Systems Neuro Final
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
How does optogenetics stimulate neurons?
Opsins are a protein that are light sensitive and function as light gated ion channels, causing an influx in Na+ leading to Action Potentials when exposed to light
What are two motor brain regions related to saccadic eye movements
Superior colliculus - takes in visual information (how it is moving, where it is) to make a motor plan and create a saccade to contralateral side
Striatum of the basal ganglia - disinhibits the superior colliculus by inhibiting SNr, helps to activate the saccade
What type of eye movement is used for steadily tracking something
Smooth pursuit eye movement
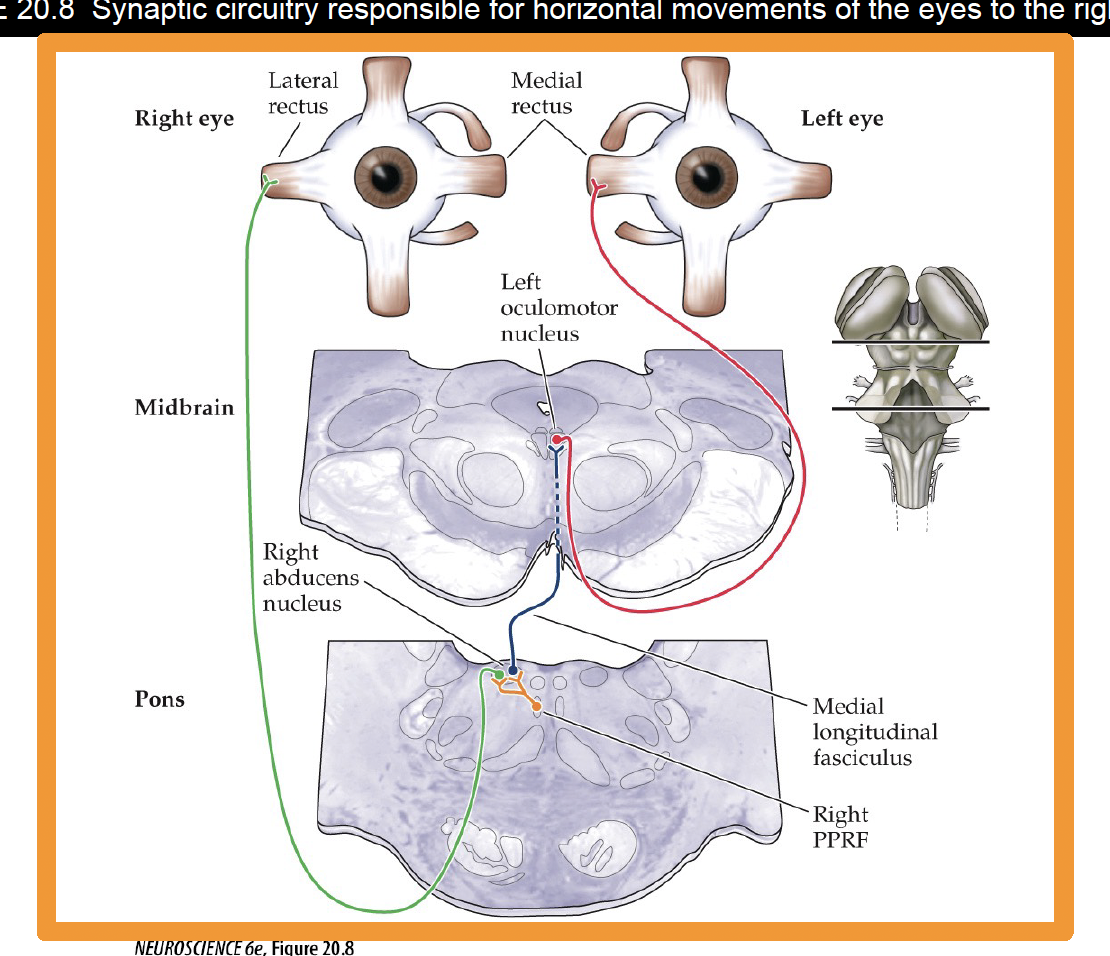
How do you make an eye saccade to the left
Left PPRF (gaze center) will excite the left lateral rectus directly and the right oculomotor nucleus, which will the excite the contralateral right medial rectus.
If I want an enjoyable experience eating spicy food, what is the brain area involved
Hypothalamus - regulates response to the casaicin
What is the difference between the 1st and 2nd generation drugs to treat psychosis
1st gen: selectively an aganost to D2 (dopamine receptors) which inhibits positive symptoms of psychosis such as hallucinations
2nd gen: an aganost to D2 (dopamine receptors) and serotonin, minimizes adverse effects that worsen negative symptoms
OFC Function
Attaches value to an object of interest (reward/punishment)
PFC Function
Creates rules and context to apply the values of objects to
ACC Function
Signals conflict to adjust decisions adaptively when rules are broken
Why are retina waves important for the development of V1
retina waves are waves of APs that fire for retinal cells that are physically near each other. This establishes a retinotopic map that creates spatial maps through experience-dependent learning?LTP
Explain the Central Pattern Generator diagram
For each muscle involved, there should be one neuron: that neuron will excite its muscle and inhibit any of the other muscles involved in the circuit, and each neuron should excite each other in a cyclic pattern to continue the pattern
In the developing organism, how would the neuron know to project to muscle A and not muscle B
Chemoattractants from A and chemorepulsions from B
Broca’s aphasia
Language disorder that disrupts the prefrontal region of language that is involved in language production. Comprehension is intact, but disordered grammar & syntax (grammatical structures & rules of language)
Wernicke’s aphasia
Disrupts that “What” pathway of language. Can’t comprehend language but produces language with adequate syntax/grammar
What property of light waves determine color
wavelength
What is the role of the optic chiasm
Relays visual information contralaterally (Right visual field to left side of brain, left visual field to right side of brain)
What type of photoreceptor is responsible for scotopic vision (low light vision)
Rods
Are photoreceptors more active in the presence or absence of light
Absence
How does visual sensory info travel through the brain
APs begin with the retinol ganglion cells → travel down the optic nerve until they hit the optic chiasm → Causes the right side of the left retina and left side of the right retina to cross over (so that all right visual field is in the left and vice versa) → signals travel to the thalamus → sent to the striate cortex
Dorsal vs ventral pathway
Dorsal = parietal lobe, in charge of spatial vision (where)
Ventral = temporal lobe, in charge of object recognition (what)
Why is it important that photoreceptors don’t fire action potentials
Photoreceptor cells need to be highly sensitive to light/color to detect stimuli, and generating APs require a higher threshold of stimulation which reduces sensitivity. Also saves energy, as vision is constant
What part of the basilar membrane do low frequency waves stimulate, and why?
The apex, which is at the wider end of the basilar membrane in the cochlea - the basilar membrane is like a cone, so low frequency waves that are wider can resonate longer and travel further down the basilar membrane
What part of the ear allows sound waves to be converted to nerve signals interpretable by the brain
inner hair cells