orbital fractures
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Types of orbital injuries
Blow out fracture
soft tissue injury
supraorbital fracture
naso-orbital fracture
zygoma fracture
What is a blow out fracture
The orbit is hit & forces soft tissue content backwards without rupturing globe
Rise in IOP fractures orbital walls - medial & orbital wall
Males more than F - assault, road traffic port work related

Types of blow out fracture
Pure
trap door
linear
hanging
hinged bone crack
Depressed
or combination
Impure
Orbital rim is involved
Blow out fracture mechanism
limitation of OM = direct entrapment & damage to EOM - commonly IR
=entrapment of orbital fascia, septum, connective tissue & muscle pulley
CH
Signs inc
Periorbital echhymosis
surgical emphysema
enophathalmos
depression of globe
traumatic mydriasis
sub conjunctival haemorrhage
hyphaema
facial asymmetry
symptoms inc
diplopia - vertical
infraorbital anesthesia - from damage from the infraorbital nerve = loss of sensation of ipsilatral cheek and upper gum
pain on eye movement
VA & AHP
VA - can slightly reduce = hyphaema
AHP - Chin elevation/ depression
Maybe face turn for medial wall fractures
CT
CT with & without AHP
hypotropia - entrapment of tissue anterior = limitation in elevation
hypertropia - entrapment of tissue posterior = limitation of depression
OM
Enophthalmos
limitation in elevation & depression with orbital floor fractures
limited abduction & adduction = medial wall fracture
Retraction of globe position of maximum limitation
Diplopia may swap depending position of gaze
infraorbital anesthesia = damage or bruising to infraorbital nerve = numbing of nerve i.e cheeck, upper lps - side of nose
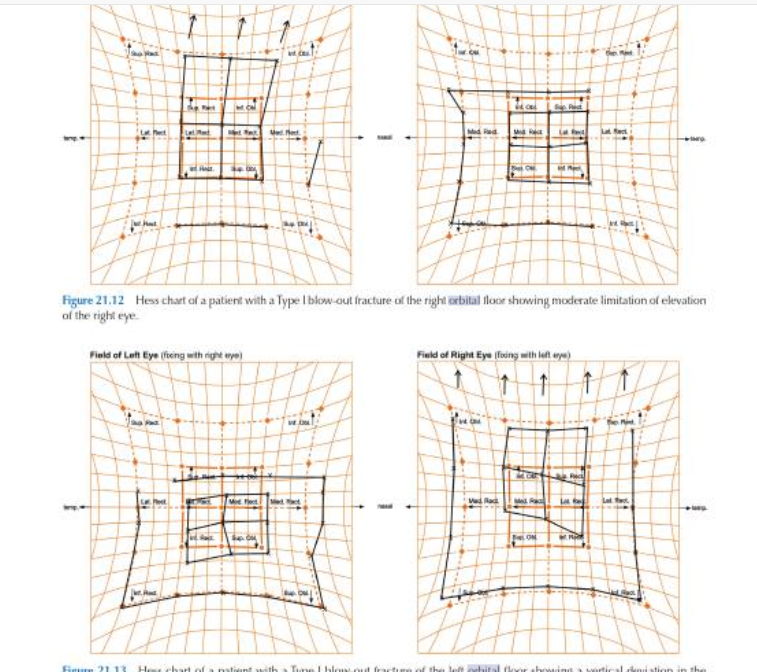
Hess chart
field of binoc single vision
Diplopia reverses w limitations in opposite position of gaze
good binoc in pp w AHP = limitation in opposite direction of gaze
examine fundus & media to check globe has been damaged or retinal detachment, vitreous detachment subluxed lens & optic nerve patency
X-ray, CT, tomography to see point of fracture
measure IOP if hyphaema
FDT - mech/neuro
Enophthalmos - exophthalmos
measure saccadic velocity
mx
wait for recovery wait apprx 14 days
younger pts responded poorly than older pts due to faster formation of fibrous scar tissue in young pts
pts w fractures involving alot of orbital floor be operated early
soft tissue thats damaged when trapped between bone fragment = fibrosis & tethering of globe
antibiotics & prednisolone help ↓ infection & inflammation
treatment options orbital injuries
observation
conventional treatments - prisms, exercises & occlusion
surgical
indications for surgery - dulley & fells
Diplopia not resolving
enophthalmos >3mm
large fracture
incarceration of tissues w globe restriction
IOP increase on upgaze
aims of surgery
free trapped tissue & repair fracture site
correct strabismus
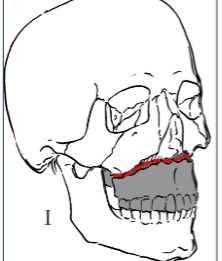
Le fort classification
Le Fort type I
Tooth bearing portion separated from upper maxilla
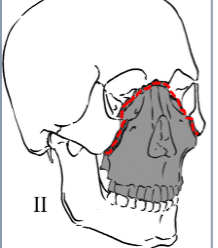
Le Fort type II (pyramidal fracture)
Fracture across orbital floor and nasal bridge (involves medial wall
and floor)
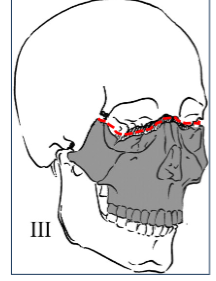
Le Fort type III (craniofacial separation)
Fracture across fronto-zygomatic suture line, entire orbit and nasal
bridge (involves floor, medial and lateral walls

soft tissue injury
due to trauma to orbital area - not causing fracture of any bone = damage to orbital area
muscle damage
lacerations
damage to nerve supply to EOMS
hemorrhage = limitations of movement & proptosis
lid injuries inc
lid lacerations
injuries involving lacrimal canal
swelling & pseudoptosis
levator damage with traumatic ptosis
ocular signs
sub conjunctival haem
corneal abrasions
lens dislocation
damage to iris with traumatic mydriasis
hyphaema
retinal detachment
optic nerve damage
choroidal ruptures
Supraorbital fracture
sharp object going through orbital roof
characteristics
superior periorbital swelling & haem
lid oedema
supraorbital anesthesia
damage to levator and nerve supply
diplopia due to muscle damage
depression of supraorbital rim = globe retraction
CSF fluid discharge
naso orbital fracture
direct trauma to naso orbital area
due to road traffic
charactristics
dish face appareence
oedema & bruising
epistaxis
nasal obstruction
surgical emphysema
damage to tear duct and lacrimal sac
zygoma fracture
bone displaced outwards = traumatic enophthalmos = swelling
bone displaced inward = traumatic proptosis
characteristics
muscle or nerve damage
oedema - impair OM
infra orbital anesthesia
white eye
IR caught in trap door orbital floor fracture
urgent surgical to prevent ischemic muscle damage
Painful restriction of eye movement.
Double vision (diplopia).
Enophthalmos (a sunken appearance of the eye).
Autonomic symptoms like nausea and vomiting
lack of significant soft tissue trauma (like bruising or swelling) around the eye, despite the presence of a fracture and potential muscle entrapment