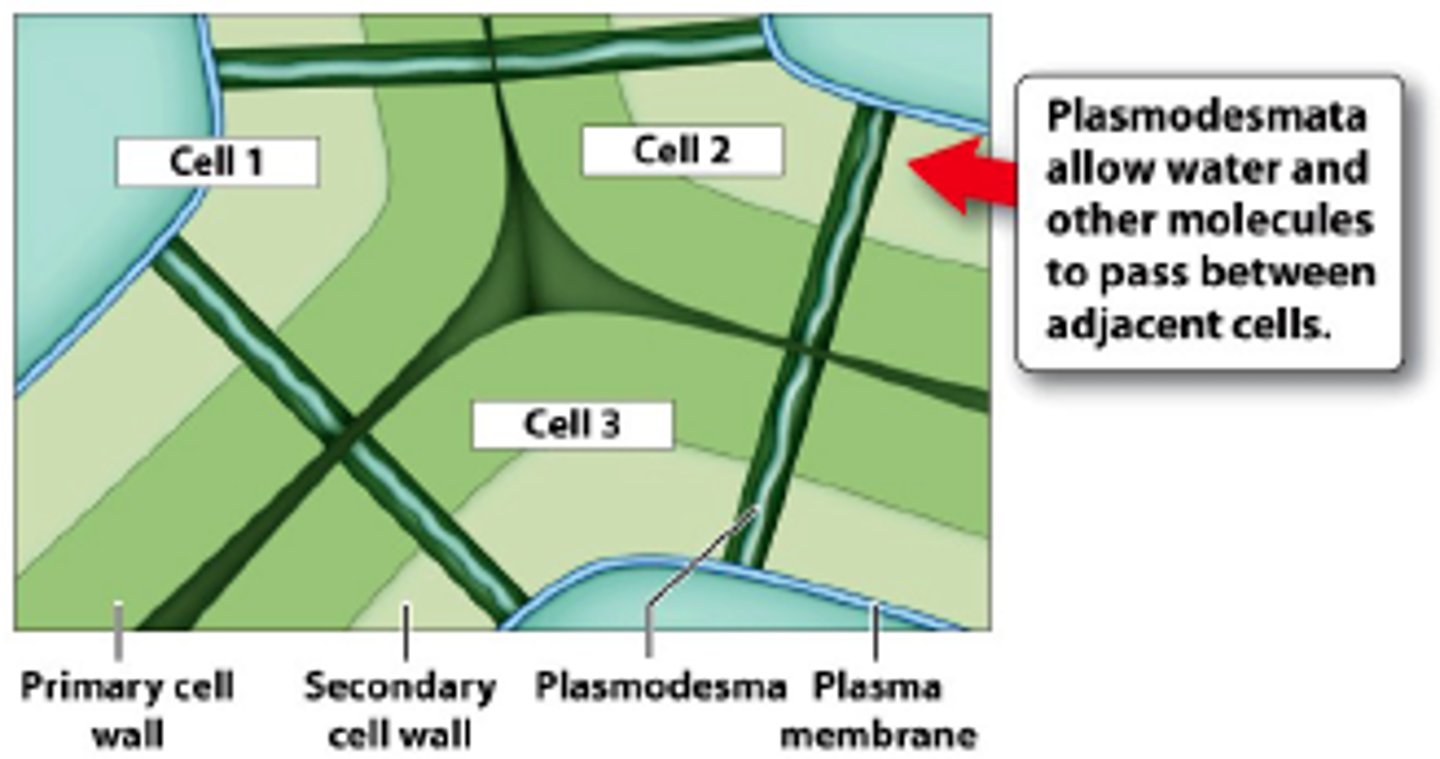
Plant cells are connected by...
