Proteins, amino acids and DNA
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Describe the optical activity of amino acids
All, expect glycine mare chiral as there are 4 different groups around the C - will rotate plane-polarised light
Give the general structure of amino acids
NH2 - CHR - COOH
Describe the structure of acidic amino acids
Have an extra carboxylic acid group on R group
Describe the structure of basic amino acids
Have an extra amine group on R group
Define zwitterion
The form amino acids exist as even in solid state
Describe the structure of zwitterions
Compounds with no overall electrical charge, but which contain separate parts which are positively and negatively charged
Explain the relatively high melting points of amino acids
due to ionic interactions between zwitterions as opposed to the weaker hydrogen bonding that would occur in the no-charge form
Describe what happens when you add an alkaline to a solution of amino acid
The hydrogen ion is removed from the -NH3+ group and reacts with OH- ions to produce water - the amino acid is now a negative ion, not a zwitterion
Describe what happens when you add acid to a solution of amino acid
The COO- part of the zwitterion picks up a hydrogen ion to form -COOH - the amino acid is now a positive ion, not a zwitterion
Describe the structure of a DNA nucleotide
A phosphate ion bonded to 2-deoxyribose which in turn is bonded to one of 4 nitrogenous bases
What molecule is removed when 2 nucleotides are joined?
Water
Describe the structure of a single strand of DNA
A polymer of nucleotides linked by covalent bonds between the inorganic phosphate group of one and the sugar of another nucleotide
How does DNA exist as 2 complementary strands?
Due to hydrogen bonding between complementary base pairs, arranging the strands in a double helix
How many hydrogen bonds form between adenine and thymine?
2
How many hydrogen bonds form between cytosine and guanine?
3
Give a use of cisplatin
Anti cancer drug
Draw the structure of cisplatin
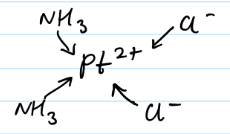
Why does only cisplatin and not transplatin work at preventing DNA replication?
As two chloride ions are displaced and the molecule joins onto the DNA - stops the replication of cancerous cells
How does cisplatin prevent DNA replication in cancerous cells?
By ligand replacement reaction with DNA in which a dative covalent bond is formed between platinum and a nitrogen atom on guanine
Why can cisplatin have adverse effects?
Can also prevent the replication of healthy cells by bonding on to healthy DNA (can be minimised by giving cis-platin in small doses)
Why can a stereo specific active site only bond to one enantiomer of a substrate or drug?
The substrate molecule must bond to the amino acid side chains through a variety of interactions, which are highly specific
How do drugs act as enzyme inhibitors?
Block the active site (often binding strongly so stopping the substrate attaching to the enzyme)
What can be used to design enzyme inhibiting drugs?
Computers
Describe the structure of a protein
A polymer/sequence of amino acids joined by peptide links
Describe the primary structure of proteins
The sequence of amino acids joined by condensation reactions with peptide links
Describe the secondary structure of a protein
The basic 3D arrangement of amino acids
Describe an alpha helix structure in proteins
The polypeptide chains coils into a corkscrew shape and is held in place by hydrogen bonds between the H on N-H and O of C=O
Describe the beta pleated sheet structure in proteins
The protein chain folds into parallel strands side by side - held in shape by hydrogen bonds between the H on N-H and O of C=O on the amino acid much further along the chain but in the parallel region
Describe the tertiary structure of a protein
The folding of the secondary structure into more complex shapes
How is the tertiary structure of a protein held together?
By interactions between the R side groups in more distant amino acids eg, hydrogen bonding, Sulfur-sulfur bonds, ionic interactions
Between which amino acids do Sulfur bridges form?
Cysteine
What type of bond are Sulfur bridges?
Covalent