Year 11 Biology
1/488
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
489 Terms
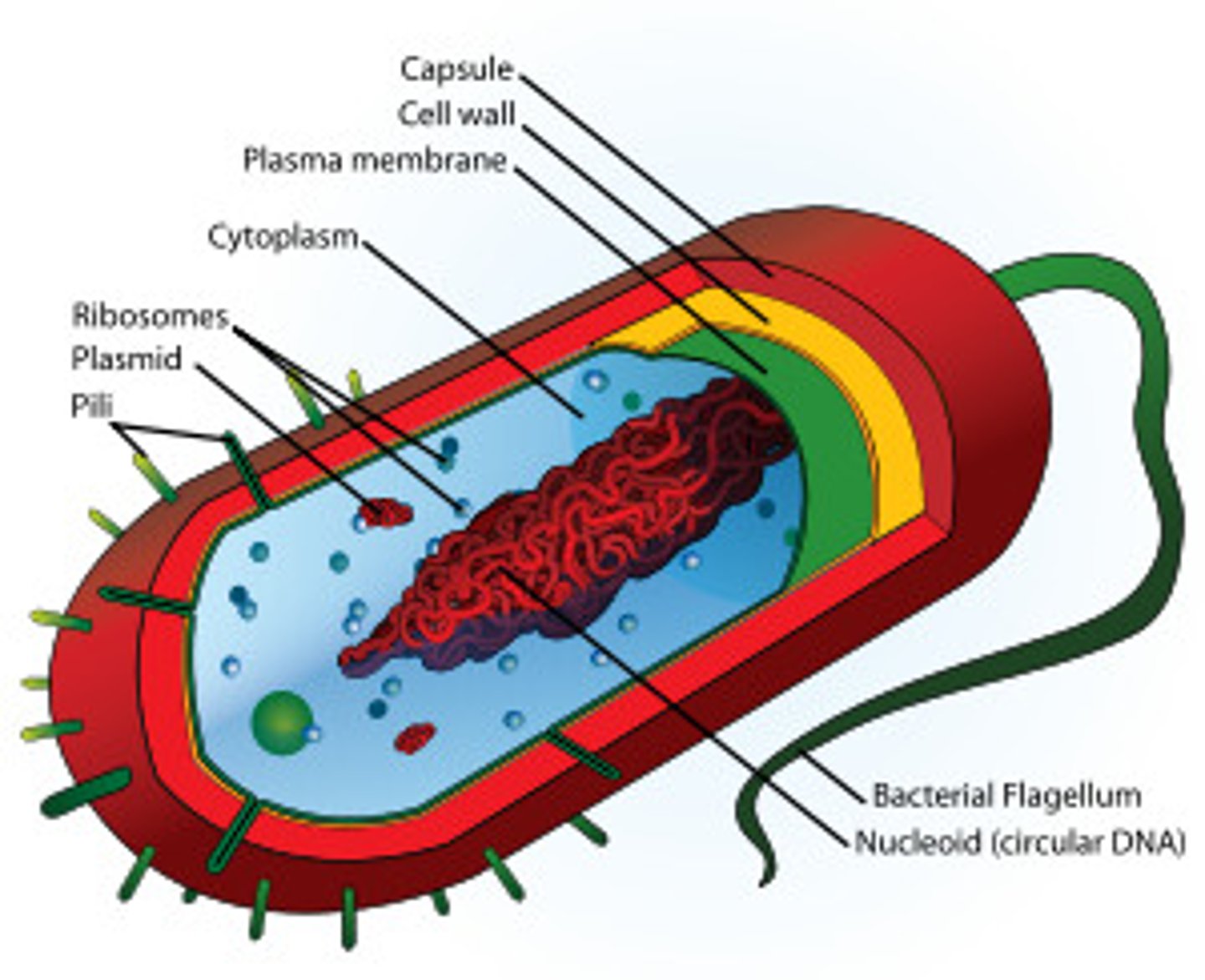
what are prokaryotes
unicellular organisms that lack a nucleus
prokaryotes are usually around what size?
