Electricity key terms, symbols and equations CIE Checkpoint
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Wire (circuit diagram symbol)

Cell (circuit diagram symbol)
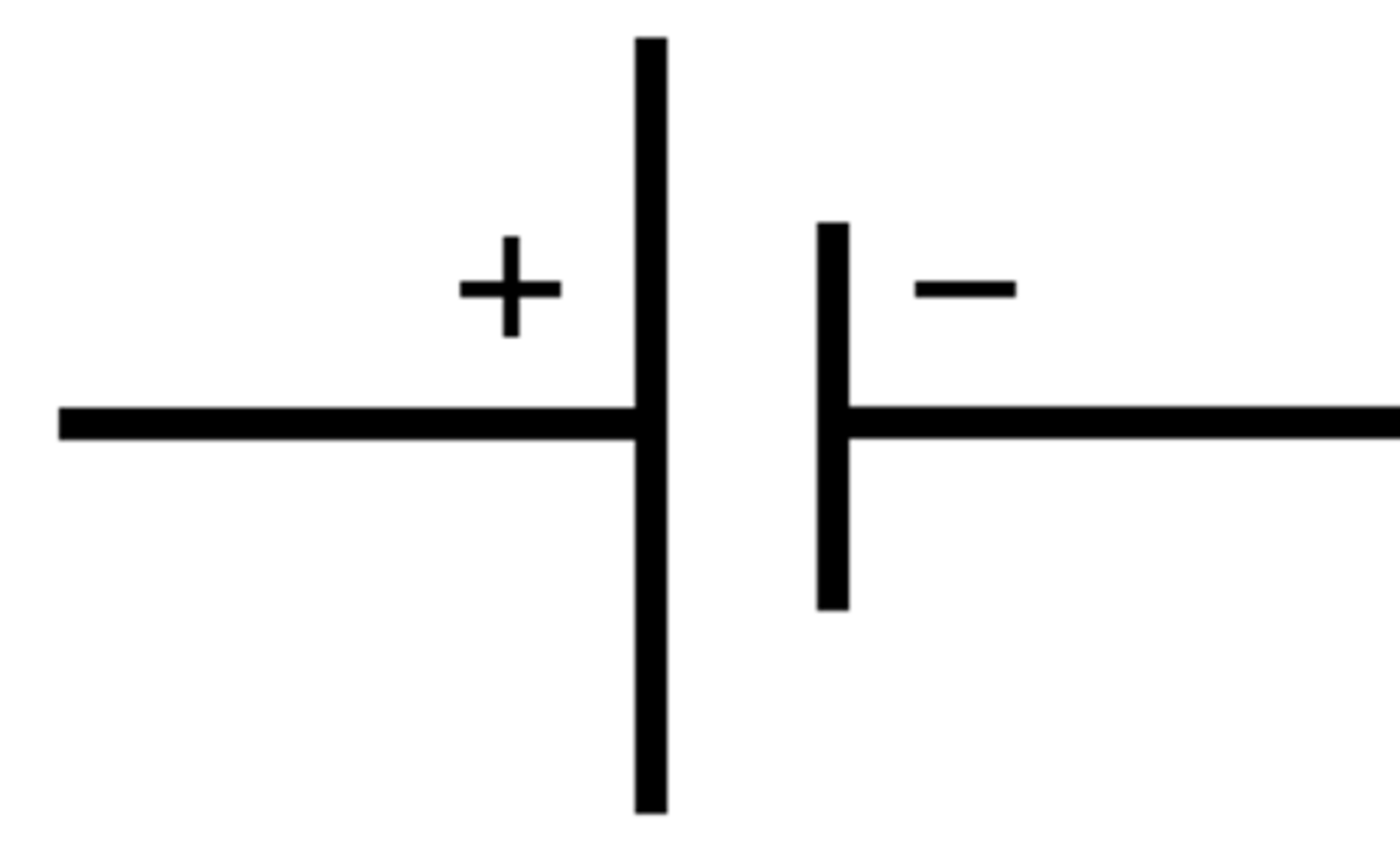
Battery (circuit diagram symbol)
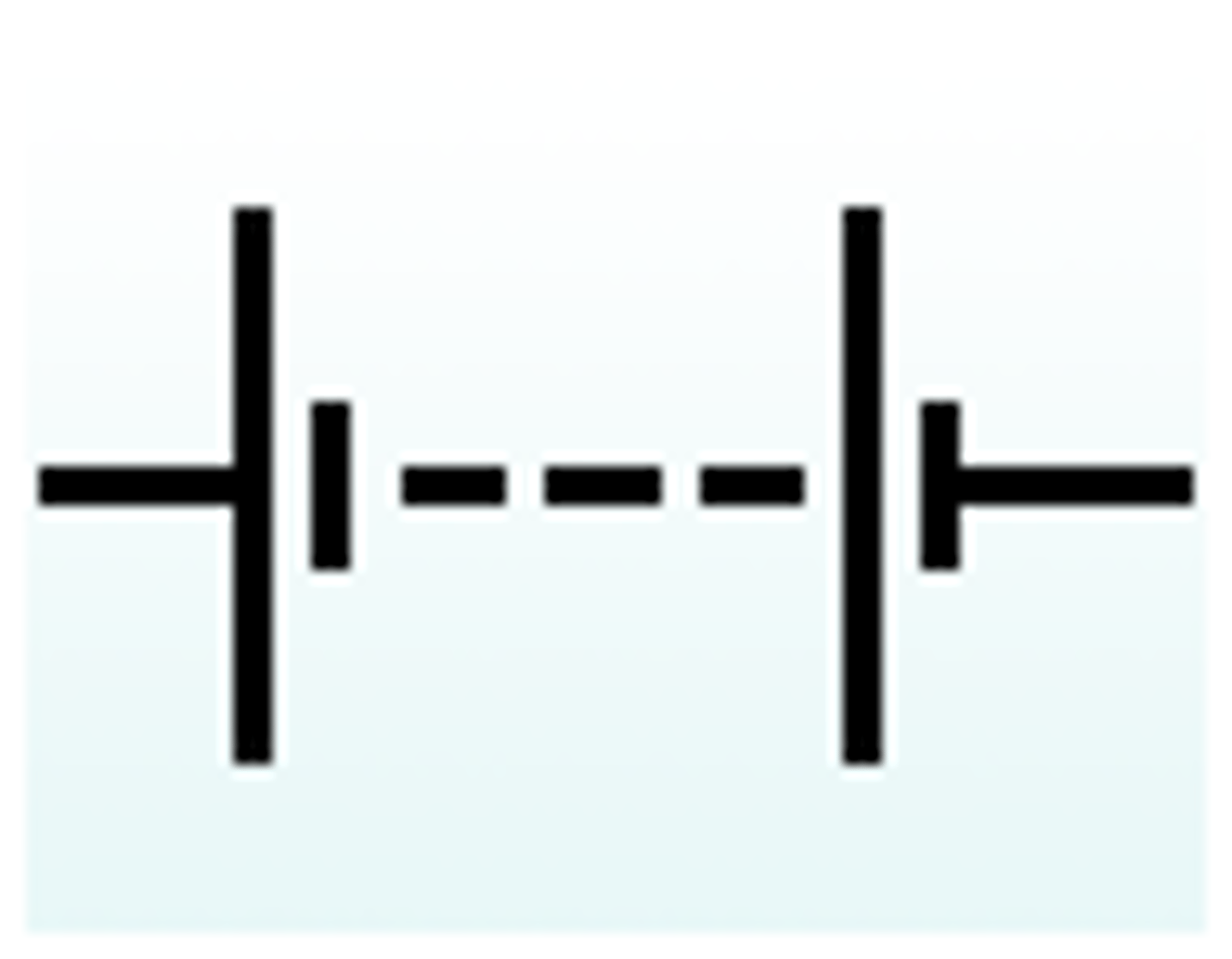