Plasmodesmata - Gaps in the cell wall, where the plasma membranes cytoplasm and smooth ER of two cells connect
Animal Cells Gap Junctions
Connect adjacent cells by forming channels
These channels allow the flow of small molecules between cells (multiple channels for communication)
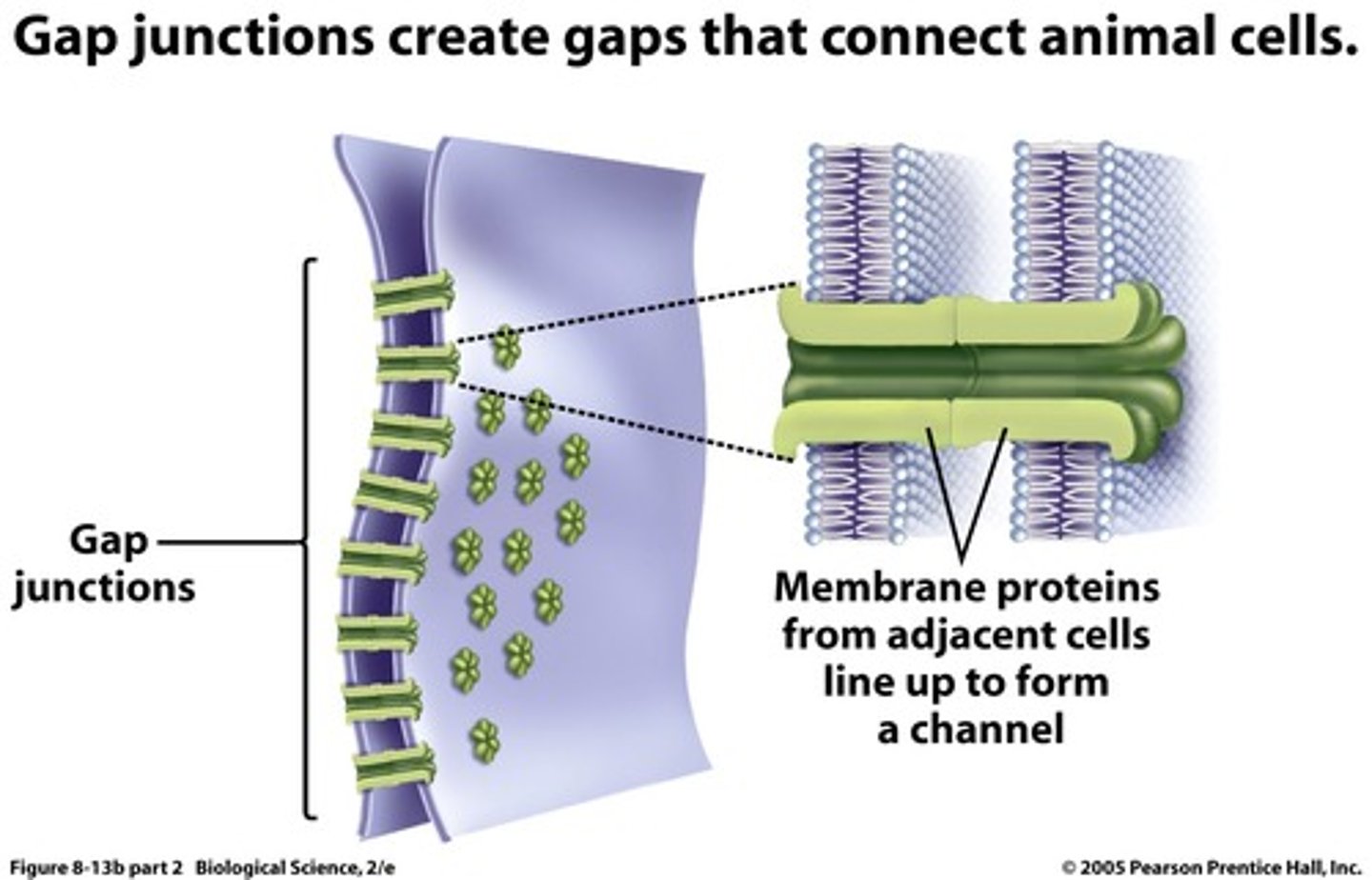
Bind adjacent cells to each other:
Middle lamella (plants)
Continuous ECM (animal)
Tight Junctions: water tight seal
Desmosomes: passive transport
BINDING OF CELLS
Allow adjacent cells to communicate:
Plasmodesmata (plants)
Gap Junctions (animals)
COMMUNICATION
Small molecules may be transported through plant tissues within...