5um
DNA in a prokaryote are
circular without a protein
Ribosomes in a prokaryote are what size
70s
Prokaryotes usually have __________________
a cell wall
cell division in prokaryotes are usually undertaken by what method
binary fission
sexual recombination does not occur in a prokaryote, it
transfers DNA
the flagellum of a prokaryotic cell is the
"tail"
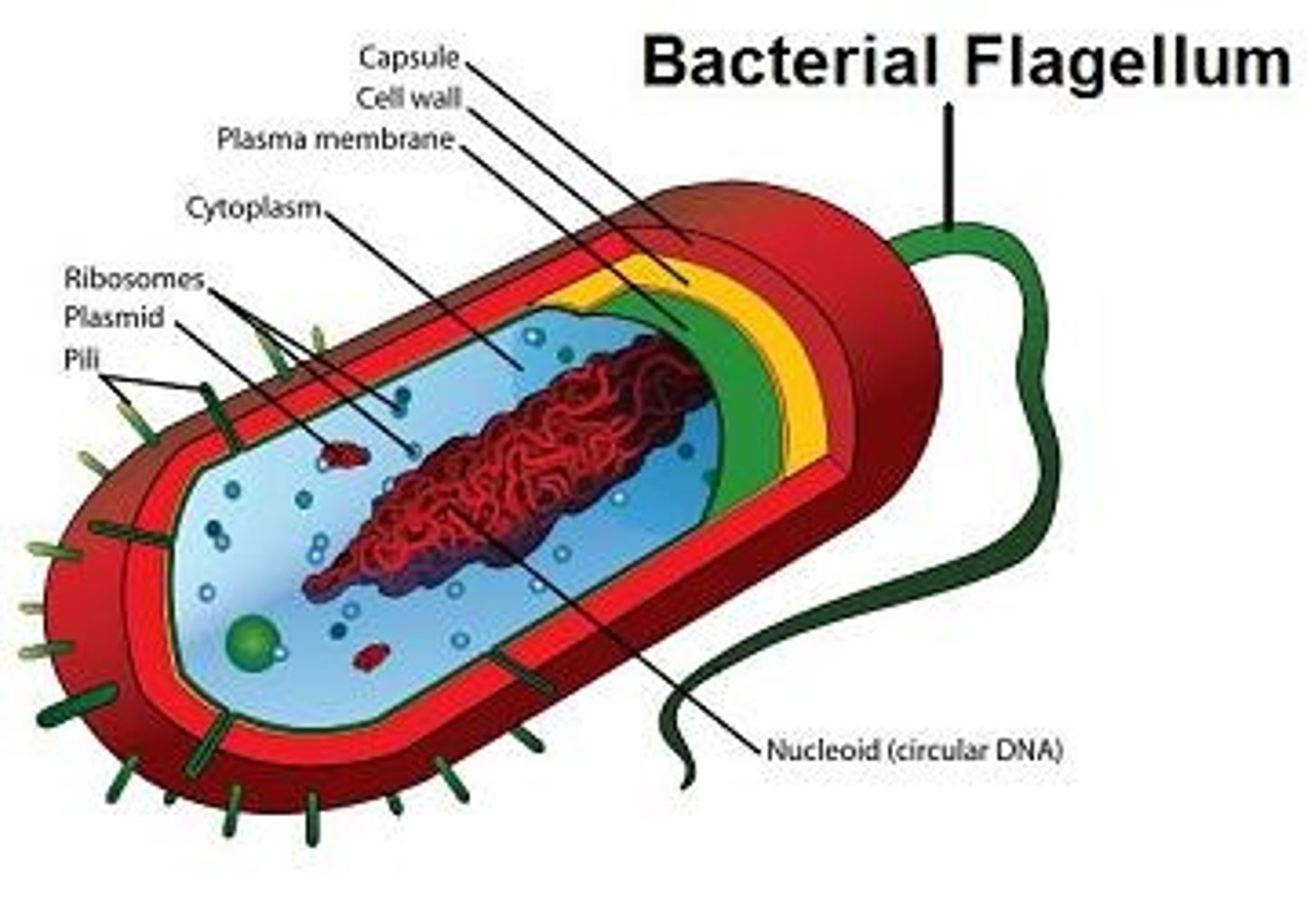
the pili of the prokaryotic cell is the
short hair-like substances on the outside of the cell
the nucleoid of a prokaryotic cell is the
place where DNA is held
the capsule of a prokaryotic cell is the
outermost layer of the cell
the plasmid of a prokaryotic cell is the
double stranded extra chromosomal DNA
the ribosomes of a prokaryotic cell are the
site of protein synthesis in the cell
the cytosol of a prokaryotic cell is
everything found inside the plasma membrane
a Eukaryotic cell is a cell that has a ______________ and _________________.
nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles
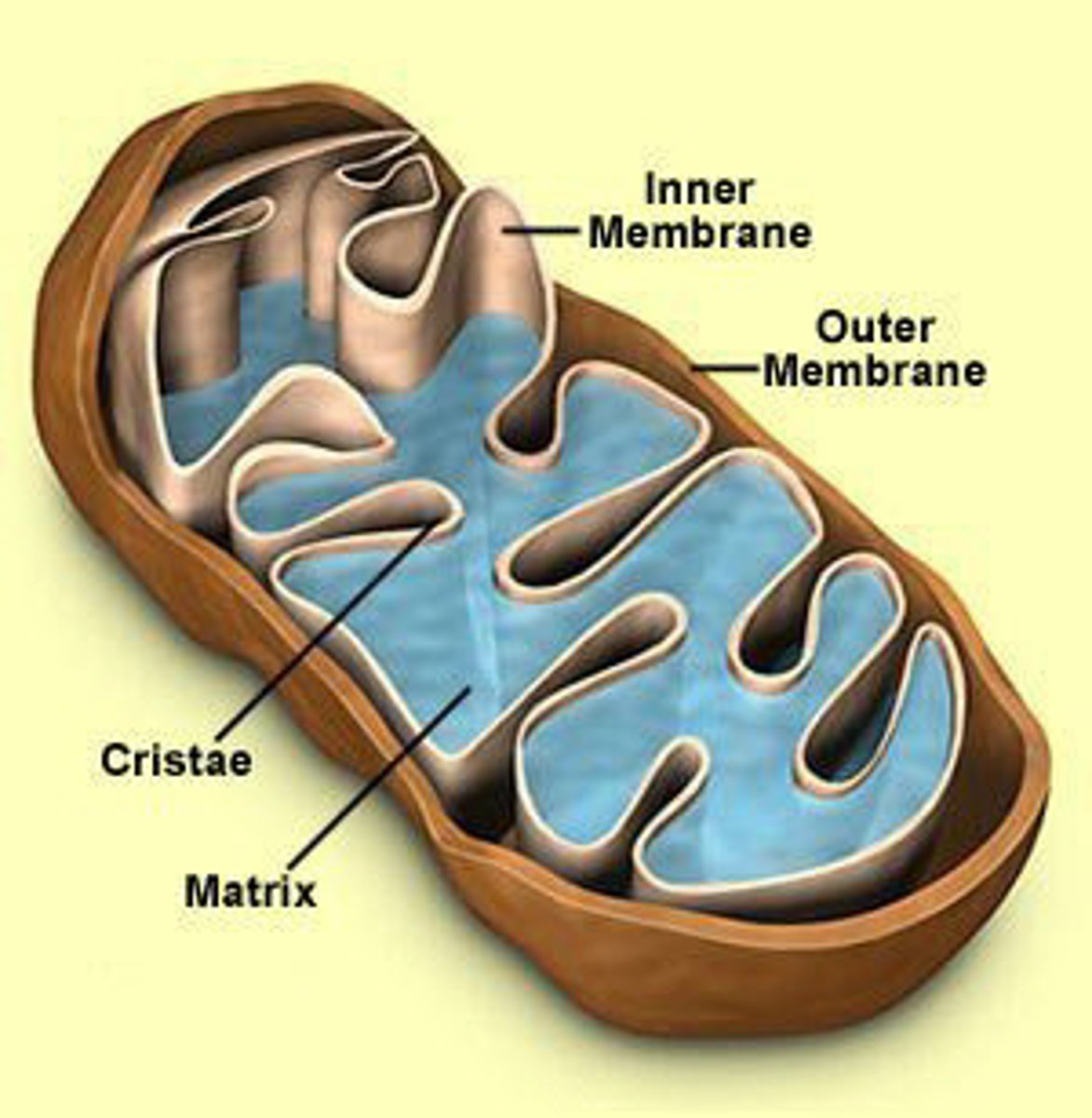
what does the mitochondria do?
produces ATP via cellular respiration and the transformation of Glucose via glycolysis.