Fixed resistor (circuit diagram symbol)
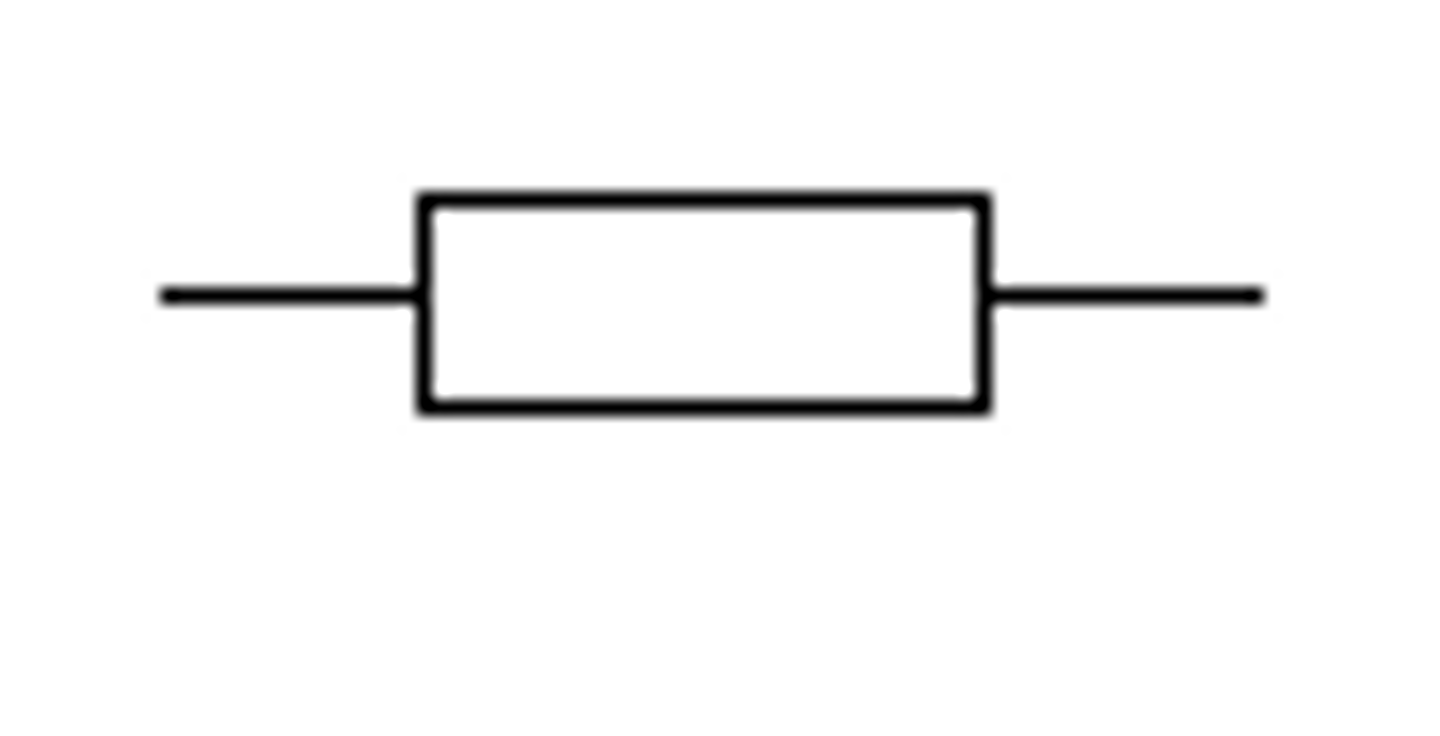
Lamp/bulb (circuit diagram symbol)
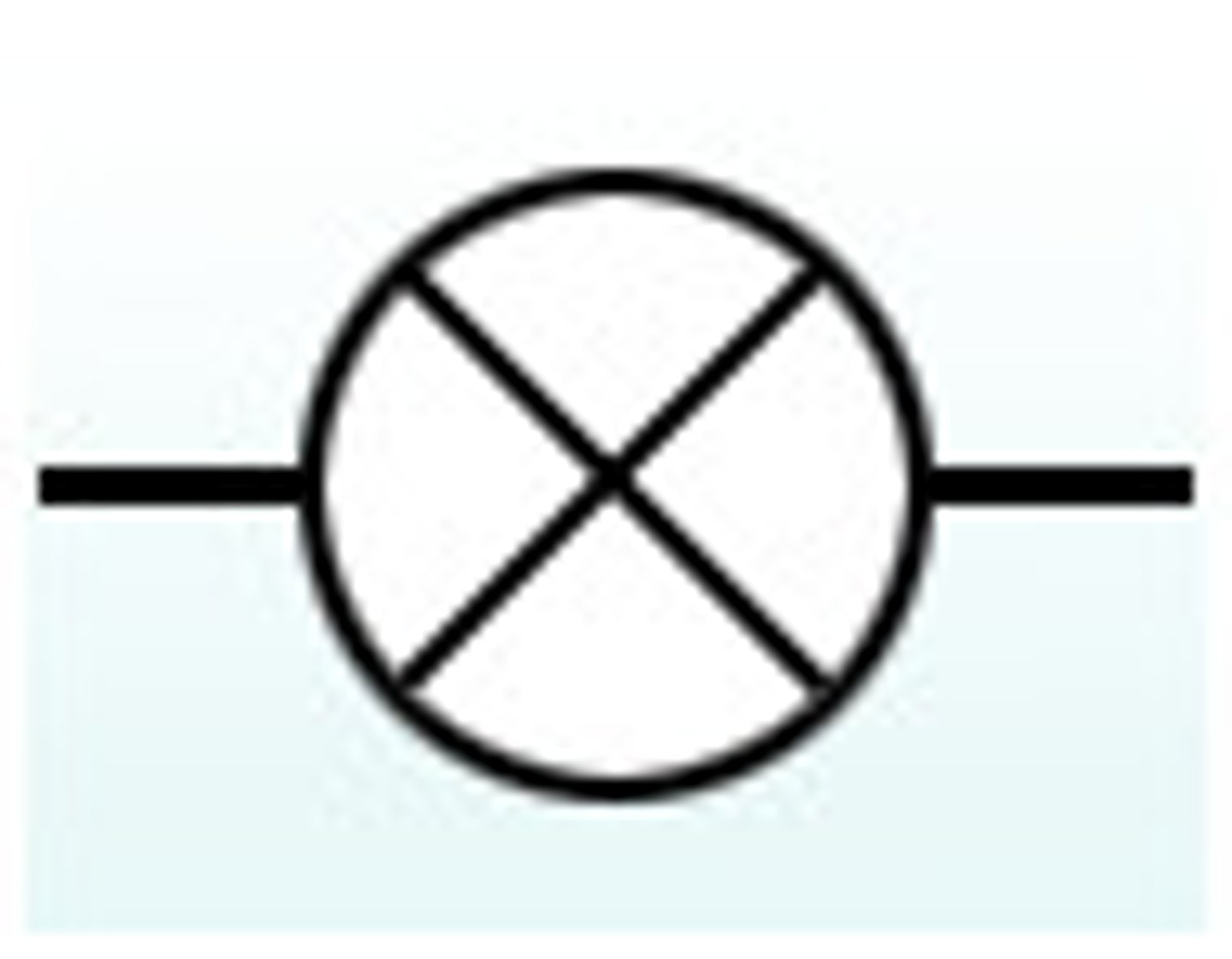
Buzzer (circuit diagram symbol)

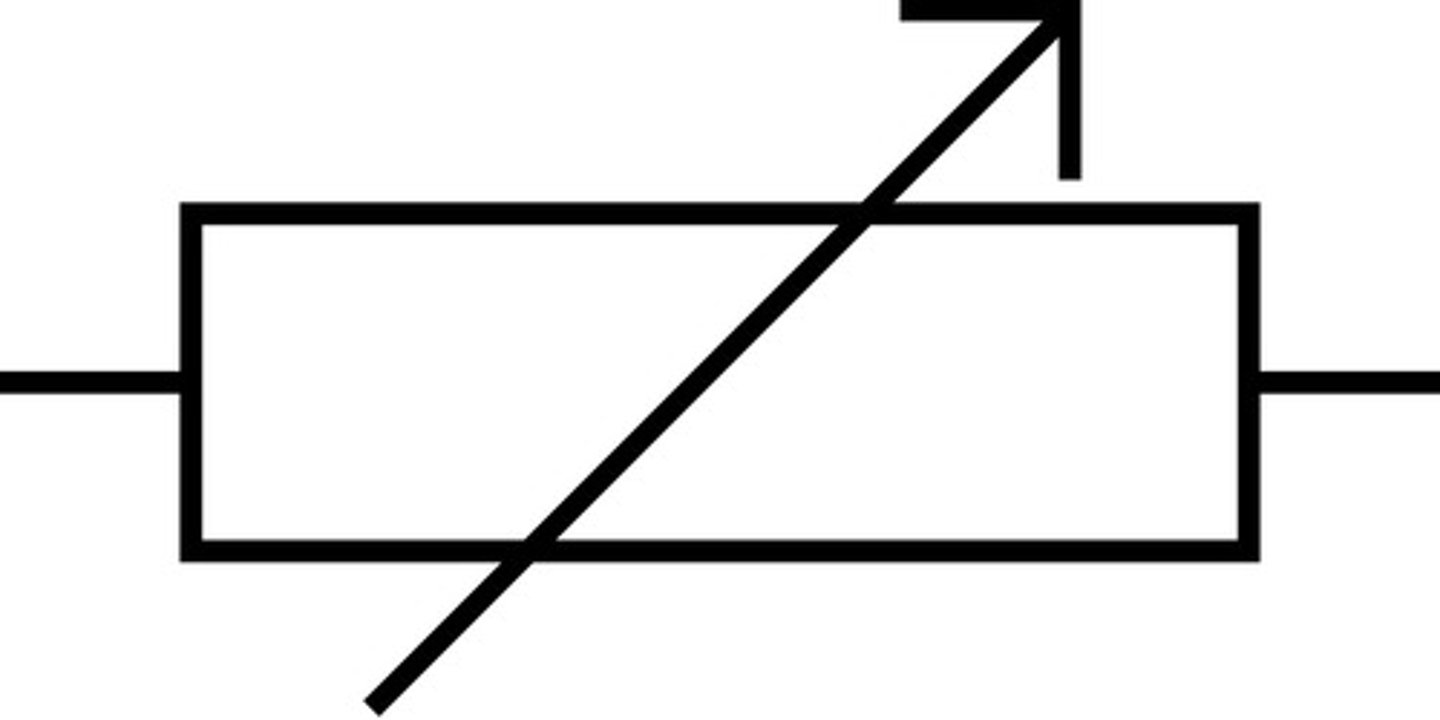
Variable resistor (circuit diagram symbol)
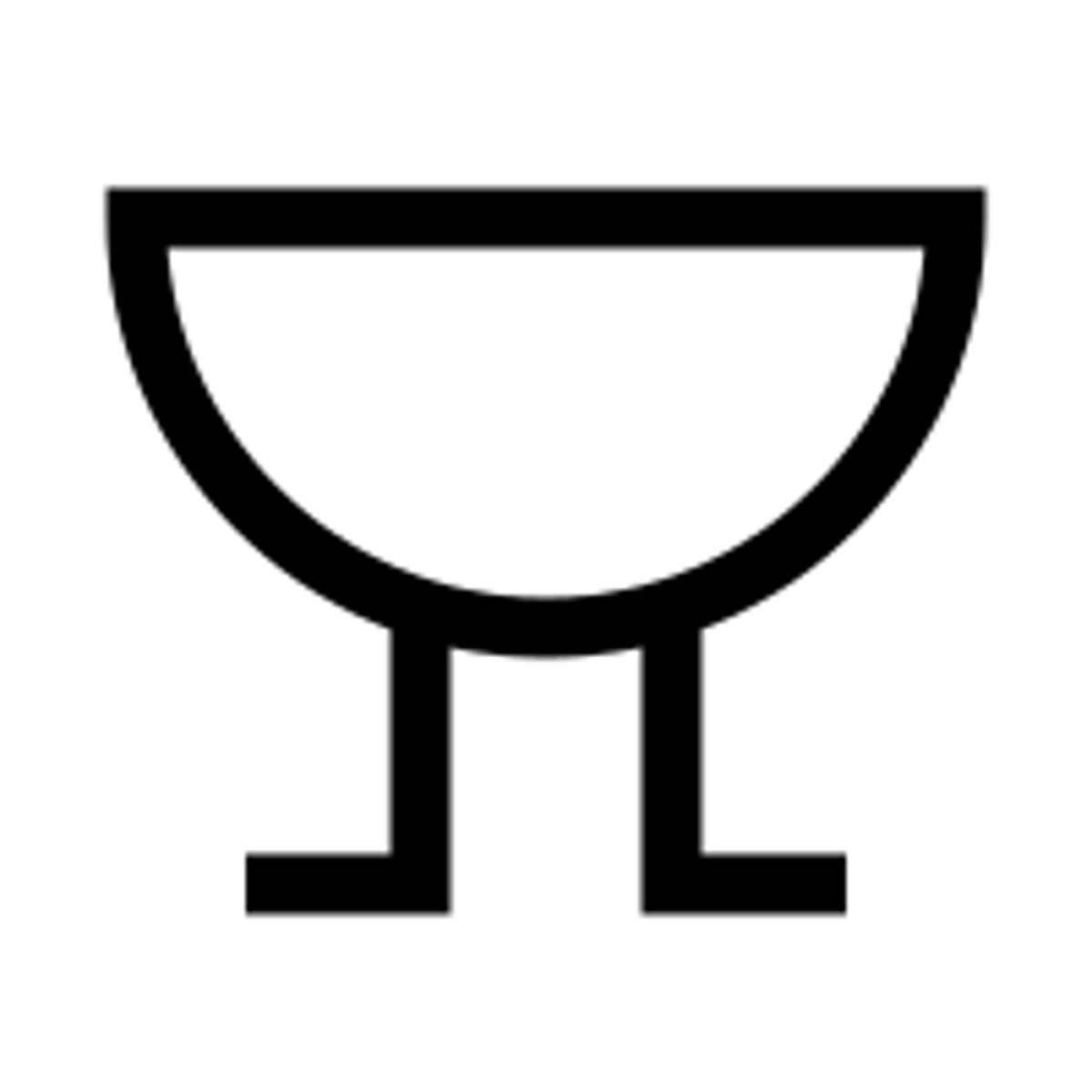