Symplast - cytoplasms connected by plasmodesmata (shared cytoplasms)
Apoplats - region outside the plasma membrane (extracellular space)
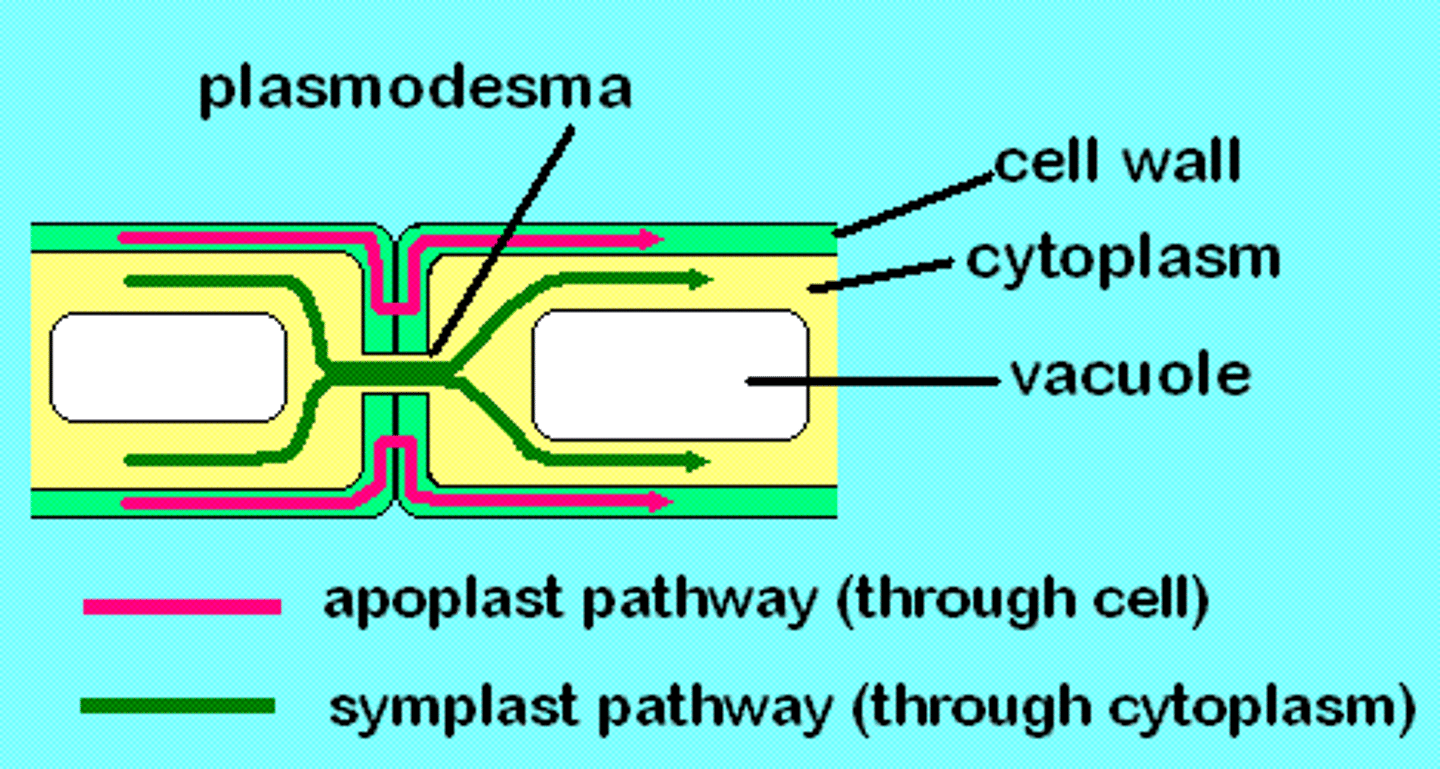
Gap junctions and plasmodesmata
Allow adjacent cells to transmit information
Hormone
Information-carrying molecules
Secreted from a cell; Circulates in the body
Acts on target cells far from the signaling cell
Hormones are usually
Small molecules; present in minute concentrations
They deliver their signals by binding to receptor molecules
Lipid-soluble hormones (water-insoluble)
Diffuse across the plasma membrane (hydrophobic region); go into their target cells cytoplasm
Lipid-insoluble (water-soluble)
Are large or hydrophilic; do not cross the plasma membrane
Bind to a receptor on the cell's plasma membrane (surface)
Signal receptor
A protein that changes its shape and activity after binding to a signaling molecule
This change in shape is how a signal is passed from the signaling molecule to its receptor
Signal Transduction Pathways
