Study Guide -- Marine Biology
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Terminology and Key Concpe
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Plate tectonics
the process of the entire planets surface drifting
mid ocean ridges
The continuous chain of volcanic submarine mountains that extends around Earth
oceanic crust vs continental crust
oceanic is younger and continental is older, thicker, and less dense
subduction
The downward movement of a tectonic plate into the mantle that occurs in trenches, which are also known as subduction zones.
biogenous sediments
composed of the mineral calcium carbon ate (CaCO3 )
calcareous ooze
Types of oozes
calcareous ooze (foraminiferan)
siliceous ooze (diatomaceous, radiolarian)
Sea water solutes
sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-) are the most abundant, making up roughly 85% of the dissolved ions.
Waves: causes and types
Waves are caused by a disturbance that transfers energy, most commonly by wind, gravity (tides), or geological events (tsunamis). They are categorized into two main types: mechanical waves, which require a medium like water or sound, and electromagnetic waves, which can travel through a vacuum, such as light
Pressure
changes dramatically with depth in the ocean because the amount of water above gets greater
Winds: causes
Density
the mass of a given volume of a substance
if two substances are mixed the denser materials tends to sink and the less dense to float
Gyres
Under the influence of the Coriolis effect, the wind-driven surface currents combine into huge, more or less circular systems
Light and water, turbidity
Turbidity is the measure of how clear water is, and it directly impacts how deeply light can penetrate the water column
Secchi disk
a simple, cost-effective tool used in marine biology to measure water transparency and clarity
Physical and energetic properties of water
polarity, high specific heat, high heat of vaporization, and unique density pattern
Where do the solids that are dissolved in seawater come from?
the weathering of rocks on land, which transports minerals to the ocean via rivers and runoff, and underwater volcanic activity and hydrothermal vents, which release dissolved minerals directly from the Earth's crust
Coriolis effect/ the Ekman spiral.
a rotating column of water that forms when water moves at an angle to the wind direction due to the Coriolis Effect
Rising and falling air: where on earth
Air rises most prominently at the equator due to intense solar heating, and sinks at about the 30° latitude (both north and south) where cooler air descends
Upwelling
the process where deep, cold, nutrient-rich ocean water rises to the surface, replacing warmer, surface water
Tides: types, reason for spring vs neap, causes.
depend on the alignment of the sun, Earth, and Moon. Spring tides occur during the new and full moon, when the sun, Earth, and Moon are in a straight line, and the combined gravitational forces create higher high tides and lower low tides. Neap tides occur during the first and third quarter moons, when the sun and Moon are at right angles to each other, and their gravitational forces partially cancel out, resulting in lower high tides and higher low tides
Salinity
the measure of the dissolved salt content in water or soil
Diffusion
the net movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration down a concentration gradient
osmosis
the net movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of low water concentration, or from a less concentrated solution to a more concentrated one
osmoregulation vs osmoconformers
Osmoregulatory actively maintain a constant internal osmotic pressure different from their environment, a process that requires significant energy. In contrast, osmoconformers lack active regulation and allow their internal osmotic pressure to match that of their surroundings, which saves energy but limits them to stable environments
Surface to volume relationships
govern fundamental physiological processes for organisms of all sizes, from microscopic plankton to giant whales
This principle explains how marine life manages essential functions like nutrient absorption, waste removal, gas exchange, and temperature regulation, all of which depend on the surface area available to the organism's internal volume
Basic taxonomy
the scientific method of organizing ocean-dwelling organisms into hierarchical groups based on evolutionary relationships and shared characteristics, such as Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species
Foundational evolutionary theory
built on the principles of variation within populations, inheritance of traits, and a "struggle for existence" where individuals with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing those traits on to their offspring
General Marine ecology-population
the study of how populations of marine organisms change over time and the factors that drive those changes
community and ecosystems
a community is a group of different populations of marine organisms, while an ecosystem is that community plus the non-living (abiotic) factors of their environment, like water, sunlight, and temperature
3 basic lifestyle groups
plankton, nekton, and benthos
Fig. 10.11
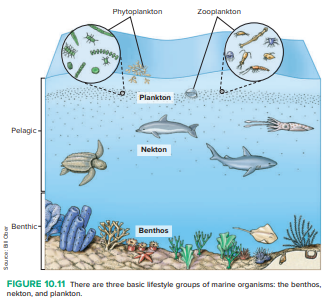
plankton
tiny organisms that drift in the ocean and are essential to marine ecosystems as they form the base of the food chain
nekton
strong-swimming aquatic animals that can propel themselves independently of ocean currents, such as fish, whales, sharks, and squid.
neuston
small aquatic organisms inhabiting the surface layer or moving on the surface film of water.
benthos
the organisms living on, in, or near the bottom of a body of water, such as the ocean, rivers, or lakes
neritic
the shallow, biologically rich part of the ocean that overlies the world's continental shelves, from the low tide mark to the edge of the shelf
Marine biotic zones
intertidal zone (between high and low tides), pelagic zone (open ocean water column), benthic zone (ocean floor)
Fig. 10.12
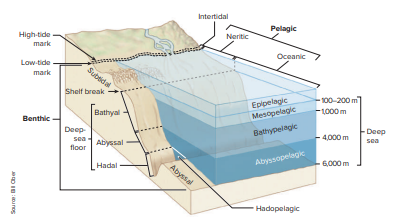

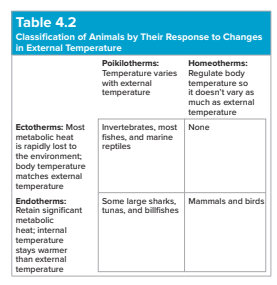
Endothermy
the ability of an organism to regulate its body temperature from within, primarily through internal metabolic processes like increasing metabolic rate
ectothermy
a biological trait where an organism relies on external sources like the environment to regulate its body temperature
heterothermy
a physiological strategy where an animal's body temperature fluctuates significantly over time or across different body regions
poikilothermy
thermoregulatory process; internal temperature varies/fluctuates with respect to variation in ambient environmental temperature
Table 4.2 - Response to Changes in External Temperature
calcareous ooze
a type of biogenous sediment that is made of the calcium carbonate shells and skeletons of marine organisms