AP Macro Unit 6
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
balance of payments accounts (BOP)
a summary of a country's transactions with other countries in a given year
-the current account
-the capital and financial account
credit
money inflows
debit
money outflows
the current account (CA)
a country's balance of payments on goods and services plus net international transfer payments and factor income
-net exports
-factor income
-net transfers
net exports
value of exports minus value of imports
-DOES NOT ALWAYS BALANCE
trade surplus
when a country exports more than it imports
trade deficit
situation in which a country imports more than it exports
factor income
income from the factors of production
-including interest payments on loans from foreign investors and profits of foreign owned corporations
-ex: money earned by japanese car producers in the US
net transfers
money sent by residents of one country to residents of another country
-ex: donations, aids and grants, official assistance, and remittances
capital and financial account (CFA)
measures international ownership of financial assets and international capital transfers
-ex: a korean company buys a factory in ohio
-ex: an american buys a japanese government bond
net capital outflow
the difference between domestic purchases of foreign assets and foreign domestic assets
CFA surplus
inflow is greater than outflow
CFA deficit
outflow is greater than inflow
if a country has a deficit in the current account, they must have a...
surplus in the CFA
CA =
-CFA
T or F: all foreign trade transactions require currency to be paid in the other country's currency
TRUE
-the buyer (importer) must exchange their currency for that of the seller (exporter)
the exchange rate
The measure of how much one currency is worth in relation to another.
demand for a currency is based on what
the demand for the country's goods, services, and financial assets
the foreign exchange market
A market for converting the currency of one country into that of another country
-shows the inverse relationship between the ER and the quantity demanded of a currency
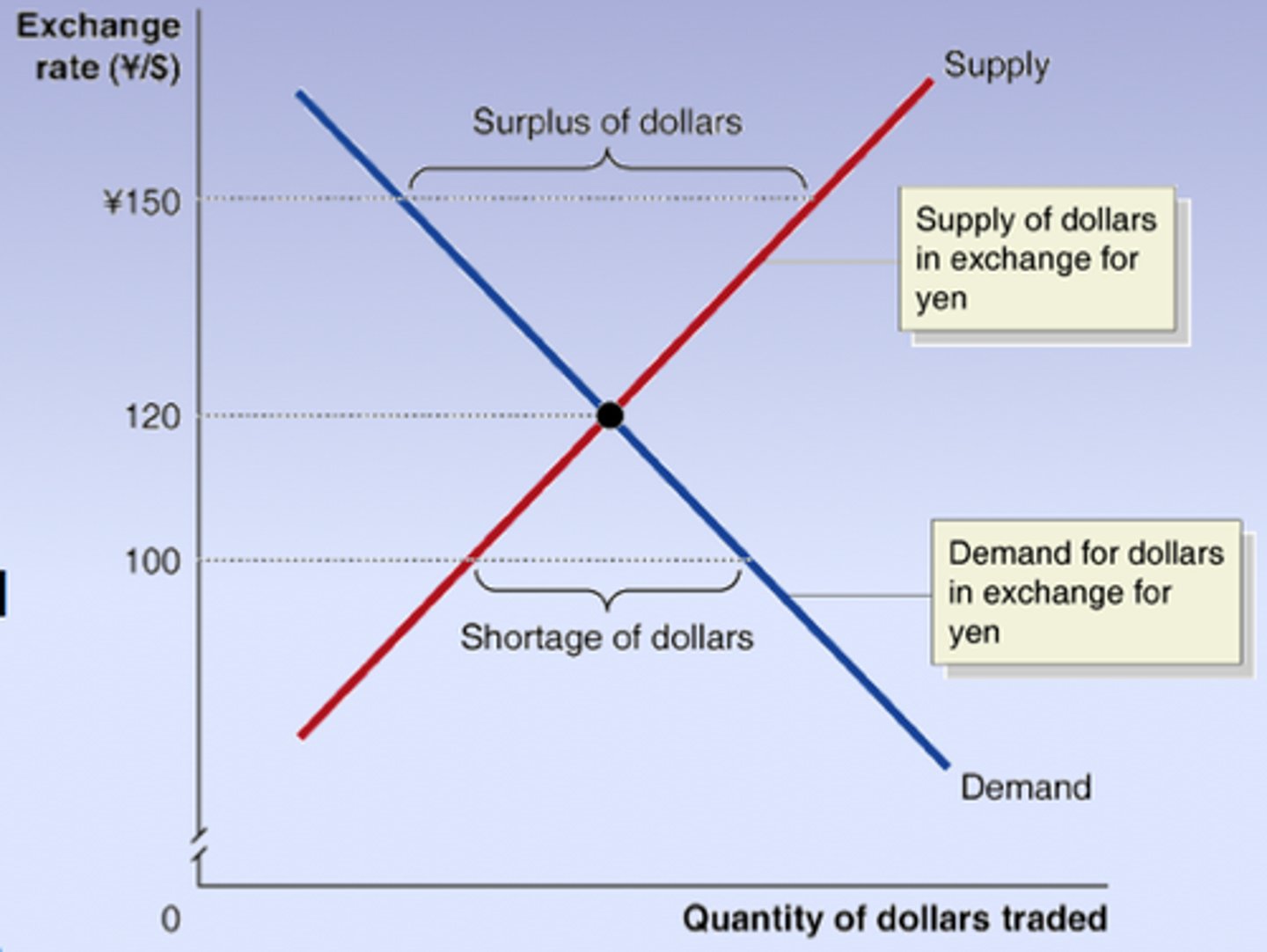
supply of a currency arises from...
making payments in the other currencies
-shows the positive relationship between the ER and the quantity supplied of a currency
shifters of the demand for currency
the demand curve for a currency will shift when...
-foreign buyers demand for domestic goods, services, and financial assets changes
-foreign buyers need the domestic currency
shifters of the supply of currency
the supply curve for a currency will shift when...
-domestic buyers demand for foreign goods, services, and financial assets changes
-domestic buyers need the foreign currency
if a currency appreciates, what happens to exports and imports?
imports become cheaper and exports become more expensive, potentially leading to a decrease in exports and an increase in imports.
government policies
tariffs and quotas on imports lead to decreased demand for foreign currency and decreased supply of domestic currency
changes in income
ex: us income increase due to expansionary fiscal policy
-us demand for pounds increases and the supply of US dollars increases
-pound appreciates and dollar depreciates
changes in relative PL/inflation rate
ex: expansionary fiscal policy leads to inflation in the us so the demand for cheaper imports increases
-us demand for pounds increases and the supply of USD increases
-pound appreciates and USD depreciates
changes in relative interest rates
Ex: US has a higher interest rate than Britain.
British people want to put money in US banks
Capital Flow increase towards the US
British demand for U.S. dollars increases...
British supply more pounds
Pound-depreciates
Dollar- appreciates
a change in the value of a country's currency in the foreign exchange market will cause a change in that country's...
net exports and aggregate demand
if a currency appreciates...
exports will decrease and imports will increase, causing net exports to decrease therefore AD will decrease
-trade balances moves to trade deficit
if a currency depreciates...
exports will increase and imports will decrease, causing net exports to increase therefore AD will increase
-trade balances moves to trade surplus
contractionary monetary policy
increase in real interest, increase demand for domestic currency, decrease supply of domestic currency, increase in ER, increase in supply of loanable funds, decrease in interest rates
expansionary monetary policy
decrease real interest rate, decrease demand for domestic currency, increase supply of domestic currency, decrease ER, decrease supply of loanable funds, increase IR