Ammeter (circuit diagram symbol)

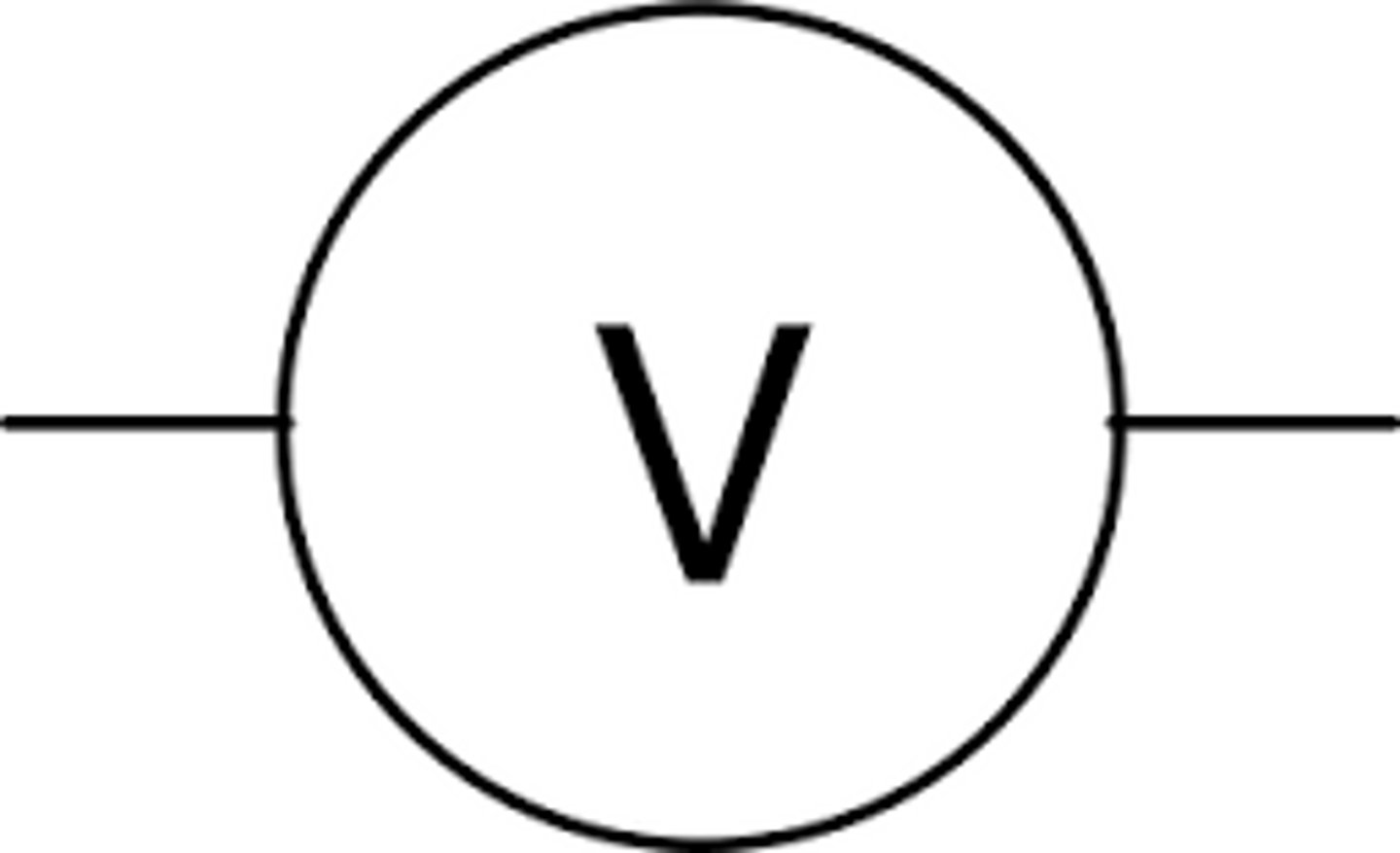
Voltmeter (circuit diagram symbol)
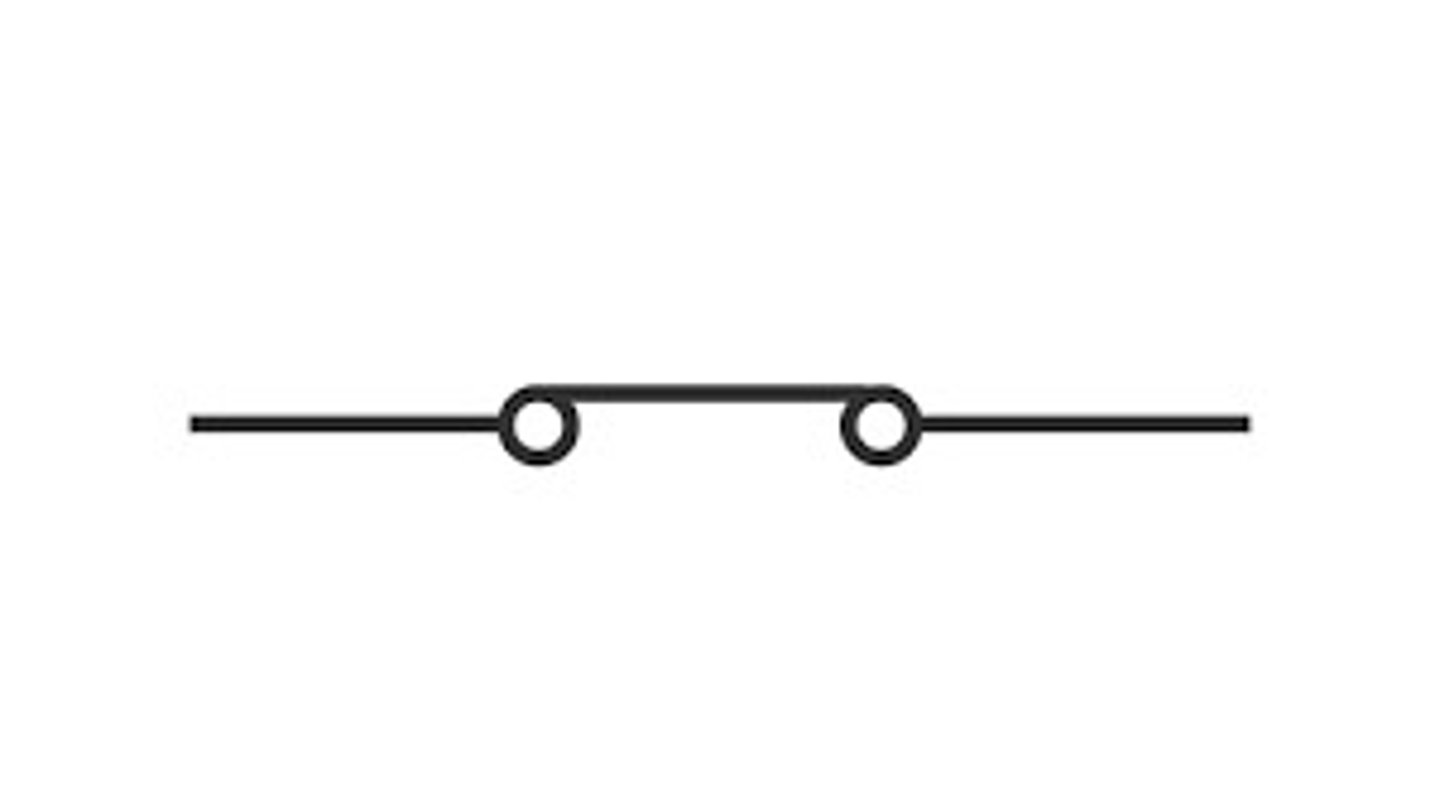
Closed switch (circuit diagram symbol)
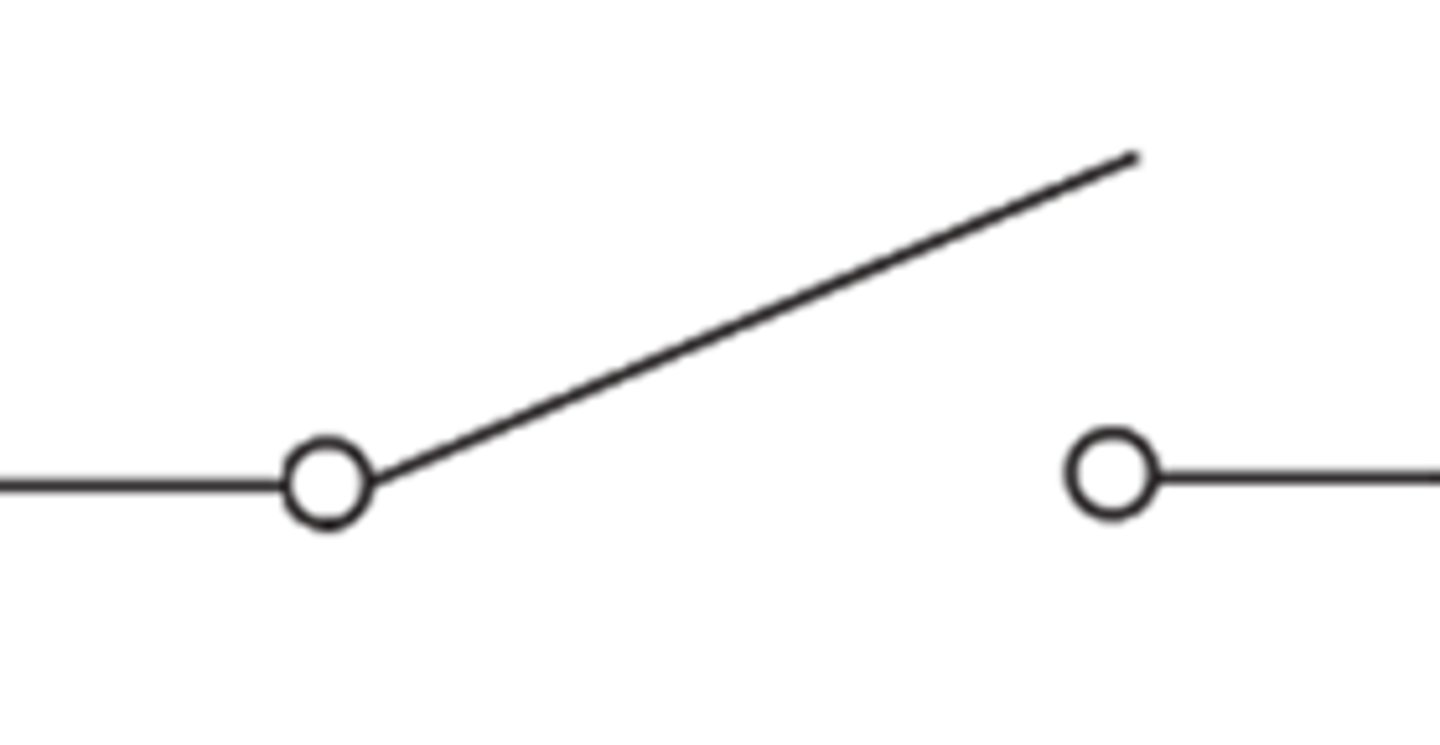
Open Switch (circuit diagram symbol)
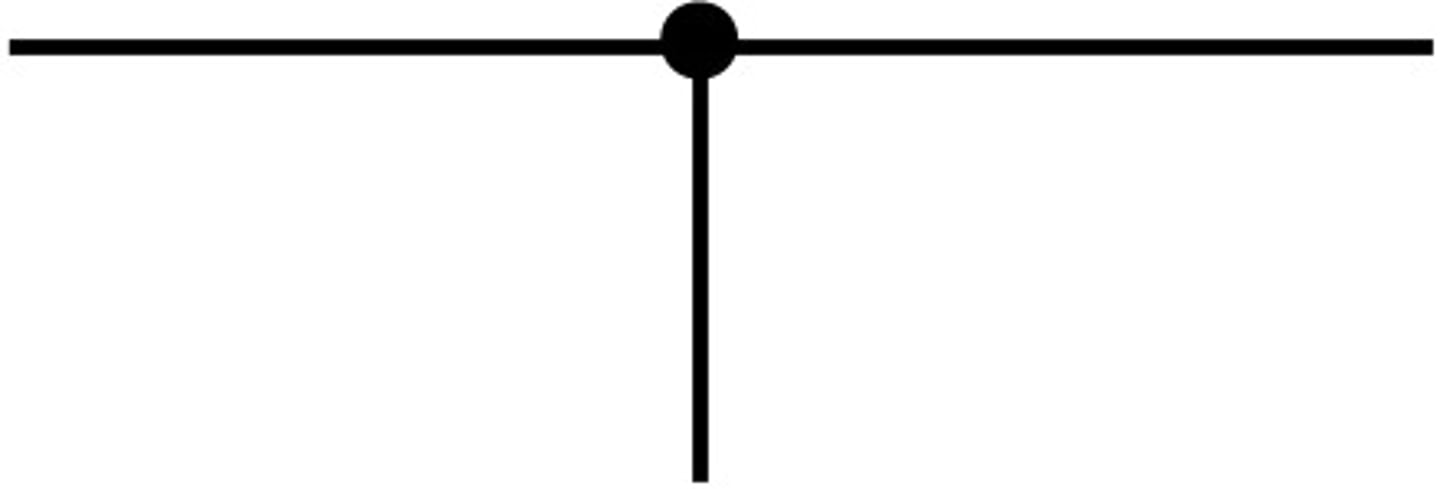