What does the Rough ER do?
creates proteins via the ribosomes which are found on the outside of the Rough ER and is used to make proteins.
what does the smooth ER do?
synthesis of carbohydrates
what does the chloroplast do
produces energy through the release of oxygen and is responsible for synthesis of amino acids, nucleotides, vitamins etc.
what does the nuclear envelope do?
separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm and provides a framework for the nucleus.
What does the Golgi apparatus do?
directs proteins (rough ER) and lipids (smooth ER) produced by the ER to their final destination, transported by vesicles
what does the nucleus do
stores DNA and directs all cellular activities
what does the cell membrane do
controls what goes in and out of the cell
what does the cytosol do
allows for the diffusion of molecules throughout the cell
what does the cell wall do
provides strength to the cell and prevents osmotic stress
what is osmotic stress
when there is abnormal pressure outside the cell, leading to an imbalance in water concentrations
what does the vacuole do
stores food, water, and waste
what does the liver do to remove amino groups from a compound
it deaminates them, which forms ammonia.
what does the vesicle do
transports substances across the membrane
a Eukaryote has a larger cell size then a prokaryote with approximately _______________ in size
10-100um
a eukaryote has a ___________ and internal _________________.
nucleus, membrane bound organelles
a eukaryote has linear__________ with proteins
DNA
what is the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes
prokaryotes are bacteria and are unicellular, eukaryotes are plants and animals cells and are multicellular
Eukaryotes have larger ________ than prokaryotes
ribosomes
some Eukaryotes have
cell wall
cell division of a eukaryote is undertaken by ____________.
mitosis
mitosis is when
A cell reproduces itself by splitting to form two identical offspring
meiosis is when
a cell divides twice to produce four genetically different daughter cells with one-half the number of chromosomes of a body cell.
Eukaryotes have sexual recombination which is undertaken by _________
meiosis
the mitochondria produces about __________% of the chemical energy need for cellular survival
90
there are ___________ mitochondria in high requirement cell areas e.g. liver and muscles
multiple
mitochondria have a double __________.
membrane
the inner membrane of a mitochondria is ____________, and is called the _________________.
folded, cristae
the cristae has increased surface area for _______________ and _________________.
enzyme controlled reactions, faster ATP production
the cell wall is made up of ____________, which humans and animals cannot break down.
cellulose
__________ can break down cellulose
bacteria
the cell membrane is a barrier that is ________________ and only allows certain substances through
semi-permeable
the cell membrane acts to maintain a relatively stable ______________________ via the movement of substances
internal environment
the plasma membrane allows enzymatic reactions to be ________________.
localized (which helps the enzymes do their different jobs)
the plasma membrane keeps potentially harmful __________________.
reactions and substances contained
a greater membrane surface area allows the membrane to have more ____________________.
membrane-bound reactions.
greater membrane surface area can increase speed and efficiency of ________________.