Are created when water-soluble hormones (lipid-insoluble) bind to cell-surface receptors and convert an intercellular signal into an intracellular signal
Intracellular signals can be amplified because many activated molecules are enzymes
Cell-cell signaling occurs in four steps
1. Signal reception
2. Signal processing
3. Signal response
4. Signal deactivation
Lipid-soluble (hydrophobic) steriod hormones
Bind to receptors inside the cell
Trigger a change in cell's activity directly
(go straight through the plasma membrane (pass directly))
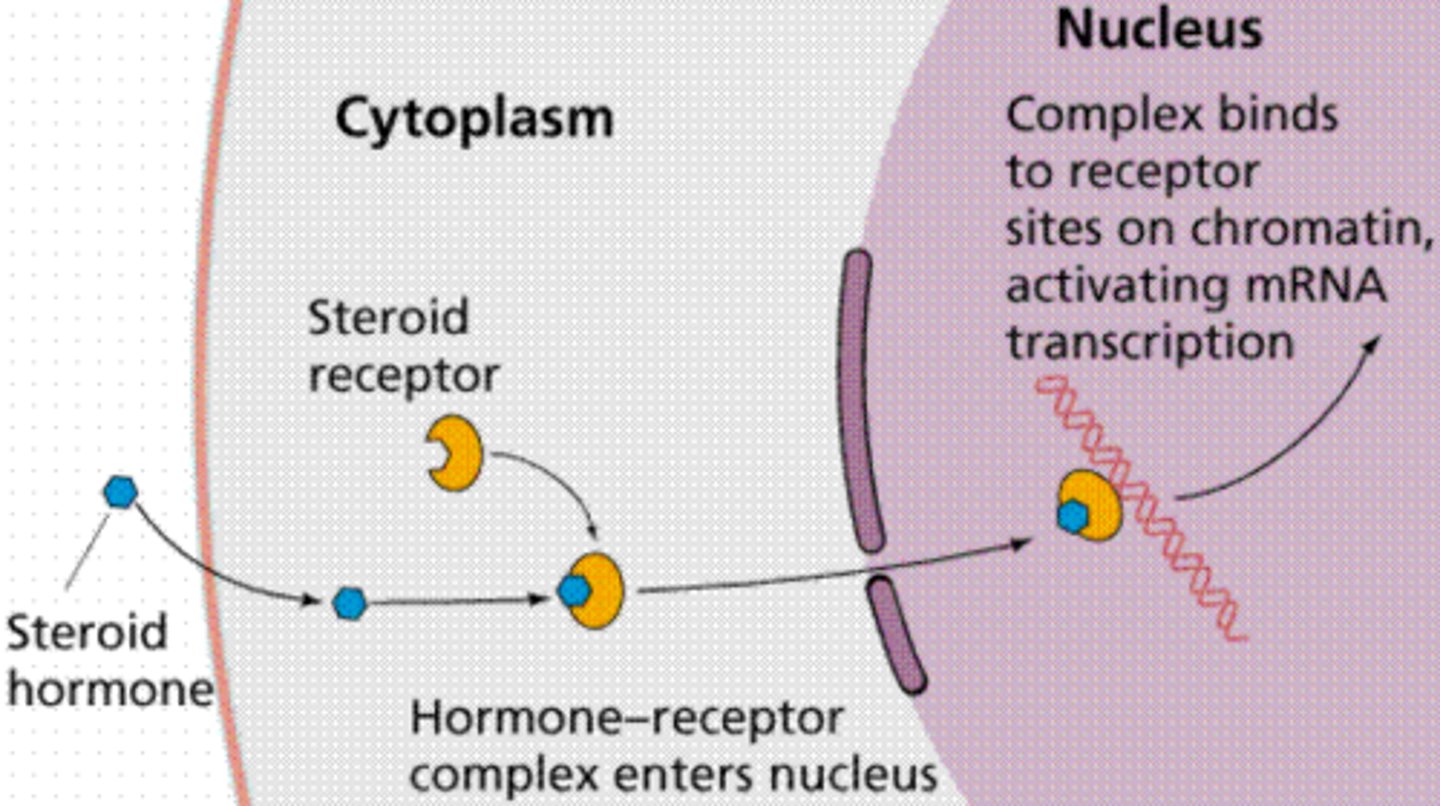
The hormone-receptor complex
Is transported to the nucleus where it alters gene expression (alter function or shape of cell)
Lipid-insoluble (water-soluble) steroid hormones
Hormones that cannot diffuse across the plasma membrane (bind to receptors outside the cell)
When a signal binds at the cell surface, it triggers a complex series of events, collectively called a signal transduction pathway, converts the extracellular hormone signal to an intracellular signal
(indirectly sent)
Signal transduction