Junction (circuit diagram symbol)
Cell
A single unit that provides electrical energy to a circuit.
Battery
Two or more cells joined together to provide energy.
Fixed Resistor
A component that limits the flow of electric current.
Lamp (Bulb)
A component that converts electrical energy into light energy.
Variable Resistor
A resistor whose resistance can be adjusted.
Ammeter
Measures the electric current in a circuit (in amperes, A). Must be attached in series.
Voltmeter
Measures the potential difference (voltage) across components (in volts, V). Must be attached in parallel.
Buzzer
Produces sound when current flows through it.
Component
A part of an electrical circuit that has a specific job.
Potential difference
Also known as Voltage. The difference in energy transferred between two points in a circuit, measured in volts (V).
Current
The flow of electric charge, measured in amperes (A).
Resistance
How much a component resists the flow of current, measured in ohms (Ω).
Series Circuit
A circuit where components are connected one after another in a single loop.
Parallel Circuit
A circuit where components are connected in separate branches.
Volts (V)
The unit of potential difference or voltage.
Amps/ Amperes (A)
The unit of current.
Equation for resistance
Resistance = Voltage ÷ Current
Current and voltage in a series circuit
Current is equal everywhere. Voltage is shared between components
Current and voltage in a parallel circuit
The current splits between the branches. The voltage across each branch is the same.