metabolic reactions
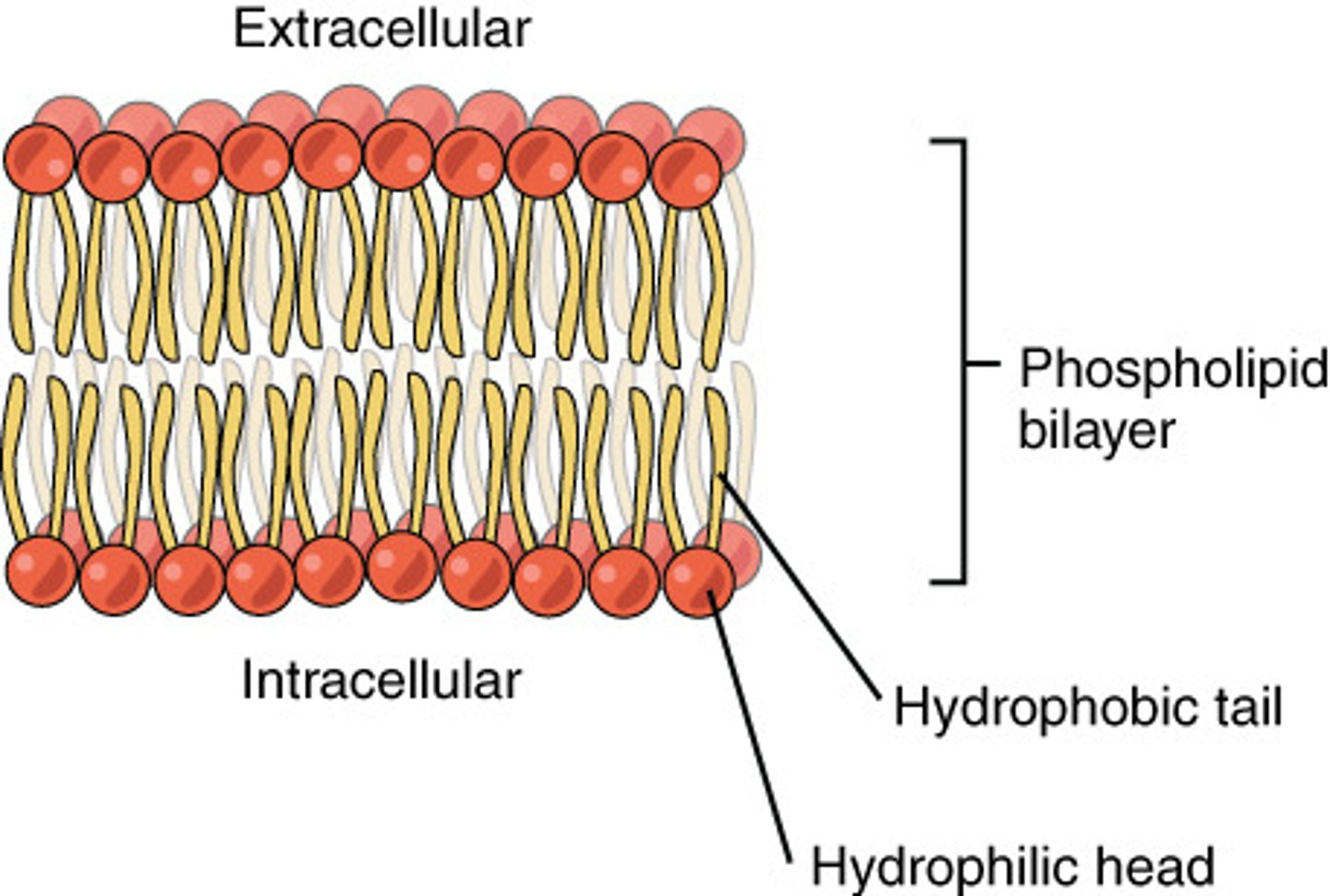
the fluid mosaic mode was proposed by Singer an Nicholson in_____________.
1972
the fluid mosaic model proposed the idea that membranes are not rigid but a flexible ____________ made up of ______________.
bilayer, phospholipids
Phospholipids have a _____ head and a _____ tail.
polar (water-attracting), nonpolar (water-repelling)
the polar head of a phospholipid is water-attracting and is made up of ____________ and ______________ molecule.
phosphate, glycerol
the non-polar tail of a phospholipid is water repelling and is made up of _______________.
2 fatty acids
due to the nature of the phospholipids, they form a bilayer, where the _______________________ shield the ___________________ from water
polar heads, non-polar tails
phospholipid molecules in the membrane move and allow ___________ soluble substances to pass through
lipid
examples of lipid soluble substances include
-________________
-________________
-________________
vitamin D, Estrogen, Testosterone
cholesterol is found only in ___________ cell membranes
animal
name 4 effects of cholesterol interacting with the fatty acids in phospholipids.
-immobilize the outer surface of the membrane, reducing fluidity.
-makes the membrane less permeable to super small water soluble molecules.