The conversion of a signal from one form to another (increase amount)
An increase number of intracellular signals makes it possible for hormones to affect different molecules in the cell
EITHER BY G PROTEINS OR ENZYME-LINKED RECEPTORS
Signal Transduction: G Proteins
Intracellular peripheral membrane proteins
Closely associated with transmembrane signal receptors
(trigger the production of an intracellular messenger)
Trigger Second Messengers
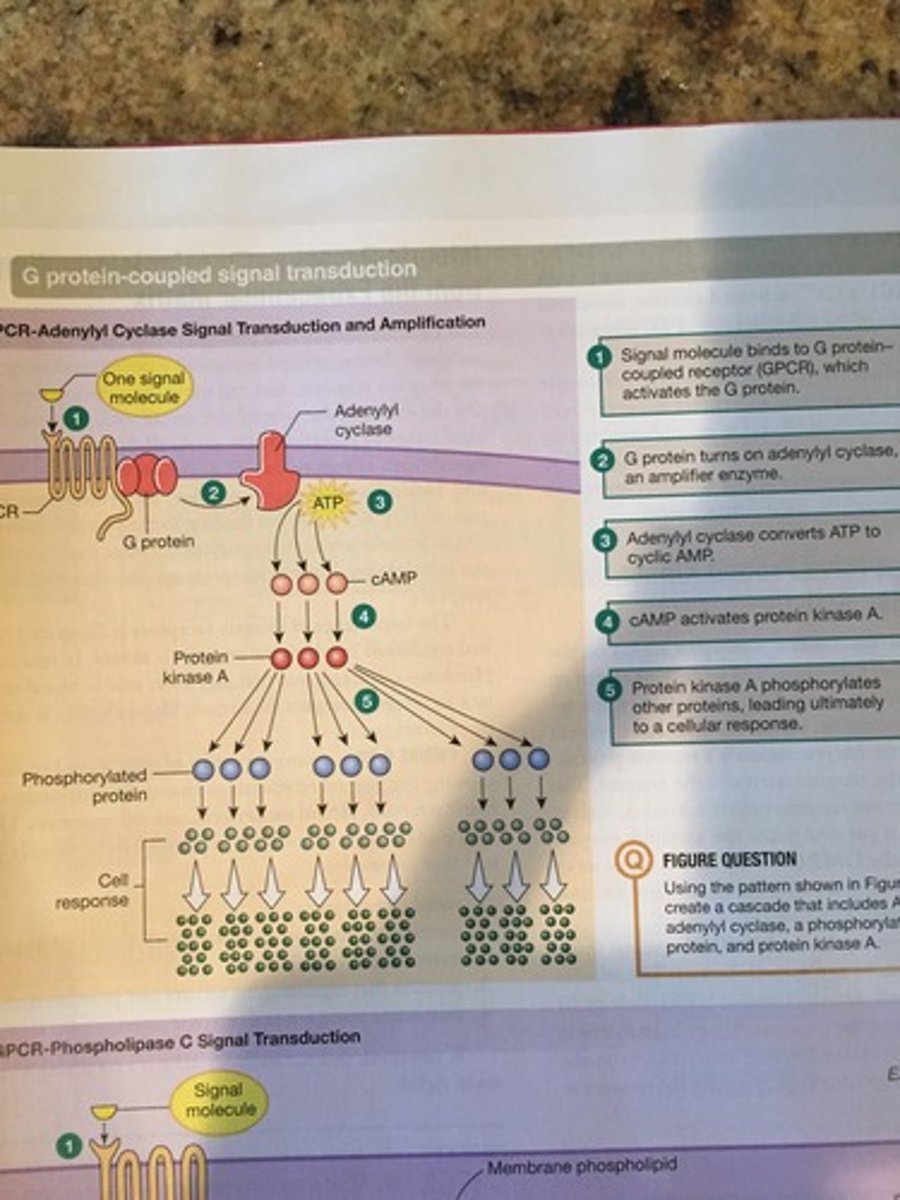
Several Second Messengers
Activate protein kinases which are enzymes that activate other proteins by adding a phosphate group (phosphorylation)
G Proteins
link the receipt of an extracellular signal to the production of an intracellular signal
Activated when they bind to GTP and deactivated when they take off a phosphate group making it GDP
Second Messengers: Are small molecules that diffuse rapidly; Amplify the hormone signal
Signal Transduction: Enzyme Linked
Are transmembrane proteins
Bind to a hormone signal
Directly catalyze a reaction inside the cell
The Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTK's) are the best-known group of enzyme-linked receptors
Receptor Tyrosine Kinases and Signal Transduction
Signal is sent from protein receptor to protein receptor and so on (phosphorylation) Uses a lot of ATP (energy)
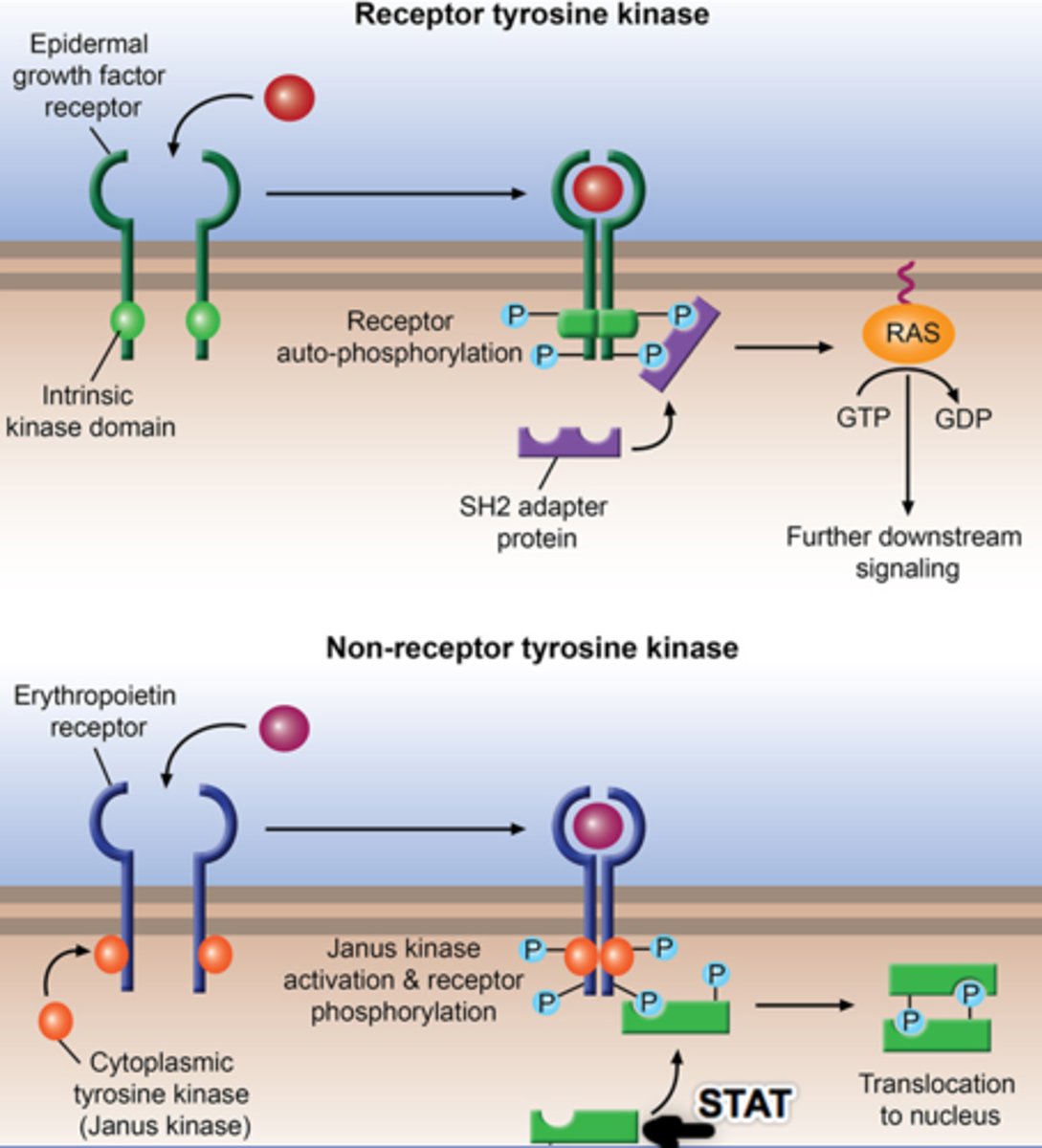
Many of the key signal transduction events observed in cells occur via
G proteins and Enzyme Linked receptors
The signal transduction event has two results:
1. Easily transmitted extracellular message is converted into an intracellular message
2. Original message is often amplified many times over
The ultimate response to cell-cell signal varies from signal to signal and from cell to cell
Falls into two general catagories:
1. A change in which genes are being expressed (DNA) in the target cell
2. Activate or deactivate a particular target protein that already exists in the cell
The end result of cell sensitivity to hormonal signaling is
An integrated whole-organism response to changing conditions
Occurs both inside and outside the multicellular organism