-separates phospholipid tails and prevents membrane crystilisation
-helps secure peripheral proteins, which are temporary attachments to the outer surface of the cells membrane, and they help with different cellular activites.
what proteins span the outside of the membrane
extrinsic/peripheral
what proteins span the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane
intrinsic/integral.
what do proteins in the cell membrane do to support the membrane
they provide structural support
How do proteins contribute to the transport of materials around the cell membrane?
by acting as carriers to assist in the transportation
What are hydrophilic channel proteins and how do they support the rapid transport of substances across the membrane while avoiding the hydrophobic center?
Hydrophilic channel proteins are membrane proteins that span the lipid bilayer and facilitate the rapid transport of substances across the membrane by avoiding the hydrophobic center.
Do proteins in the membrane serve as receptor sites by combining with complementary shaped molecules, thus initiating reactions?
Yes, proteins in the membrane can act as receptor sites by binding with complementary shaped molecules, which then trigger specific reactions.
what are protein channels
protein channels are proteins that allow large or lipid molecules to pass through selectively permeable cell membrane through facilitated diffusion.
what are carrier proteins
specialized membrane proteins that change shape during the transport process of large polar molecules and ions.
do carrier proteins need ATP to carry out the process of transportation
There is no use for facilitated diffusion but for active transport there is a use of ATP.
what do glycoproteins and glycolipids do in a cell
act as recognition sites
there are 4 main ways of transporting small substances across the membrane:
-diffusion
-facilitated diffusion
-osmosis
-active transport
what are the three ways of passive transport
-diffusion
-osmosis
-facilitated diffusion
is energy required for passive transport
no energy is required
in passive transport particle movement is via what concentration
high concentration to low concentration to reach equilibrium
is equilibrium able to be reached generally in concentrations of molecules
not generally, especially not in living organisms.
what molecules does diffusion usually transport over the membrane
-oxygen
-carbon dioxide
-water
-fat soluble molecules
rate of diffusion depends on different factors including
-concentration gradient
-size of the molecules
-distance
-surface area
-temperature
-number of pores/channels
what is concentration gradient with regard to rate of diffusion
the greater the concentration on the other side of the membrane of molecules, the faster they move.
what is distance with regard to rate of diffusion
the shorter the distance needed to travel to the diffusion, the faster the molecules move.
what is size of molecules with regard to rate of diffusion
the smaller the molecule, the faster it diffuses.
what is surface area with regard to rate of diffusion
the larger surface area, the faster the diffusion
what is temperature with regard to rate of diffusion
the higher the temperature the faster the diffusion.
how does the number of pores/channels in the membrane affect rate of diffusion
the higher the numbers of pores/channels that molecules are able to pass through the membrane, the faster the diffusion.
what is osmosis
diffusion of water over the cell membrane
what are aquaporins
Channel proteins which facilitate water diffusion through the membrane by forming hydrophilic channels.
water in the cell moves from what concentration
high to low concentration.
How does the concentration of the surrounding solution influence the state of a cell?
if the concentration of substrate is higher outside the cell, the substrate will move out of the cell. If the concentration of substrate is lower inside the cell, the substrate will move into the cell.
there are 3 possible concentrations that affect the state of the cell
-isotonic
-hypotonic
-hypertonic
what is isotonic with regards to concentration of water outside the cell
no net movement of water due to concentrations inside and outside the cell are equal.
what is hypotonic with regards to concentration of water outside the cell
high concentration of water outside the cell, so water moves inside the cell
what is hypertonic with regards to concentration of water outside the cell
there is a higher concentration of water inside the cell, so water moves out of the cell.
what proteins does facilitated diffusion use
carrier and channel proteins
Which molecules and atoms require facilitated diffusion through the cell membrane due to their size and charge limitations?
large molecules and charged atoms.
what do channel proteins do to the membrane
produce pores in the membranes so charged particles can move through
what do carrier proteins do to allow larger molecules in or out of the cell via facilitated diffusion
they change their shape
does facilitated diffusion use energy
no energy
how does facilitated diffusion transport molecules with regard to the concentration of the molecules
high concentration to low concentration.
which increases faster with regards to cells - volume or surface area
volume